TS 10th Class Social Important Questions 4th Lesson Climate of India
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Observe the following map and answer the following questions?
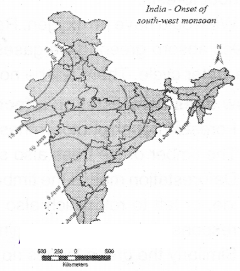
Question (a) When do monsoons reach Maharashtra?
Answer:
On June 10th monsoons reach Maharashtra
Question (b) When do monsoons reach Kerala?
Answer:
On June 1st monsoons reach Kerala
Question 2.
In whIch monsoon season does the Coromandel coast receive less rainfall?
Answer:
During southwest monsoon season, the Coromandel coast receives less rainfall
Question 3.
Write down the reason for the low temperature In India In the months of December and January?
Answer:
- Pleasant and clear sky
- Low humidity
- Angle of incidence
Question 4.
Observe the map and answer the following questions?
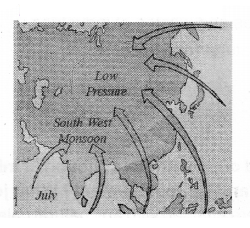
Question (a) Why do winds always blow towards low-pressure regions?
Answer:
- In low-pressure regions temperature is high and evaporation is more
- Warm air rises, so cool air replaces It
Question (b) When do the southwest monsoons blow in India?
Answer:
Beginning of June, July
Question 5.
Mention any two actions that you would take if you were the officer, to prevent deforestation?
Answer:
- I would strictly implement the existing forest laws
- I would bring awareness among the people on the need for the protection of forests
Question 6.
Name any two factors that influence climate and weather?
Answer:
Question 7.
Why does Coromandel Coast get high rainfall during northeast monsoons?
Answer:
Question 8.
Which refers to weather?
Answer:
Question 9.
What are the elements of weather and climate?
Answer:
- temperature
- atmospheric pressure
- wind,
- humidity and
- precipitation
Question 10.
What are called chromatographs?
Answer:
Question 11.
What do climograph show?
Answer:
Question 12.
What are called climatic controls?
Answer:
Question 13.
What are the factors that are influencing climate and weather?
Answer:
- Latitude
- Land-water relationship
- Relief
- Upper air circulation
Question 14.
Name some hill stations?
Answer:
Question 15.
Which is the coldest month in India?
Answer:
Question 16.
Which areas enjoy a moderate climate?
Answer:
Question 17.
How India during winter?
Answer:
Question 18.
What are called Loo?
Answer:
Question 19.
What are the two branches of southwest monsoon?
Answer:
Question 20.
Expand AGW?
Answer:
Question 21.
Which is more powerful in these two gases - Methane or Carbon dioxide?
Answer:
Question 15.
Expand IPCC?
Answer:
2 Marks Question
Question 1.
Classify the seasons according to Indian calendar and write the months?
Answer:
| Seasons |
Months according to the Indian calendar |
| Vasantha |
Chaitra - Vashaka |
| Grishma |
Jyestha - Ashadha |
| Varsha |
Sravana - Bhadra |
| Sharad |
Aswayuja - Karthika |
| Hemantha |
Margashira - Pushya |
| Shishara |
Magha - Phalguna |
Question 2.
Write briefly about South-West monsoons?
Answer:
- The monsoon forms m the tropical area approximately between 2ON and 20S latitudes
- The heating of Land creates low pressure on the Landmass of Indian subcontinent
- Southwest monsoon onset reaches Kerala and gives rain to western ghats and northeast India except in coramandal coast
- It is operated in two branches, Arabian sea branch and Bay of Bengal branch
- Retreat of the monsoon Is marked by clear skies and rise in temperature
- Lower pressure conditions move to Bay of Bengal by early November
- Bulk of the rainfall of the coromandel coast is derived from depressions and cyclones
Question 3.
Observe the map given and answer the questions (a) and (b)?
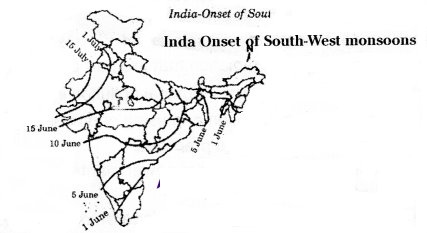
Question (a) When do southwest monsoons enter Ralasthan?
Answer:
South-west monsoons enter Rajasthan by 15th July
Question (b) What is meant by onset of monsoons?
Answer:
Low pressure in the Indian sub-continent; High pressure in the Indian Ocean. The southwest monsoons reach India by the beginning of June
Question 4.
Keeping the warning of scientists in mind, suggest measures to minimize Global warming?
Answer:
To minimise the Global warming quarrying, mining are to be reduced and afforestation should be increased. Burning of coal should be decreased. Fossil fuel burning is also decreased electronic appliances usage should be minimised so as to minimize the global warming
Question 5.
What is the relation between the temperature of atmosphere and insolation?
Answer:
The temperature of the atmosphere at a particular place near the Earths surface depends upon the insolation (heat from sun rays) received at that location. This is more intense in the low latitudes than in the high latitudes. As we move away from the equator towards the poles, the average annual temperature decreases
Question 6.
Explain the latitudinal extent of India?
Answer:
India is situated roughly between 8° and 37° N latitudes and the country is divided into almost two equal parts by the Tropic of Cancer. The part south of the Tropic of Cancer lies in the tropical zone. The part north of the Tropic of Cancer lies in the temperate zone
Question 7.
What are called western disturbances and what do they cause?
Answer:
Cyclone depressions coming from Mediterranean Sea called Western Disturbances and cause low to moderate. rainfall over northern India. This rainfall is boon to wheat crop which is generally cultivated in Rabi season
Question 8.
What is the effect of northeast trades on India?
Answer:
India lies in the trade wind belt of Northern HemIsphere - north-east trades blow over India from land to sea and are therefore dry. However, some amount of rainfall occurs on the Coromandel coast of Taniil Nadu from these winds, as they pick up moisture from the Bay of Bengal wtle crossing it
Question 9.
Write about mango showers In Telangana and Andhra Pradesh?
Answer:
Towards the end of the summer season, pro-monsoon showers (bursting monsoon) are common in the Deccan Plateau. These help in the early opening of mangoes and other plantation crops in peninsular India. Hence they are locally known as mango showers in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh
Question 10.
What is known as Onset of monsoon?
Answer:
The Arabian Sea Brandi arrives at the west coast of India and moves northward. Both the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal branches reach India by the beginning of June, which is known as Onset of monsoon
Question 11.
What is known as October heat?
Answer:
October-November is a period of transition from a hot wet condition to dry winter condition The retreat of the monsoons is marked by clear skies and rise in temperature. The land is still moist, Owing to the conditions of high temperature and humidity, the weather becomes rather oppressive. This is commonly known as October heat
Question 12.
Write about the Indian traditional seasons?
Answer:
In the Indian tradition, a year is divided Into six two-monthly seasons. This cycle of seasons that the people n north and central India follow is based on their practical experience and age-old perception of weather phenomena. There is a slight variation in the timing of the seasons between northern and southern India
The seasons are:
- Vasantha
- Grishma
- Varsha
- Sharad
- Hemantha
- Shishira
Question 13.
What is called Greenhouse effect?
Answer:
Keeping us warm is one of the most important things that the atmosphere does for us. It is like a light but effective, blanket enveloping Earth. The atmosphere traps a lot of the solar energy that reaches it. Earth by preventing it from totally escaping back into space. This is called Greenhouse effect
Question 14.
What is called AGW?
Answer:
Earlier cycles of cooling end warming happened over very long periods of time. This allowed much of the life on Earth the time to adapt to the changes. The problem now is that the heating is much mere rapid and could lead to catastrophic changes.Much of the warming that has been occurring since the Industrial Revolution is because of human activities. Hence, the current global warming trend Is called AGW (Anthropogenic Global
Warming; anthropogenic means caused by humans)
Question 15.
What does climate refer to?
Answer:
Climate refers to such conditions over a large area and follows a similar general pattern over many years. What have been the general conditions, year after year, over thirty years or more, gives us the climate
Question 16.
Explain the word monsoon?
Answer:
The climate of India is strongly influenced by the monsoon winds. The sailors who came to India during olden days noticed the regular periodic reversal of winds. They used these winds to sail towards the Indian coast. Arab traders named this seasonal reversal of wind system monsoon
Question 17.
Read the following paragraph and comment on bursting monsoon.
Towards the end of the summer season, pre-monsoon showers (bursting monsoon) are common in the Deccan Plateau. These help ¡n the early ripening of mangoes and other plantation crops in peninsular India. Hence, they are locally known as mango showers in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh?
Answer:
It is the sudden onset of rainfall in the first week of June. Around the time of arrival of monsoon, the normal rainfall increases suddenly and continues constantly for several days. This is known as burst of monsoon
Question 18.
Why do you think that the effects of climate change may be felt by all countries?
Answer:
- The effects of climate change like global warming, increase of mean sea level, degradation of Ozone layer, etc. are not limited to one particular country
- No country can escape from the negative impacts of climate change. Hence the effects of climatic change may be felt by all countries
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Analyze the relationship between the population density and geographical conditions of a particular area?
Answer:
- India is one of the most densely populated countries of the world
- The population density of India in the year 2011 was 382 persons per sq km
- Densities vary from 1102 persons per sq. km. In Bihar to only 17 persons per sq. km in Arunachal Pradesh
- Assom and most of the peninsular states have moderate population densities
- The Hilly, dissected and rocky nature of the terrain, moderate to low rainfall, shallow and less fertile soIls have influenced population densities in these areas
- The Northern plains and Kerala in the south have high to very high population densities because of the flat plains with fertile soils and abundant rainfall
Question 2.
Read the following paragraph and write your comments.
Most scientists from around the world agree on this much: AGW (Anthropogenic Global Warming: anthropogenic means caused by humans) is real, It is happening, and It is leading to rapid and drastic climate change. They warn that severe weather and other changes will increase wi the coming years and threaten titles we know it?
Answer:
Global warming: It refers to an unequivocal and continuing neither average temperature of Earths climate system?
Human activities contributing to global warming:
- Human activities contribute to climate change by causing changes in Earths atmosphere In the amount of greenhouse gases. aerosols and cloudiness
- The largest known contribution comes from the burning of fossil fuels, which releases
carbon dioxide gas to the atmosphere
- Greenhouse gases and aerosols effect climate by altering incoming solar radiation and outgoing infrared radiation that are part of Earths energy balance
- Due to industrial revolution, industrial pollution increases day by day
- Increasing of overpopulation and using of power-driven vehicles
- New methods of agricultural practices
- Mining, establishment of nuclear power plants and reckless deforestation, etc
Evil effects of global warming:
- Thee chgesotodng id warming am more rapid and Ieecng lo cashbox changes
- If the climate is raised by 2C, it leads to one-meter raise in the sea levels
- The faster melting of Himalayan glaciers would disturb the livelihood of fisher folk
Measures to minimize the influence of the global warning:
- Afforestation
- Reduction of burning of fossil fuels
- Instead of coal use of solar energy to be encouraged
- Reduction In the use of vehicles and encouragement of public transport system
- Release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere should be reduced
Question 3.
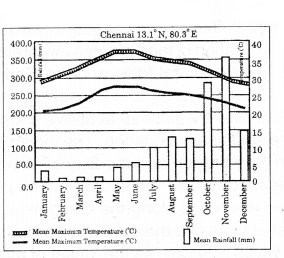
Observe the following graph and analyse it?
Answer:
- This climograph shows the details of Mean Maximum Temperature. Mean Minimum Temperature and Mean Rainfall of Chennai
- Chennai receives 38°C to 28°C maximum temperature during the year
- It receives 20°C to 28°C minimum temperature during the year
- The wettest months for Chennai are October and November
- It is because it receives rainfall during retreat of southwest monsoon or during northeast monsoon
- The driest month for Chennai is February/March and the rainfall tom the month is 15 mm
- The hottest months for Chennai are May and June
- Chennai has a moderate climate with 38°C as the highest and 20°C as the lowest temperature
- The weather in Chennai is mostly hot and humid
- The close proximity of ocean and equator makes the climate and weather in Chermai relatively consistent with less variation in the seasonal temperature
Question 4.
Name the factors influencing climate. Explain any two of them?
Answer:
The factors that affect climate are called climatic controls. These include
- Latitude
- Land-water relationship
- Relief
- Upper air circulation
- Latitude:
- Intensity of temperature depends on the latitude. It Is more intense in lower latitudes than at higher latitudes
- In India. the southern part lies in the tropical zone, closer to the equator: I has higher average temperature than that in the northern part.
Ex: The climate of Kanyakuman is different from that of Delhi
- Land-water relationship:
- The water bodies absorb and lose heat more slowly than land
- Due to this the formation of land and sea breezes influences the climate of coastal region. Ex : As Visakhapatnam is on the seashore, it is cooler than Guntur which is not on the seashore
Question 5.
Classify the monsoon winds In India and explain them?
Answer:
Monsoon winds
Climate of country is determined by various factors like Latitude. Relief, Landwater relationship and upper air circulation. Climate in India is influenced by monsoons. The Arab traders named the term monsoon. The monsoons in the tropical area are strong as low pressure forms here. The Southeast monsoon winds from the Southern hemisphere carry moisture as they flow over the Indian ocean and towards the equatorial low-pressure zones
After crossing the equator. these winds deflect towards the low pressure formed in the Indian subcontinent. The heating of land creates low pressure on the land mass of Indian sub-continent, especially over central India and the Gangetic plain. Along with this, the Tibetan plateau gets intensely heated and causes strong vertical air Currents and the formation of Pow pressure over the plateau at above 9 kms altitude.
They then flow as the southwest monsoon. The Indian peninsula divides them into two branches - the Arabian Sea branch and the Bay of Bengal branch. The Bay of Bengal branch stakes the Bengal coast and the southern face of the Shillong plateau. Then, it gets deflected and flows westward along the Gangetic valley. The Arabian Sea branch arrives at the west coast of India and moves northward. Both the branches reach India by
the beginning of June, which is known as the onset of monsoon
They gradually spread over the entire country in four to five weeks. The bulk of annual rainfall in India is received from southwest monsoon. The amount of rainfall ¡s very high along the west coast due to the Western ghats, and in north-east India due to the high peaked hills. Tamil Nadu coast (Coromandel), however, remains mostly dry during this season as it is in the rain shadow area of the Arabian Sea branch and is parallel to the Bay of Bengal branch The low-pressure conditions which once prevailed over north-western India move far South to the center of the Bay of Bengal by early November, During this period, cyclonic depressions are common which originate over the Andaman area. These tropical cyclones are often very destructive
The thickly populated deltas of the Godavari, Krishna, and Cauveri are their targets. No year ever goes disaster free. Occasionally. these tropical cyclones visit Sundarbans and Bangladesh too. Bulk of the rainfall of the Coromandel Coast is derived from depressions and cyclones
Question 6.
Explain the land and water relationship?
Answer:
The amount of sunlight that is first absorbed and then radiated back or directly reflected depends on the nature of the surface. Darker areas, such as heavy vegetated regions. tend to be good absorbers: lighter areas, such as snow and ice-covered regions, tend to be good reflectors. The ocean absorbs and loses heat more slowly than land. This affects climate in many ways. One of this is the formation of land and sea breezes
Question 7.
What is known as equable climate? When can we appreciate the effect of the sea?
Answer:
A large part of southern India. because of its long coast line, comes under the moderating influence of the sea, As such, the difference between the temperature of day and night and that of summer and winter Is not much. This is known as equable climate, If we compare similar places on the same latitude and altitude we can appreciate the effect of the sea
Question 8.
Explain upper atmospheric circulation?
Answer:
In the northern hemisphere, subtropical high-pressure belt gives rise to permanent winds. They blow towards the equatorial low-pressure belt by reflecting towards the west and are called trade winds. The German word irade means track and stands for blowing steadily the same direction and constant course. India lies in the be of dry northeast trade winds
Question 9.
Write the effect of jet streams on India?
Answer:
The climate of India is also affected by the movement of upper air currents known as jet streams. These are fast-flowing air currents in a narrow belt in the upper atmosphere, above 12,000 m. The speed vanes from about 110 kms in summer to about 184 km/h in winter. An easterly et stream develops at about 25°N latitude. A jet stream causes the neighboring atmosphere to cool. This cooling effect of the easterly jet stream causes rain from clouds already found over this latitude(25°N)
Question 10.
How is the ozone layer formed? How does It protect us?
Answer:
As Earth started to take shape from a fireball to a planet, many gases were released. These gases did not escape into outer space because of the Earths gravitational pull. It still holds them back. A thin layer of gases surrounds Earth and provides us several important benefits. For example: the oxygen that we breathe, the ozone that protects us from harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun, the nitrogen that our plants use to make proteins that we need, the medium through which fresh water is circulated, and keeps us warm
Question 11.
What are scientists discovering more recently?
Answer:
More recently, scientists are discovering large volumes of methane under the frozen tundras of the far northern latitudes (mainly in the vast expanses of northern Russia). As global temperature increases, the ice in the tundra melts more
The methane that is trapped under the ice escapes into the atmosphere, increasing the global temperatures. In turn, this causes oven more ice to melt more, releasing even more methane, and so on. Methane is said to be even more powerful than carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas
Question 12.
Why was the IPCC formed? Explain Its efforts?
Answer:
An international effort to form an agreement whereby all countries try to reduce their emission of greenhouse gases has so far not been achieved. An International organization called Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was formed to address this Issue. It has held many conferences to work out a treaty among the nations of the world to reduce AGW and try to slow down the process of climate change. None of those have been successful. The latest attempt was made at the IPCC conference in Warsaw (Poland), in 2013. This has also failed to achieve any agreement
Question 13.
Write the main characteristics of retreating monsoon?
Answer:
- The low-pressure conditions which once prevailed over north-western India move for south to the centre of Bay of Bengal by early November
- During this period cyclonic depressions are common which originate over the Andaman sea area
- No year is ever found disaster free
- Bulk of the rainfall of the coramandal coast is derived from depressions and cyclones
Question 14.
Read the following information and answer the given questions.
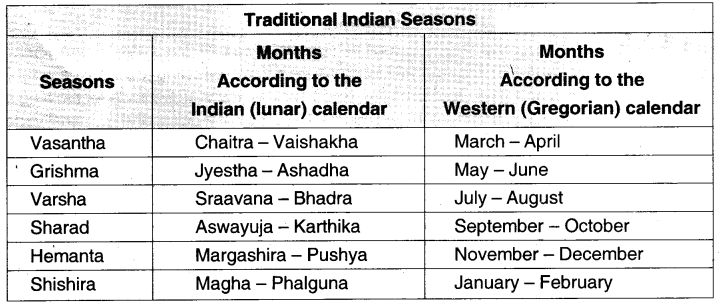
Question1. Name the two months of Grishma?
Answer:
Jyeshta and Ashadha
Question2. karthika and Aswayuja come under .........?
Answer:
Sharad
Question3. What are the Telugu months for November and December?
Answer:
Margashira and Pushya
Question4. What is the first lunar month?
Answer:
Chaitra
Question5. The western calendar can be called ......... calendar?
Answer:
Gregorian
Question6. In which Traditional seasons India experience rains?
Answer:
India experience rain an the traditional seasons of Varsha and Sharad
Question7. Which season does India experiences in Grishma and Vasantha?
Answer:
India experiences summer in the seasons of Grishma and Vasantha
Question8. Which season does India experiences from November to February?
Answer:
India experiences winter from November to February
Question9. Which Traditional season observed in the months of January and February?
Answer:
Shisira season is observed during the month of January and February
Question 15.
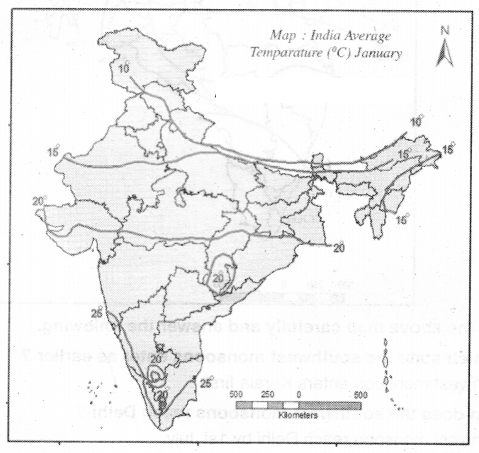 Read the above map and answer the following?
Read the above map and answer the following?
Question1. Find some places with an average of in 15°C temperature?
Answer:
Places with average temperature 15°C are Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh
Question2. What would be the range for the average temperature in the coastal regions of Tamil Nadu. Kerala and Karnataka?
Answer:
The average Ierrperature in coastal regions of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka is 25°C
Question3. What would be the average temperature of central India?
Answer:
The average temperature of central India is 20°C
Question4. Close to the line showing places where average temperature is 25°C, there is a small circle of places on 20°C. How is this possible?
Answer:
The regions which receive 20°C temperature are hilly areas and have less temperatures compared to coast sides. The effect of hot winds from sea waters is not effective on these place
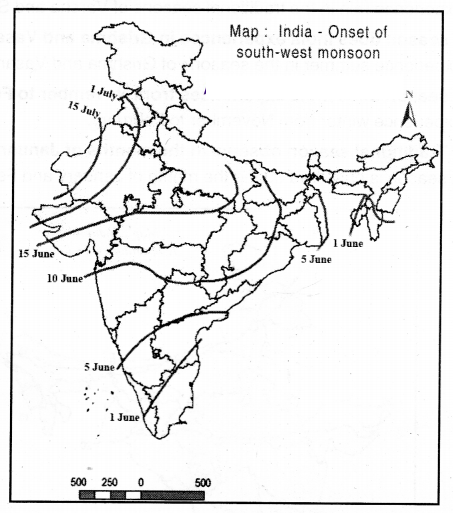 Observe the above map carefully and answer the following
Observe the above map carefully and answer the following
Question1. In which state the southwest monsoons enter as earlier?
Answer:
Southwest monsoon enters Kerala first
Question2. When does the southwest monsoons reach Delhi?
Answer:
Southwest monsoon ready Delhi by 1st July
Question3. On which date did they reach Gujarath. Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh?
Answer:
They reach Gujarath. Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh by June 15
Question4. Where does the southwest monsoons spread on 5th of June?
Answer:
On 5th June they spread to Kamataka and Andhra Pradesh touching Telangana
Question 16.
On an outline map of India, show the following?
Answer:
- Areas recorded with more than 40°C annual mean temperature
- Areas recorded with annual mean temperature less than IOC
- The direction of the southwest monsoon over India
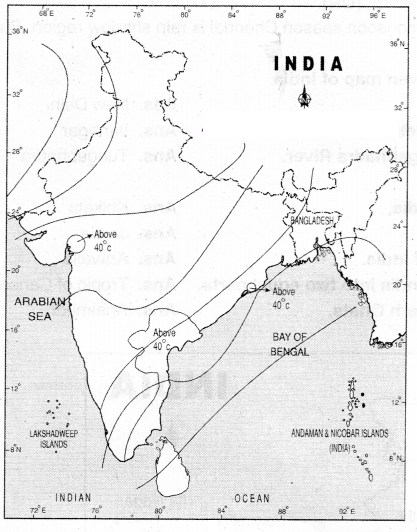
Question 17.
Observe the following Climographs and answer?
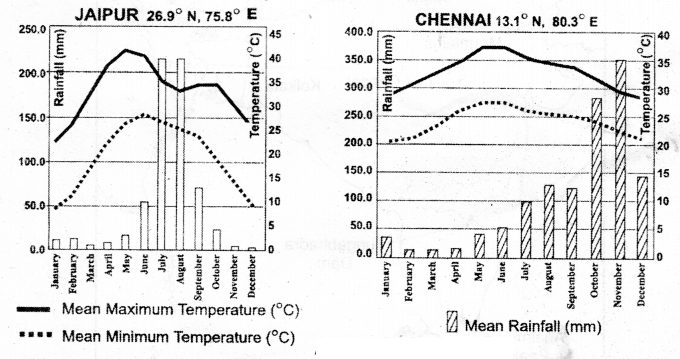
Question (a) Why is there a difference between the rainy season of Chennal and Jalpur?
Answer:
Jaipur receives rainfall by the South-West monsoons
Chennai receives rainfall by the North-East monsoons
Question (b) In which month Is the highest temperature recorded in Jaipur?
Answer:
May
Question (c) Among these two, which area gets highest rainfall?
Answer:
Chennai.
Question(d) Both the areas are rain shadow regions. Is it? How would you justify?
Answer:
Yes. In the South-West monsoon season, Jaipur and Cherna areas are rain shadow regions
(OR)
No. Only n the South-West monsoon season Chennai is rain shadow region. But not in North-East monsoon.
Question 18.
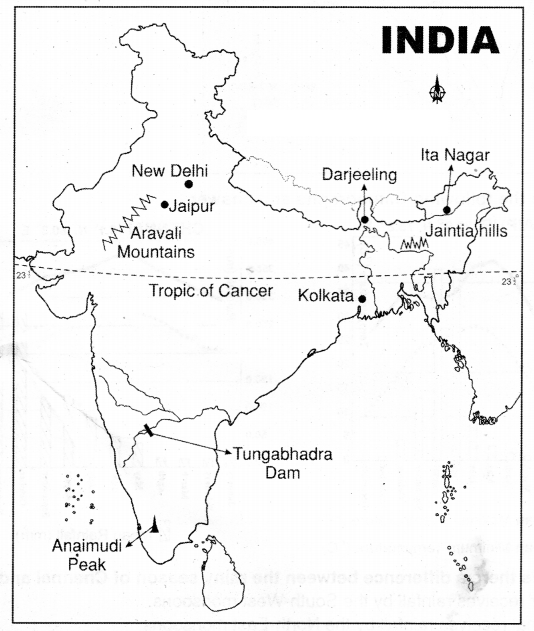
Locate the following in the given map of India?
Question1. Capital of India?
Answer:
New Delhi
Question2. Capital of Arunachal Pradesh?
Answer:
Itanagar
Question3. The Dam which is on Tungabhadra River?
Answer:
Tungabhadra
Question4. The river-based port in India?
Answer:
Kolkata
Question5. The capital of Rajasthan?
Answer:
Jaipur
Question6. The old fold mountains of India?
Answer:
Aravalis
Question7. This latitude divided the India into two equal parts?
Answer:
Tropic of Cancer
Question8. The highest peak in Western Ghats?
Answer:
Anaimudi
Question10. Jaintia Hills?
Answer:
Question 19.
"The Indian" agriculture depends completely on the monsoon." Describe the cycle of the monsoon patterns?
Answer:
The climate of India is strongly influenced by the monsoon winds. The sailors who came to India during olden days noticed the regular periodic reversal of winds. They used these winds to sail towards the Indian coast. Arab traders named this seasonal reversal of wind system monsoon
- The monsoon forms in the tropical area approximately between 20°N and 20°S latitudes
- The heating of land creates low pressure on the landmass of Indian subcontinent
- Southwest monsoon on set reaches Kerala and gives rain to western ghats and northeast India except in Coramandal coast
- It is operated in two branches, Arabian sea branch and Bay of Bengal branch
- Retreat of the monsoon is marked by clear skies and rise in temperature
- Lower pressure conditions move to Bay of Bengal by early November
- Bulk of the rainfall of the Coromandel coast is derived from depressions and cyclones