What do you mean by under-employment?
Answer:
Underemployment: Everyone is engaged in working, but no one is working to his full capacity, such employment is underemployment
Question 38.
Into how many sectors economic activities are divided?
Answer:
The economic activities are divided into 3 sectors - primary, secondary and services
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Draw the bar graph on the basis of the information given in the table below?
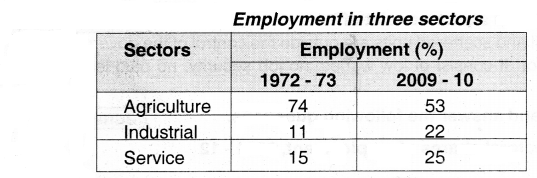
Answer:
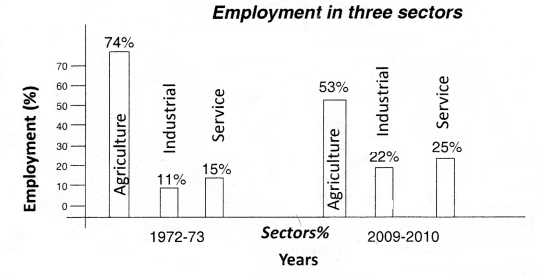 It shows how the people depend upon These sectors for enjoyment
It shows how the people depend upon These sectors for enjoyment
Question 2.
Observe the table and answer the questions.
The table shows the percentage of workers employed In different sectors in India in 1972-73 and 2009-10?
| Year |
Agriculture |
Industry |
Services |
| 1972-73 |
74% |
11% |
15% |
| 2008-09 |
53% |
22% |
25% |
Question(a) What are the major changes you observe from the above table?
Answer:
- Agriculture sector is decreased
- Industry and services are increased
- Industry is increased two times
- There is a great shift from the agricultural sector to industrial and service sectors
Question(b) What would be the reasons for the changes?
Answer:
Employment opportunities in agricultural sector are reduced from 74% to 53%. In industrial sector employment, opportunities are increased from 11% to 22%. Like that service sector employment opportunities are also increased from 15% to 25%
Reasons:
- Decline In agriculture (Problems seeds, rainfall, MSP, power cut, water.)
- Privatization is increased
- IT increased
- Opportunities in second and third sectors
Question 3.
Observe below Pie chart and analyse it
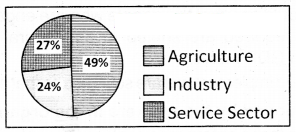 Employment in three sectors In 2011-12?
Answer:
Employment in three sectors In 2011-12?
Answer:
- There is a great shift from the agricultural sector to industrial and service sector. (or)
- The major changes like percentage of workers employed decrease in agriculture and increased both in industry and service sector are observed from the above pie chart compare with before years
Reasons:
- The important reasons like changes in farming methods setting up of new industries, and factories, and mass production of goods by factories of lower rates than agricultural goods. high payment for workers in other sectors compared to agriculture led to an employment shift from agriculture sector to service and manufacturing sectors
Question 4.
Observe the given graph and analyse it.
Shares of different sectors In
Gross Domestic Product
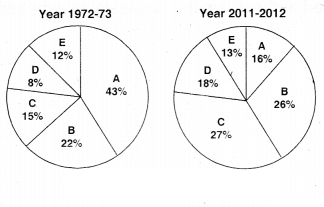
A - Agriculture
B - Industry
C - Trade, hotels, transport and communications.
D . Finance, insurance, real estate.
E - CommunIty, social and personal services?
Answer:
The graph explains about the share of different sectors in Gross Domestic Product in the year of 1972 -73.
The share of Agriculture is 43%
The share of Industry is 22%
The share of service sector joined together is 35%.
When compared to 1972 - 73 the share of different sectors in 2011 - 12 changed. In 2011 - 12 the agriculture share is only 16%. The industrial sector share Is 26%. The share of service sector joined together is - 58%. Totally in 2011 & 12 the share of agriculture is reduced. The Industrial sector share Is increasing. Finally, the service sector share increases very high
Suggestions:
To increase the share in agriculture sector the government should take the following measures
- Provide seeds, fertilizers, and pesticide motors to the farmers with a subsidy.
- The government should see that the people who are engaged in Industrial and Service sectors more than required are shifted to the agricultural sector so that the share of agricultural sector in GDP increases.
- The government should implement welfare schemes so that the agricultural sector flourishes.
Question 5.
Name the facilities enjoyed by the workers In the organised sector?
Answer:
The organised sector covers those enterprises or places of work where the terms of employment are regular and therefore, people have assured work. They are registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations which are even various laws such as the Factories Act, and Minimum Wages Act.
Shops and Establishments Act, etc. It is called organised because it has some formal processes and procedures. Workers in the organised sector enjoy the security of employment They are expected to work only for a fixed number of hours
If they work more, they have to be paid overtime by the employer. They also get several other benefits from the employees. They get paid leave, and payment during holidays. provident lund, etc. They are supposed to get medical benefits and, under the laws, the employer has to ensure facilities like drinking water and a safe working environment.
When they retire, many of these workers get pensions as well. People who work in the government or with companies or large establishments are all m the organised sector
Question 6.
Write a letter to the concerned authority on the necessity to Increase employment opportunities In rural areas?
Answer:
Letter to the concerned authority on the necessity to increase employment opportunities
In rural areas:
Jagtial.
16th April 2019.
To
The District Collector,
Jagtial district.
Jagtial.
Respected Sir,
I am a resident of the Vani Talkies area in Jagtial. I would like to bring the following few lines to your kind notice for favourable action. In recent times the population in Jagtial is increasing because in search of jobs or any source for livelihoods, many rural people are migrating to Jagtial.
As many people come to this District headquarters, congestion is increasing and people are facing problems of housing, high rents, drinking water, pure milk, schooling problems for the children of new grants and hike in the prices of vegetables. Pollution is also increased lithe industries are set up in rural areas, some people may retain there only.
Self-employment schemes should also be initiated. Transportation facilities are to be increased. Food for Work is to be enhanced. For farmers, sufficient water and power supply is essential and marketing facilities for vegetables are to be provided. Its my appeal to the government to concentrate on these opportunities at rural areas to make the people stay at their own places so as to avoid many problems.
Yours faithfully,
...........
To
The District Collector,
Jagtial District, Jaglial.
PIN: 505327
Question 7.
How can you say that organized sector Is better than unorganized sector?
Answer:
The organised sector is better than unorganised sector because of the following reasons
- Terms of employment are regular
- Firms are registered by the government
- Firms follow rules and regulations
- It gives security of employment
- Fixed working hours
- It provides paid leave
- Payment during holidays
- It provides provident fund
- It also ensures pension
Question 8.
What is the relation between population and employment?
Answer:
The Gross Domestic Product of a country has close relation with the total number of working people in that country. In every country, the population increases, it is essential that the country provides opportunities for those who are looking for work
Question 9.
"The workers in the agricultural sector are underdeveloped - support this statement?
Answer:
There are more people agriculture than Is necessary. So, even few people move out, production not be affected, In other worth, workers in agricultural sector are underdeveloped
Question 10.
Explain GDP Why are only final goods and services counted in GDP?
Answer:
- GDP is the sum of the money value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year within a country
- Only the value of final goods and services are counted in GDP because the value of final goods already includes the value of all the intermediate goods
Question 11.
Where are most of the people employed? Why did not a similar shift out of primary sector happen in case of employment?
Answer:
- Most of the working people are still employed in primary sector
- There had not been a singular shift out of agricultural sector in case of employment. The reason is: Secondary and tertiary sectors did not create enough jobs
Question 12.
Suggest any two measures to create more employment in rural India?
Answer:
Some measures to create more employment In rural India
- Irrigation facilities should be involved
- Roads should be constructed
- More education and health facilities should be provided
- Agro-based industries should be encouraged
Question 13.
Describe any three problems faced by workers In the unorganised sector?
Answer:
- This sector follows no government rules and regulations
- There is no regular employment
- They have no job security
Question 14.
How are the activities In the economy classified on the basis of employment conditions?
Answer:
Economic activities are classified into two sectors on the basis of employment conditions:
- Organised sector
- Unorganised sector
In the organised sector, the rules and regulations of employment are given to employees and everyone has to follow these rules. In the unorganised sector, there are no rules and regulations
Question 15.
Write any two differences between Intermediate goods and final goods?
Answer:
| Intermediate goods |
Final goods |
|
| 1) These goods are meant for further production |
1) These are used for final consumption |
| 2) These are not included GDP |
2) These are included in GDP |
Question 16.
How is the unorganised sector In the rural areas?
Answer:
In the rural areas, the unorganised sector mostly comprises of landless agricultural labourers, small and marginal farmers, sharecroppers and artisans
Question 17.
How is the unorganised sector In the urban areas?
Answer:
In the urban areas, unorganised sector comprises mainly of workers n small-scale Industries, casual workers in construction, trade and transport. etc. and those who work as steel vendors, head load workers, garment makers, rag pickers, etc
Question 18.
The service sector in India employs two different kinds of people. Who are they?
Answer:
Service sector In India employs the following two different kinds of people. They are:
- The people involved in such services that man directly help in the production of goods. e.g.: people involved in transportation, communication, etc
- The people involved in such services that may not directly help in the production of goods. e.g.: teachers, lawyers. etc
Question 19.
"Tertiary sector is not playing any significant role in the development of Indian economy." Do you agree? Support your answer?
Answer:
Yes. I do agree with the statement.
Over the last 5 decades, the most production has increased in the tertiary sector. It replaced the primary sector. The basic services are also provided by the government and private sector. As the income levels of the people raised, people are able to enjoy many more services like shopping, tourism, etc.
Therefore it is disputable that the tertiary sector ¡s playing a significant role in the development of the Indian economy
Question 20.
Classify the Services Sector?
Answer:
- Services sector comprises of community, social and personal services like public administration, defence, education, etc
- This sector also comprises finance, Insurance and real estate services like banks, post offices, LIC, etc
- It also comprises services like trades, hotels, transport and communication
Question 21.
How is the Organised sector different from an Unorganised sector?
Answer:
- The organised sector Is the enterprises or places of work where the terms et employment are regular and therefore, people have assured work
- The unorganised sector is characterised by small and scattered units which have remained largely outside the control of the Government. In This way the organised sector is different from an unorganised sector
Question 22.
Observe the following table and answer the questions that given below.
Contribution of organised and unorganised sectors?
| Sector |
Contribution (% of total) |
Employees |
Gross Domestic Product |
| Organised |
8 |
50 |
| Unorganised |
92 |
50 |
| Total |
100 |
100 |
Question (a) What percentage of labour in the unorganized sector get employment?
Question (b) Which sector get decent job security?
Answer:
a) 92%
b) Organized sector
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Nowadays In which economic sector the job opportunities are increasing? Give reasons?
Answer:
- Nowadays employment opportunities are available more in secondary and tertiary sectors
- Last 50 years onwards the swings are occurred in GDP all sectors, but employment is not increased. Yet, employment opportunities are increased secretary and tertiary sectors
Reasons:
- Establishment of industries in public and private sectors
- Increasing of technological methods
- Increasing of educational facilities
- Due to globalisation, Multinational companies are entering and industrial and service sectors are developed
- Transportation facilities are developing
- Migrations are increased
- Increasing of local foreign Investment
Question 2.
Suggest to Improve labour conditions in unorganized sector?
Answer:
- Wages to be increased
- Regular payment of wages
- Overtime work should be paid
- Sick leave provision and paid leave
- Better working conditions
- Retirement benefits to be provided
- Security in jobs
- Medical arid health facilities
Question 3.
What are the differences between organised and unorganised sectors in Employment?
Answer:
| Organised Sector Centre |
Unorganised Sector Centre |
| 1) It has some formal processes and procedures |
1) It has small and scattered units largely outside the control of government |
| 2) It gives the security of employment |
2) Rules and regulations are not enforced here |
| 3) It has a fixed number of work hours, and overtime will be paid by the employer |
3) Jobs here are low-paid and non-regular |
| 4) it provides paid leave, payment during holidays, provident fund, medical benefits. Etc |
4) There is no provision of overtime, paid leave, holidays leave due to sickness, etc |
| 5) It also ensures pensions. |
5) When there is less work, some people are asked to leave |
| 6) It has workers of government, companies and large establishments |
6) A lot also depends on the whims of the employer or changes In the market situation |
Question 4.
What measures should b. taken to create employment in your area?
Answer:
I should implement some steps to create employment in my area
- At first, in which the various non-farming activities are performed in a location which tails within a designated rural area
- Promoting the dairy industry
- Should give more importance to local handicrafts
- The second way hints at labour-intensive use
- For self-employment: Should provide bank loans with low rate of interests
- By creating a cost-effective school. Cyber cafes, retail outlets, transport systems etc
- Linking with industrial enterprises to rural citizens, better policies such as limit on work capacity and payment of minimum wages. etc
Question 5.
Read the following paragraph and write your comments on It.
In the past 50 years, there has been a further shift from industry to service sector for developed countries. The service sector has become the most important sector in terms of total production. Most of the working people have also made a sheath and are now employed In the service sector and most of the production activities are those of services and not manufactured goods?
Answer:
According to this paragraph, many workers are shifting from industries to service sectors in developed countries. The service sector plays an important and key role in economy. Most of the production activities are now In service sector.
There are three sectors in the economy. They are agriculture, industrial and service sectors. In developing countries, many people depend upon the agricultural sector whereas In developed countries it is the Industrial sector which gives more work but recently we observe the trend that many people are shifting from the industrial sector to the service sector for their livelihoods. In industries, the work may be strenuous to some extent and working hours are fixed. In services, there may be some relaxation of working hours and they can
render their services by doing at home on a laptop or on the internet.
IT and other services come under this category. Individual services are also a part of this. As the share of service sector is more in GDP. everybody is trying to shift to services. In services, the opportunities are increasing and new jobs are being created and so the people are moving towards services
I think that the people want to work in the sector which is providing more opportunities and where security, safety and respect are available. Job service sector provides these to some extent better than the other sectors the people shift toward service sector
Question 6.
Observe the following graph and analyse it.
Graph: Shares of three sectors - Employment and GDP - 2015-16
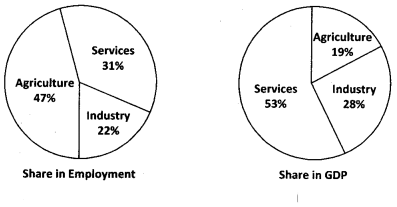 ?
?
Answer:
The given graph is about the shares of three sectors and employment and GDP. These particulars are related to 2015-16. The three sectors are agriculture, Industries and service. From agriculture sector, 47% share is there in employment. And service sector is 31% only. In Gross Domestic Product share from agriculture is 19% whereas it is more from service sector which is 53%
There are so many reasons for low share In Gross Domestic Product from agriculture. Low rainfall, power cuts, seeds problems, labourers problems, no minimum transport prices are some of the problems In the agriculture sector. In service sector fixed timings are there. They can sit m a safe place and soft work will be there. Regular salaries wi be available. Medical, casual leave facility, and proper working conditions are available. Banks will give them loans with low rate of interest.
I suggest the government to force the banks to give loans to the farmers m the agriculture sector. Subsidies should be given to the needy farmers. Seeds and fertilizers should be given to them free of cost cx at low prices. Our country is agro-based country. As more people depend on agriculture, government should concentrate on the development of farmers and so all farmers will be prosperous
Question 7.
Explain the problems faced by labourers in unorganised sector nowadays?
Answer:
In unorganized sector, the labourers are facing many problems. They have low wages. Job security is not there. This unorganized sector has small and scattered units largely outside the control of the government. Rules and regulations are not enforced here. Jobs are low-paid and not regular. If they work overtime, no additional pay is available.
No provision for paid leave, holidays and medical facilities. When there is less work some workers are asked to leave from the work. Then they will have no work at all. There is no retirement and no pension. Totally there is no guarantee for any of the facilities. Sometimes the job depends upon the whims of the employer. In organized sector, all these are in reverse. So there Is discrimination in between these two sectors
Question 8.
Observe the given table and analyse the share of GDP.
Share of GDP (2017-2018)?
| Sectors |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
| Agriculture |
16.85% |
17.15% |
16.79% |
16.17% |
16.28% |
15.45% |
| Industry |
29.4% |
28.4% |
27.66% |
26.58% |
26.16% |
| Services |
46.3% |
46.7% |
47.82% |
47.91% |
478% |
48.93% |
Answer:
The given table Is about share of GDP. The GOP is taken from 2012 to 2017. The sectors of economy are analysed in data form. The share of GDP from agriculture is very less and it has been reducing year by year. Industries are slightly decreasing from 2013. it is 29% only In 2012. But service sector is gradually increasing.
Many people nowadays are interested in working with service sector as they feel that it Is a white-collar job. Nobody is interested in agriculture. No farmer is interested to make his son a farmer because in agriculture more stress Is seen. Irregular rainfall, low prices (MSP), shortage of seeds, pesticides problem, fertiliser problems and so many problems, the agriculture sector is facing. In Industries also work conditions are not supportive. Agriculture Is technologically upgraded
Agriculture labourers are shifting to service, industrial sectors, Though 92% of workers are there in unorganised sector, they are contributing about 50% in GDP. Government should support the farmers and agriculture should be made a benefit able one
Question 9.
Read the given paragraph and write your opinion.
Majority of workers from scheduled castes, tribes and backward communities find themselves in the unorganized sector. It is worse if one is a woman from these communities. Besides getting the irregular and low-paid work, these workers also face social discrimination?
Answer:
Introduction: The given text is about the need to protect and support the unorganised sector workers who are suffering especially SCs, STs and BCs.
Interpretation: nowadays majority of workers in unorganised sector are SCs, STs and BCs.
Reasons:
- Though free education facilities were provided to those communities, due to lack of awareness towards education
- They face discrimination from centuries onwards
- Due to lack of job opportunities
My opinion: There is a need for regular wages and security in employment, safety and healthy conditions for SCs, STs and BCs who are in unorganised sector
- The government should provide minimum wages for unorganised sector workers
- Should provide safety conditions
- Hence the government should provide nutritional diets and medical facilities for unorganised sector workers
Thus the above steps will improve the both economic and social development unorganised sector workers
Question 10.
How can you say that GDP ignores some items?
Answer:
GDP records the market value of all final goods and services produced. But there are many items that are riot sold/ purchased in the market. Cries important example is the work that is done at home like cooking, and deaning. organizing. bringing up children, tending to plants and cattle, etc. In most instances, these do not involve any monetary transaction and therefore remain outside the GDP measure, though they are extremely important for the economy. Also, the unpaid work is done mostly by women even today, in India and across the globe. So. these are not included in GDP
Question 11.
Distinguish between organised and unorganised sectors?
Answer:
| Organised sector |
Unorganised sector |
| 1) This sector follows government rules |
1) This sector follows no rules |
| 2) The terms of employment are regular |
2) They are often not regular |
| 3) Working hours are fixed |
3) Working hours are not fixed |
| 4) People gel regular monthly salaries |
4) People get daily wages |
| 5) People get paid leave benefits, pensions, gratuity, etc |
5) No provision for any such benefits |
Question 12.
Explain the difference between primary. secondary and tertiary sectors with examples?
Answer:
- Primary sector: This includes those activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources. e.g.: Cultivation of paddy. This is known as primary sector because it forms the base of subsequent products that are made from it, This sector is also called Agriculture and Related sector
- Secondary sector: This sector covers those activities in which natural and primary products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing. e.g.: Manufacturing paper from banÙoo. This sector is also known as industrial sector
- Tertiary sector: This sector includes those activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. e.g.: Railways. Since they provide services to he the production, this sector is also called service sector
Question 13.
How is gross domestic product calculated? Give example?
Answer:
- The total value of goods and services produced in a country is Gross Domestic Product
- The value of intermediate goods is not considered for GDP
- Economists take the value of goods and services rather than adding number of goods
- People engaged in various economic activities In the three sectors viz, primary. secondary and services produce large number of goods and services whose total is GDP
Question 14.
Read the following paragraph and interpret It.
GOP records the market value of all final goods and services produced. But there are many items that are not sold! purchased in the market. One important example is the work that is done at home like cooking, cleaning, and organizing. bringing up children, trading to plants and cattle, etc. In most instances, these do not Involve any monetary transaction and therefore remain outside the GDP measure. though they are extremely important for the economy. Also, the unpaid work is done mostly by women even today in India across the globe?
Answer:
According to this paragraph, the domestic work done by mainly women Is not calculated under GOP and it is ignored. Women are mostly engaged in this work. These services of women are not included in the GDP. The women work is unpaid work.
A woman is the nucleus of the family in India. In our country, we give much importance to women. The woman in a family discharges her duties as a mother, wife and daughter-in-law and soon but not as an employee. Employees can be paid for their work but the work of a woman in a family cannot be paid While measuring the Grass Domestic Product the services of economic activities are considered
One should understand that the men and women discharge their duties well in their professions and different departments only while the women discharge their duties well at home. Economists may not consider these activities like cooking and cleaning. organizing, bringing up children and tending to plants and cattle in terms of money and wages. I agree with this because families depend on this work.
It is not monitorial work but a work of responsibility and affection. The work of the women also can be considered as a part of GDP. Economists should consider their work and calculate in GOP. The work done by women at home is not worthless Though they are not paid by the family members their services can be measured
Question 15.
Read the following paragraph and write whether you agree with this or not.
It means that there are more people in agriculture but everyone may not be fully occupied. So, even if few people move out, production will not be affected. in this way, more number of people are engaged than required in agriculture. This is called as disguised unemployment?
Answer:
According to this paragraph, there is no full in employment in agriculture. Partial employment Is there. It means many people depend on agriculture but they are not fully employed. It some of them move to another sector it will not affect the production.
In other words, it is called disguised unemployment. There are so many farmers like Gayathri owning about 2 or less acres of land. All the five members are working in the same fields though they dont have sufficient work. In such instances, few of them should go to work in others fields instead of doing work a little in their own fields
Hence they get full work and they get some extra income for their family. Their energies are utilized for other fields and so they lead their lives better. No one should remain idle. Not fully employed in agriculture is called underemployment. This underemployment leads to wastage of their potential. Human potentiality is to be utilised for the sake of national growth.
It is not only for the family but for the nations sake. My suggestion is that the government should collect data of this situation throughout the state and prepare plans to provide work by implementing programmes like MGNREGA, Mission Kakatiya, Jalaharam and other activities. Thus the people are engaged in some useful work and so they get sufficient work and improve their living conditions
Question 16.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion.
There are lakhs of farmers like Gayathn in India. This means that even if several people from the agricultural sector are provided with proper work elsewhere, agricultural production will not suffer. The incomes of the people who take up other work would Increase the total family income?
Answer:
It s explained in this paragraph that the small farmers in India have not sufficient work in the fields but they are not getting sufficient work as well as income. There is a suggestion for the families like Gayathri to go elsewhere for additional work so as to earn more income. Lakhs of families in India are small families having less than two acres of cultivable land. All the family members depend on the small piece of land. They get less work and they dont work up to their potentials.
This condition is called underemployment. In this condition, they should go to other work either in agricultural fields or to other sectors like Industries or service sector. So that they get sufficient work and sufficient income and their families improve their living conditions. This underemployment is seen in other sectors also. They have to find better opportunities in service sectors
First, they should try to opt for other work. Wherever the work is available where they should go for work. According to my opinion, the government should identify these people and plan to design various schemes to be implemented, in villages many people have no sufficient work. Many developmental works are needed for villages and towns. These people will be involved in that works and so they earn some income. People also think to work by organizing small shops, working as repair persons, transport persons and soon
Question 17.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion on it.
Today, we not only have to generate new employment opposites but also train many workers to work efficiently and with machines. We should invest In many industries, in both rural and semi-urban areas, so that we are able to produce many more goods and services?
Answer:
According to this paragraph, two things are very important. They are providing employment opportunities and giving training to them to work with machines, Without skill the workers and employees do not work efficiently. One more point is that the industries are to be opened in rural and semi-urban areas to increase in production of goods and services.
My opinion is that it is better to provide quality and skill-oriented training before generating employment to the people. If skill is provided they can work at any place it demands. Many Industries are being established In urban areas only.
Technology is bringing many changes in our daily life, in agriculture, industry and service sectors technology is used. Even in agriculture many machines like tractors, Combined Harvesters are there. Everyone should learn how to deal with these. For that training is necessary. This training is to be associated along with formal education also. Training in computer operations is also necessary. After Engineering many of the students are learning special skills for their employment
If skill in performing jobs and access to various opportunities are provided by establishing industries in rural and semi-urban areas. Without skill, it is not possible to run the industries. The individuals also try to learn various skills according to the needs and their interests so they can get good opportunities and the goods and services will be increased
Question 18.
Study the following table and prepare a paragraph describing It.
Contribution of organised and unorganised sectors?
| Sector |
Contribution (% of total) |
Employment |
Gross Domestic Product |
| Organised |
8 |
8 |
| Unorganised |
92 |
50 |
| Total |
100 |
100 |
Answer:
This table tells about the employment m organized and unorganized sector and its contribution in GDP. Employment In the organized sector Is only 8% whereas It is 92% in unorganised sector. The share In GDP is the same. It focuses on the conditions ol the world force depend on the unorganized sector m which the wages are low, security and respect is not observed. In organized sector the employees get regular salaries, they have specific working hours and they avail of loaves, medical benefits and other facilities. These are not available in the unorganized sector
Question 19.
Observe the following table and answer the questions that follow?
| Year |
Agriculture |
Industry |
service |
| 1972-73 |
74% |
11% |
15% |
| 2017-18 |
44% |
25% |
31% |
Question1. What is the table about?
Answer:
The table is about the percentage of workers employed In different sectors in India in 1972-73 and in 2017-18
Question2. Which sector Is providing more employment In 1972-73?
Answer:
Agricultural sector is providing more employment in 1972-73. It is about 74%
Question3. What percentage of employment Is decreased in the agriculture sector?
Answer:
30% of employment is decreased in agriculture sector
Question4. Why is the employment In agriculture decreasing?
Answer:
The employment is agriculture is decreasing because the workers are shifting to other sectors as there Is no prosperity in agriculture
Question 20.
Observe the table and answer the following questions.
Table: Distribution of Workers in India, 2017-2018 (%)?
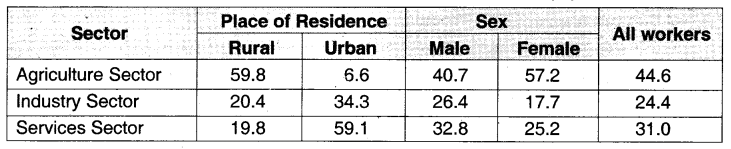
Question1. In which sector womens participation is high?
Answer:
Womens participation is high in agriculture sector
Question2. In which sector labour participation is low? Why?
Answer:
Labour participation is low in industrial sector because we are not industrially well-developed
Question3. Where more people are living, those who are engaged In service section?
Answer:
People engaged in service sector are living in urban areas
Question4. What is the reason for meagre participation of women In Industrial sector?
Answer:
Industries require physical labour and odd work hours
Question5. What does this table tell us?
Answer:
This table tells about the distribution of workers in India
Question6. Which sector Is prosperous In rural areas?
Answer:
Agricultural sector is prosperous in rural areas
Question7. Which sector is decreasing gradually?
Answer:
Agriculture sector is decreasing gradually
Question8. What have you observed In industrial sector with regard to place of residence?
Answer:
The industrial sector in urban areas Is double in comparison to rural areas
Question 21.
Observe the graph and answer the following questions.
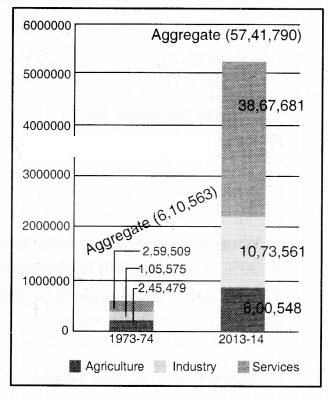
Question1. What is the graph about?
Answer:
The graph is about GDP by agriculture, industry and service sector
Question2. What is the aggregate GDP In 2013-14?
Answer:
The aggregate GDP in 2013-14 is Rs. 57,41,790 Crore
Question3. What is the aggregate GDP in 1972-73?
Answer:
The aggregate GDP in 1973-74 is Rs. 6,10,563 crore
Question4. Mention any two service activities?
Answer:
Tailoring, courier service. Etc
Question 22.
What is GDP? How do we estimate GDP?
Answer:
G.D.P. (Gross Domestic Product):
- For the country as a whole, we use the total value of goods and services produced in a country as the indicator of Income for the country
- The technical term to denote this value is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Estimation of G.D.P.:
- G.D.P. records the market value of all final goods and services produced
- G.D.P. records all of public and private consumption. Government outlays investments and exports less imports that occur within a defined territory
- Many items and services that are not sold I purchased in the market are not recorded in the G.D.P. Ex: Household works done by women
Question 23.
State why the organized sector is better than the unorganized sector?
Answer:
Organised sector is better than unorganised sector. The reasons are:
Organised sector covers those enterprises or places of work where the terms of employment are regular and therefore, people have assured work. They are registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations which are given in various laws such as the Factories Act.
Minimum Wages Act, Shops and Establishments Act etc, It is caned organised because it has some formal processes and procedures. Workers in the organised sector enjoy security of employment They are expected to work only for a fixed number of hours. If they work more, they have to be paid overtime by the employer
They also get several other benefits from the employers. They get paid leave, payment during holidays, provident fad, etc. They are supposed to get mental benefits and, under the laws, the employer has to ensure facilities like drinking water and a safe working environment.
When they retire, many of these workers get pensions as well. People who work in the government or with companies or large establishments are all in the organised sector
Question 24.
Locate the following in the given map of India?
Question1. The monsoons first enter into India into this state?
Answer:
Kerala
Question2. Locate the Jammu Hills?
Answer:
Jammu
Question3. The dun which is in Uttarakhand?
Answer:
Patti Dun
Question4. The wettest place In India?
Answer:
Mawsynram
Question5. The Great Indian Desert?
Answer:
Thar desert
Question6. The submerged point of Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
Answer:
Indira Point.
Question7. The capital of Andhra Pradesh?
Answer:
Amaravathi
Question8. The second largest river in South India?
Answer:
Krishna
Question10. Maikal plateau?
Answer: