TS 10th Class Biology 5th Lesson Coordination - The Linking System Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve your learning
Question 1.Fill In the missing sections In the following flow-chart.

Answer:

Question 2.Do you think bodys team work maintains functioning of our body? Justify your answer with an example?
Answer:
- Yes. Bodys team work maintains functioning of our body
- All our functions are carried out by an effort of several systems working together
- The human body has a set of systems which regulate the internal environment and strive to give our cells the necessary condition as they need to function
- We cannot use only the skeletal system or muscular system
- To do any function several other systems also have their own roles to play
- The pathway involving the way that our organs tissues and cells pickup signals from their surroundings and respond to them that triggers different functions in our body as well as by our body
- When all the organs and organ systems work as a unit then the organism will survive
- For example our eyes, ears, legs should coordinate with each other when crossing the road. Otherwise we may met with an accident
Question 3.Give an example of coordination in your body where both hormonal and nervous controls function together?
Answer:
- Several functions in our body are controlled by nerves, while many others are controlled by hormones
- When we are afraid, the rate of heart beat increases, the breath rate will be faster, blood pressure increases, the hair on the body becomes errect and we get goose bumps
- We might not observe our pupil dilation, skin becomes more sensitive. We come to normally only after we reach a safe spot
- The various actions of the body are controlled by hormones and coordinated by nervous system
- In these type of conditions nervous system and endocrine system work together to bring about control and coordination
- Another example for nervous and hormonal coordination. When the mother feeds the baby, the baby sucks the nipple for milk. This information is send to the brain by sensory nerve. Brain orders the pituitary gland to release the hormone oxytocin. Oxytocin helps in the ejection of milk from the mammary glands
Question 4.Consider that you are passing by a garbage disposal area and you immediately?
cover your nose. Arrange the events below in a logical order by marking them from 1 to 5 to trace the events that happen in the nervous system from detection of foul smell (stimulus generation) to covering your nose (response).
- At the end of the axon, electrical impulse releases chemicals
- Stimulus received by the dendrites of a neuron sets off chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse
- Electrical impulse transmitted through cell body and axon
- The chemicals cross the synapse and reach the next neuron. Similarly, the electrical impulse crosses several neurons
- Finally, the impulse is delivered from neuron to the gland that helps in recognition of the foul smell and muscle cells that help in covering the nose
Answer:
The following events occur in nervous system for detecting foul smell of garbage, ii, iii, i, iv, v
Question 5.What is a Synapse? How is it useful in transfer information?
Answer:
- Definition: Synapse is a functional region between two neurons where information from one neuron is transmitted or relayed to another neuron
- Through synaptic region is with minute gaps it does not have any protoplasmic connection between them
- Information is passed from one nerve cell to the other through these gaps either in the form of chemical or electrical signals or both
Question 6.Distinguish between?
- Stimulus and Response
- Afferent and Efferent nerves
- Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
- Receptor and effector
Answer:
- Stimulus and Response
| Stimulus |
Response |
| 1. It is the cause or change in organisms surroundings that causes the organism to react |
1. It is the act done by the organism |
| 2. Stimulus can not be always controlled especially external stimuli |
2. It could be controlled |
| 3. Stimulus could be of any magnitude |
3. The response could never go beyond the highest capability of an organism |
| 4. Response can not determines the stimulus |
4. Stimulus determines the response |
- Afferent and Efferent nerves
| Afferent nerves |
Efferent nerves |
| 1. Nerves coming from receptors or sense organs are called afferent nerves |
1. Nerves that carry impulses from brain or spinal cord are called efferent nerves |
| 2. These are also called sensory nerves |
2. These are also called motor nerves |
| 3. Sensory nerves carry information from sensory organs like ears, eyes, from brain or spinal cord |
3. The motor nerves carry impulses to effector nose, tongue and skin to brain and organs (muscles) and are responsible for the movement of hands and legs |
