10th Class Biology 9th Lesson Our Environment Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve your learning
Question 1. What happens to the amount of energy transferred from one step to the next in a food chain?
Answer:
Energy is transferred along food chains from one trophic level to the next
The amount of available energy decreases from one stage to the next
This is because not all the food can be fully digested and assimilate
Hair, feathers, insect exoskeletons, cartilage and bone in animal foods, cellulose and lignin in plant foods cannot be digested by most animals
These materials are excreted or made into pellets of indigested remains
Assimilated energy is available for the synthesis of new biomass through growth and reproduction
Organisms also lose some biomass by death disease or annual leaf-drop
Moreover at each tropic level, organisms use the most of the assimilated energy to fulfill their metabolic requirements - performance of work, growth and reproduction
Most of the energy is lost in the form of heat during biological processes
Only a small fraction goes to the consumer at next tropic level
Question 2. What do pyramids and food chain indicate in an ecosystem?
Answer:
The ecologists used the idea of pyramid to show relationship among organisms in an existing food chain
Ecological pyramids are of three types. They are pyramid of biomass, pyramid of number, pyramid of energy
Pyramid of biomass indicates the available biomass in an ecosystem; pyramid of number indicates the organisms present and pyramid of energy indicates the available energy in an ecosystem
The food chain in an ecosystem indicates how energy is transferred from one organism to another
The starting point of a food chain are producers and it ends with top carnivores
A food chain represents a single directional transfer of energy
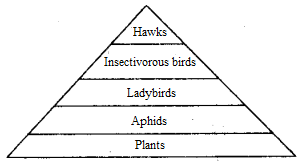
Question 3. Write a short note on pyramid of number for any food chain. What can we conclude from this pyramid of numbers?
i) tree ii) insect iii) woodpecker (OR) What is a pyramid of numbers? Write a brief note on the pyramid of numbers with the help of a block diagram.
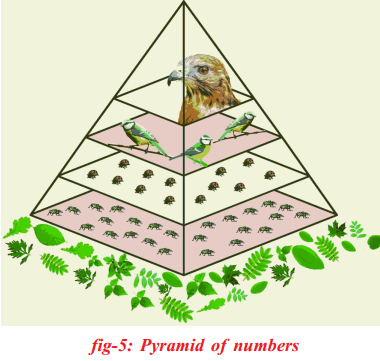
Answer:
The number of organisms in a food chain can be represented graphically in a pyramid of number
Each bar represents the number of individuals at each tropic level in a food chain
In the pyramid of numbers, from the first - order consumers to the large carnivores, there is normally an increase in size, but decrease in number
For example, in a wood, the aphids are very small and occur in astronomical numbers
The ladybirds which feed on them are distinctly larger and not so numerous
The insectivorous birds which feed on the ladybirds are larger still and are only present in a small numbers, and there may only be a single pair of hawks of much larger size than the insectivorous birds on which they prey
b. In the given pyramid, the producer is a large tree, primary consumers are small insects which are numerous in number and secondary consumers are woodpeckers which are comparatively less in number than insects
From this pyramid of number, we can conclude that sometimes the pyramid of numbers does not look like a pyramid a all
This could happen if the producer is a large plant or if one of the organisms at any tropic level is very small
Whatever the situation, the producer still goes at the bottom of the pyramid
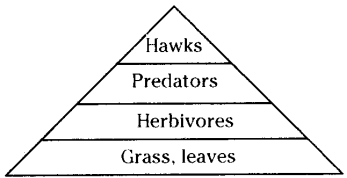
Question 4. What is biomass? Draw a pyramid of biomass for the given food chain.
i) grass leaves ii) herbivores iii) predators iv) hawk?
Answer:
Biomass is organic material of biological origin that has ultimately derived from the fixation of carbon dioxide and the trapping of solar energy
This includes trees, shrubs, crops, grasses, algae, aquatic plants* agricultural and forest residues and all forms of human, animal and plant waste
Any type of plant or animal material that can be converted into energy is called "Biomass"
Question 5. How is using of toxic material affecting the ecosystem? Write a short note on bioaccumulation and biomagnifications?
