TS 10th Class Biology Important Questions 4th Lesson Excretion
1 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
Why is urine yellow in color?
Answer:
Because of urochrome, urine is yellow in colour. It forms in the liver from dead RBC
Question 2.
Write two slogans to popularize the awareness on "Organ Donation"?
Answer:
Slogans
- Organ donation saves lives
- Donate organs today for better tomorrow
Question 3.
Write two healthy habits which you practice to protect your kidneys from diseases?
Answer:
- Drink plenty of water
- Eat low salt diet that saves kidney life
- Drink more fruit juices
Question 4.
What precautions you have to take in the observation of internal structure of mammalian kidney?
Answer:
- Wash the kidney thorougly with water
- Ensure that blood is completely drained from it
- Wash your hands with antibacterial lotion after completing the dissection
Question 5.
Write two secondary metaboiltes, which you use in your daily life?
Answer:
Gum, Rubber, Coffee are the examples for secondary metabolites which we use in our daily life
Question 6.
Why is vasopressin not secreted when a person drinks a lot of water?
Answer:
Vasopressin is secreted only when concertrated urine is to be passed out. When a person drinks a lot of water, there will be no need to secrete concentrated urine. The excess water taken by the person will be sent out ¡n the form of dilute urine. Hence, vasopressin is not secreted
Question 7.
any two Questions that you will ask your teacher about the Alkaloids?
Answer:
Question about the Alkaloids
- What are alkaloids
- Where alkaloids are produced
- What are the different types of alkaloids
- What are the uses of alkaloids
Question 8.
In urine excretory system much water is reabsorbed. What happens if it doesnt occur?
Answer:
If water is not reabsorbed it leads to excessive repeated dilute urination called diabetes insipidus. If water does not reabsorbed we would dry up and blow away like dust in the wind in a matter of hours
Question 9.
A substance given below consists of other three substances. What is that substance ? Where is it produced ? Uric Acid, Sodium, Oxalate, Urine?
Answer:
Urine contains all the other three substances. It is produced in kidney
Question 10.
Why we feel sticky of stem and leaves of a plant effected with aphids ?
Answer:
Aphids absorb so much sugar from the phloem that they cannot assimilate all of it and excretes out of the body as a sticky syrup called honey dew. Leaves which have been attacked by aphids often feel sticky as a result of honey dew
Question 11.
What is Anabolism ?
Answer:
The synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler ones together with the storage of energy
Question 12.
What is catabolism ?
Answer:
The breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, together with the release of energy
Question 13.
What are the wastes produced during metabolic activities ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, water, nitrogenous compounds like ammonia, urea, uric acid, bile pigments, excess salts etc
Question 14.
What are the substances present in blood ?
Answer:
Substances present in blood are glucose, sodium, potassium chlorides, urea, creati¬nine, uric acid, cholesterol, triglycerides, calcium, phosphorus, bilirubin, proteins, etc
Question 15.
What are the substances present in urine ?
Answer:
Substances present in urine are protein, creatinine, calcium, phosphorous, uric acid, etc
Question 16.
What are the substances present in both in blood and urine in common ?
Answer:
The substances present in the blood and urine in common are sodium, potassium, glucose, chlorides, urea, proteins, creatinine, calcium, phosphorous and uric acid
Question 17.
What are the substances that need to be removed from body ?
Answer:
Creatinine, uric acid, urea, cholesterol and calcium
Question 18.
In human beings excretory system consists of?
Answer:
A pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
Question 19.
Where do the kidneys present in human body ?
Answer:
Kidneys are present in the abdominal cavity attached to dorsal body wall one on ei¬ther side of backbone
Question 20.
What is the size of the kidney ?
Answer:
The size of the kidney is 10 cm in length, 5-6 cm in breadth and 4 cm in thickness
Question 21.
Which artery brings oxygenated blood to kidney ?
Answer:
Renal artery brings oxygenated blood loaded with waste products to kidney
Question 22.
What are the two distinct regions present inside the kidney ?
Answer:
Dark coloured outer zone called the cortex and pale coloured inner zone called medulla
Question 23.
Each kidney is made up of how many nephrons ?
Answer:
Each kidney is made up of about 1.3 to 1.8 million nephrons
Question 24
What is the other name of Nephron ?
Answer:
Nephron is otherwise known as uriniferous tubules
Question 25.
What are the two basic parts of nephron ?
Answer:
The parts of nephron are malphigian body and renal tubule
Question 26.
Which blood vessel forms glomerulus in Bowmans capsule ?
Answer:
Afferent arteriole
Question 27.
What does renal tubule consist of ?
Answer:
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Question 28.
