TS 10th Class Biology Important Questions 6th Lesson Reproduction
1 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
Give two examples of plants that are propagated by the cutting method?
Answer:
- Cutting Stems : Sugarcane, Roses, Hibiscus. Citrus plants
- Cutting (Root) : Lemon. Tamarind
Question 2.
How are cotyledons useful for the plant?
Answer:
Cotyledons have storage food for growing plant. until it forms the leaves
Question 3.
In what way does mitotic division help the living organism?
Answer:
Mitotic division helps in
- growth
- cell repair
- healing wounds
Question 4.
Give any two suggestions to create awareness to stop female foetlclde?
Answer:
- Preparing relevant slogans
- Organising rallies
- Awareness campaign by using electronic and print media
Question 5.
Write two precautions you take, while observing Rhizopus in the laboratory?
Answer:
- Dont touch the experimental bread with hand
- If you touch the bread, throughty wash your hands
- Leave the bread in the open air for about an hour
- Avoid opening of the plastic bag as much as you can
- Sprinkle water over bread
- Place the bag in a dark and warm place
Question 6.
Mention two materials you have used to observe Rhizopus on bread mould?
Answer:
Bread mould sample, plain glass slide, cover slip, water, disposable gloves
Question 7.
During favourable conditions paramoecium reproduce by?
Answer:
In favourable conditions paramoecium give rise to more of its kind from a single parent by simply splitting into two. (Binary fission)
Question 8.
In which organisms fragmentation is a common mode of reproduction?
Answer:
Algae, Fungi and many land plants
Question 9.
What is parthenogenesis ? Give examples?
Answer:
Production of a new plant or animal from a female without the sexual involvement of the male is known as parthenogenesis. Eg: Watermelon, grapes
Question 10.
What are the methods of artificial propagation?
Answer:
The methods of artificial propagation are Cutting. Layering and Grafting
Question 11.
Which method is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters?
Answer:
Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters
Question 12.
What is tissue culture?
Answer:
In tissue culture, few plant cells or plant tissues are placed in growth medium with plant hormones in it and it grows into new plants
Question 13.
What is the name of common bread mould?
Answer:
The name of common bread mould is Rhizopus
Question 14.
What is fertilisation?
Answer:
Union of male and female gametes is known as fertilisation
Question 15.
What is external fertilisation?
Answer:
If fertilisation occurs outside the body of the organism, it is known as external fertilisation. Eg: frog and fish
Question 16.
What is internal fertilisation?
Answer:
If the fertilisation occurs inside the body of the female organism, it is known as internal fertilisation.
Eg: Terrestrial animals
Question 17.
What are the parts that present in male reproductive system of man?
Answer:
A pair of testes, accessory glands and system of ducts
Question 18.
What are the accessory glands present in male reproductive system?
Answer:
One prostrate, two cowper glands are present in male reproductive system
Question 19.
What is ovulation?
Answer:
The release of ovum from graffian follicle is known as ovulation
Question 20.
What is placenta?
Answer:
Placenta is the nourishment tissue formed by the cells of embryo and mother
Question 21.
On which placenta is formed around?
Answer:
It is formed around 12 weeks of pregnancy
Question 22.
What is the membrane that forms umbilical cord?
Answer:
A membrane called allontois, which originates from the digestive canal of the embryo forming the major part of a tube like structure called umbilical cord
Question 23.
Whatis foetus?
Answer:
From the third month of pregnancy the embryo is called foetus
Question 24.
What is gestation period?
Answer:
Total time required for the development of embryo and foetus is called gestation period
Question 25.
What is the gestation period in human beings?
Answer:
It is 9 months or 280 days
Question 26.
What are labour pains?
Answer:
The rythemic contraction and relaxation of muscle layers of the uterus is known as labour pains
Question 27.
What is the need of sexual reproduction?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction help organisms to develop characters that would be help them to adapt better to their surroundings
Question 28.
What are the different parts of a flower?
Answer:
Sepals, petals, stamens and carpels are the different parts of a flower
Question 29.
What are unisexual flowers?
Answer:
Flowers containing either stamens or carpels are called unisexual flowers. Eg: Bottlegourd, papaya
Question 30.
What are the three parts of carpel?
Answer:
Stigma, style and ovary are the three parts of carpel
Question 31.
What is self pollination?
Answer:
Plants having flowers where reproductive cells of stamen of the flower fertilise the female reproductive cells of the carpel of the same flower is called self-pollination. Eg: Plants of pea family
Question 32.
What is cross pollination?
Answer:
Pollen grains of a flower are transferred to the stigma of a flower of another plant of the same species, is called cross pollination
Question 33.
What is double fertilisation?
Answer:
Union of one pollen tube nucleus with the egg and the second pollen tube nucleus with the fusion nucleus is called double fertilisation
Question 34.
Who discovered mitosis?
Answer:
Waither Flemming of Germany discovered mitosis in 1879
Question 35.
What is the meaning of the phase "Omnis cellula de cellula"?
Answer:
It means cells arise from pre existing cell
Question 36.
Cells in which organism do not divide?
Answer:
Heart and Brain
Question 37.
What is interphase?
Answer:
The period between two cell divisions is called interphase
Question 38.
What is G2, phase of the interphase?
Answer:
This is linking period between the completion of mitosis and the beginning of DNA replication. The cell size increase during this period
Question 39.
What Is S phase of the interphase?
Answer:
This is the period of DNA synthesis leading to duplication of chromosomes
Question 40.
What is G2 phase of the interphase?
Answer:
This is the time between the end of DNA replication and the beginning in mitosis
Question 41.
What are the different stages present in mitosis?
Answer:
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase are the stages present in mitosis
Question 42.
When does meiosis occur?
Answer:
Meiosis occur only during the formation of gametes in sexual reproduction
Question 43.
What is the virus that causes AIDS?
Answer:
Human Immuno deficiency Virus (HIV)
Question 44.
How does AIDS spread from one person to another?
Answer:
This disease spread by unsafe sexual contacts using infected devices, infected blood transfusion from an infected mother to child
Question 45.
What are the factors that contribute to the spread of HIV in the state?
Answer:
Illiteracy, poor health, unemployment, migration, non-traditional sex practice, unethical contacts and traffiking are some of the factors that spread HIV
Question 46.
What is contraception?
Answer:
The prevention of pregnancy in women by preventing fertilisation is called contracention
Question 47.
What are the surgical methods to prevent fertilisation?
Answer:
Vasectomy and Tubectomy are the surgical methods to prevent fertilisation
Question 48.
What is the marriage age for girl child?
Answer:
18 years
Question 49.
What Is foeticide?
Answer:
Foeticide is the act of destruction or aborting a foetus because it is female. (Or) Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
Question 50.
Who used cell fusion technique to understand the functional relationship between different phases of interphase?
Answer:
Potu Narasimha Rao and Johnson
Question 51.
Give examples for sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
Gonorrhoea, syphilis, AIDS and herpes, etc.
Question 52.
What is the advantage of reproduction through spores in the case of rhizopus?
Answer:
The spores are covered by thick walls that protect them until they come into contact with another moist surface and can begin to grow
Question 53.
Which process taking place in the nucleus of a cell leads to variation in the offspring during reproduction?
Answer:
DNA copying
Question 54.
Why is if said that sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in the offsprings?
Answer:
It is because sexual reproduction results from the fusion of two gametes coming from two different and sexually distinct indMduals. This leads to variation i.e.. necessary for evolution
Question 55.
Name the causative organism of syphilis and gonorrhoea?
Answer:
Syphilis is caused by Treponema pallidum and gonorrhoea is caused by Nisseria gonorrhoea
Question 56.
Why are variations possible in progeny of sexually reproductive individuals?
Answer:
Variations are possible in progeny of sexually reproductive individuals because copy of DNA in newly formed cell is not identical to copy DNA of original cell
Question 57.
The simple animals such as planaria can be cut into number of pieces and each niece grows into a complex organism. What is this process known as?
Answer:
Regneration
Question 58.
A student kept leaves of Bryophyllum in the soil. After a few days new plants were grown from them. why?
Answer:
Bryophyllum leaves bear buds in their notches along the margin. When a leaf kept in the soil, the buds come in contact of the soil and develop into plantlets. These plant-lets later grow into new plants
Question 59.
Name the three plants which are now grown using plant tissue culture method?
Answer:
- Orchids
- Chrysanthemum
- Asparagus
Question 60.
What does the mothers blood take away from the baby and into the placenta?
Answer:
- The mothers blood takes away waste products like carbon dioxide and waste materials such as urea, uric acid and creatinine from the baby
- The mothers blood supplies oxygen and nutrients to the baby through placenta
2 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
Write any four slogans for propaganda against female foeticide?
Answer:
- Stop female foeticide - Save the girl child
- Without girl child there is no life
- Todays girls are tomorrows ideal leaders
- Girls are the wealth of the society
- If girls become rare - what about our care
- Beti bachavo - Beti padavo
- Female foeticide is a crime - Dont commit it at any time
Question 2.
Identify the flower parts a, b, c, d and write their main function?
Answer:
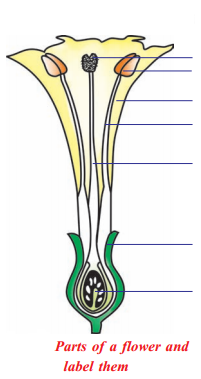
- Ovary : Female reproductive organ in flower. It produce female gametes called ovules
- Style : Ovary has a pipe like structure called style. It allows the pollen tube to enter the ovary for fertilization
- Stamen : These are male parts called androecium. It has two parts. They are filament and Anther
- Anther : Produces male gametes called pollen grain
Question 3.
Draw and label the diagram of human sperm cell?
Answer:
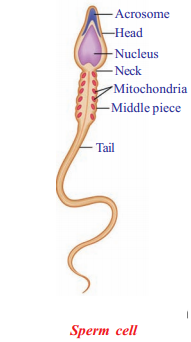
Question 4.
How will we get the desired useful triats with the help of two selected triats by using grafting method?
Answer:
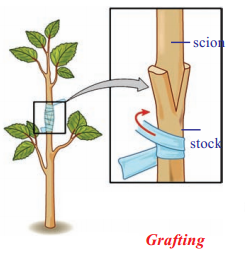
- Two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant
- One which is attached to soil is called stock and the cut stem of another plant without roots is called scion
- Both stock and scion are tied with the help of a twine thread and covered by a polythene cover
- Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters
- This technique is very useful in propagating improved varieties of plants with various flowers and fruits.
Ex : Mango, citrus, apple, rose
Question 5.
Draw the labelled diagram of Embryo-sac?
Answer:
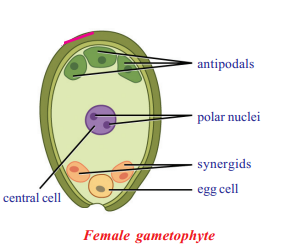
Question 6.
Observe the diagram and answer the following Questions?
Questioni.
Which phases take sanie time duration?
Answer:
G1 phase and S phase
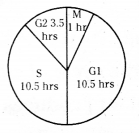
Questionii.
In which phase, DNA synthesis takes place?
Answer:
S Phase
Question 7.
Write the process involved in seedless fruit development with two suitable examples?
Answer:
In some plants ovary directly develops into fruit without the process of fertilization this phenomenon is called as parthenocarpy. Ex: Grapes, watermelon
Question 8.
What precautions will you take to keep away from diseases like AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
- Avoid sex with unknown partners or multiple partners.
- Use condom every time
- Use disposable syringes and needles
- Transfusion of safe blood to the patients
- HIV mother can have child with doctors advice only
Question 9.
Observe the diagram and answer the following Questions?
Questioni.
Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure?
Answer:
Male reproductive parts - anther / pollen grain / stamen
Female reproductive parts - ovary / ovule / style / stigma
Questionii.
Write the names of (1) and (2) In the diagram?
Answer:
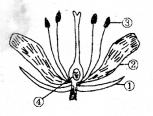
- Sepal or calyx
- Petal or corolla
Question 10.
When does Parthenogenesis occur? Write names of two animals in which parthenogenesis takes place?
Answer:
- Parthenogenesis is a process of reproduction where there is a shift from sexual to asexual mode of reproduction
- In this process generally the female gamets develops into zygote without fertilization
- This strange kind of reproduction occur in bees, ants and wasps
- The parthenocarpic zygote develop into male (Monoploid) while the fertilized one developed into female (Diploid)
Question 11.
Draw the figure of metaphase in mitosis, and write about it?
Answer:

- Chromosomes move to spindle equator, centromeres attached to spindle fibres
- Centrorneres split, separating the chromatids
Question 12.
Prepare 4 Questions on meiosis, to conduct a Quiz programme?
Answer:
- Where does meiosis occurs in?
- How many daughter cells are produced at the end of meiosis
- In which phase of meiosis karyokinesis takes place
- Name the scientist who discovered meiosis for the first time
Question 13.
Write slogans on Oaild marriages - a social evil?
Answer:
- Child marriage - A losing game
- She is a child herself, why burden her with another child
- My childhood - My right
- A child should call mother but a child should not be called mother
- Good marriages take place slowly. Go slow with childrens marriage
- Say no to child marriage
Question 14.
Write 5 slogans on the prevention of HIV/AIDS?
Answer:
- Open your eyes before Aids closes them
- late the disease but not the diseased
- Spread the knowledge not the virus
- Wear protection to prevent infection
- AIDS brings pain ! Girls please abstain
Question 15.
Write briefly about natural vegetative propagation?
Answer:
- In natural vegetative propagation new plants are produced from stem, root, leaves of old plants without the help of any reproductive organs
- In bryophyllum small plants grow at the edge of leaves
- Aerial weak stems like runners stolons, when they touch the ground give it adventitious roots
- When the connection with the parent plant is broken the stem portion with the adventitious roots develops into an independent plant
- Some examples for propagation by stem are from stolons, bulbs. corms, tuber, etc
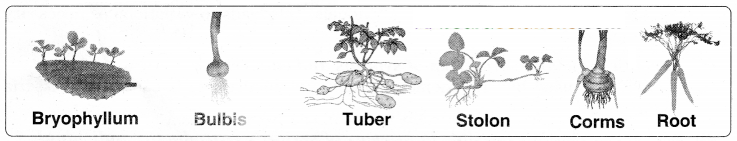
- Stolon - Vallisner . strawberry.
Bulbs - Onion AIIiumcepa)
Corms - Colacasia, Ginger
Tuber - Potato
Root - Radish. Carrot, etc
Question 16.
What is the present scenario of HlV infection in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh?
What are the causes for HIV infection?
Answer:
- Telangana and Andhra Pradesh has the highest number of HIV positive patients in the country
- According to official statistics, the state had 24 Lakh HIV positive patients in the country during 2011 - 12
- The prevalence of HIV is 1.07 percent among males and 0.73 among females in the state, which again is higher than other states
- HIV prevalence among adults (15 - 49 years) 0.90 percent, pregnant women 1.22 percent in Andhra Pradesh
- Illiteracy, poor health, unemployment, migration, non-traditional sex practise, unethical contacts and trafficking are some of the factors contributing to the spread of HIV in the state
Question 17.
What are sexually transmitted diseases and mention the ways to prevent them?
Answer:
- A disease which can be transmitted through sexual contact is called sexually transmitted disease or STD
- These include bacterial infections such as gonorrhoea, syphilis and viral infections such as herpes and AIDS
- Lack of hygiene is usually a major factor in providing conditions for spread of STDs
- But unprotected sex with multiple and unknown partners is the highest reason for the spread of STDs
- Some of the ways to prevent STD are as follows
- Being faithful to ones life partner
- Avoid sexual contact with unknown person
- Using condom during sexual intercourse
- Maintaining personal hygiene
Question 18.
Why can more complex organisms not give rise to new individual through regeneration?
Answer:
- Many organisms have the ability to give rise to new individual organisms from their body parts
- Regeneration happens through mitosis and a particular type of tissue can give rise to its own kind only
- In complex organisms, different tissues and organs have altogether different structures
- Regenerating a different kind of tissue from another kind is not possible
- Hence complex organisms are not able to give rise to new individuals through regeneration
Question 19.
What are the advantages of vegetative propagation?
Answer:
- Vegetative propagation helps to maintain fixed qualities and characteristic features of the parent plant
- It takes less time to grow plant through vegetative propagation
- Vegetative reproduction offers a uniform root stock for budding and grafting. This root stock can be selected from a plant that is immune to diseases
- In vegetative propagation it would be possible to develop new varieties with useful characters
- Vegetative reproduction is a very useful method of reproduction in plants that rarely produce flowers
Question 20.
How will an organism be benefited if It reproduces through spores?
Answer:
- Reproduction through spores gives several advantages to an organism like they are produced in very large numbers and it helps in propagation of species
- Spores can remain dormant till favourable conditions become available
- Spores help an organism to overcome unfavourahie conditions
- Spores can be spread through water, air or animals and thus is good for the spread of an organism to more places
Question 21.
What is the role of placenta in embryo development?
Answer:
- Placenta is a tissue formed by the cells from the embryo and the mother
- It is formed at around 12 weeks of pregnancy and becomes an important structure for nourishment of the embryo
- Placenta is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryos side of the tissue
- On the mothers side are blood spaces
- This provides a large surface area for diffusion of glucose, oxygen and other nutrients from the mother of the embryo
Question 22.
What causes joining up of stock and scion grafting technique of vegetative propagation in plants?
Answer:
- The stock and scion unite due to cambial cavity
- Stock is the portion on which the grafting is done and it provides the roots
- Scion is the portion of the plant which is grafted on the other plant and it contributes the stem
- The plant contributing scion should have large sized fruits and the plant contributing stock should have deep root system
Question 23.
How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Answer:
| Binary fission |
Multiple fission |
| 1. No protective coat or wall or cyst is formed around the cell |
1. A cyst or a protective coat or wall is formed around the cell |
| 2. A fully mature individual cell divides into two producing two daughter individuals |
2. The cell nucleus divides many times within the cyst to produce many daughter nuclei. Each gathers cytoplasm and forms daughter individuals |
| 3. No such phenomenon occurs |
3. The parent cell breaks away, releasing many individuals at once |
Question 24.
Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer:
- DNA is the genetic material which makes proteins which in turn give rise physical characteristics of an organism
- Copying of DNA results in transfer of information to form a fully developed organism
Question 25.
Differentiate between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction?
Answer:
- Asexual reproduction involves only a single individual. It does not require two sexes
- Sexual reproduction involves two different individuals, male and female sexes. The offspring is produced due to fusion of male and female gametes
Question 26.
Differentiate between unisexual and bisexual flower. Give two examples of each?
Answer:
- When a flower contains either stamens or carpels it is said to be unisexual. Examples: Papaya and watermelon
- When a flower contains both stamens and carpels it is said to be bisexual. Examples: Hibiscus and mustard
Question 27.
How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Answer:
- Pollination is the process by which the pollen from another reaches the stigma of the flower of the same species
- Fertilisation is the process in which the male gamete fuses with the egg to form zygote
Question 28.
If a woman is using a copper-T will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
- Copper-T is a contraceptive method which prevents implantation of the zygote inside the uterus
- It cannot prevent a woman from sexually transmitted diseases
- Sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted by contact which cannot be prevented by copper-T
Question 29.
Arjun Tendulkar injured his knees while fielding at ground. The injury was healed after some days. Arjun was eager to know the process behind it. Describe the process involved in wound healing?
Answer:
- The process behind healing of wounds of Arjun is mitosis
- Due to mitosis cuts, bruises and injuries heal themselves in a few days
- Cells present at the margins of wound divide repeatedly by mitosis and the resulting daughter cells fill the wound once the entire wound is filled up these cells stop dividing
Question 30.
Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
OR
Why is vegetative propagation adopted over other types of propagation ?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is practised in some plants because
- It is the only method of reproduction in seed less plants
- We get more number of matured plants in a very short time
- Thousands of plants can be grown in very short time
- This method can help the breeder in preserving the characters he need
- It is very easy and economical method for the multiplication of ornamental plants
Question 31.
Chromosomal number is reduced to half in the daughter cells produced by meiosis. What happens if the number is not reduced to half in daughter cells?
Or
In Meiosis, the chromosome number in the daughter cells are reduced to half that of their parent cells. Guess, what would happen, If the reduction of
chromosome number is not done.
Answer:
- If the reduction of chromosomes number is not done, the chromosomal number is doubled in the offsprings
- The change in chromosomal number changes completely the characters in the individual
- The offspring differs to parental generation
- Abnormal characters will be formed in new generation, which are not useful for the existence of individual
Question 32.
What are the Questions you asked the doctor who visited your school to know "the ways of transmission of HIV" ?
Answer:
I shall ask the following
Questions to the doctor
- What are the ways of transmission of HIV
- How, can we prevent the spread of HIV
- What precautions should we take while doing transfusion of blood
- How does HIV transmit from mother to baby
- Why should we use disposable syringes
4 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
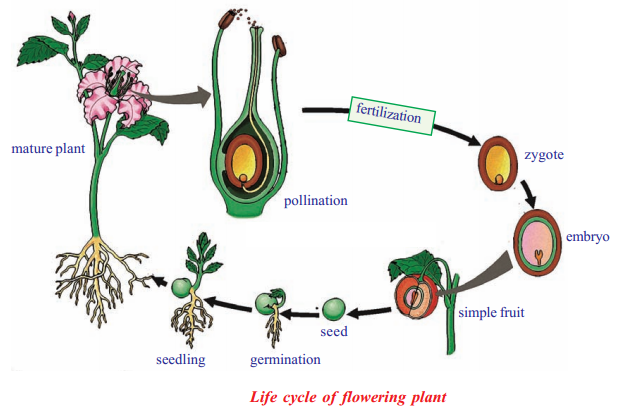
Describe the life cycle of a flowering plant with a help of neat labelled diagrams?
OR
Draw the life cycle of a flowering plant.
Answer:
- Adult plant produces flowers:
When the plant matures and is ready to reproduce, it develops flowers. Flowers are special structures involved in sexual reproduction, which includes pollination and fertilisation
- Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel is called pollination
- Fertilisation
- After pollen grains falls on the stigma fertilization occurs when the male gamete
present in pollen grains joins with the female gametes present in the ovule
- In the ovary the male gamete of pollen combines with the nucleus of female gamete or egg present to form zygote
- Formation of fruit and seed: After fertilisation, a combined cell i.e. zygote grows into an embryo within a seed formed by the ovule
- Each seed contains a tiny plant called an embryo which has root, stem and leaf parts ready to grow into a new plant when conditions are favourable
- Another part of the flower (the ovary) grows to form fruit, which protects the seeds and helps them spread away from the parent plant to continue the cycle
Question 2.
Analyze the following information and answer the following Questions?
Answer:
| S.No |
Name of the plant |
Method of propagation |
| 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6. |
Mango
Rose, Hibiscus
Jasmine
Bryophyllum
Colacasia
Onions |
Grafting
Cutting
Layering
Small plants grow on edges of leaves
Corms
Bulbs |
Questioni.
What do you call the given reproduction methods?
Answer:
Given reproduction methods are called vegetative propagation
Questionii.
What is the major difference between sexual reproduction and vegetative reproduction in plants?
Answer:
In sexual reproduction gametes formed zygote. But it is not seen in vegetative reproduction. It is one of a sexual method
Questioniii.
Potato plants do not produce seeds. How can you propagate this plant?
Answer:
Potato plants propagates through the eyes
Questioniv.
What are the advantages of propagating plants with the above given methods?
Answer:
In vegetative propagation
- More plants are produced in less time
- Characters are not changed
- It would be possible to develop new varieties with useful characters
Question 3.
Explain the methods of artificial propagation in various plants?
Answer:
Artificial propagation
- Cutting : Some plants can grow individually when a piece of the parent plant having bud is cut off from the existing plant. The lower part of this cutting is buried in moist soil. After few days the cut parts having buds grow as an individual plant after developing roots. E.g. Rose, Hibiscus.
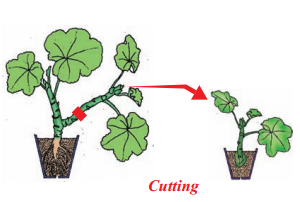
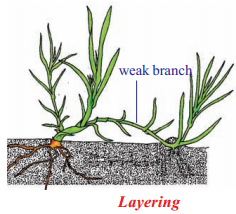
- Layering : A branch of the plant with atleast one node is bent towards the ground and part of it is covered with moist soil. After a few days new roots develop from the part of the branch buried in the soil. The branch is then cut off from the parent plant. E.g: Nerium, Jasmine
- Grafting : Two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant. This technique is very useful in propagating improved varieties of various flowers and fruits. Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable character. E.g: Mango, citrus, apple, rose
Question 4.
Mention the stages of Mitosis with the help of diagrams. Explain the changes that takes place in Prophase?
Answer:
Mitosis is a method of cell division, in which the nucleus divides into two daughter nuclei each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus mitosis takes place in all body cells which retains same number of chromosomes
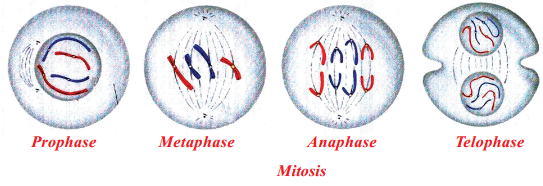 Different stages of mitosis:
Different stages of mitosis:
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
Prophase : In this phase chromosomes condense and get coiled. They become even in light microscope and nucleoli becomes smaller. Chromosome split lengthwise to form chromatids connected by centromeres. Nuclear membrane breaks down. Centrosome containing rod like centrioles, divide and form ends of spindle
Question 5.
Describe the process of double fertilization in plants. Explain the uses of endosperm that is formed?
