TS 10th Class Social Important Questions 8th Lesson Rampur: A Village Economy
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Write any two aspects of Rampur villages economy which you like?
Answer:
- In Rampur no land is left ¡die
- Non-agricultural sector also developed
- Due to development of transport sector, other sectors of economy also developed
Question 2.
What is multiple cropping?
Answer:
To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the same year is called multiple cropping
Question 3.
What are the main non-farm production activities taking place in your region?
Answer:
- Transportation
- Dairy farming
- Brick making
- Carpentry
- Basket making
- Poultry
- Shopkeeping
- Fishing, etc
Question 4.
Who are called labour force?
Answer:
Labour force: People, in the age group of 15 - 59 are labour force
Question 5.
Create a slogan on the importance of agriculture?
Answer:
- Without agriculture - There is no future
- No farmer - No food
Question 6.
How do the small farmers procure the capital needed for farming?
Answer:
The small farmers procure the capital needed for farming by borrowing money from
- Large farmers
- Moneylenders
- The traders who supply various inputs for cultivation
Question 7.
What is the difference between Physical Capital and Working Capital?
Answer:
The differences between Physical Capital and Working Capital:
| Physical Capital |
Working Capital |
| The capital used for the purchase of machinery for the production of goods for many years |
The capital used for bung raw materials and other payments to complete the production |
Question 8.
Which is the main production activity ¡n villages across India?
Answer:
Farmings the main production activity in villages across India
Question 9.
Name any two non-farming activities in Rampur village?
Answer:
Small-scale manufacturing, dairy farming, transport services, etc
Question 10.
Who owns the majority of land n Rampur village?
Answer:
80 upper caste families own the majority of land in Rampur village
Question 11.
What educational facilities are available in Rampur village?
Answer:
Rampur has two primary schools and one high school
Question 12.
What health facilities are available in Rampur village?
Answer:
Rampur has a primary health centre run by the government and one private dispensary where the sick are treated
Question 13.
What Is the maIn aim of production?
Answer:
The main aim of production is to produce goods and services required by the people
Question 14.
What is marketable surplus?
Answer:
The difference between the quantity of output that a fanner produces during a year and the quantity that he keeps with himself for his own and familys consumption is called marketable surplus
Question 15.
Who are small farmers?
Answer:
Farmers who own less than 2 hectares of land are known as small farmers
Question 16.
Who are the medium farmers?
Answer:
Farmers who own more than 2 hectares and less than 10 hectares of land are called medium farmers
Question 17.
Who are large farmers?
Answer:
The farmers who own more than 10 hectares of land are known as large farmers
Question 18.
What is the basic constraint In raising farm production?
Answer:
Land area under cultivation is the basic constraint si raising farm production because it is fixed and scarce
Question 19.
What is the minimum wage rate for a farm labourer?
Answer:
The minimum wages for a farm labourer set by government ¡s Rs, 60/- per day
Question 20.
Which is the most abundant factor of production?
Answer:
Labour Is the most abundant factor of production
Question 21.
What do medium and large farmers do with their earnings from surplus farm produce?
Answer:
A part of the earning from surplus farm produce is saved and kept for buying capital for the next season. Mother part may be utilised for lending to small farmers who require loan
Question 22.
How did the spread of electricity help the people of Rampur?
Answer:
- Electricity helped farmers in running tube walls in the fields
- It is also used for carrying out various small-scale businesses in the village
Question 23.
What are the sources of Irrigation?
Answer:
- Canals
- Tubewells
- Tanks and
- Rains
Question 24.
What is fixed capital?
Answer:
Tools, machines and buildings are caned fixed capital because these can be used in production for several years
Question 25.
What is working capital?
Answer:
Raw materials arid money form part of working capital. The capital which s used for production is known as working capital
Question 26.
Classify the capital investment on various Items In production?
Answer:
There are two types of capital investments in production
- Physical or fixed capital
- Working capital
Question 27.
Name the items/factors that are needed for production?
Answer:
There are four factors of production. They are:
- land
- labour
- capital and
- organisation
Question 28.
What is the main factor of production in the agricultural sector?