What is the major function of proximal convoluted tubule ?
Answer:
Reabsorbs useful substances like glucose, amino acids, phosphate, potassium, urea and other organic solutes from the filtrate.
Question 29.
What is the function of loop of Henle?
Answer:
- In the descending loop of Henle reabsorption of water from the filtrate takes place
- Ascending loop of Henle is impermeable to water and only ions diffuse out into the surrounding cells
Question 30.
What is the function of Distal convoluted tubule?
Answer:
It maintains proper concentration and PH of the urine
Question 31.
Formation of urine involves how many stages ? What are they?
Answer:
Four stages. They are
- Glomerular filtration
- Tubular reabsorption
- Tubular secretion and
- Concentration of urine
Question 32.
The amount of water absorption in the tubule depends on?
Answer:
Amount of excess water present in the body and the amount of dissolved wastes to be excreted
Question 33.
75% of water content of the nephric filtrate is reabsorbed in the region of?
Answer:
Proximal Convoluted tubule
Question 34.
The hormone that is secreted when concentrated urine is to be passed?
Answer:
Vasopressin
Question 35.
What is micturatjon?
Answer:
It is the process of discharge of urine from the urinary bladder
Question 36.
What are the composition of various substances ¡n urine?
Answer:
Urine contains 96% of water, 2.5% of organic substances and 1.5% of inorganic solutes
Question 37.
What is uremia?
Answer:
If kidneys stop working completely, our body is filled with extra water and waste products. This condition is called uremia
Question 38.
What are the symptoms of uremia?
Answer:
Hands or feet may swell. Tiredness and weakness persists as the body needs clean blood to function properly
Question 39.
What is haemodialysis?
Answer:
Filtering the blood of a person whose kidneys are damaged with dialysis machine is called haemodiaiysis
Question 40.
What are the organs that can be transplanted from brain dead patients?
Answer:
Kidney, liver, heart, lungs, pancreas, skin, bone, intestines and eyes (cornea)
Question 41.
Where the transplanted kidney fired in the body of kidney failed patient ?
Answer:
The new kidney is fixed inside lower abdomen connected to renal artery and renal vein, without disturbing failure kidney
Question 42.
What is cadaver transplantation?
Answer:
The process of transplantation of organs from brain dead patients to another is called cadaver transplantation.
Question 43.
What are the other excretory organs in human beings?
Answer:
Lungs, skin, liver, large intestine, endocrine glands
Question 44.
What are the waste products removed by lungs?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide and water
Question 45.
Sebum of sebaceous glands in skin contains wastes like?
Answer:
Waxes, sterols, hydro carbons and fatty acids
Question 46.
What are the metabolic wastes of haemoglobin of red blood cells in liver?
Answer:
Bile pigments like bilirubin, biliverdin and urochrome
Question 47.
How is urea produced in liver?
Answer:
By the deamination of proteins urea is formed in the liver
Question 48.
What are the wastes excreted by intestine?
Answer:
Excess salts of calcium, magnesium, undigested food and iron are excreted by epithelial cells of colon (large intestine)
Question 49.
How do unicellular organisms remove waste products?
Answer:
Diffusion from the body surface to the surrounding water
Question 50.
What is the osmoregulatory organelle in amoeba and paramoecium?
Answer:
Contractile vacuole
Question 51.
Water bathes almost all their cells in body of organisms belonging to these animal phyla?
Answer:
Porif era and coelenterates
Question 52.
What are the processes used by plants to get rid of excess water?
Answer:
Transpiration and guttation
Question 53.
What are Raphides?
Answer:
In Yam plants waste gets stored in the fruits in the form of solid bodies called Raphides
Question 54.
What are tannins?
Answer:
Tannins are alkaloids which are carbon compounds
Question 55.
In which group of plants does resin occur?
Answer:
Gymnos perms
Question 56.
Give two examples for gum yielding plants?
Answer:
Neem and Acacia
Question 57.
What is latex?
Answer:
Latex is a sticky, milky white substance secreted by plants
Question 58.
Rubber is prepared from the latex of?
Answer:
Hevea braziliensis
Question 59.
From the latex of which plant bio-diesel is obtained?
Answer:
Jatropa plant
Question 60.
What happens if some materials are above normal limits in the blood and urine?
Answer:
If some materials are above normal limits in the blood and urine it leads to accumulation of poisonous wastes and leads to death of the person
Question 61.
Why the nephron is considered to be the structural and functional unit of the kidney?
Answer:
- Kidney is made up of number of microscopic tubular structures hence nephron is a structural unit of kidney
- Filtration of blood takes place in the nephrons hence it is considered as the functional unit of kidney
Question 62.