Answer:
Double fertilization: In flowering plant germinated pollen rain forms pollen tube. The end of the pollen tube ruptures and two male gamets are released in the Embryosac. Out of two male gamets one male garnet fuses with female garnet which is called fertilization another male garnet fuses with the secondary nucleus and forms endosperm so in flowering plant fertilization occurs twice hence it is called double fertilization
Uses of Endosperm:
- Cotyledons develop by utilizing endosperm
- The cotyledons utilize the stored food in the endosperm
- Some of the plants utilize the endosperm completely and change into seed
- Because of the stored food the size of the cotyledons increases
Question 6.
Read the following table and answer the following Questions?
Answer:
| SI. No. |
Structure |
Location |
| 1. |
Tricuspid valve |
Right auriculo-ventricular aperture |
| 2. |
Guard cells |
Epidermis of leaves |
| 3. |
Glomerulus |
Nephron |
| 4. |
Alveoli |
Lungs |
| 5. |
Acrosome |
Above the head of a sperm |
Questioni.
Name the structure concerned to the heart?
Answer:
Tricuspid valve
Questionii.
What is the function of acrosome?
Answer:
It helps the sperm in penetrating into ovum
Questioniii.
Name the structures which are helpful for gaseous exchange?
Answer:
Alveoli and guard cells
Questioniv.
Name the part performing Excretion?
Answer:
Glomerulus
Question 7.
Explain any two natural and two artificial vegetative propagation methods to produce more number of plants In less time period with examples?
Answer:
Natural propagation
- Leaves - Small plant grow at the edge of the leaves. Ex: Bryophyllum
- Stems
- Stolon - Ex : Jasmine, strawberry
- Bulbs - Ex : Onion
- Corns - Ex: Colocasia
- Rhizome - Ex : Ginger
- Tuber - Ex: Potato
- Root - Ex: Roots of murayya, guava
Artificial propagation:
Cutting: Some plants can grow individual when a piece of parent plant having bud is cut off from the existing plants.
Ex: Rose, Hibiscus
Layering: A branch of the plant with at least one node is bent towards the ground and a part of it is covered with moist soil leavings the tip of the branch exposed above the ground. Ex: Nerium, Jasmine
Grafting: Two plants are joint together in such a way that stems join and grow as a single plant one which is attached to soil is called stock and stem of another plant without roots is called scion. Both stock and scion are tied with a twine thread and cover by a polythene cover. Ex: Mango, citrus, apple, rose
Question 8.
Observe the following table?
| Reproduction system |
Organisms |
| Fission |
Paramoecium, Bacteria |
| Budding |
Yeast, Hydra |
| Fragmentation |
Flatworms, Spirogvra |
| Rhizome |
Ginger, Turmeric |
| Cutting |
Rose, Hibiscus |
| Grafting |
Citrus, Apple |
On the basis of information given In the table write the answers to following
Questions
Questioni.
Write the names of two organisms that show Asexual reproduction?
Answer: Yeast, Hydra, Bacteria, Paramoecium (any two you may write)
Questionii.
Write two artificial vegetative propagation methods mentioned in the table?
Answer: Cutting, Grafting
Questioniii.
Write the names of two plants, which undergo natural vegetative propagation mentioned in the table?
Answer: Ginger, Turmeric
Questioniv.
In fission, how many organisms can we get from one organism?
Answer: Two
I. Conceptual Understanding
Question 1.
Among the following organisms can we see asexual reproduction? Write about the method of asexual reproduction in any of the two organisms?
- Paramoeclum
- Yeast
- Spirogyra
- Amoeba
- Planaria
Answer:
Yes, we can see asexual reproduction in all the following organisms
- Method of asexual reproduction - Organism
- Binary fission - Paramoecium, amoeba
- Budding - Yeast
- Fragmentation - Spirogyra
- Regeneration - Planaria
- Binary fission In Paramoeclum : A single cell divides into two equal daughter cells. First the cytoplasm divides into two parts followed by nuclear division
- Asexual reproduction in Yeast : Budding is the common method of asexual reproduction in yeast. In this method, yeast cell wall at a particular region becomes soft and bulges into an outgrowth called bud. Cytoplasm enters into this bulge and then nucleus divides mitotically into two nuclei, one moves into the bud. Finally bud is detached from the parent cell and grows into an independent yeast cell
Question 2.
See the adjacent picture. Which type of pollination will occur in this? Why do you think so?
Answer:
Self pollination occurs if stamens and carpels matures at the same time. If they mature at different times cross pollination occurs. Cross pollination occurs in this plant. For cross pollination to occur the pollen grains are to be carried to from other plants belonging to the same species

The mechanism of dispersal of pollen grains from one plant to other plant is facilitated mostly by wind and insects. Cross pollination is believed to be advantageous for the plant because the seeds produced by the flower will contain another source of genetic material which may contain genes which are advantageous to the survival of the seedlings
Question 3.
Describe different artificial vegetative methods to produce large scale production of plants?
Answer:
- Different artificial vegetative propagation methods are cutting, layering, grafting and tissue culture methods
- Culling : Some plants grow individually when a piece of parent plant having bud is cut from the existing plant. After burying in the soil the cut parts having buds grow as an individual plant after developing roots. E.g. Rose
- Layering: A branch of the plant with at least one node is bent towards the ground and part of it is covered with moist soil. After sometime, new roots develop from the part of the branch burned in the soil. The branch is then cut off from the parent plant. E.g: Nerium, Jasmine
- Grafting: Two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant. This technique is very useful in propagating improved varieties of various flower and fruits. Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable character. E.g : Mango. citrus, apple, rose
- Tissue culture: In this method, few plant cells or plant tissues are placed in a growth medium with plant hormones in it and it grows into new plants. Thousands of plants can be grown in very short Interval of time
Question 4.
- Labelled parts of A, B, C, D above drawn Human female reproductive system
- In which part ferifiization takes place
- Which part is in connection with Implantation
- What is ovulation
Answer:
- A : Fallopian tube
- B : Ovary
- C : Uterus D : Vagina
- Fertilization takes place in fallopian tube
- Uterus
- Release of ovum from graffian follicle of ovary is known as ovulation
Question 5.
Write the differences between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction?
Answer:
- Asexual reproduction - Sexual reproduction:
| Asexual reproduction |
Sexual reproduction |
| 1. Involves single organism |
1. Involves one or two organisms |
| 2. No production of gametes |
2. Male and female gametes are produced |
| 3. There is no fusion of gametes |
3. It involves fusion of male and female gametes |
| 4. It requires only mitotic divisions |
4. It requires meiotic division followed by mitotic division |
| 5. It produces offsprings that are identical to the parent |
5. Offspring will have some characters from male parent and others from female parent. Some characters may not be present in either of the parents |
| 6. In this chance of genetic variation is only through random mutation |
6. In this reproduction there is more chance for genetic variation |
| 7. Asexual reproduction is not very useful for natural selection in evolution of species |
7. Sexual reproduction is highly useful for natural selection in evolution of specie |
| 8. It occurs by budding, fragmentation, sporulation |
8. It occurs due to pollination and fertilization |
Question 6.
Briefly explain about artificial vegetative propagation?
OR
Describe about cutting, layering and grafting in vegetative propagation.
Answer:
- The process of growing many plants from one plant by man-made methods is called artificial propagation of plants
- The three common methods for the artificial propagation of plants are
- Cutting
- Layering and
- Grafting



- A small part of a plant which ¡s removed by making a cut with a knife is called cutting. A cutting may be a piece of stem, root or even to a leaf. Eg: Rose, Bougainvillia, Sugarcane, Banana, etc
- In Layering a branch of the plant with at least one node is bent towards the ground and a part of it is covered with moist soil leaving the tip of the branch exposed above the ground. After some time, new roots develop from the part of the branch buried in the soil. The branch is then cut off from the parent plant. Ex : Nerium, Hibiscus
- In grafting two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant. Eg: Mango, Citrus, Apple, Rose etc
Question 7.
Describe the structure of male reproductive system in human beings. With neat labelled diagram explain the structure of male reproductive system in human beings?
Answer:
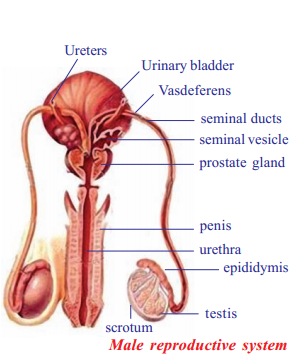
- The male reproductive system of human beings consists of a pair of testes, accessory glands and a system of ducts
- Testes are male reproductive organs and produces spermotozoa or sperms and also secretes male sex hormone Testosterone
- Inside each testis several lobules are present. Each lobule has several tubules called seminiferous tubules
- Germinal epithelial cells in the seminiferous tubules undergo meiotic division to produce spores
- The accessory glands include one prostrate gland and two cowper glands. Secretion of these glands produce semen
- The duct system consists of vas efferentia. They collect spermatozoa from seminiferous tubules
- Vasefferentia continue as epididymis where sperms are stored temporarily
Question 8.
Describe briefly about the female reproductive system in human beings?
Answer:
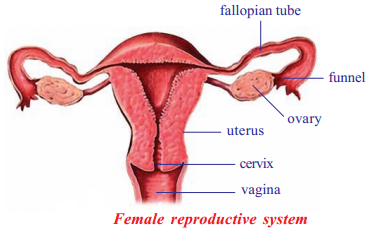
- A pair of ovaries are the reproductive organs in woman
- They are present just below the kidneys in the abdominal cavity
- Each ovary has severed sac like structures called ovarian follicles or Graffian follicles
- Every time only one follicle matures and releases one ovum into body cavity
- Just above the ovaries are the tubes called oviducts or fallopian tubes
- The two oviducts connect to a bag like organ called uterus at their other ends
- The uterus is connected through a narrow opening called cervix to another tube called vagina which opens to the outside of the body
- Vagina is a tubular structure and is also called birth canal because it is through this passage that the baby is born after the completion of development inside the uterus of the mother
Question 9.
Write a short note on child birth?
Answer:
- Total time required for the embryonic and foetal development is about 9 months or 280 days
- After this time, foetus is expelled from the uterus by the mother. This is child birth
- Child birth is a complicated process and involves the participation of child and mother
- The foetal hormones produced inside, stimulate the contraction of the muscles present in the walls of uterus
- These contractions called labour pains help in the expulsion of the foetus from the uterus
- During this process the amnion ruptures, placenta is separated from the walls of the uterus
- At child birth the head usually comes out first
- The foetus is still attached to the mothers uterus through the umbilical cord, which is later separated by the doctors
Question 10.
Describe the structure of flower with a neatly labelled diagram?
Answer:
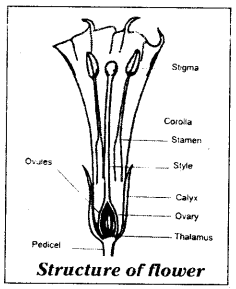
- A typical flower consists of an outer whorl of green sepals (calyx. which protects the parts within
- The second whorl has petals (corolla. which are usually brightly coloured. They sometimes have fragrance also
Petals are soft and are useful to attract insects to facilitate cross pollination
- The third whorl of the flower consists of stamens Androecium. which are the male reproductive organs
- Each stamen is made up of a filament and an anther
- Each anther usually has two anther lobes. The anther produces pollen grains microspores
- The inner most fourth whorl is gynoecium or pistil. It consists of ovary, style and stigma
- Ovary occupies central portion on the thalamus. A swollen ovary is present on the thalamus
- Inside the ovary future seeds, known as ovules are present
- Ovary has a pipe like extension called style. The tip of the style ends in stigma. The stigma receive the pollen grains
Question 11.
Describe briefly about the meiosis or reduction division?
Answer:
- Meiosis occurs only during the formation of gametes in sexual reproduction
- During meiosis only one set of chromosomes are passed on to the daughter cells. Hence daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes of the mother cells
- In meiosis karyokinesis and cytokinesis occur two times
- During first phase of meiosis the parent cell divides twice, though the chromosomes divide only once
The second phase meiosis is similar to normal mitosis, but chromosomes do not duplicate, more over the chromosomes are distributed equally to each cells
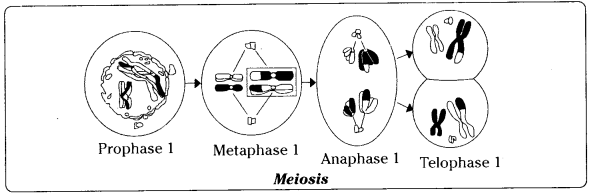
- Thus the four daughter cells have just half the number of chromosomes of the parent cells
- These are haploid (containing only one set of chromosome
- Thus meiotic division is also called reduction division
Question 12.
What is contraception ? What are the contraceptive methods followed for birth control ?
Answer:
- The prevention of pregnancy in women by preventing fertilisation is called contraception
- Any device or chemical (drug. which prevents pregnancy in woman is called contraceptive
- Physical devices such as condoms and diaphragm (cap. are used. This prevents reaching of sperms to ova for fertilisation
- Chemicals in the form of pills are induced either orally or inserting into female reproductive organ vagina
- Pills for males kill the sperms and hence are called spermicide
- The use of intra - uterine device called copper - T, loop, etc. are also very effective in preventing pregnancy
- Surgical methods of birth control are available for males as well as females
- In males a small portion of vas deferens sperm duct. is removed by surgical operation and both ends are tied properly. This method is called Vasectomy
- In females a small portion of oviducts (fallopian tubes. is removed by surgical operation and the cut ends are tied. This method is called Tubectomy
Question 13.
Describe the developmental stages of human embryo after fertilization?
Answer:
- During fertilization, chromosomes of the ovum and the chromosomes of the sperm make up into pairs and the resulting cell is called zygote
- Fertilization takes place in the oviduct or fallopian tube
- The zygote which is diploid travels down the fallopian tube. As it moves it undergoes several mitotic divisions
forming the embryonic stage called blastocyst
- Blastocyst moves towards the wall of the uterus and finally gets attached and embedded in the wall of the uterus. This is called implantation
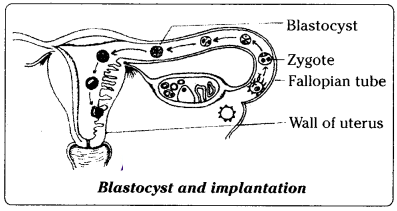
- The growing embryo forms two membranes chorion and Amnion
- Chorion establishes connection with the walls of the uterus and helps in the supply of nutrients to the embryo and removal of wastes from the embryo
- Amnion forms a sac like structure around the embryo. The space between the amnion and embryo is filled with a fluid called amniotic fluid
- Amnion and amniotic fluid give protection to the embryo against minor mechanical injury
- Placenta is a tissue formed by the cells from the embryo and the mother. It is formed around 12 weeks of pregnancy
- Placenta nourishes the growing embryo
- A tough cord called umbilical cord is also formed by the embryo which is connected to the walls of the uterus through the placenta
- From 3 months of pregnancy, the embryo is called foetus
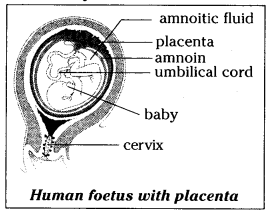
- Pregnancy lasts on an average 9 months or 280 days. This period is called gestation period
- After this time foetus is expelled from the uterus by the mother - this is child birth
- This process is complicated and involves the participation of foetus and mother
Question 14.
What is the significance of cell division in human beings ?
Answer:
- The process of cell division is same in unicellular organisms to highly evolved multicellular organisms like human beings
- Cell division is the process that transforms a human fertilized egg into a baby in nine months and into an adult in the next 20 years
- Cell division and function in a multicellular organism is highly regulated. It occurs only when there is a need for it
- Cells in some organs, such as heart and brain of an individual never divide
- On the other hand bone marrow cells actively divide to produce red blood cells, which have a short life span (120 days. in the body
- For example, if you cut your finger and bleed, soon a blood clot forms to stop the bleeding
- This brings in various chemicals to the site that stimulate skin cells to divide and heal the wound
- Cell division ceases or stops as the wound is completely healed
- In contrast, cancer cells do not respond to such growth regulating factors and continuously divide at the expense of normal cells. Thus ultimately killing the host
- So it becomes important to understand the processes involved in cell division
Question 15.
Illustrate the process of regeneration in planaria with the help of suitable diagram?
Answer:
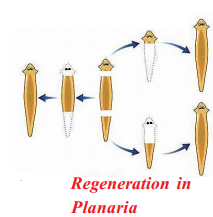
- Planaria can be cut into many number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete planaria
- This development of pieces of an organism into an individual is known as regeneration
- Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells
- These cells proliferate and form large number of cells
- In this mass of cells differentiation occurs to form various types of cells and tissues
- These changes take place in an organised sequence referred to as development
- This results in formation of an individual planaria
II. Asking Questions And Making Hypothesis
Question 1.
What are the consequences if meiosis not happens in the body cells of the organism ?
Answer:
- Each organism has a fixed number of chromosomes
- This number has to be maintained in its offspring
- Any sudden change in the number of chromosomes will be harmful to the off-spring. Assume parent has 10 chromosomes
- In the absence of meiosis during sexual reproduction gametes will also have the same number of chromosomes as parent i.e., 10 chromosomes
- Union of female and male gametes occur forming zygote during sexual reproduction. The zygote will have the double number of chromosomes as compared with the parent organism, i.e. the number of chromosomes in zygote will have 10 + 10chromosomes
- In the next generation, the offspring will have forty chromosomes. If this continues cells in the offsprings will have thousands of chromosomes within few generation
- This results in formation of abnormalities in each generation. Hence by way of meiotic division, the chromosome number is maintained constant from generation to generation
Question 2.
What happens in flowering plant if single fertilization only takes place ?
Answer:
- If single fertilization takes place in flowering plants it forms zygote (pollen tube nucleus + eggs) or Endosperm (pollen tube nucleus + fusion nucleus) only
- After many changes zygote divides several times to form an embryo within ovule
- Another part of flower (ovary) grow to form fruit. With single fertilization only fruit (or) embryo with in ovule will form
Question 3.
What happens if the fallopian tubes are partially blocked and the ovulated eggs are prevented from reaching the uterus?
Answer:
Fertilization may take place but the zygote may develop in the tube instead of uterus
Question 4.
What will happen if there is no mitosis at all in living organisms ?
Answer:
- If mitosis is not present, growth and development of organism will not take place
- Wound healing does not take place
Question 5.
Ravis father wants to cultivate potato in his field. He wants to clarify some doubts with the agricultural officer. Prepare a list of doubts in form of Questions for him?
Answer:
- Which type of soil is suited for growing potato
- What are used as seeds for sowing potato crop
- What are climatic conditions required for potato crop
- What are the vegetative propagation methods to grow potato crop
- What are the best ways to prevent early and late blight disease
- How are weeds controlled in potato crop
- What are the fertilizers required for potato crop
III. Experimentation And Field Investigation
Question 1.
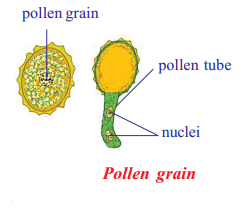
What procedure do you adopt to see pollen grain with pollen tube ?
Answer:
Aim : To observe the pollen tube.
Apparatus : Microscope, Sugar solution, flowers (Alium cepa) slide, coverslip, brush.
Procedure
- Collect any mature flower keep them in sugar solution for 6-7 hours. It enhances the germination of pollen grain
- Take a slide, put a drop of water on it
- With the help of brush tap on flower to collect pollen from flowers already kept in sugar solution
- Observe under microscope. Draw what you have seen in your notebook
Question 2.
Sameer wants to observe Rhizopus under microscope. For this?
- What are preparatory activities he has to do
- What procedure does he follow ? And
- What precautions should he take
Answer:
- To observe Rhizopus he has to do the following preparatory activities
- He has to grow Rhizopus or common mould on his own in a controlled environment
- Take a bread slice, leave in open air for about an hour, place the bread in plastic bag
- Sprinkle water over it to have dampness then seal the bag, leaving some air inside, place it in a dark warm place
- After 2-3 days, you will find black patches (or) thread like growth with masses of black, grey and green fine dotted structures on it
- Materials required: Mould sample, plain glass slide, coverslip, water, disposable gloves, microscope, tooth pick.
Procedure:
- Place a drop of water in the centre of the slide
- Using a toothpick, scrape very little of the mould and place it on the drop of water
- Take the cover slip and set it at an angle to the slide, so that one edge of it, touches the water drop, then carefully lower it over the drop so that the cover slip covers the specimen without trapping air bubbles underneath
- Use the corner of a tissue paper or blotting paper to blot up any excess water at the edges of the cover slip
- View the slide with a compound microscope first observe under low power
Observation:
- The common bread mould consists of fine thread like projections called hyphae and thin stems having knob like structures called Sporangia
- Each sporangium contains hundreds of minute spores
- When the sporangium bursts, the tiny spores are dispersed in air
Precautions:
- Keep away from mould who is suffering from allergies and asthma
- Do not touch mould with bear hands. If you touch it be sure to thoroughly wash your hands afterwards
Question 3.
How will you stain a microscopic slide showing mitosis in on ion roots?
Answer:
Place the cut tip on a clean microscopic slide. Add 2-3 drops of acetocarmine stain to the slide. Observe it under a compound microscope
IV. Information Skills And Projects
Question 1.
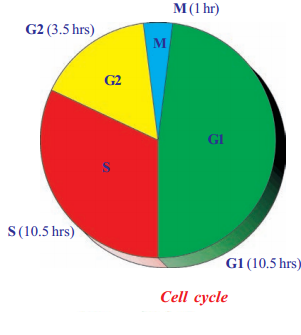
Observe the following mitotic cell division diagram and answer the Questions given below?
Questioni.
How much time does G1 phase require?
Answer: G1 phase requires approximately 10.50 hours
Questionii.
What is Sphase?
Answer: S phase period of DNA synthesis (synthesis phase)
Questioniii.
What is G2 phase ? What changes occur during this phase?
Answer: G2 phase is the time between the end of DNA replication and the beginning of mitosis.
Cell organelles divide and prepare chromosome for mitosis
Questioniv.
What is M phase ? How much time does it require?
Answer: M phase is cell division phase. It requires 1 hour to complete
Questionv.
How much time is required to complete mitotic cell cycles?
Answer: Approximately 25.30 hours
V. Communication Through Drawing, Model Making
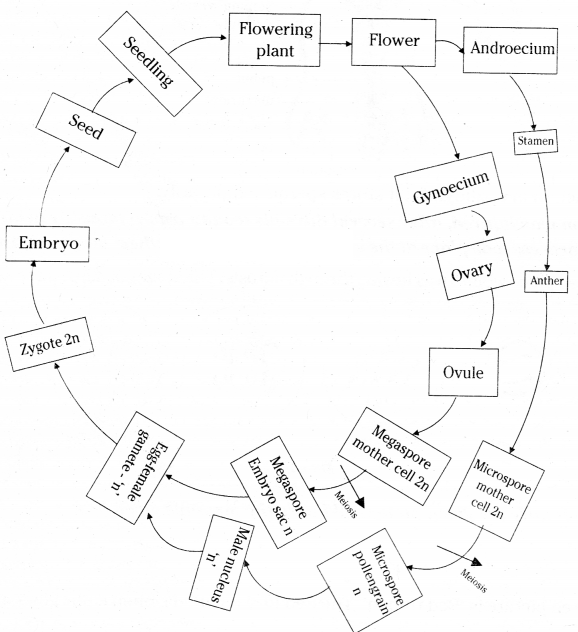
Question 1.
Draw the life history of flowering plant in the form of block diagram?
Answer:
Life history of a flowering plant:
Question 2.
Label the parts for given diagram and write functions of labelled parts 1, 2, 6 and 7?
Answer:
- Stigma
- Anther
- Petals
- Stamen
- Style
- Sepals
- Ovary
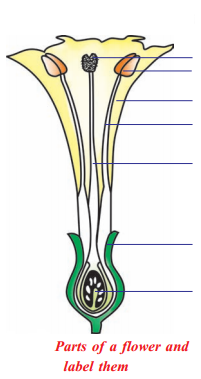 Functions of Stigma, Anther, Sepals and Ovary:
Functions of Stigma, Anther, Sepals and Ovary:
- Stigma: It receives pollen grains
- Anther: Produce pollen grains
- Sepals: Give protection to inner whorls
- Ovary: It forms ovules and later seeds
Question 3.
Draw labelled diagram of Human male reproductory system. What is the function of epididymis?
Answer:
 The function of epididymis: It stores sperms temporarily
The function of epididymis: It stores sperms temporarily

Identify the given picture. What is the message given by it?
Answer:
The given picture is Red ribbon. The Red Ribbon / Red ribbon clubs gives awareness about HIV / AIDS
VI. Application To Daily Life, Concern To Biodiversity
Question 1.
Write what programmes you are conducting to provide awareness of a health cleanliness and family planning?
Answer:
- Organising Health camps on World Health day to people of the village
- Conducting immunisation programs for every three months
- Supplying tablets on the deworming day
- Organising seminars by expert doctors on individual health and cleanliness programs
- Propagating small family norms conducting camps for family planning operations
- Educating the masses through pamplets on the needs of taking balanced diet
- Need of using toilets and washing hands and legs before and after meals
- Educating the people by conducting adult education centres. This is basically required for enlightening the people on health aspects
Question 2.
Describe what life skills one should develop in Adolescent stage?
Answer:
In order to face challenges of life especially in the context of adolescent stage
- Decision making skills : This means critical thinking and making right decisions in life
- Inter personal skills: It means healthy relationship between friends and classmates
- Communication skills: It means freely expressing their views, fears, doubts, anxiety etc
- Coping skills: It means to adjust with situations of life
- Handling peer pressure : It means making value judgements on request from friends
- Building caring relationships: It means respecting friends and others, especially of the opposite gender
Question 3.
Write some slogans against female foeticide?
Answer:
- Stop female foeticide - Save girl child
- Dont kill our mother, wife, daughter - Because all are girls
- Your daughter may be tomorrows a Doctor, an Engineer, a Scientist or a Teacher save them."