Answer:
The main factor of production in the agriculture sector is land
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Write a letter to the Tasildar (MRO), explaênin9 the problems faced by the farmers because of famine?
Answer:
Siricilla
Date xxxxxxxxx.
To,
The TasPdar,
Mandai Revenue office, Sincilia.
Sub: Problems faced by farmers due to famine- request for write-off old loans.
Respected Sir,
I am from Ramnagar, Sincilla. I would like bring to your notice the following one and for favourable help. The rains are very less In the previous year. So. crops left much loss. The farmers get into debt. They cant repay the loans. They need money for purchasing seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides and to cultivate the land. It will be highly difficult to get a loan again from a bank.
Hence, I request you to place it in front of the government, write - off the old loans and give them the new loans. I hope you provide immediate help to the farmers without loss to them to grow the crop this year.
Thanking you sir,
Yours truly,
xxxxxxxxxx.
Address on the envelope:
To
The Tasildar,
Mandai Revenue office.
Siricilla Mandai, Siriodla
Karimnagar (Dist)
Question 2.
Mention the factors of production?
Answer:
Factors of production are
- Land
- Labour
- Capital
- Knowledge and enterprise
Question 3.
Today, why is there a need of expansion of non-farm activities In rural areas?
Answer:
Nowadays farming is not providing regular employment to rural people and they are not getting sufficient income also. Thats why expansion of non-farm Activities in rural areas Is needed. Nowadays people with some amount of capital can set up non-farm activities
It requires very little land, Banks provides loans to sell employment purpose. People can get market facilities to sell their goods. Neighbouring towns and cities provide more demand to the village goods. Ex: Milk, jaggery, broomsticks etc
Question 4.
Explain any one factor of production?
Answer:
Land: An area of ground, especially when used for a particular purpose such as farming or building; A necessary factor for production.
Labour: Workers especially people who do practical work with their hands.
Working Capital: The requirement of raw materials and money which are used up n the production cycle.
Fixed capital: Physical Capital Toots, machines and buildings, which are not used up or consumed immediately in the production process
Knowledge: It is essential to use all the above in a meaningful way to produce some goods or services
Question 5.
How do the farmers get their capital for agriculture?
Answer:
For capital, farmers face many troubles. They get their capital by borrowing from large farmers and village money lenders. They take loans from traders who supply various inputs for cultivation. They get from banks also but very less and rare
Question 6.
Modern farming methods require more Inputs which are manufactured In Industry. Do you agree?
Answer:
Yes, modern farming methods like the use of fertilizers, pesticides, high-yielding variety of seeds, power-driven tubewells of Irrigation, latest tools and implements like tractors. harvesters threshers, etc. require more Inputs which are manufactured In industry
Question 7.
Is it Important to increase the area under irrigation? Why?
Answer:
- It is very important to increase the area under irrigation because it s not wise to depend on monsoon rains which were uncertain and erratic
- To increase production we have to bring more area under irrigation
- It helps us to improve the farming pattern or adopt modem fariTwig methods li those areas
Question 8.
Give the characteristics of Rural Industries?
Answer:
- Rural industries are small-scale manufacturing units
- They involve very simple production methods
- The output is very small
- The work is usually carried out by the members of the family
- The work is carried out at home and not in workshops
- The profits earned are also less
Question 9.
Explain Multiple Cropping in your own words?
Answer:
Growing more than one crop on a piece of land during the year is known as multiple cropping. It is the most common and traditional practice to increase production on a given piece of land. All farmers In Rampur grow at least two main crops
Question 10.
Which changes have taken place In the way of farming practices In India?
Answer:
- Traditional seeds have been replaced by HYVS
- Natural manures were replaced by chemical fertilizers
- Use of pesticides
- Use of farm machinery
- Use of tube wells for irrigation, instead of Persian wheels
Question 11.
Excessive use of chemical Fertiliser and pesticides declines the Fertility of land. Give your opinion on this?
Answer:
- Experience shows fertility of lands declining due to overuse, and excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides
- The situation of water Is equally alarming
- Underground water tables have fallen rapidly across the country.
- Pesticides sprayed act on only 10% on pest remaining act on environment
- The use of natural resources also has not always been judicious while Increasing production
Question 12.