Which substances are present above the normal limits both in the blood and urine?
Answer:
Substances present above the normal limits ¡n the blood are: creatinine, uric acid and cholesterol.
Substances Present above the normal limits in the urine are : creatinine, calcium, uric acid and urea
Question 63.
Why is more urine excreted?
Answer:
A large intake of liquids or water-rich food increases the volume of water in the blood, hence more urine is excreted
Question 64.
What are the uses of tannins?
Answer:
Tannins are used in tanning of leather and in medicines
Question 65.
What is the economic importance of gums ?
Answer:
Gums are valuable being used as adhesives and binding agents in the preparation of the medicines, food, etc
Question 66.
What is osmoregulation?
Answer:
The regulation of the water content of the cell is called osmoregulation
Question 67.
Which organ of the plant body helps in osmoregulation?
Answer:
Leaves
Question 68.
Which organ of the cell in animals helps in osmoregulation?
Answer:
Contractile vacuole
Question 69.
What is the basic reason of urine production?
Answer:
Blood carries nitrogenous waste in the form of urea or uric acid which needs to be removed, It is done by kidneys by filtering the blood and removing uric acid in the form of urine
Question 70.
Due to availability of less water, how does the plants cope up with lack of water in desert conditions?
Answer:
They open their stomata at night and stomata remain closed during day time to conserve moisture
Question 71.
What are nitrogenous wastes?
Answer:
Nitrogenous wastes are residuals derived from the degradation of proteins. They are made from chemical transformation of the amine group of amino acid molecules
Question 72.
What are the three main types of nitrogenous wastes excreted by living beings?
Answer:
The main nitrogenous wastes excreted by living beings are ammonia, uric acid and urea
Question 73.
Why does the ingestion of alcohol increase urination?
Answer:
Alcohol inhibits the secretion of vasopressin by the pituitary That is why when it is drunk to excess the person urinates too much
Question 74.
What would happen to amoeba if osmoregulation did not take place?
Answer:
If osmoregulation did not take place, the organism would get flooded with water and burst
Question 75.
Which arteriole has more diameter, afferent or efferent?
Answer:
Afferent arteriole has more diameter
Question 76.
What are the substances that are filtered into the glomerular capsule?
Answer:
The substances that are filtered into the glomerular capsule are waste molecules, nutrient molecules and water
Question 77.
If you drink more water will you pass more urine?
Answer:
Yes. 1f we drink more water, we will pass more urine
Question 78.
What are the substances reabsorbed into the peritubular network from Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PC7)?
Answer:
Glucose, water, salts, potassium ions, calcium ions and amino acids are reabsorbed into peritubular network
Question 79.
What are the substances that secretes into distal convoluted tubule (DC7)?
Answer:
Extra salts, ions of K+, Na+, Cr- and H+ secrete from peritubular capillaries into DCT
2 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
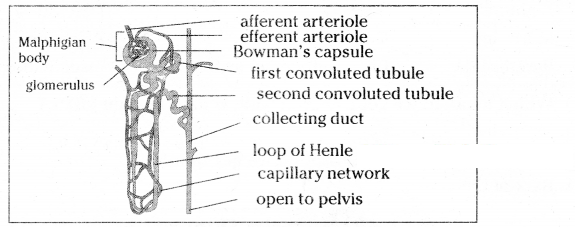
Draw the structure of an excretory organ, which contains Bowmans capsule and loop of henle and label it?
Answer:
Question 2.
Prepare four Questions to find the reasons for obstructions in excretory system?
Answer:
- What do we call the complete and irreversible kidney failure
- What happens if kidney stop working completely
- What is uremia
- Is there any solution to this problem
Question 3.
Name the secondary metabolites which are useful in leather and rubber Indutry.
From which plants we obtain them?
Answer:
- Latex used in rubber and Tannins used in Leather Industry
- Latex - Hevea brasiliensis (Rubber Plant) Tannins - Cassia, Acacia
Question 4.
Prepare four Questions you will ask a nephrologlst about Kidney failure?
Answer:
- When does kidney fail
- What are the symptoms of kidney failure
- What precautions can we take to prevent failure of kidney
- Which alternative method can we adopt if kidney fails
Question 5.
Observe the following table?
| Name of the phylum / organism |
Excretory system / organ |
| Protozoa |
Diffusion |
| Porifera |
Water bathes all their cells |
| Platyhelminthes |
Flame cells |
| Annelida |
Green glands |
| Reptiles, Aves and Mammals |
Kidney |
On the basis of above table, write answers to the following
Questions
Questioni.
In above table, which living organisms contains kidneys as excretory organs like human beings?
Answer:
Reptiles and Aves
Questionii.
Write the excretory organs present in Earthworm and Cockroach?
Answer:
Earthworm - Nephridia
Cockroach - Green glands
Question 6.
Observe the following table and answer the Questions given below?
| Alkaloid |
Name of the plant |
Uses |
| Quinine
Nicotine
Morphine
Pyrethroids |
Cinchona
Tobacco
Opium
Chrysanthemum species |
Anti malarial drug Pesticides
Pain killer Insecti |
Questioni.
Which alkaloid we get from the fruit, is used as pain killer?
Answer:
Morphine
Questionii.
From which part of the plant do we get Quinine?
Answer:
Bark of Cinchona
Question 7.
Nephron is called structural and functional unit of kidney. Why?
Answer:
- Each kidney is made up of more than one million microscopic and thin tubular units called nephrons or uriniferous tubules. Hence nephron is known as structural unit of kidney
- Nephrons chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. Hence it is known as functional unit of kidney
Question 8.
Blood is filtered in Bowmans capsule of nephron. For the filtration of blood some pressure is needed. How this pressure happens to blood?
Answer:
Blood flows inside the glomerulus of Bowmans capsule under the influence of pressure due to the large diameter of afferent arteriole, This increases or rise the blood pressure in the glomerulus capillaries leading to ultrafiltration of the blood in the Bowmans capsule
Question 9.
Classify the substances given below.
Ptya line, Leptin, Morphine, Riboflavin, Testosterone, Thyamln, Niacine, Sucrase, Nicotine, Amylase, Retinol, Quinine, Calciferol, Adrenaline, Tripsin?
Answer:
The above substances can be classified into Enzymes, Hormones, Alkaloids and Vitani
- Enzymes : Ptyaline, Sucrase, Amylase. Tripsin
- Hormones : Testosterone, Adrenaline, Leptin
- Alkaloids : Morphine, Nicotine, Quinine
- Vitamins : Riboflavin, Thyamin, Niacine, Retinol, Calciferol
Question 10.
Explain the external features of kidney in human beings?
Answer:
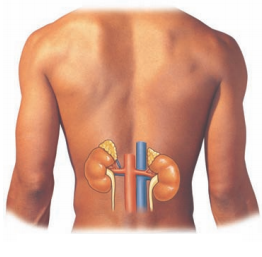
- In human beings. there are a pair of bean shaped, reddish-brown structures in the abdominal cavity attached to dorsal body wall one on either side of the backbone
- The size of the kidney is 10cm in length, 5 - 6cm in breadth, and 4cm in thickness
- Each kidney is convex of the outer side and concave on the inner side
- The position of the right kidney is lower than the left kidney due to the presence of liver above
- The Inner side of each kidney has a fissure or hilus for the entry of a renal artery, exit of a renal vein and an ureter
- Renal artery brings oxygenated blood loaded with waste products and renal vein carries deoxygenated blood
Question 11.
Why are weeds and wild plants not affected by insects and pests?
Answer:
- Weeds and wild plants produce waste products which are stored in leaves, hark and fruits
- Several compounds are synthesized by weeds and wild plants for their own use especially for defence
- Several weed and wild plants prepare chemicals and store them in different parts for protection against herbivores, insects and pests
- Most of these chemicals are unpleasant to taste and hence insects and pests do not prefer to eat such plants
- Some of the chemicals are toxic and may even kill the insects and pests that eat them
- Hence weeds and wild plants are not affected by insects and pests
Question 12.
People in cold countries get very less / no sweat. What changes occur in their skin and in other excretory organs?
Answer:
- Exposure to cold causes a reduction in blood flow to the surface of the skin by constriction of blood vessels
- This reduces the overall volume of the circulatory system so increasing the blood pressure
- The bodys response to this is to reduce the fluid volume by getting rid of water in the urine
- Usually human skin has a unique system keep in equilibrium state with the surrounding temperature
- During winter season the temperature is low and the body temperature should be heated to balance the tolerance
- So the water content in our body is sent out in the form of urine
- Hence, people in cold countries get less sweat or no sweat
Question 13.
State the role of kidneys in human transport system?
Answer:
- Remove or excrete nitrogenous wastes
- Regulate water content of the body (osmoregulation)
- Maintain mineral balance in blood
Question 14.
Why are glomeruli considered as dialysis bags?
Answer:
- The main function performed by the glomeruli is selective filtration
- They filter small molecules containing glucose, salts, urea and liquid serum, etc
- The large molecules such as protein remain in blood
- Thus glomeruli of kidney function as dialysis bags
4 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
Where is the transplanted kidney fixed in the body of a kidney failure patient?
Answer:
Kidney transplantation involves placing a healthy kidney into the body where it can perform all of the fuctions that a failing kidney cannot. The new kidney is placed on the lower right or left side of the abdomen where it is surgically connected to nearby blood vessels
Placing the kidney in this position allows it to be easily connected to blood vessels and the bladder. The vein and the artery of the new kidney are attached to the bodys vein and artery. The new kidneys ureter is attached to the bodys bladder to allow urine to pass out of the body
Question 2.
What about the failure of kidneys?
Answer:
In most cases the old kidneys will not be removed. This is because even failed kidneys release chemicals that help the body work. However if those kidneys have a disease that cause on going problems such as persistent kidney infections or intestinal blockage,then the transplanting would be considered removing the old kidney. The two most common medical conditions requiring "native nephrectomy" or "congenital reflux" disease and polycystic disease
Question 3.
Can donor lead normal life with single kidney without any complications?
Answer:
Once a living donor candidate has been completely evaluated and cleared, the chance of the donation affecting his or her life span or life style is extremely low with any surgery and anaesthesia, however, there are risks. Nationally the risk of having a life threatning problem with donating a kidney is one in three thousand
The risk of minor complications such as a minor wound infection is about 2 to 4%. Because the kidney donor operation is a major surgical procedure; donors find they have less energy and need about 4 to 6 weeks to return to their full resurgical activity level
Question 4.
Do plants excrete like animals?
Answer:
- Plants do not have specific organs to excrete the waste materials which are formed during metabolism
- As in animals carbon dioxide, water, ammonia and other nitrogenous wastes are also formed in plants
- In plants, carbon dioxide released during respiration is sent out through stomata of leaves
- Plants discharge the excess water in the form of water vapour during transpiration by leaves. Due to this, the heat in the plants is reduced
- In germinating seeds carbon dioxide formed during respiration is released into atmosphere
- Plants have the capacity to utilise the by products of one metabolic activity as the raw materials for another metabolic activity
- For example, oxygen released during photosynthesis is utilised for respiration; carbon dioxide released during respiration is utilised for photosynthesis. Plants convert nitrogen and ammonia into nitrates
Question 5.
How do plants manage or send out waste products from its body?
Answer:
- Plants can get rid of excess water by a process like transpiration and guttation. Waste products may be stored in leaves, bark and fruits
- When these dead leaves, bark, and ripe fruits fall off from the trees, then waste products in them are got rid off
- In some plants, waste gets stored in the fruits in the form of solid bodies called Raphides. Example : Yam
- Several compounds are synthesized by the plants for their own use specially for defense
- Several plants prepare chemicals and store them in shoots, leaves, seeds for protection against herbivores
- Most of the chemicals are unpleasant to taste and hence herbivores do not prefer to eat such plants. Some of the chemicals are toxic and may even kill the animal that eats them
- Some of the plants release attractantS for other organisms which will help the plants for pollination. For example, plants having root nodules secrete chemicals to attract rhizobia into the surroundings of the roots and form a symbiotic relationship with the rhizobium
Question 6.
| S.No. |
Test |
Present level |
Normal range |
| A. Blood Test |
| 1. |
Blood Pressure (BP) |
160/90 mm/Hg |
120/80 mm/Hg |
| 2. |
Glucose (Before food) |
120-mg/dl |
60-100 mg/dl |
| 3. |
Glucose (After food) |
220 mg/dl |
160-180 mg/dl |
| 4. |
Bilirubin |
1.0 mg/dl |
0.1-0.8 mg/dl |
| B. Urine Test |
| 1. |
24 hrs protein |
150 mg/day |
100 mg/day |
| 2. |
Sodium |
140 mmol/L |
125-250 mmol/ |
QuestionA.
Which test is required to know bilirubin?
Answer:
Blood test is required to know bilirubin
QuestionB.
How the sugar disease is confirmed?
Answer:
In blood test if the glucose levels in blood before and after food are more than the normal, the sugar disease is confirmed
QuestionC.
By observing the above report, what would be the other problems faced by that patient?
Answer:
The blood pressure of the patient 160/90 as the normal is 120/80 mm/Hg.
The Glucose levels in the blood of the patient shows more than the normal before and after food.
So he is suffering from Hypertension and diabetes
QuestionD.
What are the organs affected by these problems?
Answer:
The organs affected by these problems are heart and kidneys
Question 7.
Analyse the following information and answer the Questions?
| Alkaloid |
Part of the plant |
Uses |
Quinine
| bark |
Anti malarial drug |
| Nicotine |
leaves |
Insecticide, stimulant |
| Morphine |
fruits |
Pain killer, sedative. |
| Caffeine |
seeds |
Central Nervous System stimulant |
| Pyrethroids |
flowers |
Insecticides |
| Scopolamine |
fruits, flowers |
Sedative |
- Which parts of the plants are used as alkaloids
- What are the alkaloids which are used to control the diseases that occur in plants
- Name the parts of the plant from which we get alkaloids used as sedative
- Name the alkaloid which is used to prevent malaria
Answer:
- The plant parts used as alkaloids are
-
- bark
- leaves
- fruits
- seeds
- flowers
- Pyrethorids are the alkaloids used as insecticides to control the diseases that occur in plants
- The fruits and flowers of scopolamine alkaloid are used as sedative
- The alkaloid used to prevent malaria is the bark of Quinine
Question 8.
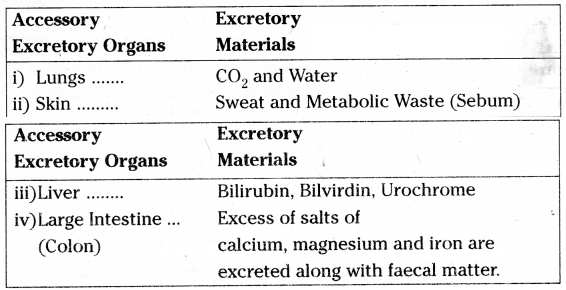
Write about the accessory excretory organs and their excretory substances In human beings?
OR
What are the accessory excretory organs in human body? How does the liver carry out excretion as a secondary function?
Answer:
Question 9.
Explain the temporary and permanent methods to be adopted for Kidney failure (ESRD) persons?
Answer:
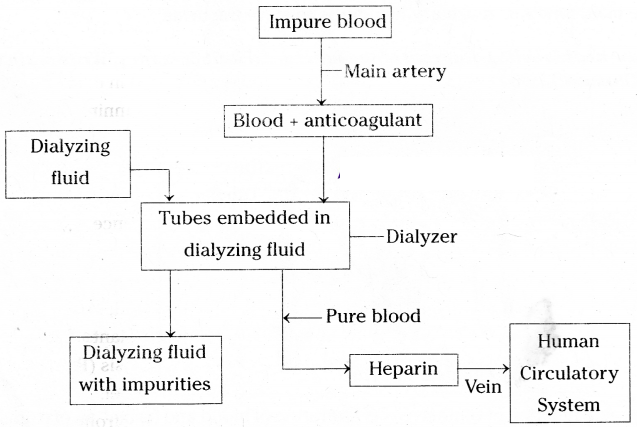
Temporary method for ESRD persons is dialysis (artificial kidney). Permanent method is transplantation of kidney
Dialysis:
- Blood is taken out from the main artery, mixed with an anticoagulant, such as heparin and then pumped in to dialyzer
- In dialyzer blood flows through cellophane tubes and these tubes are embeded in the dialysing fluid
- The membrane separates the blood flowing inside the tube and dialysing fluid same as plasma without nitrogenous waste)
Kidney transplantation:
- A functioning kidney is used in transplantation from a donor preferably a close relative
- The kidney that is received by a recipient must be a good match to his body, to minimise the chances of rejection by the immune system of the recipient
- Nowadays the process of organ donation helps a lot for kidney failure patients
I. Conceptual Understanding
Question 1.
Explain the formation of urine in a flow chart?
Answer:
Dissolved substances of blood like urea, glucose, amino acids, minerals, salts etc., are filtered out in Bowmans capsule under high filtration pressure. Glomerular filtrate is called primary urine.
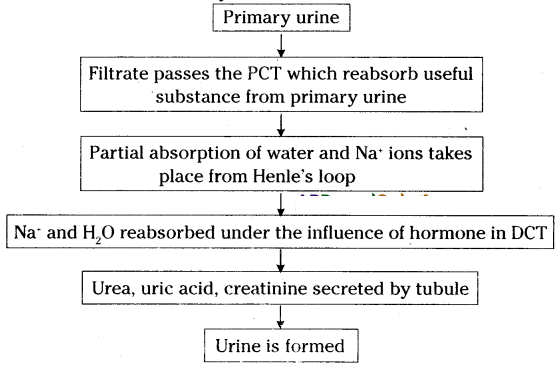
Question 2.
Excreting wastes from the human body not only by kidneys but also by other organs you help. How do you support it?
Answer:
- In human body wastes are excreted not only by kidneys but also by other organs
- Kidney filters blood and eliminates nitrogenous wastes and other harmful things. Filters urea from blood
- Apart from kidney lungs, skin, liver, intestine, salivary glands and lacrymal glands
-
- Lungs remove carbon dioxide and water in respiration
- Skin excrete wastes in the form of sweat which contains water and certa salts
- Liver eliminates bile pigments bilirubin and biliverdin through urine
- Excess salts of calcium, magnesium and iron are excreted by epithellial cells ocolon for elimination along with faeces by intestine
- Eccrine glands present on the forehead, the bottoms of the feet and the palms allow excess water to leave the body
- Salivary glands and lacrimal glands excrete small amounts of nitrogenous waste through saliva and tears
Question 3.
Not only the food of plants but also their wastes are useful to us. What evidences do you give for it?
Answer:
- Plants are providing food for the entire living world through the process of photosynthesis
- They are also excreting different waste materials produced during various metabolic activities
- They are known as secondary metaboiltes which include Alkaloids, Tannins, Resins, Gums and Latex etc
- Alkaloids used for various purposes are
Alkaloid - Use
Quinine Antimalarial drug
Nicotine Insecticide
Morphine, cocaine Pain killer
Reserpine - Medicine for snake bite
Nimbin Antiseptic
Pyrethroids - Insecticides
Casteine - Central nervous system stimulant
- Tannins are used in tanning of leather and in medicines. e.g: Cassia, Acacia
-
- Resins are used in varnishes. e.g:pinus
- Gums are economically valuable and used as adhesives and finding agents in the preparation of the medicines, food etc
- From the latex of Hevea braziliensis (Rubber plant) rubber is prepared. Latex from Jatropa is the source of biodiesel
- Chewing gum originally made of chicle, natural latex from plant
Question 4.
Give an account of excretory system found in different phyla of animal kingdom?
OR
Write information in tabular form of different phyla and excretory system in animal kingdom.
Answer:
- Different organisms use varied strategies in excretion
-
- Following are the excretory system found in various organisms
-
| Name of the phylum / organism |
Excretory system / organ |
| Protoxzoa |
Simple diffusion from the body surface into the surrounding water. |
| Porifera and coelenterates |
Water bathes almost all their cells |
| Platyhelminthes and Nematoda |
Flame cells |
| Annelids |
Nephridia |
| Arthropoda |
Green glands, Malphigian tubules |
| Mollusca |
Meta nephridia |
| Echinodermata |
Water vascular system |
| Reptiles, Birds and Mammals |
Kidneys |
Question 5.
Describe the excretory system of man?
Answer:
- The excretory system of man consists of
- a pair of kidneys
- ureters and
- urinary bladder and
- urethra
- Kidneys are bean shaped and are located in the abdominal region on either side of vertebral column
-
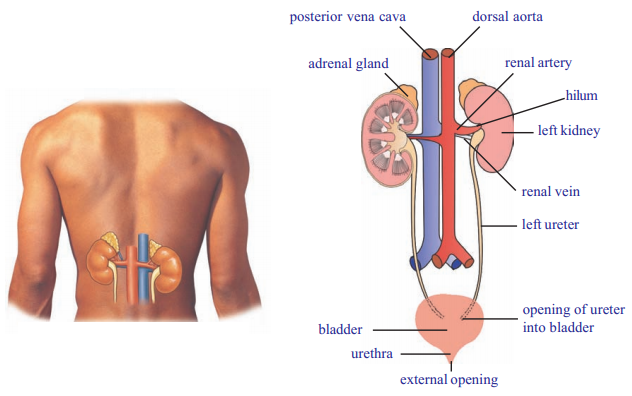
- From hilus of each kidney there are a pair of whitish, narrow tubular structures arise. They are known as ureters
- The ureter travels downwards and open, in the sac like structure called the urinary
bladder, which stores urine
- Urethra is a tube that takes urine from urinary bladder to outside
- The opening of urinary bladder into urethra is guarded by a ring of muscles or sphincter
Question 6.
Describe the internal structure of kidney with the help of diagrams?
Answer:
- L.S. of kidney shows two distinct regions. Dark coloured outet zone called cortex and pale coloured inner zone called medulla
- Each kidney is made up of approximately more than one million (1.3 to 1.8 million) microscopic and thin tubular functional units called nephrons or uriniferous tubules
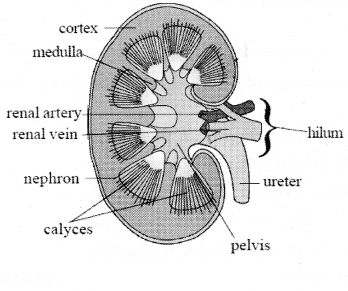
- Each nephron has basically two parts. One is maiphigian body and other is renal tubule
-
- Malphigian body consists of a blind cup shaped broader end of nephron called Bowmans capsule and bunch of fine blood capillaries called glomerulus
- Glomerulus develops from afferent arteriole and it gives to rise to an efferent arteriole
-
- Glomerulus functions as a filtration unit
Question 7.
