Improve Your Learning
I. Reflections on concepts
Question 1.
Explain the difference between the valence electrons and the covalency of an element.
Answer:
| Valence Electrons |
Covalency |
| 1. The electrons present in the outermost orbital of an atom are called valence electrons. |
1. The total number of covalent bonds that an atom of an element forms is called covalency of the element |
| 2. Valence electrons depend upon the number of electrons present in that atom. |
2. Covalency depends upon the valence electrons. |
Question 2.
A chemical compound has the following Lewis notation:
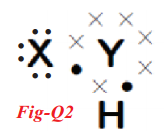
(a) How many valence electrons does element Y have?
(b) What ¡s the valency of element Y’ x . X
(c) What is the valency of element X?
(d) How many covalent bonds are there in the molecule? H
(e) To which groups the elements X and Y belong?
Answer:
(a) Six electrons.
(b) Two. because it has combined with two elements namely X and H.
(c) One
(d) Two covalent bonds one in Y - X and another one is Y - H.
(e) X is Hydrogen and Y is oxygen. I suggest the molecule is H2O (water).
Question 3.
How bond energies and bond lengths of molecule help us in predicting their chemical properties? Explain with examples.
Answer:
1. Bond length: Bond length or bond distance ¡s the equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two atoms which form a covalent bond.
2. Bond energy: Bond energy or bond dissociation energy ¡s the energy needed to break a covalent bond between two atoms of a diatomic covalent compound in its gaseous state.
3. If the nature of the bond between the same two atoms changes, the bond length also changes. For example, the bond lengths between two carbon atoms are C-C>C=C>C ≡ C.
4. Thus the various bond lengths between the two carbon atoms are ¡n ethane 1.54 Å, ethylene 1.34 Å. acetylene 1.20 Å.
5. The bond lengths between two oxygen atoms are in H2O2(O-O) Is 1.48 A° and in O2(O = O) is 1.21 Å.
6. Observe the table.
| Bond |
Bond length(Å) |
Bond (dissociation) energy (KJ mol-1’) |
| H -H |
0.74 |
436 |
| F-F |
1.44 |
159 |
| Cl-Cl |
1.95 |
243 |
| Br-Br |
2.28 |
193 |
| I-I |
2.68 |
151 |
| H-F |
0.918 |
570 |
| H-Cl |
1.27 |
432 |
| H-Br |
1.42 |
366 |
| H -I |
1.61 |
298 |
| H-O(of H2O) |
0.96 |
460 |
| H-N(of NH3) |
1.01 |
390 |
| H-C(of CH4) |
1.10 |
410 |
7. When bond length decreases, then bond dissociation energy Increases.
8. When bond length increases, then bond dissociation energy decreases.
9. Bond length of H -H in H2molecule is 0.74 Å and its bond dissociation energy is 436 KJ/mol, whereas bond length of F – F In F2molecule is 1.44 Å and its bond dissociation energy Is 159 K/mol.
10. Melting and boiling points of substances also can be determined by these bond energies and bond lengths.
Question 4.
Draw simple diagrams to show how electrons are arranged in the following covalent molecules:
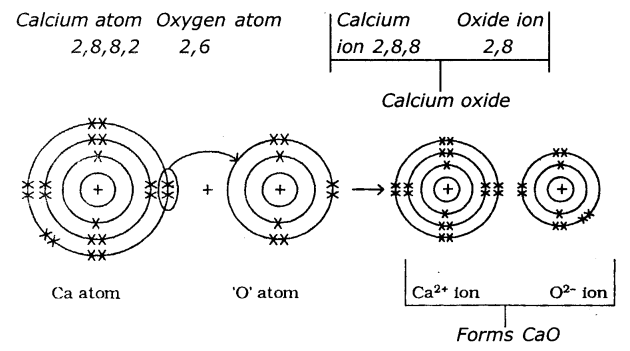
(a) Calcium oxide (CaO)
(b) Water (H2O)
(c) Chlorine (Cl2)
Answer:
(a) Calcium oxide (CaO)
(b) Water (H2O):
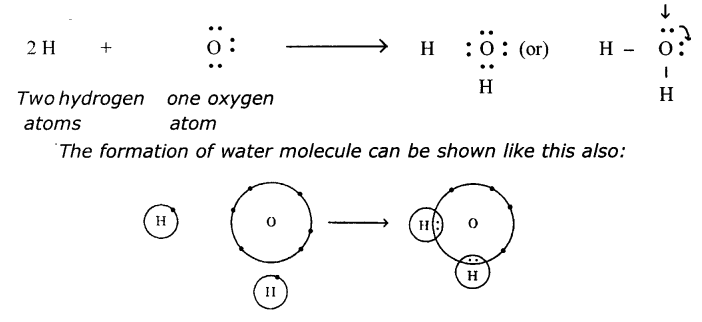
One oxygen and two hydrogen atoms form a water molecule, H2O
(c) Chlorine (Cl2):
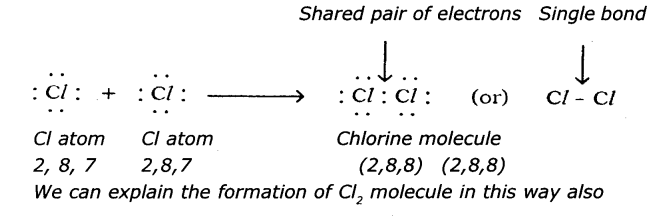
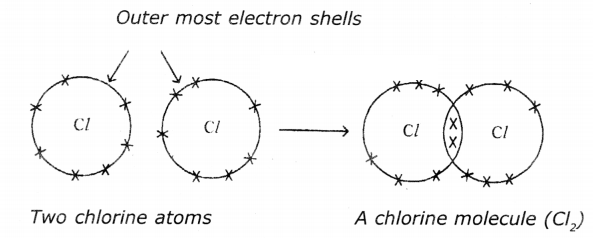
Question 5.
Represent each of the following atoms using Lewis notation.
(a) Beryllium
(b) Calcium
(c) Lithium
(d) Bromine gas(Br2)
(e) Calcium Chloride (CaCl2)
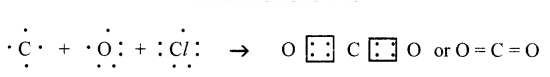
(f) Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Answer:
(a) Beryllium:
Beryllium atomic number = 4
Be -Valency electrons = 2
(b) Calcium:
Calcium atomïc number = 20
Ca -Valency electrons = 2
(C) Lithium:
Lithium atomic number = 3
Li -Valency electron = 1
(d) Bromine gas (Br2):
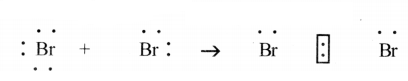
(e) Calcium Chloride (CaCl2):
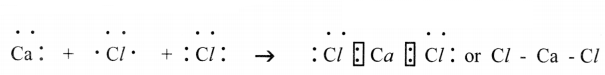
(f) Carbon dioxide (CO2):
Question 6.
Why do only valence electrons involve in bond formation? Why not electron of Inner shells? Explain.
Answer:
- When two atoms come sufficiently close together the valence electrons of each atom experience the attractive force of the nucleus in the other atom.
- The nucleus and the electrons ¡n the inner shell remain unaffected when atoms come close together.
- only the electrons in outermost shell of an atom get affected.
- Thus electrons in valence shell are responsible for the formation of bond between atoms.
Question 7.
List the factors that determine the type of bond that will be formed between two atoms.
Answer:
There are several factors that determine the type of bond which will be formed between two atoms. They are
- The force of attraction or repulsion between the electrons and protons.
- Number of valence electrons present in the valence shell of the atom.
- Electronegative difference between the atoms.
If the E.N difference between the two atoms is > 1.9, ionic bond is formed.
If the E.N difference between the two atoms is <1.9, covalent bond is formed.
- Atomic size
- Ionisation potential
- Electron affinity.
Question 8.
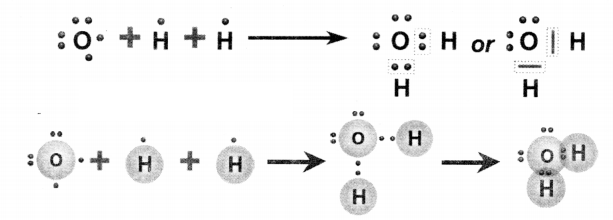
Represent the molecule H2O using Lewis notation.
Answer:
Question 9.
What is octet rule? How do you appreciate the role of the ‘Octet rule’ in explaining the chemical properties of elements?
Answer:
Octet rule: “The atoms of element tend to undergo chemical changes that help to leave their atoms with eight outer-shell electrons”.
→ Role of ‘Octet Rule :
- ‘Octet rule’ helps to explain the chemical activities of atoms of many elements.
- It explains why some elements are more reactive towards chemical reaction and some are not.
- It can explain the high reactivity of Alkali, Alkaline earth metals.
- It can also explain the high reactivity of halogens.
Question 10.
What is hybridization? Explain the formation of the following molecules using hybridization.
(a) BeCl2
(b) BF3
Answer:
(i) Hybridisation is a phenomenon of intermixing of atomic orbitals of almost equal energy which are present in the outer shells of the atom and their reshuffling or redistribution into the same number of orbitals but with equal properties like energy and shape.
(a) Formation of BeCl2(Beryllium chloride) molecule:
(ii) The atomic number of Beryllium is 4
(iii) The electronic configuration of Beryllium atom in its ground state is 1s22s2.
(iv) The electronic configuration of Beryllium atom in its excited state is 1s22s12p1.
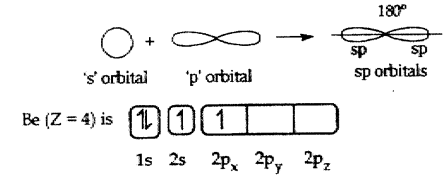
(i) In the excited Beryllium atom its ‘2s’ and ‘2px‘ orbitals intermix to give two equivalent ‘ sp ‘ hybrid orbitals.
(ii) The electronic configuration of Be is 1S22s12px1. It has one half-filled ‘p’ orbital.
(iii) The electronic configuration of 17 Cl is 1s2 2 s22p63s23px23py23pz1
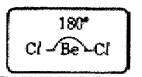
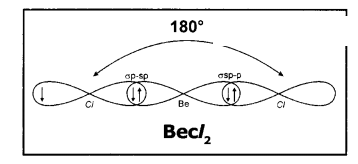
(iv) The half-filled 3pzorbitals of two chlorine atoms overlap with ‘sp’ hybrid orbitals of beryllium atom in their axes to form two σsp-pbonds.
(v) BeCl2 molecule so formed has linear shape. The bond angle in BeCl2 is 180°.
(b) Formation of Boron Trifluoride BF3:
(i) The central atom in BF3 is boron.
(ii) The electronic configuration of boron atom in its excited state is 1s22s12p2
B(Z=5)is
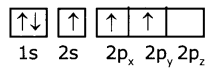
(iii) In the excited boron atom 2s’ orbital and two ‘2p’ orbitals intermix to give three equivalent sp2 hybrid orbitals.
(iv) In the formation of BF3 molecule, three sp2 hybrid orbitals of boron overlap with half-filled 2pz orbitals of three fluorine atoms. in their axes to give three bonds.
(v) BF3 molecule so formed has trigonal planar structure.
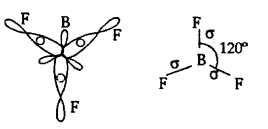
(iv) The bond angle ¡n BF3is 120°.
Application of Concepts
Question 1.
Explain the formation of sodium chloride and calcium oxide on the basis of the concept of electron transfer from one atom to another atom.
Answer:
1. Formation of sodium chloride (NaCl): Sodium chloride is formed from the elements sodium and chlorine. It can be explained as follows.
(a) Formation of Cation: When sodium atom loses one electron to get octet electron configuration it forms a cation (Na+) and gets electron configuration that of Neon (Ne)
Na → Na++e
E.C: 2, 8, 1 2,8 +1e
(b) Formation of anion: Chlorine has shortage of one electron to get octet in its valence shell. So It gains the election that was lost by Na to form anion (Cl) and gets electron configuration of Argon (Ar)
Cl + e→ Cl
E.C: 2,8,7 2,8,8
(c) Formation of the compound NaCl from ions: Transfer of electrons take place between ‘Na’ and ‘Cl’ atoms while they form Na+and Clions. These oppositely charged ions get attracted towards each other due to
electrostatic forces and form the compound sodium chloride (NaCl).
Na+(g)+ Cl(g)→ NaCl(s)
2. FormatIon of calcium oxide (CaO) Calcium Oxide Is formed from the elements Calcium and Oxygen. It can be explained as follows :
(a) Formation of Cation: When Calcium atom loses two electrons to get octet electronic configuration it forms a cation (Ca+2) and gets electron configuration of Argon (Ar)
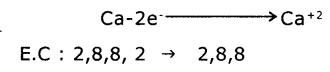
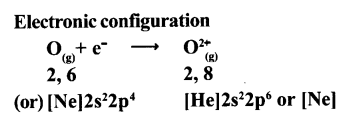
(b) Formation of anion: Oxygen has shortage of two electrons to get octet in its valence shell. So it gains the electrons that were lost by Ca to form anion (O-2) and gets electron configuration of Neon (Ne)
O + 2e-→ O-2
E.C: 2, 6 → 2,8
(c) Formation of the compound CaO from ions : Transfer of electrons between ‘Ca’ and ‘O’ atoms takes place while they form Ca+2and O-2ions. These oppositely charged ions get attracted towards each other due to
electrostatic forces and form the compound calcium oxide (CaO).
Ca+2(g)+ O-2(g)→CaO(s)
Question 2.
A, B and C are three elements with atomic numbers 6, 11. and 17 respectively.
(i) Which of these cannot form Ionic bond? Why?
(ii) Which of these cannot form covalent bond? Why?
(iii) Which of these can form Ionic as well as covalent bonds?
Answer:
(i) ‘A’ cannot form ionic bond. Its valence electrons are 4. It is difficult to lose or gain 4e–to get octet configuration. So it forms covalent bond [Z of A is 6 so it is carbon (c)].
(ii) ‘B’ cannot form covalent bond. Its valence electrons are 1 only. So it is easy to donate the electron for other atom and become an ion. So it can form ionic bond [Z of B is 11, so it is sodium (Na)].
(iii) Element C can form ionic as well as covalent bonds. The element with atomic number 17 is Cl. It is able to participate with Na in ionic bond forming NaCl and with hydrogen in HCl molecule as covalent bond.
Question 4.
How Lewis dot structure helps in understanding bond formation between atoms?
Answer:
- The valence electrons in an atom are represented by putting dots (.)on the symbol of the element, one dot for each valence electron.
- By knowing the valence electrons of two different atoms by Lewis dot structure, we can understand which type of bond is going to establish between them and forms corresponding molecule.
Question 5.
Explain the formation of the following molecules using valence bond theory.
(a) N2molecule,
(b) O2molecule
Answer:
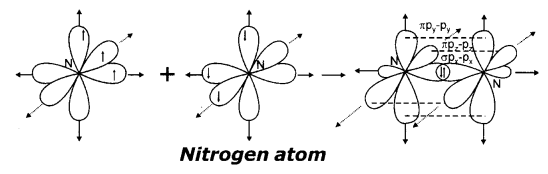
(a) Formation of N2molecule:
7N has electronic configuration 1s22s22px12py12pz1Suppose that ‘px’orbital of one ‘N’ atom overlaps the ‘px’ orbital of the other ‘N’ atom giving σpx-pxbond along the inter-nuclear axis. The pyand pzorbitals of one ‘N’ atom overlap the pyand pzorbital of other ‘N’ atom laterally, respectively perpendicular to internuclear axis giving 2π py-pyand pz– pzbonds. Therefore N2molecule has a triple bond between two nitrogen atoms. (N ≡ N)
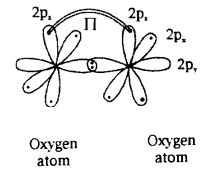
b) Formation of O2molecule:
- 8O has electronic configuration 1s22s22px22py12pz1
- If the ‘py’ orbital of one ‘O’ atom overlaps the ‘py’ orbital of other ‘O’ atom along the internuclear axis, a sigma py– pybond ((σpy- py) is formed.
- pzorbital of one ‘O’ atom overlaps the pzorbital of other ‘O’ atom laterally, perpendicular to the inter-nuclear axis giving a Πpz-pzbond.
- O2molecule has a double bond between two oxygen atoms. (O=O)
Question 6.
Predict the reasons for low melting points for covalent compounds when compared with ionic compounds.
Answer:
- The melting point is low due to the weak Vander Waal’s forces of attraction between the covalent molecules.
- The force of attraction between the molecules of a covalent compound is very weak.
- Only a small amount of heat energy is required to break these weak molecular forces, due to which covalent compounds have low melting points and low boiling points. :
- But some of the covalent solids like diamond and graphite have, however very high melting points and boiling points.
Higher Order Thinking questions
Question 1.
Two chemical reactions are described below.
(i) Nitrogen and hydrogen react to form ammonia.
(ii) Carbon and hydrogen bond together to form a molecule of methane (CH4)
For each reaction, give
a) The valence of each of the atoms involved in the reaction.
b) The Lewis structure of the product that ¡s formed.
Answer:
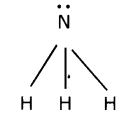
i) Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form Ammonia. The reaction is
N2+ 3H2→ 2NH3
a) The valency of each atom involved in the reaction.
Valence of Nitrogen = 3
Valence of Hydrogen = 1
(b) The Lewis structure of the product that is formed
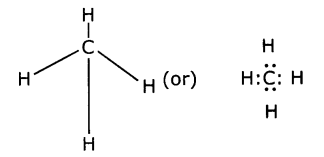
(i) Carbon reacts with hydrogen to form a molecule of methane. The reaction is
C + 2H2→ CH4
(a) The valency of each atom involved in the reaction
Valence of Carbon = 4
Valence of Hydrogen = 1
(b) The Lewis structure of the product
Suggested Projects
Question 1.
Collect the information about properties and uses of covalent compounds and prepare a report?
Answer:
A. Properties of covalent compounds:
- Covalent compounds are usually liquids or gases, only some of them are solids.
- They are usually liquids or gases due to the weak force of attraction between their molecules.
- They have usually low melting and low boiling points.
- They are usually insoluble in water but they are soluble in organic solvents.
- They do not conduct electricity.
- They show molecular reactions.
Uses of covalent compounds:
- Covalent compounds form 99% of our body.
- Water is a covalent compound. We know many uses of water.
- Sugars, food substances, tea, and coffee are all covalent compounds.
- Air we breathe in contains covalent molecules of oxygen and nitrogen.
- Almost everything on earth other than most simple inorganic salts are covalent compounds.
Page 150
Question 1.
How do they(elements)usually exist?
Answer:
Elements usually exist as group of atoms.
Question 2.
Do they exist as a single atom or as a group of atoms?
Answer:
Except inert elements, all others exist as group of atoms. Inert elements exist as single atoms.
Question 3.
Are there elements which exist as atoms?
Answer:
Inert elements exist freely as atoms.
Question 4.
Why do some elements exist as molecules and some as atoms?
Answer:
Inert elements exist as atoms as they won’t form any bond other atoms form bonds and exist as molecules.
Question 5.
Why do some elements and compounds react vigorously while others are inert?
Answer:
Elements which do not have octet conflgurtion in their valence shelf react vigorously with other elements to form stable entities and which have octet configuration in their valence shell are chemically inert in nature.
Question 6.
Why is the chemical formula for water H20 and for sodium chloride NaCl, why not HO2 and NaCl2’?
Answer:
In water, oxygen atom bonds with two hydrogen atoms where as sodi + ion forms single bond with chloride in NaCl – ion.
Question 7.
Why do some atoms combine while others do not?
Answer:
Elements which do not have octet configuration in their valence shell combine with other elements and which have octet in their valence shell are chemically inert in nature.
Question 8.
Are elements and Compounds simply made up of separate atoms Individually arranged?
Answer:
No. They are arranged
Question 9.
Is there any attraction between atoms?
Answer:
Yes, there is attraction chemical bond.
Question 10.
What is that holdlng them together?
Answer:
Force of attraction called chemical bond.
Page 152
Question 11.
Why there is absorption of energy in certain chemical reactions and release of energy In other reactions?
Answer:
The absorption of energy in chemical reactions occurs when the reactants ‘‘ less chemical energy than the product where as release of energy in chemical reactions occurs when the reactants have higher chemical energy than the products.
Question 12.
Where the absorbed energy goes?
Answer:
The energy absorbed by the molecules makes electrons to reach excited s e and Increases kinetic energy of the molecule.
Question 13.
Is there any relation to energy and bond formation between atoms?
Answer:
The interacting energy is the potential energy between the atoms. It is negative if the atoms are bound and positive if they can move away from each other. The interaction energy is the integral of the force over the separation distance so these two quantities are directly related. The interaction energy is turning at the equilibrium position. This value of the energy Is called the bond energy and is the energy needed to separate completely to infinity (the work that needs to be done to overcome the attractive force.)
Question 14.
What could be the reason for the change in reactivity of elements?
Answer:
Number of valence electrons In the atoms of the element.
Question 15.
What could be the reason for the less reactivity of noble gases?
Answer:
All the noble gases have eight electrons in the outermost shell, except Helium (He). Thus they have no valency electrons and are less reactive or not at all reactive.
Page 155
Question 16.
What have you observed from tSe above conclusions about the main groups?
Answer:
Main group elements lose or gain electrons to get noble gas electronic configuration.
Question 17.
Why do atoms of elements try to combine and form molecules?
Answer:
To get stable electronic configuration In their valence shell.
Page 156
Question 18.
Is it accidental that IA to VIlA main group elements durIng chemical reactions get eight electrons In the outermost shells of their ions, similar to noble gas atoms?
Answer:
No. It cannot be simply accidental, Eight electrons in the outermost shell definitely gives stability to the ion or atom. Based on the above observations a statement known as The Octet Rule” Is framed.
Page 157
Question 19.
Explain the formation of ionic compounds NaCl, MgCl2, Na2O and AlCl3 through Lewis electron-dot symbols (formulae).
Answer:
(1) Lewis electron-dot symbol for NacI :
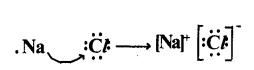
Formation of sodium chloride (NaCl) :
Sodium chloride Is formed from the elements sodium and chlorine. It can be explained as follows.
Na(s)+ 1/2 Cl2(g)→ Nacl(s)
Cation formation: When Sodium (Na) atom loses one electron to get octet electron configuration it forms a cation (Na+) and gets electron configuration that of Neon (Ne) atom.
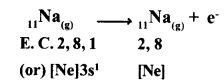
Anion formation: Chlorine has shortage of one electron to get octet in its valence shell. So It gains the electron from Na atom to form anion and gets electron configuration as that of argon (Ar).
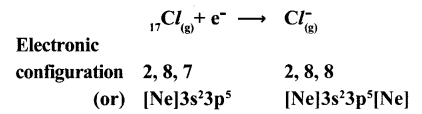
Formation of compound NaCl from its ions: Transfer of electrons between Na and cl atoms, results in the formation of Na+, and Cl- ions. These oppositely charged ions get attracted towards each other due to electrostatic forces and form the compound sodium chloride (NaCl).
Na+(g)+ Cl-(g)→ Na+(g)Cl-(a)or NaCl
2. Lewis electron-dot symbol for MgCl2:
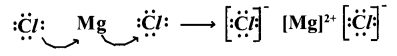
Formation of magnesium chloride (MgCl2) :
Magnesium chloride is formed from the elements magnesium and chlorine. The bond formation MgCl2 in brief using chemical equation is as follows :
Mg(a)+Cl2(g)→ MgCl2(a)
Cation Formation :
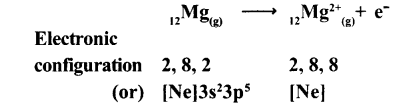
Anion formation :

The compound MgCl2 formation from its ions :
Mg2+ gets Ne configuration and Each Cl- gets Ar configuration.
Mg2+(g)+ 2Cl-(g)→ MgCl2(a)
One ‘Mg’ atom transfers two electrons one each to two ‘Cl’ atoms and so formed Mg2+and 2Cl- attract to form MgCl2.
3. Lewis electron-dot symbol for (Na2O) :
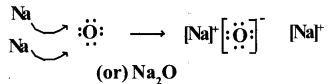
Formation of di-sodium monoxide (Na2O) :
Di-sodium monoxide formation can be explained as follows :
Cation formation (Na+ formation) :
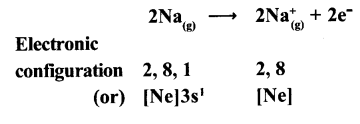
Anion formation (O2-, the oxide formation) Electronic configuration
The compound Na20 formation from Its ions is as shown.
2Na+(g) + O2-(g) → Na2O(g)
Two ‘Na; atoms transfer one electrons each to one oxygen atom to form 1Na+ and 02-.
Each Na+ gets ‘Ne’ configuration and 02- gets ‘Ne’ configuration.
These ions (2Na+ and 02-) attract to form Na2O.
4. Lewis electron-dot symbol for (AlCl3) :
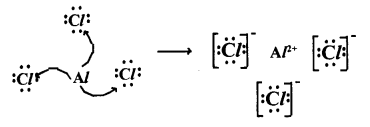
Question 20.
How do cations and anions of an ionic compound exIst in its solid state?
Answer:
Cations and anions are surrounded themselves In three-dimensional lattices to give properly shaped crystals.
Question 21.
Do you think that pairs of Na+Cl-as units would be present in the solid crystal?
Answer:
No, electrostatic forces are non-directional. Therefore, it is not possible for one Na+to be attracted by one Cl-and vice-versa. Depending upon the size and charge of a particular ion, number of oppositely charged Ions get attracted by it, but, in a definite number. In sodium chloride crystal each Na is surrounded by 6 Cl-and each Cl-by six Na ions. Ionic compounds in the crystalline state consist of orderly arranged cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces of attractions in three dimensions
Page 161
Question 22.
Can you explain the reasons for all these?
Answer:
An ionic bond is formed between atoms of elements with electronegativity difference equal to or greater than 1.9.
Page 162
Question 23.
Can you say what type of bond exists between atoms of nitrogen molecules?
Answer:
Triple Bond
Page 164
Question 24.
What do you understand from bond lengths and bond energies?
Answer:
Bonds formed between two atoms in different molecules have different bond lengths and bond energies
Page 165
Question 25.
Are the values not different for the bonds between different types of atoms?
Answer:
Different for different molecules.
Page 167
Question 26.
What is the bond angle in a molecule?
Answer:
It is the angle subtended by two imaginary lines that pass from the nuclei of two atoms which form the covalent bonds with the central atom through the nucleus of the central atom at the central atom.
Page 169
Question 27.
How is HCl molecule formed?
Answer:
The ‘is’ orbital of ‘H’ atom containing unpaired electron overlaps with ‘3p’ orbital of chlorine atom containing unpaired electron of opposite spin.
TS 10th Class Physical Science Chemical Bonding Activities
Activity 1
Question 1.
Write the Lewis structure of the given elements ¡n the table. Also, consult the periodic table and fill in the group number of the element.
Answer:
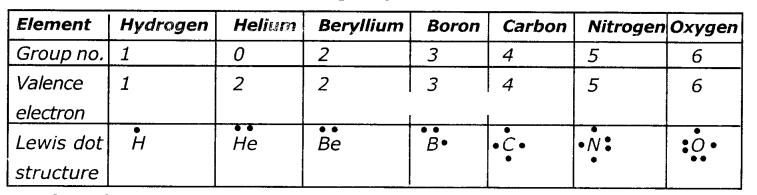
Question 2.
Look at the periodic table. Do you see any relation between the number of valence electrons and group numbers’?
Answer:
For groups 2-6 the number of valence electrons is its group number. Group 1 has one outer electron, group 2 has two, where groups 13-17 number of valence electrons is (Group number-10). 3, 2, 1 respectively. (ie, 8-5=3;8-6=2;8-7= 1)
Question 3.
What did you notice in Lewis dot structure of noble gases and electronic configurations of the atoms of these elements shown in table – 1.
Answer:
It was found that the elements get octet or ns2 np6 configuration except helium, duplet.