Labour in an essential item for production. Read the statement and Interpret It?
Answer:
- Labour means people who do the work either highly trained and educated or who can do manual work
- Each worker is providing the necessary labour for production
- Skilled or semiskilled or unskilled labour in are providing labour for production
- Thus labour is an essential item In production
Question 13.
The expenditure on tools, machines and buildings is called physical capital. Explain why?
Answer:
- The expenditure on tools, machines and buildings is called physical capital
- They are not used up or consumed immediately in the process of production
- They help to produce goods over many years
- They require some repel and maintenance so that they remain useful and can be used year after year
- That is why they are called fixed or physical capital
Question 14.
Ground-level waters are rigorously declining nationwide. Suggest some alternatives?
Answer:
- Underground water levels are deteriorating at a faster rate throughout India
- To conserve water schemes like watersheds, and soaking pits. check-dams, afforestation, bund construction, etc. should be taken up
- Digging borewells should be allowed only for drinking water but not irrigation
- Farmers should look for alternate crops which use lesser water
Question 15.
Name some dairy activities in your area?
Answer:
- Many families in my region are engaged in milk production
- Various types of grass, maize, bajra. etc. is used to feed the cattle
- Two tradesmen established milk collection and storing points
- Family labour and especially women take care of the rearing of animals
Question 16.
Explain the business tactics of a small businessman In your area?
Answer:
- One Mr, Venkateswara Rao organised cloth business in my region
- In the beginning, he used to wander every household to sell clothes and collects money weekly
- By conducting his business reliably and supplying quality items he became popular
- Later he set up his own business firm and till date it is running well
Question 17.
What are the aims and objectives that are directed by the landless rural workers or labourers?
Answer:
The aim and objectives that are directed by the landless rural workers or labourers:
- Some more days of work
- Still better wages
- Better education to their children in the local govt. school
- No social discrimination
- Chances of leadership activities, etc
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Read the given paragraph and interpret it.
Labour being the most abundant factor of production, It would be ¡deal ¡f the new ways of farming used much more labour. Unfortunately, such a thing has not happened. The use of labour on farms is limited. The labour, looking for opportunities is thus migrating to neighbouring villages, towns and cities. Some labour has entered the non-farm sector in the village?
Answer:
- Labour means people who do the work either highly trained and educated or who can do manual work
- Each worker is providing necessary labour for production
- Skilled or semiskilled or unskilled labour - all are providing labour for production
- Thuslabour is essential item in production
Conclusion: If government provides loans to landless labour for agricultural purposes, motor pump sets, engines, etc. more labour we will find in the agricultural sector.
Question 2.
Observe the following table and analyse It.
Data refers to the land cultivated by farmers?
| Type of farmers |
Size of plots |
% of farmers |
% of cultivated area |
| small farmers |
Less than 2 hectares |
87% |
48% |
| Medium and Large Farmers |
More than 2 hectares |
13% |
52% |
Answer:
- The given data refers to the Land cultivated by farmers
- As per the data, 87% of the total farmers, i.e. small farmers are cultivating only 48% of the total land
- The remaining 13% of the farmers are medium and large farmers. They are cultivating the remaining 52% of the land
- This indicates that there is no equal distribution of land among farmers
- I opine that the distribution of cultivated land Is unequal in India
Question 3.
Mention the factors of production and explain any two of them?
Answer:
- The aim of production is to produce the goods and services that we want
- There are four requirements for production of goods and services
They are:
- Land
- Labour
- Capital
- Physical or fixed capital
- Working capital
- Knowledge and enterprise
- Land: The first requirement is land, and other natural resources such as water, forests minerals. It is a free gift of nature and it is neither created nor destroyed
- Labour: It is a factor which helps in production. There are three types of labour - skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled. Some production activities require highly educated workers to perform the necessary task. Other activities require manual work. Each worker provides the labour necessary for production
Question 4.
Describe the wor1i of a farmer with 1 hectare of land?
Answer:
A farmer who works n a farm of 1-hectare land has to face so many problems. A small farmer knows that he cannot meet his both ends and means just by working on such a small piece of land. So after working on his own field he has to work as a labourer in the fields of some big farmers for a petty amount of Rs. 35.40 per day
Even to start cultivating his own land he has neither means nor money for buying seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, etc. Being a very small farmer he does not have any equipment or working capital
To arrange all these things the farmer has to take a loan either from a village farmer or a trader or a moneylender at a hefty Interest rate. Even after putting so much labour, there is always a chance for him to be trapped in a debt cycle which will be always a big cause of tension for him
Question 5.
Discuss some ideas that would prevent overuse of water by?
- Farmers
- Industrialists
- Households
Answer:
- Farmers
- By providing free power to farmers
- Through appropriate incentives and penalties
- Industnalists
- Cheap water that can be rapidly pumped from underground aquifers
- Industrial wastes should not be drained into canals and rivers
- Households :
- Turning off the taps property
- Control over use of pesticides and chemicals
- Having more plants in gardens in houses
Question 6.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion.
The land is the most crucial factor necessary for farm production. Land area under cultivation, however, is practically fled. In Rarrur, since 1921., there has been no expansion in land area under cultivation. By then, the nearby forests had been cleared and some of the wastelands in the village were converted to cultivable land. There is no future scope to increase agriculture production by bringing new land under cultivation?
Answer:
The given paragraph says that land is essential for agriculture. The cultivable Land is not expanding. In some areas, a few forest lands are cleared and the waste Land is being converted to agricultural land. There is no other way of expansion of land
My opinion Is that the issue discussed in this paragraph is correct The basic factor of production is land, The population is increasing day by day. The food grain production is not increasing or expanding in proportion to the population. It is the time for searching new ways of increasing production of food grains. Green revolution is also to be encouraged
Rampur village s a model for us. The villagers depend on other activities also for their earnings. By involving in transportation, shopkeeping and so on Is better for livelihood but it doss not help in increasing food grains.
In conclusion, I would like to say that there is much land without irrigation. Due to some other reasons Irke power cut, lack of capital, non-availability of groundwater the farmers are not able to Involve in farm activities. The government should concentrate on these issues and try to solve them so as to increase the cultivable land and increase the food grains
Question 7.
Read the following paragraph and write your comments.
Most small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the wo capital. The borrow from large farmers or the village moneylenders or the traders who supply various inputs for cultivation. The rate of interest on such loans is very high. They are put to a eat distress to repay the loan?
Answer:
According to the given paragraph, small farmers in villages take loans from the money lenders. They dont have sufficient capital for farming activities As they are charged high rate of interest, they are put to distress. This is the real situation of the small farmers
I do agree with this. My comments on this paragraph are as follows. Generally, large farmers have sufficient capital for next crop. Small farmers depend on others for loans. Some small farmers depend on the owners of land where they work. Most of the small farmers work on others land becu& of their small farms
The money lenders and traders charge high rate of interest and so the debts release. Sometimes crop failures lead to bankrupts and they commit suicide. Banks dont give loans to small farmers as they dont have collateral.
Government should concentrate on providing loan facility to the small farmers without collateral. Farmers cooperative societies are to be encouraged. Minimum facilities and needs are to be identified and fulfilled
Question 8.
Read the following paragraph and Interpret.
There Is often a loss in farm activities, especially when crops are damaged because of floods, pests, etc. The other risk is sudden fall in the price of agricultural produce. In such a situation, farmers find it difficult to recover the working capital they had spent?
Answer:
According to the paragraph given itas clearly understood that when there is a natural hazard like floods or pests the farmers life will be in risk. In those conditions, they hardly survive. Many of (tie farmers commit suicide because of this situation.
Farmers normally desire to grow more food grains, They hope the yield must be more. They spend much on agriculture. They depend on moneylenders for loans. Sometimes they take loans from banks also. They have to pay all these loans when the yield comes
Due to the pests, floods or drought they dont have money to pay the loans or for their survive. Many a time, they commit suicides that we have been observing m the newspaper and watching on television news.
The farmer is the backbone of economy in India. When they face this type of situation the government should give them a helping hand. They should be saved from losing their lives. Agriculture should not be neglected because of these reasons, New schemes should be launched for the sake of tanners who lose because of these natural hazards. Otherwise, agriculture is discouraged. By this time, already its share in GDP is decreasing. It is not expected to the country which stands in second rank in population
Question 9.
The distribution of farmers in India and the amount of land they cultivate are in the following table?
| Type of Farmers |
Size of Plots |
Percentage of Farmers |
Percentage of Cultivated Area |
| Small farmers |
Less than 2 ha |
87% |
48% |
| Medium and Large Farmers |
More than 2 ha |
13% |
52% |
Read the above table and answer the following questions
Question 1. How many types of farmers are there? Name them?
Answer:
There are 2 types of farmers.
They are
- small
- medium and large
Question 2. Which type of farmers are ¡n high percentage?
Answer:
Small farmers (87%) are high in percentage
Question 3. What is the difference between the percentage of cultivated area?
Answer:
Theie 4% difference in percentage of the cultivated area
Question 4. What is the cause and reason for the high concentration of cultivated area In the hands of medium and large batteries?
Answer:
The landholdings of large and medium farmers are high
Question 10.
Based on the pie chart and the particulars given below, answer the questions?
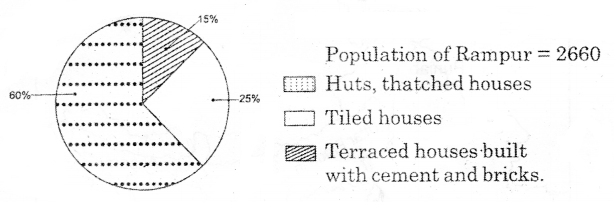
Question (A) Which kind of houses are more In Rampur Village?
Answer:
Huts and thatched houses are more in Rampur village
Question (B) In which category does 60% of Rampur village belong?
Answer:
60% of Pampur village belong to the poor class
Question (C) State approximately, the number of middle-class people In Rampur village?
Answer:
25% people of Rampur belong to middle class
Question (D) Which category of people live in the terraced houses built with cement and bricks?
Answer:
Rich people live in the terraced houses built with cement and bricks
Question 11.
Read the table given below and answer the following questions?
img
Question (a) What are the works done only by male workers?
Answer:
Ploughing
Question (b) What are the works done only by female workers?
Answer:
Transplanting, Picking cotton
Question (c) In which works, the wages are different for male and female?
Answer:
Sowing, Weeding, Harvesting. Winnowing, Threshing
Question (d) What are the reasons for paying less wages to female workers than male workers?
Answer:
The concept existing in the society is that the women do less work then men
Question 12.
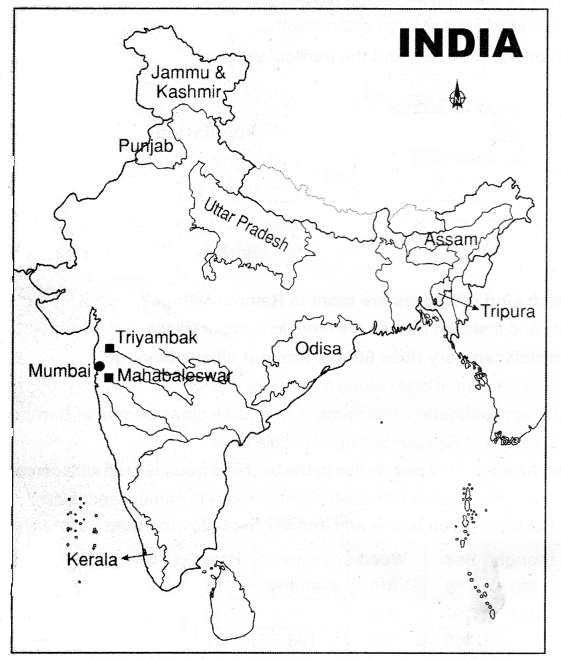
Locate the following in the given map of India?
Question 1. Capital of Maharashtra?
Answer:
Mumbai
Question 2. The birthplace of river Godavari?
Answer:
Thyambak
Question 3. The birthplace of river Krishna?
Answer:
Mahabaleshwar
Question 4. Santal tribal people are in this state?
Answer:
Odisha
Question 5. Tripura?
Answer: