Improve Your Learning
I. Reflections on concepts
Question 1.
What information do you get from a balanced chemical equation?
Answer:
- A chemical equation gives information about the reactants and products by means of their symbols and formulae.
- It gives the ratio of molecules of reactants and products.
- It gives the relative masses of reactants and products.
- If the masses are expressed in grams, then the equation also gives the molar ratios of reactants and products.
- We can calculate the volumes of gases liberated at given condition of temperature and pressure using molar mass and molar volume relationship.
- Using molar mass and Avagadro’s number we can calculate the number of molecules and atoms of different substances.
Question 2.
Why should we balance a chemical equation?
Answer:
Chemical reactions obeys law of conservation of mass. So, the total number of atoms of each element in the reactants must be equal to the total number of atoms of each element in the products. So we should have to balance chemical equation.
Question 3.
Balance the following chemical equations.
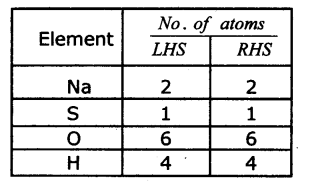
(a) NaOH + H2SO4→ Na2SO4+ H2O
Answer:
Step 1: Write unbalanced equation
NaOH + H2SO4→ Na2SO4+ H2O
Step 2: Compare number of atoms of each element on both sides. Add the suitable coefficients to balance equation.
2NaOH + H2SO4→ Na2SO4+ 2H2O
Step 3 : Make sure the coefficients are reduced to their smallest whole number values.
2NaOH + H2SO4→ Na2SO4+ 2H2O
Step 4: Check the answer
(b) KClO3→ KCl + O2
Answer:
Step 1: Write unbalanced equation.
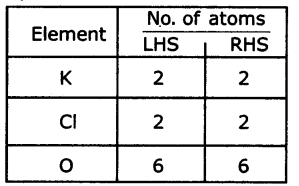
KClO3→ KCl +O2
Step 2: Add suitable coefficients to balance equation on both sides.
2KClO3→ 2KCl +3O2
Step 3: Make sure the coefficients are reduced to their smallest whole number values.
2KClO3→ 2KCl +3O2
Step 4: Check the answer.
(c) Hg (NO3)2+ Kl → Hg I2+ KNO3
Answer:
Step 1: Write unbalanced equation
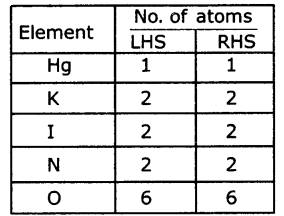
Hg(NO3)2+KI → HgI2+KNO3
Step 2: Add suitable coefficients to balance equation on both sides
Hg(NO3)2+2KI → HgI2+2KNO3
Step 3: Make sure the coefficients are reduced to their smallest whoíe number values.
Hg(NO3)2+2 Kl → Hg I2+ 2KNO3
Step 4: Check the answer
Question 4.
Mention the physical states of the reactants and products of the following chemical reactions and balance the equations.
(a) C6H12O6→ C2H5OH + CO2
Answer:
C6H12O6(aq) → 2C2H5OH(aq)+2CO2(g)
(b) NH3+ Cl2→ N2+ NH4Cl(s)
Answer:
8NH3(g)+3Cl2(g)→ N2(g)+6NH4Cl
(c) Na+H2O → NaOH+H2
Answer:
2Na(s)+2H2O (l) → 2NaOH (aq)+H2(g)
II. Application Of Concepts
Question 1.
Balance the following chemical equations after writing the symbolic representation.
(a) Calcium hydroxide (s) + Nitric acid (aq) → Water(l) + Calcium nitrate(aq)
(b) Magnesium (s) + Iodine(s) → Magnesium Iodide (s)
Answer:
(a) Calcium hydroxide (s) + Nitric acid (aq) → Water(l) + Calcium nitrate(aq)
Answer:
Ca(OH)2(sol)+ 2HNO3(so1)→ 2H2O(l)+ Ca(NO3)2(aq)Double displacement reaction
(b) Magnesium (s) + Iodine(s) → Magnesium Iodide (s)
Answer:
Mg(s)+ I2(s)→ MgI2(s)
Chemical combination reaction.
Question 2.
Write the following chemical reactions including the physical states of the substances and balance chemical equations
(a) Sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form sodium chloride and water.
Answer:
(a) Sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form sodium chloride and water.
Answer:
NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) ) → NaCl (aq) +H2O (l)
(b) Barium chloride reacts with liquid sodium sulphate to leave Barium sulphate as a precipitate and also form liquid sodium chloride.
