TS 10th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 11 Principles of Metallurgy
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
What are minerals?
Answer:
The elements or compounds of the metals which occur in nature in the earths crust are called minerals.
Question 2.
What are ores?
Answer:
The minerals from which the metals are extracted without economical loss are called ores.
Question 3.
Name few highly reactive metals, which are never found in nature in free state.
Answer:
K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al.
Question 4.
Name few moderately reactive metals.
Answer:
Zn, Fe, Pb, Cu.
Question 5.
Name few metals which occur in native state in nature. Why do they occur so?
Answer:
Gold, Platinum and Silver are the metals which occur in native state in nature because of their low chemical reactivity.
Question 6.
What is dressing of an ore?
Answer:
The process of removal of impurities from an ore Is called dressing of the ore or concentration of the ore.
Question 7.
What is activity series?
Answer:
Arranging the metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity is known as activity series
K>Na>Ca>Mg>Al>Zn>Fe>Pb>H>Cu>Hg>Ag>Au
Highly reactive Moderately reactive Less reactive
Question 8.
How do you extract highly reactive metals?
Answer:
Highly reactive metals can be extracted by electrolysis of their fused compounds.
Question 9.
How do you extract moderately reactive metals?
Answer:
These metals are generally present as sulphides or carbonates. They are converted to oxides before reducing them to metals.
Question 10.
What Is roasting? Give an example.
Answer:
The process in which the ore s heated in the presence of oxygen or air below its melting point Is called roasting.
Eg: 2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2
Question 11.
What is calcInation ? Give an example.
Answer:
The process in which the ore is heated in the absence of oxygen or air is called calcination.
Eg: MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
Question 12.
Mention some properties of metals.
Answer:
Malleability, Ductility, Sonarity, Lusture, Electrical conductivity, etc., are some properties of metals.
Question 13.
Define Metallurgy.
Answer:
Metallurgy is the process of extraction of metals from their ores.
Question 14.
What is the major source of metals?
Answer:
Earth’s crust is the major source of metals.
Question 15.
Why do we call the oxygen-sulphur group chalcogen family?
Answer:
We know that most of the ores of many metals are oxides and sulphides. This is why the oxygen-sulphur (16-group) group is called chalcogen furry. (Chalco-oregenus produce).
Question 16.
Arrange the following metals In descending order of their reactivity. K, Zn, Ag, Fe, Ca, Au, Na, Pb.
Answer:
Highly reactive metals: K, Na, Ca
Moderately reactive metals: Zn, Fe, Pb
Low reactive metals: Ag, Au
The descending order of their reactivity: K, Na, Ca, Zn, Fe, Pb, Ag, Au,
Question 17.
What is concentration or dressing?
Answer:
Concentration or dressing means, simply getting rid of as much of the unwanted rocky material as possible before the ore is converted Into the metal.
Question 18.
How to choose a physical method in enriching of the ore?
Answer:
The physical methods adopted in dressing or enriching of the ore depends upon difference between physical properties of ore and gangue.
Question 19.
Give an example for reduction of metal oxide with carbon.
Answer:
The oxides are reduced by coke In a dosed female which gives the metal and carbon monoxide.
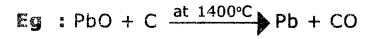
Question 20.
Give an example for reduction of oxide ore with CO. (ASI)
Answer:
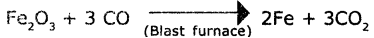
Question 21.
What is refining?
Answer:
The process of obtaining the pure metal from the impure metal is called refining of the metal.
Question 22.
Mention some important methods of refining.
Answer:
The important methods of refining are.
a) Distillation
b) Poling
c) Liquation
d) Electrolysis.
Question 23.
What is flux?
Answer:
Flux Is a substance added to the ore to remove the gangue from it by reacting with ore. It the impurity is acidic substance, basic substance is used as flux and vice-versa.
Question 24.
What is the role of furnace in metallurgy?
Answer:
The furnace is the one which is used to carry out pyrochemical processes In metallurgy.
Question 25.
Why do we add impurities to electrolytes during electrolytic extraction of metals?
Answer:
A large quantity of electricity is required to keep the ore in molten state, during electrolysis. Hence suitable impurities are added to the ore (electrolyte) to decrease its melting point.
Question 26.
How do various metals In the activity series react with chlorine on heating?
Answer:
All the metals react with chlorine on heating to form their respective chlorides
But the reactivity decreases from top to bottom.
Question 27.
Is Silver is mineral or Ore? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Silver neither mineral nor ore. It Is a metal.
Question 28.
What is Gangue?
Answer:
The impurities obtained during dressing of ore is called gangue.
Question 29.
Where are used the thermite process in daily life?
Answer:
Joining railings of railway tracks.
Joining cracked machine parts.
Question 30.
Give any two examples of ores with their formulas.
Answer:
Bauxite AlO2.2H2O
Magnesite MgCO3
Question 31.
What are the preventive methods do you take for rusting iron materials?
Answer:
Iron materials can be prevented from rusting by
Painting material
Preventing the surface of the iron material to come in contact with atmosphere
Coating the materials with non-rusting materials by electroplating method.
Applying oil to prevent rusting.
Question 32.
How do you know the reactivity of metals with chlorine, decreases from top to bottom?
Answer:
We know that the reactivity of metals with chlorine decreases from top to bottom from the heat evolved when the metal reacts with one mole of chlorine gas to form chloride.
Question 33.
Aluminium occurs in combined state in nature whereas gold Is found In free state. Why?
Answer:
Gold has low reactivity and so occurs In free state. Aluminium is electropositive metal and has high reactivity and occurs as oxide or chloride.
Question 34.
Why is carbon not used for reducing aluminium from aluminium oxide?
Answer:
The oxide of aluminium is very stable and can be reduced by electrolytic process.
Question 35.
An ore gives CO2on treatment with dilute acid. Identify th. ore and name the process that should be used to concentrate this ore.
Answer:
The ore gives CO2 on treatment with dilute acid, therefore It is a carbonate ore. The ore after concentration is converted Into free metal by
CalcInation
Smelting or Reduction or
Electrolybc process
Question 36.
Name two metals other than aluminium which are obtained by electrolytic reduction.
Answer:
Sodium and Magnesium.
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Silicon Is a metalloid. How do you support this?
Answer:
Silicon exhibits following properties, so I conclude that it is a metalloid.
It has metallic lustre by nature.
It exists in several metallic and non-metallic compounds.
It is brittle in nature.
All metalloids are usually occurs in combined states both metals and non-metals.
Question 2.
Mention the most important metals and non-metals from the following products.
a) Annapurna salt
b) Liquid used in thermometer
c) Lead of the pencil
d) Chlorophyll
e) Filament in electric bulb
f) Enamel layer on teeth
Answer:
a) Annapurna salt: Iodine, chlorine: Non-metals
b) Liquid used in thermometer: Mercury: Metal
c) Lead of the pencil: Graphite: Non-metal
d) Chlorophyll : Magnesium: Metal
e) Filament in electric bulb: Tungsten: Metal
f) Enamel layer on teeth: Calcium phosphate: Non-metal
Question 3.
Identify the metal present In the following Ores.
i) Epsom Salt
ii) Horn Silver
iii) Cinnabar
iv) Galena
Answer:
i) Magnesium
ii) Silver
iii) Mercury
iv) Lead
Question 4.
What Is meant by extraction of metals?
Answer:
The separation of metals from ores Is called extraction of metals.
Question 5.
Write the chemical equations of thermite reactions.
Answer:
2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe + Heat
2Al + Cr2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Cr + heat
Question 6.
Give an example of auto reduction of sulphide ores.
Answer:
In the extraction of Cu, from its sulphide ore, the ore is subjected to partial roasting in air to give its oxide.
2Cu2S + 3O2→ 2Cu2O+ 2SO2
When the supply of air Is stopped and the temperature Is raised, the rest of the sulphide reacts with oxide and forms the metal and SO2
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2
Question 7.
Explain the process of hand-picking.
Answer:
If the ore particles and the impurities are different in one of the properties like colour, size, etc., the ore particles are hand-picked, using that property. Thus, the metal particles are separated from their impurities.
Question 8.
What is the role of washing In enriching the ore?
Answer:
Washing is one of the physical methods la enriching the ore.
Ore particles are crushed and kept on a sloppy surface. They are washed with controlled flow of water.
Less sensitive impurities are carried away by water flow leaving the more dense ore particles behind.
Question 9.
Write the reactions inside a blast furnace.
Answer:
The reactions inside a blast furnace are :
2C (Fuel) +O2 → 2CO
Fe2O3 (Haemette)+ 3C0 → 2Fe + 3CO2
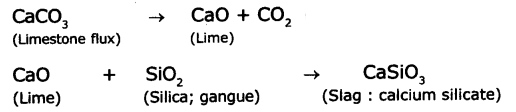
Question 10.
Do all furnaces have same structure? Explain.
Answer:
Different furnaces have different structures.
In a blast furnace, both firebox and hearth are combined in bg chamber, which accommodates both ore and fuel. It has a cup and cone arrangement at its top to send the ore Into the furnace.
Reverberatory furnace has both firebox and hearth separated, but the flames obtained due to the burning of the fuel touch the ore in the hearth and heat it.
In furnaces like retort furnaces, there is no direct contact between the hearth and firebox and even the flames do not touch the ore.
Question 11.
How do various metals in activity series react with steam?
Answer:
The metals from potassium to iron displace H2 (Hydrogen gas) from steam with decreasing reactivity. That means the reaction of potassium with steam is violent but the reaction of iron Is very slow.
The metals from lead to gold are unable to displace hydrogen from steam.
Question 12.
How do various metals in the activity series react with dilute strong acids?
Answer:
1) The metals from potassium to lead displace hydrogen from dilute strong acids with decreasing reactivity.
a) The reaction of potassium is explosive
b) The reaction of magnesium is vigorous
c) The reaction of Iron is steady
d) The reaction of lead is slow
2) The metals from copper to gold do not displace H, from strong dilute acids.
Question 13.
How do you reduce purified ore to the metal of the top of activity series? Explain.
Answer:
The reduction of ore to particular metal mainly depends on position of metal in the activity senes.
Extraction of metals at the top of activity series
Simple chemical reduction methods like heating with C, CO etc., to reduce the ores of the metals are not possible with metals like K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al.
The temperature required for the reduction is too high and more expensive.
The only method used to extract these metals is by electrolysis of their fused compounds.
Question 14.
What are the preventive techniques used in corrosion of metals?
(OR)
Write two precautions to prevent corrosion of metals in your daily life.
Answer:
Prevention of corrosion of metals
Covering the surface of metal with paint or by some chemicals like bisphenol which prevent the surface of the metallic object to come In contact with atmosphere.
Covering the surface of metal by other metals like tin or zinc that are Inert or react themselves with atmosphere to save the metal.
An electrochemical method in which a sacrificial electrode of another metal like magnesium and zinc etc., corrodes itself to save the metal.
Question 15.
Give some examples for corrosion.
Answer:
Examples for corrosion:
The rusting of iron (Iron oxide)
Tarnishing of silver (Silver sulphide)
Development of green coating on copper (Copper carbonate) and bronze.
Question 16.
What is 22-carat gold? Why It Is preferred for making jewellery?
Answer:
Pure gold, known as 24-carat gold is very soft.
So it is not suitable for making jewellery.
It is alloyed with either silver or copper to make it hard.
So they use 22-carat gold m which pure gold is alloyed with 2 parts of either sliver or copper for making gold jewellery.
Question 17.
Write about the electrolysis of NaCl.
Answer:
1) Fused NaCI is electrolysed with steel cathode and graphite anode.
2) The metal sodium (Na) will be deposited at cathode and chlorine gas liberates at the anode.
At Cathode : 2 Na+ + 2e- → 2Na
At Anode: 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
Question 18.
What is a furnace? Explain various parts of furnace.
Answer:
Furnace: Furnace Is the one which is used to carry out pyrochemical processes in metallurgy.
Furnace has mainly three parts :
Hearth: The hearth is the place inside the ore is kept for hearting.
Chimney: ChImney is the outlet through which flue (waste) gass o out of the furnace.
Firebox: Firebox is the part of the furnace where the fuel is kept for burning.
Question 19.
Why alloying s preferred for metals? Explain with examples.
Answer:
Alloying is a method of improving the properties of a metal. We can get desired properties by this method.
For example, iron is the most widely used metal. But it Is never used In its pure state.
This is because pure Iron Is very soft and stretches easily when hot.
But, if it is mixed with a small amount of carbon, It becomes hard and strong.
When iron is mixed with nickel and chromium we get stainless steel which is not corrosive.
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
The results of reactions of metals A, B, C, D, and E with different solutions are given In the table below. Observe the table and write answers.
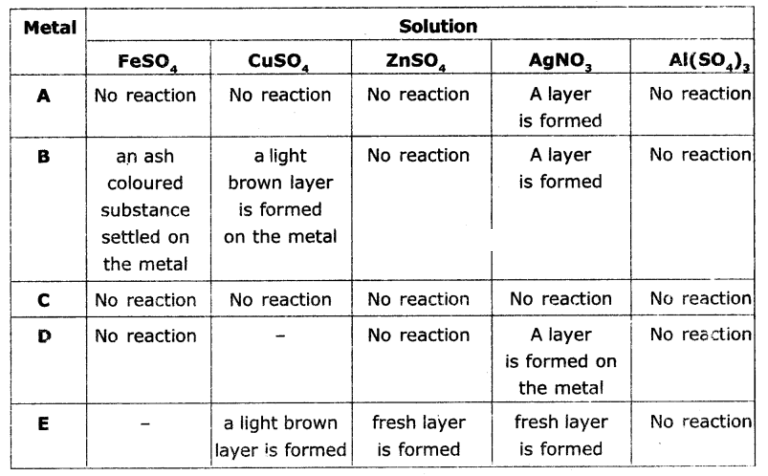
a) Which Is the highly reactive metal? Why?
b) Which is the least reactive metal? Why?
c) Which metals form brown layer?
d) Arrange the metals A, B, C, D, E In the order of their reactivity?
Answer:
a) Metal ‘E’ is more reactive among all the metals given because it displaces all the elements from the compounds given In the table.
b) Metal ‘C is the least reactive metal because it does not displace any other metal from the compounds given in the table.
c) Metals B and E will form brown layer.
d) The ascending order is as follows C < A < D < B < E.
Question 2.
Explain purification or refining of crude metal.
(OR)
Write the short notes on each of the following.
a) Distillation
b) Poling
C) Liquation
d) Electrolysis
(OR)
State the methods used to the purification of crude metals. Explain In which context these methods are used.
Answer:
1) The process of obtaining the pure metal from the impure metal is called refining of the metal.
2) Some of the processes of refining are
Distillation
Poling
Liquation
Electrolytic refining.
3) The process that has to be adopted for purification of a given metal depends on the nature of the metal and its Impurities.
i) Distillation: This method is very useful for purification of low boiling ‘metals like zinc (Zn) and mercury (Hg) containing high-boiling metals as impurities: The extracted metal in the molten state ¡s distilled to obtain the pure metal as distillate.
ii) Poling: The molten metal Is stirred with logs of green wood: The impurities are removed either as gases or they get oxidized and form sum (slag) over the surface of the molten metal. Blister copper is purified by this method.
iii) Liquatlon: In this method, a low-melting metal like Tin can be made to flow on a slope surface to separate it from high-melting impurities.
iv) Electrolytic refining:
1. In this method, the impure metal is made to act as anode.
2. A strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode.
3. They are put in a suitable electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal.
4. The required metal gets deposited on the cathode in the pure form.
5. The metal constituting impurity, goes as the anode mud. The reactions are:
At anode: M → Mn++ n.e
At cathode: Mn++ n. e- → M
(M = pure metal, n 1, 2, 3,)
Question 3.
Write the physical methods used for the concentration of the ore. Explain the method used for concentration of the sulphide ore.
Answer:
Methods used for the concentration of ore:
Hand-picking
Washing
Froth flotation
Magnetic separation
Forth flotation process is used for concentration of sulphide ore.
Froth Flotation process
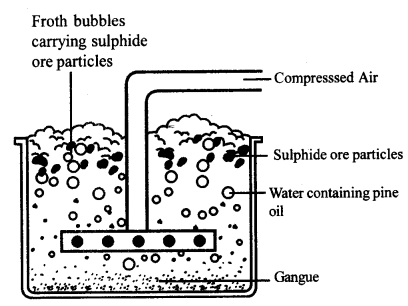
Froth Floatation process for the concentration of sulphide ores
This method ¡s mainly useful for sulphide ores which have no wetting property where as impurities get wetted.
The ore with impurities is finely powdered and kept In water taken in a floatation cell.
Air under pressure Is blown to produce froth In water.
Froth so produced takes the ore particles to the surface whereas, impurities settle at the bottom.
Froth is separated and washed to get ore parties.
Question 4.
What Is corrosion? Explain the chemistry of corrosion. (or) Explain the process involved In corrosion.
Answer:
Corrosion: Corrosion is the deterioration of a metal as a result of chemical reaction between it and the surrounding environment.
Chemistry of corrosion:
1. The chemistry of corrosion in quite complex but it may be considered essentially as an electrochemical phenomenon.
2. During corrosion at a particular spot on the surface of an object made of iron, oxidation takes place and that spot behaves as anode.
Anode : 2Fe → 2 Fe2+ + 4e-
3. Electrons released at this anodic spot move through the metal and go to another spot on the metal and reduce oxygen at that spot in presence of H+.
4. This spot behaves as cathode with the reaction.
Cathode : O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O
5. The overall reaction is: 2Fe + O2 + 4H+ → 2Fe2+ + 2H2O
6. The ferrous ions (Fe2+)are further oxidised by atmospheric oxygen to ferric Ions (Fe3+) which come out as rust In the form of hydrated ferric oxide (Fe2O3. XH2O) and with further production of hydrogen ions.
Question 5.
How do you extract metals In the middle of activity series?
Answer:
Extraction of metals In the middle of the activity series:
The ores of these metals are generally present as sulphides or carbonates. Therefore prior to reduction of ores of these metals, they must be converted into metal oxides.
The metal oxides are then reduced to the corresponding metals by using the following methods:
1. ReductIon of metal oxides with carbon: The oxides are reduced by coke in closed furnace which gives the metal and carbon monoxide (CO).
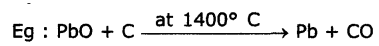
2. ReductIon of oxide ores with CO:

3. Auto (self) reduction of sulphide ores: In the extraction of copper (Cu) from its sulphide ore, the ore is subjected to partial roasting In air to give its oxide.
2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
When the supply of air Is stopped and Increase temperature results in the reaction of rest of sulphide ore with oxide to form metal and SO3.
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2
4. Reduction of ores (compounds) by more reactive metals: When highly reactive metals such as sodium, calcium, aluminium etc., are used as reducing agents, they displace metals of low reactivity from the compound.
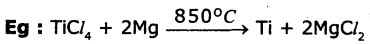
Question 6.
How do you extract metals at the bottom of the activity series?
Answer:
1. Metals at bottom of the activity series are often found in free state.
2. The oxides of these metals can be reduced to metals by heat alone and sometimes by displacement from their aqueous solutions.
3. When cinnabar (HgS) is heated In air, It s converted into HgO, then reduced to mercury on further heating.
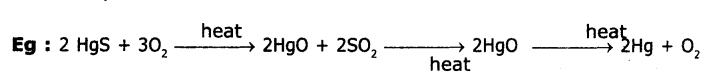
4. Displacement from aqueous solution. When Ag2S is dissolved in KCN solution it forms di cardio argentite (1) ions. From these ions by treating with Zn dust powder Ag is precipitated.
Eg : Ag2S + 4CN- → 2[Ag(CN)2)]- + S2-
2 [Ag(CN)2]-(aq) + Zn(s) → [Zn(CN)4]2-(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Question 7.
Draw the diagram of blast furnace and label it parts.
Answer:
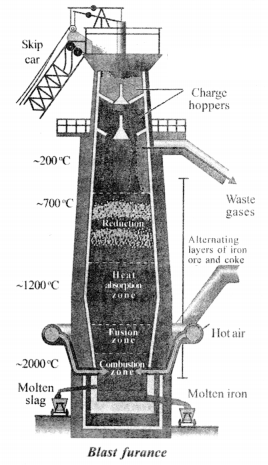
Question 8.
What are various types of furnaces? Explain.
Answer:
Various types of furnaces:
Blast furnace: Blast furnace has both firebox and hearth are combined in big chamber which accommodates both ore and fuel.
Reverberatory furnace: It has both firebox and hearth separated. but the vapours(flame) obtained due to burning of the fuel touches the ore in the hearth and heat it.
Retort furnace: In this furnace, there is no direct contact between the hearth or fire box and even the flames do not touch the ore.
Do You Know?
Alloying is a method of improving the properties of a metal. We can get desired properties by this method. For example, iron is the most widely used metal. But it ¡s never used in its pure state. This is because pure iron is very soft and stretches easily when hot. But, if it is mixed with a small amount of carbon, it becomes hard and strong. This alloy is called steel.
When iron is mixed with nickel and chromium we get stainless steel which will not rust.
Pure gold, known as 24-carat gold, is very soft. It is, therefore, not suitable for making jewellery. It is alloyed with either silver or copper to make it hard. Generally in India, 22-carat gold is used for making ornaments. It means that 22 parts of pure gold is alloyed with 2 parts of either silver or copper. (Page 248)