Answer:
Use of toxic materials such as pesticides, herbicides and fungicides creates new problems in the ecosystem
As these toxic materials are often indiscriminate in their action and vast numbers of other animals may be destroyed
Some of them may be predators which naturally feed on these pests, others may be the food for other animals
Thus causing unpredictable changes in food chains and upsetting the balance within the ecosystem
Some toxic substances have a cumulative effect
Some of them are degradable, can be broken down into harmless substances in a comparatively short time usually a year
Others are non-degradable which are potentially dangerous as they accumulate in the bodies of animals and pass right through food web
This process of entering of pollutants in a food chain is known as "Bioaccumulation"
The tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one tropic level to the next is known as "Biomagnifications"
Question 6. Should we use pesticides as they prevent our crop and food from pests or we should think of alternatives? Write your view about this issue and give sound reason for your answer?
(OR) Why should we think of alternatives to pesticides? Give reasons.
Answer:
We should think of alternatives. This is because these pesticides are toxic chemical whose usage leads to Bioaccumulation and Biomagnifications
When we use pesticides, they prevent our crop and food from pests effectively but indiscriminately destroys a vast number of other animals
This is causing unpredictable changes in food chains and upsetting the balance within the ecosystem
Most of the chemical pesticides that contain mercury, arsenic or lead are non -degradable
They enter into food chain, accumulate in the bodies of animals and pass right through food web
Being further concentrated at each step until animals at the top of the pyramid may receive enough to do considerable harm
This is one of the reasons for ever decreasing number of butterflies, bees, small and large birds
Some of the pesticides are nerve poisons and might bring about changes in behaviour
As the human beings are at the end of the food chain, these pesticides may get accumulated in our bodies also.
This shows some adverse effects on us, when their concentration becomes sufficiently high.
Question 7. What is a tropic level? What does it represent in an ecological pyramid?
Answer:
The various steps in a food chain at which the transfer of food takes place is called tropic level
Tropic level means the feeding level of the organism
In an ecological pyramid, the first tropic level represents the primary producers, and their number, biomass or energy
Second tropic level represents the herbivores or primary consumers and their number, biomass or energy
The tropic level represents the lower carnivores or secondary consumers and their number, biomass or energy
The fourth tropic level represents the higher carnivores or tertiary consumers and their number, biomass or energy
Question 8. If you want to know more about the flow of energy in an ecosystem, what questions do you ask?
Answer:
I will ask the following questions to know more about flow of energy in an ecosystem
How does the energy flow in an ecosystem from one organism to other
Is the energy transformation from one level to other 100% efficient
What per cent of energy transfers from one level to other
What happens to the remaining energy
How does the ecosystem lose its energy during energy transformation
Which tropic level in an ecosystem has more energy and which has less
What is the ultimate source of energy in an ecosystem
Question 9. What will happen if we remove predators from food web?
Answer:
Removal of organisms from any tropic level of a food chain or food web disturbs the ecosystem and leads to ecological imbalance
If we remove predators from food web, the prey population will increase enormously as there is no natural control over them
The producers population will decrease rapidly as the organisms feeding on them increase
After few generations the prey population also begins to decrease as some of the preys begin to die due to starvation
Some adaptations may also be developed by the organisms to bring the ecological balance
But it may take some generations, till that the ecosystem will be disturbed and imbalanced
For example, if we remove all the predators (carnivorous) from a forest ecosystem, the herbivorous animal population will increase as there are no carnivores to hunt them
As a result plant population will decrease as the ever increasing herbivores feed more and more on plants
After some generations the herbivore population begins to decrease as the decreasing number of plants are not sufficient to feed
Then some herbivorous animals may adapt to feed on other herbivores to increase their survival
Then scope for survival will increase for plants again which leads to ecological balance
But this may take lot of time to evolve new predators and to form ecological balance
Question 10. Observe a plant in your kitchen garden, and write a note on producer-consumer relationship?
Answer:
When I observe a plant in kitchen garden, I came to know the following things
Though it may be relatively small, a garden is a complete ecosystem
It has the same components as any other large and elaborate ecosystems had
The plant in a kitchen garden is a producer as it produces their own food from sunlight
There are two types of consumers in this ecosystem, a) Primary consumers and b) Secondary consumers
Primary consumers feed on plants. This tropic level consists of caterpillars, bees and butterflies
Secondary consumers feed on primary consumers. This tropic level consists of birds, garden lizards and spiders
Fungi, bacteria, insects and worms make up decomposers
The producer and consumer relationship can be shown in the following food chain. Plant ? Plant eaters such as caterpillars, bees, butterflies ? Meat-eaters such as birds, garden lizards, spiders Producers ? Primary consumers ? Secondary consumers
The pyramid of number appears like this
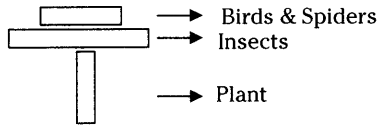
The pyramid of Biomass appears like this
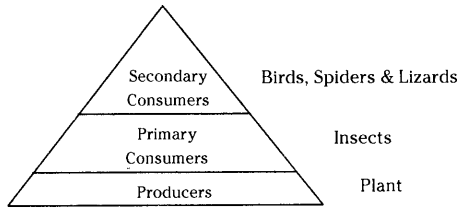
The pyramid of energy appears like this
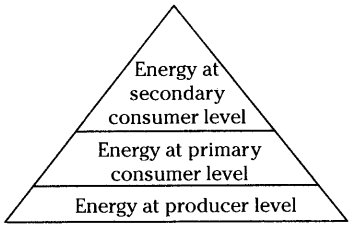
Question 11. What type of information do you require to explain the pyramid of biomass?
Answer:
To explain the pyramid of biomass, we require the following information
The type of ecosystem
Producers in the ecosystem
Primary consumers in the ecosystem
Secondary consumers in the ecosystem
Tertiary consumers in the ecosystem
Number of organisms at each tropic level
Size of organisms at each tropic level
Weight of organisms at each tropic level
All forms of waste produced at each tropic level and
In total, total amount of biomass produced at each tropic level
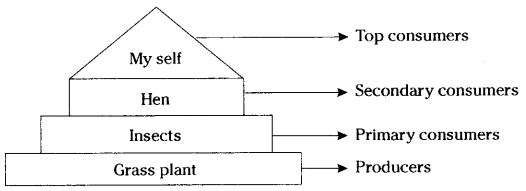
Question 12. Draw a pyramid of numbers considering yourself sis top level consumer. Pyramid of numbers?
Answer:
Pyramid of numbers
Ex: 1
Ex: 2
Question 13. Prepare slogans to promote awareness in your classmates about eco-friendly activities. All the living things have the right to live on this earth along with us. Prepare slogans to promote awareness in public about the conservation of biodiversity?
(OR) Which slogans do you prefer to promote awareness in your locality about eco-friendly activities?
Answer:
Live and let live
If we protect the environment, it protects us
Conserve nature - Conserve life
Save mother earth
Earth needs you
Go ecofriendly
Clean the environment, live happily
Heal our planet! Turn it into a better planetv
Plant a tree for your environment
Think ecofriendly and live ecofriendly
Earth enables you to definitely stand. Allow it to stand the actual way it is
Youve only got one planet. Dont trash it
Question 14. Suggest any three programmes on the prevention of soil pollution in view of avoiding pesticides?
(OR) Suggest any four eco-friendly methods for prevention of soil pollution in view of avoiding pesticides. (OR) In your area, soil is polluted by the enormous usage of pesticides. Suggest any two programmes for the prevention of soil pollution.
Answer:
To prevent the soil pollution caused by pesticides following programmes should be implemented
Rotation of crops
Same crop should not be grown in the same field in successive seasons
Rotation of crops reduce occurance of pests and damage due to pests will be decreased
Biological control: Introducing natural predator or parasite of the pest
Sterility: Sterilising the males of a pest species reduces the population of pests
Genetic strains: The development of genetic strains which are resistant to certain pest
Studying the life histories of the pests: When this is done it is sometimes possible to sow the crops at a time when least damage will be caused
Choose the correct answer.
1. What does a food chain always start with?
A.The herbivore
B.The carnivore
C.The producer
D.None of these
Answer: C
2.Which of the following do plants not compete for?
A.Water
B.Food
C.Space
D.All the above
Answer: B
3.Ban all pesticides, this means that?
A.Control on the usage of pesticides
B.Prevention of pesticides
C.Promote eco-friendly agricultural practices
D.Stop biochemical factories
Answer: C
4.According to Charles Elton?
A.Carnivores at the top of the pyramid herbivore
B.Energy trapping is high at the top of the pyramid
C.No producers at the top of the pyramid
D.A and C
Answer: D
10th Class Biology 9th Lesson Our Environment InText Questions and Answers
Question 1. Are all terrestrial ecosystems similar?
Answer:
No. All the terrestrial ecosystems are not similar
Basing on variations in climatic conditions such as rainfall, temperature and the availability of light, there are various kinds of ecosystems
The major types of terrestrial ecosystem are
Tundra
Coniferous forest
Deciduous forest
Savannah
Tropical forest and
Deserts
Question 2. If we want to show a food chain consisting of grass, rabbit, snake and hawk then connect the given picture of organisms by putting arrows and make a food chain?
Name the producers and consumers in the above food chain
Try to guess what does the arrows marked by you are indicate
Identify at least four other food chains from your surroundings. Name the producers and different levels of consumers in those food chains
Answer: Grass ? Rabbit ? Snake ? Hawk
In the above food chain grass is the primary producer. Rabbit is the primary consumer, snake is the secondary consumer and hawk is the tertiary consumer
The arrows indicate the flow of energy from one organism to another. So these are always pointed from the food to the feeder
Plant ? insect ? frog ? bird
Plant ? insect ? frog ? snake
Aquatic plants ? insects ? fish ? crane
Plant ? mice ? snake ? vulture
Plant ? aphids ? spiders ? birds
Question 3. Why do most of the food chains consists of four steps?
Answer:
Most of the food chains are quite short and mostly consists of four steps
This is because only 10% of the energy present in a tropic level transfers to the other tropic level
Remaining energy is dissipated as heat produced during the process of respiration and other ways
Thus about three steps in a food chain very little energy is still available for use by living organisms
Question 4. Why do the number of organisms get decreased as we move from producer to different level of consumers?
Answer:
As we move from producers to different levels of consumers the energy available will decrease gradually
Only ten per cent of the energy present in one tropic level transfer to another tropic level
Biomass also decreases gradually as only 10 - 20% of the biomass is transferred from one tropic level to the next in a food chain
As there is less energy & less biomass available at top levels, number of organisms also less, generally
So, the number of organisms get decreased as we move from producer to different level of consumers
Question 5. Draw the pyramid of number for the following food chains?
Banyan ? insects ? woodpecker
Grass ? rabbit ? wolf
Are the pyramid of number having same structure in both of the above two cases as compare to the example given in the earlier paragraph? B) If there is a difference, then what it is
Answer:

No. The pyramid of number in the above two cases doesnt have the sme structure as compared to the example given in the textbook
In the example (given in the textbook), number of organisms at producers level is more. This number gradually decreased in consumers level step by step. So the pyramid of number formed has typical pyramid shape with broad base and the narrow apex
But in the first case given here, on a single Banyan tree, a large number of insects live and feed. These insects become food for few Woodpeckers. So producers number is less than primary and secondary consumers, and secondary consumers are less than primary consumers. So the pyramid of number does not look like a pyramid. It consists of narrow base, broad middle part and medium apex
In the second case, grass which are large in number become food for few rabbits. Rabbit provides food for several wolves which are comparatively less in number than grass. So primary consumers are less in number than secondary consumers and producers. So the pyramid of number for this food chain also does not look like a pyramid. It consists of broad base, narrow middle part and medium apex. Thus it differs from case (i) also
Question 6. Think why the pyramids are always upright?
Answer:
In ecology not all the pyramids are always upright
Pyramid of number may be upright, inverted or partly upright.
Pyramid of biomass may be upright or inverted
But the pyramid of energy is always upright
This is because energy will decrease when we move from producers to the high level consumers
Only 10% of the energy from one tropic level transfers to the other through food chain
So the energy at base is more, gradually decreases, and very less at the top
As a result the energy pyramid is always upright
Question 7. Observe the data given in the following table?
| Classes |
Area in 1967(Km2) |
Area in 1967(Km2) |
| Lake - water spread area |
70.70 |
62.65 |
| Lake with sparse weed |
0 |
47.45 |
| Lake with dense weed |
0 |
15.20 |
| Lake-liable to flood in rainy season |
100.97 |
0 |
| Aquaculture ponds |
0 |
99.74 |
| Rice fields |
8.40 |
16.62 |
| Enchrochment |
0.31 |
1.37 |
| Total |
180.38 |
180.38 |
i) In which year lake-water spread area is more? Why?
Answer:
In the year 1967. Because lake was not brought under cultivation
ii) How do you think weeds are more in the lake?
Answer:
Excessive nutrient addition, especially from anthropogenic sources, led to explosive weed growth. Ex: Eichornia, pistia
iii) What are the reasons for decrease in lake area?
Answer:
In 1996, almost entire lake was brought under cultivation
Industries came along in ever growing intensity in the catchment area of the lake
iv) How do the above reasons lead to pollution?
Answer:
Consequently, the drains and rivulets carry substantial quantity of various types of pollutants into the lake
The major sources of pollution are agricultural runoff containing residues of several agrochemicals, fertilizers, fish tank discharges, industrial effluents containing chemical residues
v) How was the threat to the lake due to pollution discovered?
Answer:
The water of the lake turned alkaline in nature, turbid, nutrient rich, low in dissolved oxygen and high in biochemical oxygen demand
Water borne diseases like diarrhoea, typhoid, amoebiasis and others are said to be common among the local inhabitants who are unaware of the state of pollution in the lake water
Vector borne diseases were also increased
vi) What could be the reasons for the migration of birds to this lake?
Answer:
To avoid extreme cold weather conditions in Northern Asia and Eastern Europe birds migrate to Kolleru lake
Question 8. Observe the following table showing different activities in the lake and their influence?
Legend: (+) means has influence on the mentioned problem (-) means has no influence on the mentioned problem
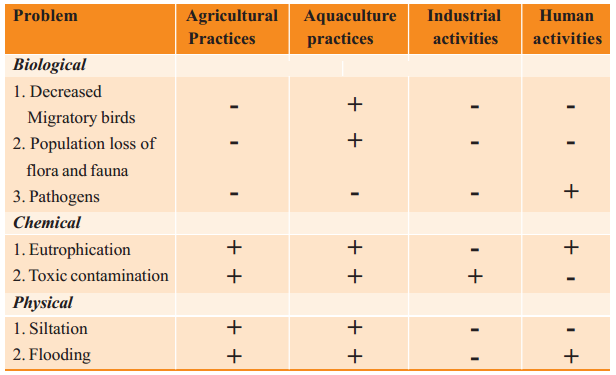
i) What are the factors that affected the number of migratory birds to decrease?
Answer:
Aquaculture practices.
ii) Do you find any relationship between biological and physical problems?
Answer: Yes. Aquaculture practices have influence on these problems
iii) What are the reasons for chemical problems ?
Answer: Agricultural practices, aquaculture practices, industrial activities and human activities are the reasons for chemical problems
iv) What happens if the dissolved oxygen reduce in lake water ?
Answer: If the dissolved oxygen reduces in lake water, sufficient amount of oxygen will not be available to organisms that live in the lake. This leads to the death of organisms in the lake
v) Is BOD of turbid and nutrient rich water high or low? What are its consequences?
Answer: High. Its consequences are water borne diseases and death of organisms
vi) People living in catchment area of Kolleru faced so many problems. Why?