Answer:
BaCl2(aq)+ Na2SO4(aq)→ BaSO4↓ +2 NaCl(aq )
Question 3.
Potassium nitrate and Sodium nitrate reacts separately with copper sulphate solution. Write balanced chemical equations for the above reactions.
Answer:
- Potassium nitrate reacts with copper sulphate to form potassium sulphate and copper nitrate.
2KNO3+ CuSO4→ K2SO4+ Cu(NO3)2
2. Sodium nitrate reacts with copper sulphate to form sodium sulphate and copper nitrate.
2NaNO3+ CuSO4→ Na2SO4+ Cu(NO3)2
Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
2 moles of zinc reacts with a cupric chloride solution containing 6.023 × 1022formula units of CuC12. Calculate the moles of copper obtained.
Zn(s) + CuCl2(aq)→ ZnCl2(aq)+ Cu (s)
Answer:
Given equation i.s
Zn(s) + CuCl2(aq)→ ZnCl2(aq)+ Cu(s)
1 mol + 1 mole → 1 mole + mole
From the above equation it is clear that 1 mole of zinc react with 1 mole of CuCl2solution to give 1 mole of copper.
2 moIes of Zn required 2 moles (12.046 × 1022formula units) of CuCl2, But only 1 mole (6.023 × 1022formula units) of CuCl2is available.
So, the No. of moles of copper obtained depends on amount of CuCl2present.
∴6.023 × 1022formula units (1 mole) of CuCl2products 1 mole of copper.
Question 2.
1 mole of propane (C3H8) on combustion at STP gives A’ kilo Joules of heat energy. Calculate the heat liberated when 2.4 ltrs of propane on combustion at STP.
Answer:
The chemical equation for combination of propane is
C3H8+ 5O2→ 3CO2+ 4H2O + A (heat energy)
1 mole of propane gives ‘A kilojoules of heat energy.
(1 mole of any gas occupies 22.4 litres at SW)
i.e., 22.4 ltrs. of propane gives ‘A’ kilojoules of heat energy
⇒ 2.25 ltrs. of propane gives 2.24/22.4 x A = 1/10 A (0.1 A) heat energy.
Question 3.
Calculate the mass and volume of Oxygen required at STP to convert 2.4 kg of graphite Into carbon dioxide.
Answer:
The chemical equation is
C + O2→ CO2(∴ graphite is also carbon)
12 gm + 32 gm → 44 gm
1 mole + 1 mole → 1 mole
From the above equation
12 gm of Graphite requires 32 gm of oxygen
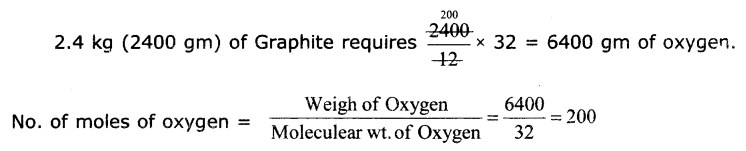
1 mole of oxygen occupies 22.4 litres
200 moles Is oxygen occupIes 22.4 x 200 4480 litres.
Page 20
Question 1.
How do we know a chemical reaction has taken place?
Answer:
a. The original substances lose their characteristic properties. Hence these may be products with different physical states and colours permanently.
b. Chemical changes may be exothermic or endothermic i.e. they may involve liberation of heat energy or absorption of heat energy.
c. They may form an insoluble substance known as precipitate.
d. There may be gas liberation in a chemical change.
Page 21
Activity 1.
Take about 1 g of quick lime (calcium oxide) in a beaker. Add 10 ml of water to this.
Touch the beaker with your finger.
Question 2.
What do you notice?
Answer:
We notice that the beaker is hot when we touch it. The reason is that the calcium oxide (quick lime) reacts with water and in the process heat energy Is released. Calcium oxide dissolves in water producing colourless solution of Ca(OH)2.
Question 3.
What is the nature of the solution?
Answer:
This solution Is a basic solution because a red litmus paper turns blue when dipped in the above solution
Activity 2
Take about 100 ml of water in a beaker and dissolve a small quantity of sodium sulphate (Na2SO4).
Take about 100ml of water In another beaker and dissolve a small quantity of barium chloride (BaCl2) observe the colours of the solutions obtained.
Question 4.
What are the colours of the above solutions?
Answer:
Colourless solutions
Question 5.
Can you name the solutions obtained?
Answer:
Sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution
Question 6.
Add Na2SO4solution to BaCl2solution and observe. Do you observe any change on mixing these solutions?
Answer:
A white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed
Activity 3
Take a few zinc granules in a conical flask. Add about 5 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid to the conical flask.
Question 7.
What changes do you notice?
Answer:
Effervescence Is observed
Question 8.
Keep a burning match stick near the mouth of the conical flask. with happens to burning match stick?
Answer:
It is put out. A pop sound is also heard.
Question 9.
Touch the bottom of the conical flask with your fingers. What do you notice?
Answer:
It Is hot
Question 10.
Is there any change in temperature?
Answer:
Temperature increases.
Page 22
Question 11.
Can you write a chemical reaction in any other shorter way other than the way we disused above?
Answer:
The reaction of calcium oxide with water can be written using symbols of elements.
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
Page 23
Question 12.
Is the number of atoms of each element are equal on both sides?
Answer:
The number of atoms of each element on both sides is equal.
Question 13.
Sodium sulphate reacts with barium chloride to give white precipitate, barium sulphate.
Na2SO4+ BaCl2→ BaSO4↓ + NaCl
Question 14.
Do the atoms of each element on left side equal to the atoms of the elements on the right side of the equation?
Answer:
No, the sodium and chlorine atoms are not balanced.
Page 25
Question 15.
Is it a balanced equation as per rules?
Answer:
Yes. But the coefficients are not the smallest numbers.
Question 16.
How do you say?
Answer:
Though the equation is balanced, the coefficients are not the smallest whole numbers. It would be necessary to divide all coefficients of equation by 2 to reach the final equation.
C3H8+ 5O2→ 3CO2+ 4H2O
Think And Discuss
You have brushed the wall with an aqueous suspension of Ca(OH)2. After two days the wall turned to white colour.
Question 1.
What are the steps involved in whitewashing of walls? (P.No. 23)
Answer:
A solution of slaked lime [Ca(OH)2] is prepared by adding water to quick lime [CaoO]. When Ca(OH)2is applied to the wall ¡t reacts with carbon dioxide in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate giving a shiny finish to the walls.
Question 2.
Write the balanced chemical reactions using the appropriate symbols. (P.No. 23)
Answer:
CaO(s)+ H2O(l)→Ca(OH)2(Aq)+ Q(heat energy)
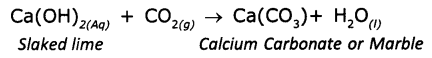
Activity 1
Question 1.
How can you demonstrate action of quick lime with water? What is the nature of the product? (2 Marks)
Answer:
- Take about 1 g of quick lime (Calcium oxide) in a beaker. Add 10 ml of water to this. Touch the beaker with your fingers
- We will notice that the beaker is hot when we touch it. Hence that’s an exothermic reaction.
- The reason is that the Calcium oxide reacts with water and in that process heat energy is released.
- Calcium oxide dissolves In water producing colourless solution, This solution turns red litmus to blue. Hence the product is a base.
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2+ Q
Activity 2
Question 2.
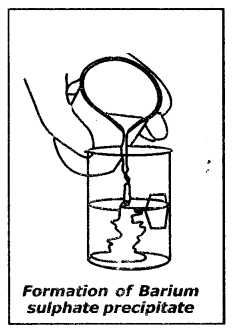
Explain the reaction between Sodium sulphate and Barium chloride.
Answer:
- luke about 100 ml of water in a beaker and dissolve a small quantity of sodium sulphate (Na2SO4)
- Take about 100 ml of water in another beaker and dissolve a small quantity of Barium chloride (BaCl2).
- These two solutions are colourless.
- Add Na2SO4solution to BaCl2solution and observe.
- Sodium sulphate solution on mixing with Barium chloride solution alarms a precipitate of Barium sulphate and also soluble Sodium chloride.
Na2SO4(aq)+ BaCl(aq)→ BaSO4(s)↓ + 2NaCl(aq)
- This is a double displacement reaction.
Question 3.
Explain the reaction of Zinc with HCl and write a balanced equation.
(OR)
Write the required material and experimental procedure for the experiment, “Hydrochloric acid reacts with ‘Zn’pieces and liberates H2”.
Answer:
Material required :
(i) Conical flask
(ii) Zinc granules
(iii) HCl
(iv) Matchbox.
- Take a few zinc granules in a conical flask.
- Add about 5 ml of dilute Hydrochloric acid to the conical flask.
- We observe a gas evolving out.
- Now keep a burning match stick near the mouth of the conical flask.
- The match stick is put out with a ‘pop’ sound.
- I Touch the bottom of the conical flask. We feel hot. Hence it is an exothermic reaction.

Zn(s) + 2HCl(l) → ZnCl2(s) + H2(g) ↑