| 4. These are incoming nerves |
4. These are outgoing nerves |
- Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
| Central nervous system |
Peripheral nervous system |
| 1. It consists of Brain and spinal cord |
1. It consists of nerves that arise from brain and spinal nerves |
| 2. Both of them have nerve cells and glial cells |
2. It has 43 pairs of nerves. Among them 12 pairs are cranial nerves and 31 pairs are spinal nerves |
| 3. Brain and spinal cord are continuous with each other |
3. Cranial nerves take their origin from brain and spinal nerves take their origin from spinal cord. |
| 4. Brain and spinal cord receive infor¬mation |
4. The cranial nerves carry information to the sense organs and spinal nerves from organs to spinal cord |
| 5. Central nervous system coordinates all neural functions |
5. These supply information required for the movement of the muscles |
- Receptor and effector
| Receptor |
Effector |
| 1. The sense organs which are made up of cells called receptors |
1. Muscles or tissues which are linked with nerves are called an effector |
| 2. Receptors respond to stimulus |
2. Effectors are the organs that produce response |
| 3. These send information to central nervous system |
3. They follow the commands of central nervous system.
|
| 4. These are connected to sensory organs |
4. These follow the motor nerves |
| 5. Nervous system sense the changes inside and outside the body through receptors |
5. Effectors receive messages from brain or spinal cord through motor nerves |
Question 7.How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer:
- Bending of plants towards light is called phototropism. (Photo = light) (tropism = movement)
- For example a creeper which is growing near the window bend towards sunlight
- Auxins are the phyto hormones which are present at the tip of the shoot respond the plant to bend towards sunlight
Question 8.Give an example and explain how plants may immediately respond to a stimulus?
Answer:
- The plant responding to stimulus is mimosa pudica is the example
- Mimosa pudica leaves have pad like sweelings at the base are called PULVINI
- Here cells contain water and large intercellular spaces. Due to water pressure pulvini hold the leaf errect
- When we touch the leaves, an electrical impulse is generated due to plant hormone
- Because of this hormone water in the pulvini cells which are closer to the leaf vein migrate to other sideof the cells
- Then pulvini loss its fitness hence leaves become fold. After 20 to 30 minutes water comes back leaves become errect
Question 9.Suggest an experiment to show how roots grow away from light in most plants?
Answer:
Aim: To prove that roots grow away from light in most plants.
Material required: Glass jar, Bean seed.
Procedure:
- A plant jar is taken and filled with mud
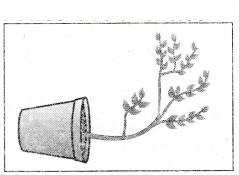
- A bean seed is sown just adjacent in the inner wall of the jar
- So that it is easy to observe the growth of root and shoot
- After 4-5 days the germination of the seed is observed
- Keep the jar in the sunlight. We observe the growth of roots and shoot
- Finally the jar is tilted to keep the growing plant horizontally
- After the growth of 4-5 days, tilt the glass jar and keep the plant horizontally
Observation: It is observed that the roots extends downwards to the earth that is away from the sun light and the shoot grows towards sunlight.
Conclusion: By the above experiment it is proved that roots grow towards gravity (earth) away from sun light.
Question 10.Give an example to show how hormones can influence visible changes in your body?
(OR)
What are the effects of hormones on human beings?
Answer:
- Endocrine glands secrete chemical substances called Hormones directly into blood
- Hormones act on the cells of other organs and increase or decrease the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats
- The external features by which the males and females can be distinguished are called secondary sexual characters
- Testosterone in males and estrogen in females promotes the development of secondary sexual characteristics
- For example, if a dog chases us, our nervous system stimulate the adrenal glands to secrete more adrenaline hormone into our body
- When we are afraid, the rate of heart beat increases, the breath rate will be faster, blood pressure increases, the hair on the body becomes errect
- All these changes occur due to the production of Adrenaline hormone
Question 11.How does a neuron differ from an ordinary cell in structure? Write notes?
Answer:
| Neuron (Nerve cell) |
Ordinary cell |
| 1. It is the longest cell in our body |
1. Generally cells are round or oval shaped |
| 2. It belongs to only nervous system |
2. These are the structural units of body |
| 3. Nerve cell has three parts: 1. Cyton 2. Axon 3. Dendrites |
3. Commonly divided as 1. Cytoplasm and 2. Nucleoplasm |
| 4. These cells carry impulses to brain and spinal cord |
4. Involve in metabolic activities |
| 5. These are not regenerated |
5. The cells have cell division and replace the death cells |
| 6. Nerve cells end with dendrites |
6. These cells do not have end points |
| 7. Some nerve cells are covered with lipid coat |
7. Generally these are covered with plasma membrane |
| 8. Nissl granules are special character of nerve cells |
8. These cells do not have Nissl granules |
Question 12.Is the structure of neuron suitable for transmission of impulses? Analyse?
Answer:
- Yes. The structure of neuron is suitable for transmission of impulses
- Neurons are the functional units which receive and process information and generate responses
- Cell body is the centre for all the synthetic activity of the neuron.
- Dendrites arise from the cell body receive information from other neurons and carry this information to the cell body
- The axon or nerve fibre gives out several branches that end in nerve terminals. These make connect with the dendrites or the axons of another neuron
- Myelinated sheath prevents the leakage of electrical currents from axon. Myelinated axons conduct impulses much faster than unmyelinated axons
Question 13.Man is the most intelligent animal. What could be the fact that helped us to reach such a conclusion?
Answer:
- Man is the most intelligent animal in animal kingdom
- This is possible by well development of brain and its marvellous function
- Human brain has abilities to learn from concepts
- It understands, applies logic and reason
- The brain also recognizes patterns and comprehends ideas
- The human brain has ability in making plans, solving problems, making decisions and retaining information
- Man is the only animal who uses language to communicate
- Intelligence enables humans to experience and think
- It has also consciousness and self-awareness
Question 14.The axon of nerve cell in hand is shorter than the axon of nerve cell in leg. Do you support this statement? Why?
Answer:
- Yes, I support the above statement
- The axon of nerve cell in hand is shorter than the axon of nerve cell in leg
- The sciatic nerve is the large nerve in humans and animals. It begins in the lower back and runs through the buttock and lower limbs
- Sciatic nerve present in the leg is the largest and widest single nerve in the human body. It measures about 1 mt in length
- Usually the length of leg is more in size than hand. Hence the axon of nerve cell in hand is shorter than the axon of nerve cell in leg
Question 15.Organs respond to the external stimulus by a fraction of second. How do you feel about such controlling mechanism of human body?
Answer:
- Organs responding for the external stimuli by a fraction of second are due to reflex action
- Reflex actions are very important as they save us from painful or dangerous stimuli
- Reflex actions or reflexus are fast, immediate automatic and involuntary responses of the body
- They help in the body as they save us from painful or dangerous stimuli
- Reflexes occur without our thinking
- Brain is not involved in the execution of several reflexes
Ex: Withdrawing our hand when we touch hot subject.
Question 16.State whether the following actions are voluntary action, reflex action or conditioned reflex?
- Blinking
- Cleaning the table
- Playing on the key board
- Salivating when food is put in the mouth
- We close our ears when we hear unbearable sound
Answer:
- Blinking: Involuntary action or reflex action
- Cleaning the table: Voluntary action
- Playing on the keyboard: Conditioned reflex
- Salivating when food is put in the mouth: Involuntary or Reflex action
- We close our ears when we hear unbearable sound: Involuntary or reflex action
Question 17.What will happen to the potted plant kept near window in the room?
(OR)
Draw a diagram of a plant showing phototropism. Explain why plants possess such type of response.
(OR)
A plant which grows near a window bends towards sun light. Write the reason for it.
Answer:
- The potted plant which is kept near the window in the room, grows towards light

- Auxins acts on bending of stem of show a response to the sun light
- More auxin collects on the light illuminated side of the stem. So cells on that side grow faster
- On opposite side cells grow slow to make the stem bend
- Auxins are the plant hormones responsible for the growing of the stem towards light
- Auxins are synthesized at the tip of the stem (meristematic tissue
)
- Bending of the plant towards light is called phototropism
Question 18.What happens if all the functions of the human body are controlled only by brain?
Brain controls all the functions of the human body. Comment on it.
Answer:
- If all actions of the human body are controlled by brain, our body will get harm in dangerous situations
- Some actions may be delayed and our brain could not conduct reflex actions, which require immediate action to a stimulus
- For example, when we touch a hot object, we require an immediate response to save our hand. If the brain controls this action, the time taken will be more and our hand will burn
- So, it is controlled by spinal cord, the response will be quick, and we may escape the danger
- Nerves can not reach the every corner of the body, whereas hormones of endocrine glands can do that
- So its not good that all functions are controlled by brain
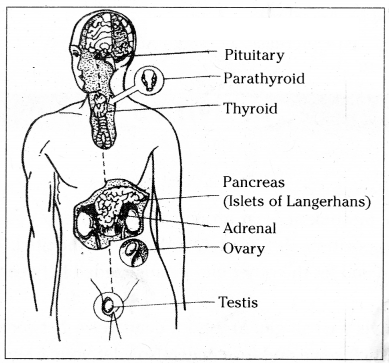
Question 19.If you visit a doctor, what doubts you would like to clarify about pancreas?
Answer:
- What is pancreas
- Where is pancreas located in our body
- Why is it called mixed gland
- What is the exocrine part of pancreas
- What is the endocrine part of pancreas
- What are the cells that secrete hormone insulin
- What is the function of insulin
- What happens if required amounts of insulin is not produced
- What are the symptoms of diabetes
- How can diabetes be controlled
Question 20.Take a small potted plant. Cover base portion of the plant tightly and hang the part upside down. Observe the plant for a week. Based on your observation how can you support phototropism?
Answer:
Aim: To prove that phototropism is a character that is carried by stem.
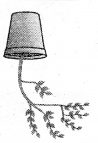 Apparatus: Potted plant, a strong small rope.
Procedure : Take a small potted plant. Cover the base portion of the plant tightly so that the plant along with soil do not fell down. Now take a rope and hang the potted plant upside down to a support firmly.
Observe the plant after a week.
Observation: We observe that the end of the stem which is upside down takes U turn and grows towards light.
Conclusion: Phototropism is a response of plants towards light. That the stem grows towards light that is negatively to gravitation. Auxins are responsible for phototropism
Apparatus: Potted plant, a strong small rope.
Procedure : Take a small potted plant. Cover the base portion of the plant tightly so that the plant along with soil do not fell down. Now take a rope and hang the potted plant upside down to a support firmly.
Observe the plant after a week.
Observation: We observe that the end of the stem which is upside down takes U turn and grows towards light.
Conclusion: Phototropism is a response of plants towards light. That the stem grows towards light that is negatively to gravitation. Auxins are responsible for phototropism
Question 21.Take a cock feather touch smoothly at different parts of your body. Findout which portion of the body has high sensation. Is this similar during sleeping ? Prepare a report on it?
Answer:
Aim: To prove that our body shows high sensation in different parts.
Apparatus : Cock feather.
Procedure: Take a cock feather. Touch smoothly at different parts of our body with the cock feather.
Observation : It is observed that some of the body parts like palms of hands and soles of feet there is less sensation than the other body parts because the skin is thick. Some other parts where the skin is thin, the sensation is more.
Report: The nerve endings are situated in the skin. These nerve endings are responsible for the sensation of the body
Question 22.What procedure you follow to understand the effect of plant growth hormones (in agar medium) in the terminal portion of the tip of stem (coleoptile) ?
Answer:
Aim: To show the growth of Avena coleoptile involves a chemical substance
Apparatus: Oat seedlings (Avena sativa), coleoptile, a slice of agar, a sharp blade. Procedure:
- Take some oat seedlings
- Their coleoptile tips are cut off
- Place the tips on a slice of agar and leave them for about an hour
- Cut the agar into small blocks and place a block on one side each stump of the decapitated plants
- The plants were kept in the dark during the entire experiment
- Observe the plants after one hour
Observation :
- Within one hour a distinct bending away from the side on which the agar block was placed is observed
- Agar block that had not been contact with coleoptile doesnt show any bending
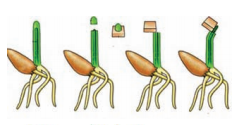
Conclusion : The coleoptile tip exerted its effect by means of a chemical stimulus such as an electrical impulse. This chemical stimuls came to be known as auxin.
Question 23.Collect information on the actions controlled by spinal cord by using reference books from your school library?
Answer:
Spinal cord
Spinal cord is a long and cylindrical structure. It passes through vertibral column extending all along the dorsal surface of trunk.
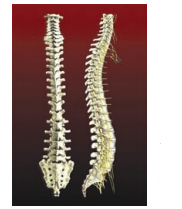
Vertebrae of the vertebral column protects the spinal cord
The spinal cord has two major functions, a) carrying information coordinating reflexes
It receives sensory information through the afferent nerves from the sensory receptors throughout the body and send them to the brain
It also carries information from the brain through efferent fibres to the muscles and glands
It coordinates reflexes without the involvement of the brain.
Thus the spinal cord has both communicative and integrative functions
Reflex actions:
Excepting the sensory and motor functions spinal cord controls some other important function also. These are called as reflex actions
The spinal cord does not take any assistance from the brain. Reflex actions are automatic, unlearned, involuntary and in born responses
Therefore these actions are suddenly in nature and have a purpose of protecting the individuals or his / her organs from sudden danger
Question 24.Read the following sentences and compare with endocrine glands?
Pheromones are chemical substances secreted by organisms. These act as chemical signals secreted by exocrine glands. Pheromones are used as signals by the members of same species. Honey bee secretes pheromones that attract other bees to the location of food.
Answer:
| Pheromones |
Secretions of Endocrine glands (or) Hormones |
| 1. Pheromones are chemical substances secreted by organisms |
1. Hormones are chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands |
| 2. These act as chemical signals |
2. These are the chemical messengers |
| 3. Pheromones are used as signals by the members of same species |
3. Hormones change or control the metabolic activities in the organisms |
| 4. Honey bee secretes pheromones that attract other bees to the location of food |
4. Hormones help for growth, and stimulated organs function |
Question 25.Collect the information about cranial nerves, spinal nerves from internet or from your school library?
Answer:
Spinal cord :
- Spinal cord is a long and cylindrical structure passing through the vertebral column
- The vertebrae (back bones) of the vertebral column protect the spinal cord from injuries
- From the sides of spinal cord, 31 pairs of nerves take their origin one from each side and supply branches to various parts of the body.
- Basic function of spinal cord is to act as a relay station - receiving information from various parts of the body parts below the head and send this information to the brain
- Similarly, it receives information from brain and sends this information to other parts of the body
- In addition to this, spinal cord also plays a major role in the RFELEX ACTIONS
- The message received from the sensory nerve is passed into spinal cord. It is analyzed by the INTER NEURON present in the spinal cord and response is given. It is conveyed to the effector organ through motor nerve. The effector organ shows the response
- Thus spinal cord saves us from dangerous stimuli through its REFLEX ACTIONS
Question 26.Draw a picture representing connection between dendrite - dendrite, axon - dendrite. Why do they connect like that?
Answer:
- The nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of nervous system
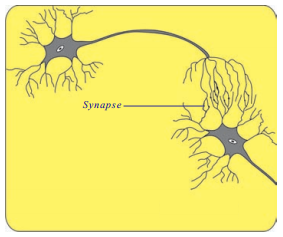
- It consists of more than 100 billion of them, which communicate with each other in a specific manner
- Dendrites of one nerve cell connects to the other or to the axons of another nerve cell through connect points called as a synapse
Question 27.Draw a neatly labelled diagram of Brain and write few points how it is protected?
Answer:
Protection of Brain
Brain is present in the hard bony box called CRANIUM
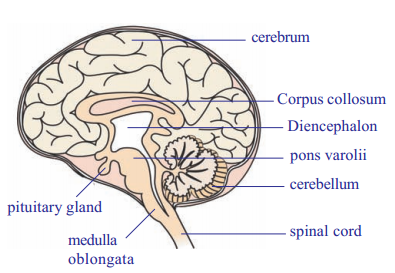
It is covered by three layers called MENINGES
The space between the inner layer is filled with fluid called cerebrospinal fluid
It serves a shock-absorbing medium and protects brain against shocks/ jerks along with the meninges and cranium
Question 28.You are walking in the traffic suddenly you heard a loud sound. How does coordination take place in this situation among respected organs? Draw a block diagram to explain this situation?
Answer:
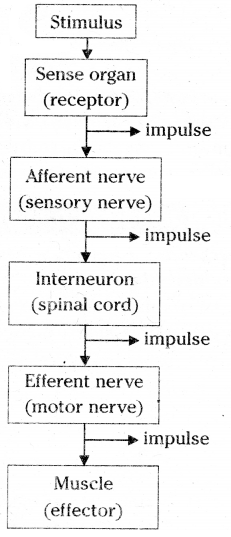
Question 29.Make a model of neuron using suitable materials?
Answer:
Required materials: A chart, twine thread, fevicol, sticker.
Question 30.Observe different actions performed by your classmate for a period of 45 minutes. Out of these actions which are controlled by voluntary and involuntary pathways?
Answer:
Voluntary actions
- Standing
- sitting
- laughing
- drinking
- moving
- clapping
- carrying books
- reading
- writing
- talking
Involuntary actions:
- Blinking of eyes
- swallowing
- breathing
- listening etc
Question 31.Its very interesting to watch a creeper entwining its tendril to the support. Is not it? How do you express your feelings in this situation?
(OR)
Plants also respond to external stimuli. How do you feel about this?
Answer:
- A very interesting thing in plants is movement of tendrils.

- All plants show positive response to phototropism
- But creepers like cucumber, bittergourd the stem is weak and thin. Hence plant cannot grow erect
- Tendrils play a vital role to make the plant erect. Tendrils are thin thread-like growth on the leaves or stems of climbing plants
- They grows towards support and wind around them
- This type of response to make contact or touch is called thigmotropism
- Nature only finds its way to grow and survive on the earth
Question 32.Hormones are released at a specific place, specific time for a specific function. Prepare a cartoon on the hormones with a nice caption?
Answer:
Fill in the blanks.
- The largest region of the brain is ----
- A point of contact between two neurons is ----
- ---- phytohormone is responsible for cell elongation and differentiation of shoots and roots
- Thyroxine is responsible for ----
- Gibberellins and auxins promote growth in plants while absciscic acid arrests the same. Some situations are discussed here. State which hormones would be needed and why
- A gardener wants large dahlias, he should use along with nutrients and other things ---- hormone
- In a dwarf plant the branches have to be thickened one would use the ---- hormone
- Seeds are to be stored a long time ---- hormone can help.
- Cutting the apex or tip of plants so that there are several lateral buds ---- hormone can be used
- The part of the brain that helps you in solving puzzles is ----
Answer:
- cerebrum
- synapse
- Auxin
- General growth rate and metabolic rate
Auxin b) Gibberellin c) Absciscic acid d) Cytokinins e) Cerebrum
Choose the correct answer.
1.
A person has loss of control on emotions, which part of brain stops its function ? [ ] ?
- Cerebrum
- Diencephalon
- Mid brain
- Cerebellum
2.
Leaf movement in mimosa helps to [ ] ?
- Reduce photosynthesis
- Protect from grazers
- Releasing phytohormones
- Regulate its growth
3.Diabetes is related to this gland. [ ] ?
- Thyroid
- Pancreas
- Adrenal
- Pituitary
10th Class Biology 5th Lesson Coordination - The Linking System InText Questions and Answers
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 95
Question 1.What helps us to respond to such signals?
Answer:
There is a sequence of events that bring about responses. They start from detecting changes in environment
Question 2.Why does the living body respond to such signals?
Answer:
The ability to react to particular stimulus in a particular situation must be of great importance in ensuring the survival of the organism
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 96
Question 3.What did Galen conclude after his observations?
Answer:
After the observations of his patient, Galen a Greek physiologist concluded that nerves were of two types - those of sensation and those of action
Question 4.Why do you think Galen drew such a conclusion?
Answer:
According to Galen the blow in the neck of his patient had damaged the nerves of sensation but had not affected its action. Then Galen concluded that nerves were of two types
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 98
Question 5.Which organ of our body was the detector and which was the effector in Activity -1?
Answer:
In Activity -1, Eye was the detector and fingers were the effector
Question 6.What do you think that the information carried on the afferent and efferent nerves?
Answer:
The information carried by afferent nerve is "scale is falling".
The information carried by the efferent nerve is "to hold the scale"
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 99
Question 7.What other effectors would act under these circumstances?
Answer:
- Withdraw our hands, when our fingers touch a hot object
- Closing eyes when bright light is focussed on eyes
- We sneeze when something enters the nose
- We cough when inhaled dust or some other circumstances
Question 8.What does this tell us about the association nerves?
Answer:
The sensory nerves in the spinal cord makes connections with other neurons in the grey matter. These neurons are called association neurons or interneurons. The association neurons process the information and generate responses
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 100
Question 9.According to you what would be the function of the spinal cord?
Answer:
Functions of the spinal cord
- Spinal cord sends information received from different parts of the body to brain
- Also it sends the information to various parts received from brain
- Spinal cord also play a major role in reflex actions
Question 11.Are all functions of our body under direct control of the brain and spinal cord? Why do you think so?
Answer:
Yes. All the functions of our body are under direct control of the brain and spinal cord. The 43 pairs of peripheral nervous system associated with brain and spinal cord plays an important role in disposing our body functions
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 103
Question 12.Which root according to you gets signals from afferent nerves?
Answer:
The dorsal root of the spinal cord gets signals from afferent nerves
Question 13.What do you think the end of these nerves act at the muscular end?
Answer:
At the ends of these nerves can involuntarily control several functions of regions like internal organs, blood vessels, smooth and cardiac muscles and is called an autonomous nervous system. It has voluntary control of muscles of some areas of skin and the skeletal muscle
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 104
Question 14.To which organs of the body do the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column?
Answer:
The organs like heart, lungs, stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, kidneys, hand fingers of the body, the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 105
Question 15.What are the organs that receives nerves starting from the brain?
Answer:
Eye, mouth, tongue, salivary glands are the organs receives nerves starting from the brain
Question 16.Which are the organs whose activities are influenced by the sympathetic nervous system?
Answer:
Eye - pupil, heart, lungs, blood vessels, sweat glands, digestive tract, kidneys, penis are the organs influenced by the sympathetic nervous system
Question 17.Which are the organs whose activities are influenced by the parasympathetic system?
Answer:
Stomach, intestines, salivary glands, reproductive organs, etc., are influenced by para sympathetic system
Question 18.What do you understand about the functions of parasympathetic nervous system?
Answer:
Parasympathetic nervous system slows down the body functions such as feed & breed, rest & digest, sexual arose, lacrimation, urination, defecation and digestion
Question 19.What do you understand about the functions of sympathetic nervous system?
Answer:
Sympathetic nervous system speeds up the body functions. Dilates pupil, heart - increases rate, force of contraction, lungs dilates, blood vessels contraction, etc. are the functions controlled by sympathetic nervous system
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 107
Question 20.Have you ever observed the duration of anger?
Answer:
The duration of anger will be sometimes ten minutes or fifteen minutes or according to the situation
Question 21.Why does anger come down?
Answer:
Anger is always short lived factor. Increased levels of adrenalin are responsible for anger. When the levels of adrenalin in the blood come down slowly. We came to normal state
Question 22.What may happen if anger persists for a longer period?
Answer:
If anger persists for longer time, regular metabolic activities are disturbed
Question 23.What will happen if it is continued for longer periods of time?
Answer:
The sugar levels in the blood rise than normal level. Blood pressure increases, burning sensation in the heart, stomach upsets are the some of the abnormal conditions may happen
10th Class Biology 5th Lesson Coordination - The Linking System Activities
Activity - 1
Holding a falling stick?
Answer:
Take a long scale or stick at least around V2 meter. Keep your fingers in holding position. Ask your friend to hold the stick / scale near the end and let the other end be suspended between your fingers.
Let there be a very small gap around a centimeter between your thumb and stick/scale and fore finger. Now let you friend allow it to fall. Try to hold it.

1. Could you hold it exactly at the point where it was suspended between your fingers?
Answer:
No. I cannot hold it exactly at the point
2.How far up was this point from the end suspended between your fingers?
Answer:
2 cm up (nearly at the end of the scale)
3.Why did this happen?
Answer:
Because it is the sudden action. To hold it fastly. The exact point went up
4.How fast do you think the process was?
Answer:
The process was so fast in a fraction of a second
5.What makes this kind of communication possible?
Answer:
Rapidity of response indicates an efficient communication system linking those parts that pick up stimuli that trigger a response by the nervous system
Activity - 2
Observe the permanent slide of nerve cell or neuron under microscope and try to find out its parts. Compare with the following diagram?
Answer:
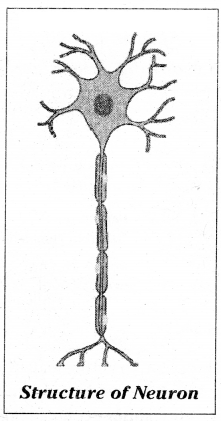
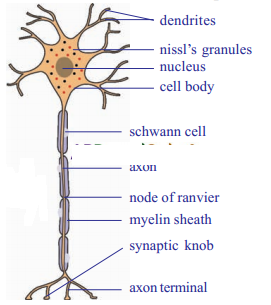 Structural unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell or neuron. Neuron is highly specialised cell. Neurons carry impulses or messages. New nerve cells are not produced to replace the damaged or destroyed nerve cell. A neuron has three parts. They are
Structural unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell or neuron. Neuron is highly specialised cell. Neurons carry impulses or messages. New nerve cells are not produced to replace the damaged or destroyed nerve cell. A neuron has three parts. They are
- cyton
- axon and
- dendrites
- The cyton
- It is also called the cell body
- It has a large and round nucleus
- In the cytoplasm of the cyton, nissl granules are present
- Axon
- It is the long and cylindrical process that arises from the cyton
- In some nerve cells, axon is surrounded by a layer of fatty material known as myelin sheath
- The myelin sheath is not continuous throughout length of the axon
- It is broken at regular intervals
- These broken spots are called as nodes of Ranvier
- Dendrites: Arise from the cyton they are much branched, when compared to axon
Activity - 3
What is knee jerk reflex?
Answer:
Cross the legs, in a seated position, so that the lower half of the uppermost leg hangs freely over the other. Strike the area below the knee cap sharply, while firmly grasping the front part of the thigh with the other hand. Note the changes in shape of the thigh muscles

1.What changes do you observe in the thigh muscle?
Answer:
The thigh muscles get contracted and becomes short
2.What do we call this type of response?
Answer:
This type of responses are called involuntary actions. Such type of actions in the body are carried by without our involvement and our knowledge
3.What do we call the action of kicking a foot ball?
Answer:
Kicking of a foot ball is a voluntary action These actions are within our control
4.How is the knee jerk action takes place?
Answer:
In the knee jerk action a nerve pathway was involved.
v) Do you think most of the functions in our body go about in an involuntary manner? Why ? Why not
Answer:
Most of our body functions are done without the involvement of our knowledge. For example, heart beating, respiration, digestion, etc., are the involuntary actions which are carried by our body
Activity - 4
Touch the leaves of Mimosa pudica (athipathi, touch me not) plant and observe the response of leaves.

1.Are they folding?
Answer:
When the leaves of Mimosa are touched the leaves get folding. Touching the leaves is the stimulus and folding is the response
2.In which direction the folding of the leaves take place?
Answer:
The folding of the leaves take place inward direction
3.Give some examples of situations in plants responding to a certain stimulus?
Answer:
Examples: The sun flower turning to the direction of sun, the bending response of the plant when it is kept in the dark. Some of leaves of the trees opens at the day time and closes after sun set.
Phototropism of stem and geotropism of roots, hydrotropism of roots of plants growing towards water and thigmotropism where the creepers like cucumber, bitter - gourd takes the help of tendrils and wind around the support are some of the examples of response to stimulus in plants
Activity - 5
Take a glass jar and fill with soil. Sow a bean seed near the wall of the jar. After 4 - 5 days you will notice seed germination. Keep the jar under the sun. Observe how root and shoot grows. Then tilt the glass jar and keep the plant horizontally. Observe the direction of the root and shoot growth for more than a week.
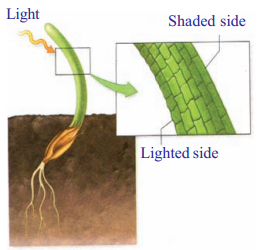
1.Does the shoot take a horizontal tilt after a week?
Answer:
After a week the shoot takes a horizontal tilt
2.Which side of the shoot may have grown more and which side less to bring about this effect?
Answer:
The shoot grown more towards the light and less where light is not falling
3.Do you find any difference in the shape of epidermal cells?
Answer:
The straight portions of the epidermal cells shows no bending but the bending portions of epidermal cells shows bending
4.Who performed experiments on phototropism?
Answer:
Charles Darwin and his son Francis Darwin performed some experiments on phototropism
5.What did they do in their experiment?
Answer:
Charles Darwin and his son Francis Darwin performed experiments on phototropism. They covered the terminal portion of the tip of stem (coleoptile) with a cylinder of metal foil. Exposed the plant to light coming from the side
6.What did they observe by that experiment?
Answer:
They observed that the bending towards the light (characteristic) of the seedling did not occur. If light was permitted to penetrate the cylinder bending occurred normally
7.What did Charles Darwin and his son Francis Darwin state on their experiment?
Answer:
They stated that when seedlings are freely exposed to a lateral light some influence is transmitted from upper to the lower part causing the material to bend
8.What are the experiments of F.W. Went and how did he succeeded in separating influence from the plant?
Answer:
F.W. Went cut off coleoptile tips from oat seedlings. He placed the tips on a slice of agar and left them for about an hour.
He then cut agar into small blocks and placed a block on one side each stump of the decapitated plants. They were kept in the dark during the entire experiment. Within one hour he observed a distinct bending away from the side on which agar block was placed
9.How did Went come to know about auxin?
Answer:
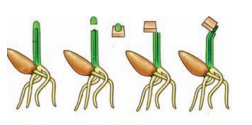 Went interpreted these experiments as showing that the coleoptile tip exerted its effect by means of chemical stimulus rather than a physical stimulus such as an electrical impulse.
This chemical stimulus came to be known as auxin. In this way the first plant hormone auxin was discovered by F.W. Went
Went interpreted these experiments as showing that the coleoptile tip exerted its effect by means of chemical stimulus rather than a physical stimulus such as an electrical impulse.
This chemical stimulus came to be known as auxin. In this way the first plant hormone auxin was discovered by F.W. Went
10.What is the meaning of auxin in Greek?
Answer:
The Greek word auxin means to increase