Answer: Vector borne disease increased. The lands adandoned are useless for agriculture
Question 9. Name any two pesticides / insecticides you have heard about?
Answer:
DDT, Aldrin, Malathian, Altrazine, Monocrotophos, Endosulphan etc
Question 10. How are the food grains and cereals being stored in your house and how dojyou protected them from pests and fungus?
Answer:
To protect food grains and cereals from pests and fungus, we will follow the following rules in our house
First of all we will dry and clean our grain before storing
We will avoid moisture in bagged grains by storing them on wooden structures, bamboo mats or polythene covers
We use domestic bins or improvised storage structures such as Gaade, Kotlu, Paatara, RCC bins and flat bottom metal bins etc
We fumigate the storage room with Ethylene Di-bromide (EDB) ampoules to avoid insect damage
We use anticoagulant for rat control in houses
Question 11. Where from pollutants enter to the water sources?
Answer:
The used water from industries and run off water containing agricultural effluents bring pollutants into water sources. Municipal and domestic sewage also pollute water sources
Question 12. How can you say fishes living in water having heavy metals in their bodies?
Answer:
The bioaccumulation of heavy metals in tissues of fish particularly in liver, kidney and gills were analysed and found their presence
Question 13. Researchers found that pollution levels increase during monsoon season. Why they found so?
Answer:
Pollution levels increase during monsoon season in water bodies.
During monsoon season heavy rainfall occurs
The rain water brings residues of agrochemicals, fertilizers and different types of organic substances, municipal and domestic sewage
Hence pollution levels increase in monsoon season
Question 14. Why did people also suffer from various diseases after consuming fishes living in local water reservoir?
Answer:
The heavy metals could find their way into human beings through food chain
This bioaccumulation cause various physiological disorders such as hypertension, sporadic fever, renal damage, nausea etc
Question 15. What is the food chain that has been discussed in the above case?
Answer:
The food chain discussed in the above occurrence is Crops ? Locust ? Sparrow ? Hawk
Question 16. How did the campaign disturb the food chain in the fields?
Answer:
Crop yields after the campaign were substantially decreased
Though the campaign against sparrows ended it was too late
With no sparrows to eat the locust populations, the country was soon swarmed
Locust coupled with bad weather led to the great Chinese famine
Question 17. How did these disturbances affect the environment?
Answer:
The number of locust increased
Use of pesticides against locust population further degraded the land
Question 18. Is it right to eradicate a living organism in an ecosystem? How is it harmful?
Answer:
No, it is not right to eradicate a living organism in an ecosystem
It disturbs the existing food chain
Question 19. Were the sparrows really responsible? What was the reason for the fall in crop production?
Answer:
No, the sparrows were not really responsible for the loss of food grain
With no sparrows to eat the locust population crops were damaged and this led to fall in crop production
Question 20. What was the impact of human activities on the environment?
Answer:
The human activities badly affected the environment
Use of pesticides against the pest degraded the land
Question 21. What do you suggest for such incidents not to occur?
Answer:
I suggest to use organic manures and organic insecticides to kill the insects
Rotation of crops is the best method to protect the crops from pests
We should not kill any organism on this earth because every organism has a role to play
Think before you start action
10th Class Biology 9th Lesson Our Environment Activities Activity - 1
Observe any water ecosystem in your surroundings and identify the different food chains and food web operating in this ecosystem. Write the following details in your notebook?
WORKSHEET
Names of the students in a group: ------- Date: ----
Name of the ecosystem: -------
Topography: -------
Names / Number of plants (producers) identified: -------
Names / Number of animals identified: -------
Identify the different types consumers and name them & mention their number below :
Herbivores (Primary consumers): ------- Carnivores (Secondary consumers): ------- Top carnivores (Tertiary): -------
Food relationships among them: food habits/preferences: -------
Show / draw the different food chains: -------
Showcase the food web: -------
List out all abiotic factors existing in the ecosystem: -------
( A check list can be given, and asked to tick)
Is there any threat to the ecosystem ? Yes / No -------
If yes, what ? and how ? ------- Suggest few remedial measures -------
Answer: Students Activity