Differentiate between afferent arteriole and efferent arteriole?
Answer:
| Afferent arteriole |
Efferent arteriole |
| 1. Formed by the branching of renal artery |
1. Formed by the joining of the glomerular capillaries |
| 2. Its lumen is twice as thick as that of the efferent arteriole. |
2. Its lumen is twice as narrow as that of the afferent arteriole |
| 3. Brings oxygenated blood into the kidney |
3. Carries oxygenated blood away from the Bowmans capsule |
| 4. Brings blood which contains large amount of water and nitrogenous metabolic wastes |
4. It carries away blood that is relatively thicker and free of toxic wastes |
| 5. Divides to form the glomerulus which is a khot inside the Bowmans capsule |
5. Divides to form vasa rectae enveloping the renal tubule |
Question 8.
Explain briefly about the different secondary metabolites and their uses?
Answer:
- The secondary metabolites are the materials which do not require for normal growth and developments
- Examples for the secondary metabolites are alkaloids, Tannins, Resins, Gums and Latex
- Alkaloids are nitrogenous by-products and poisonous. They are stored in different parts of the plant
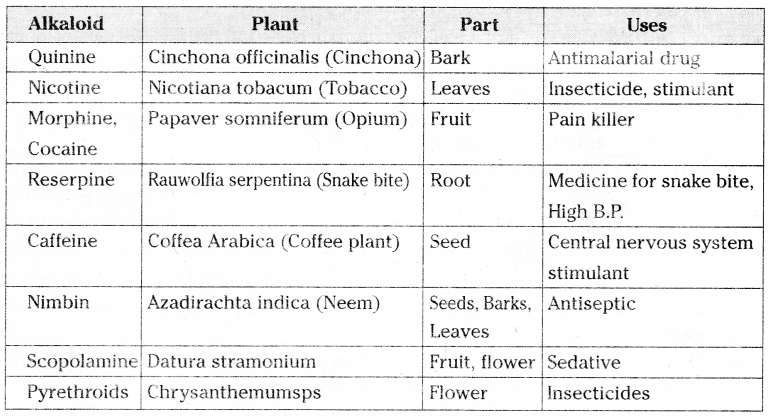
- The alkaloids secreted by plants and their uses are
- Quinine is used as antimalarial drug
- Nicotine is used as insecticide
- Morphine and cocaine are used as pain killers
- Reserpine is used as medicine for snake bite
- Caffeine is used as stimulant for central nervous system
- Nimbin is used as antiseptic
- Scopolamine is used as sedative
- Tannins are carbon compounds which are deep brown in colour. Tannins are used in tanning of leather and in medicines, e.g.: Cassia, Acacia
- Resin occur mostly in Gymnosperms in specialized passages called resin passages. They are used in varnishe.
e.g.: Pinus
- When branches of trees are cut a sticky substance called gum is secreted. The gumswells by absorbing water and helps in the healing of damaged parts of a plant. e.g. : Neem, Acacia
- Economically gums are valuable, being used as adhesives and binding agents in the preparation of the medicines,
food etc
- Latex is a sticky milky white substance secreted by plants. Latex is stored in latex cells or latex vessels
- From the latex of Heavea braziliensis (Rubber plant) rubber is prepared. Latex from Jatropa is the source of bio-diesel
II. Asking Questions and Making Hypothesis:
Question 1.
A student observed a patient undergoing haemodialysis. He has many doubts about haemodialysis. What might be his doubts?
Answer:
He got following doubts about haemodialysis
- What is the use of dialysis
- How the impurities are separated from blood
- How much time needed to complete dialysis
- How frequently, does a patient should undergo dialysis
- How to prevent blood coagulation during dialysis
- What is major difference between kidney and artificial kidney
- Can this process done at home
Question 2.
What might be reason for getting odour when potted plant shift from its place?
Answer:
- As per Brugman scientist, plant excrete small amount of waste material in surrounding of its roots
- Hence when rotted plant shifted from its place we will get bad odour
III. Experimentation and Field Investigation:
Question 1.
In the observation of kidney external and internal features experiment, what are your observations?
Answer:
External features of mammal kidney are:
- It is bean shaped and brown in colour
- Top of the kidneys you will observe adrenal gland
- 3 tubes corne out from hilus. First one is ureter, second one is renal artery and third one is renal vein
Internal features of kidney:
- Each kidney is convex on the outer side and concave on the inner side
- Outer zone in kidney T.S. is light brown colour whereas inner zone is dark brown colour
- Outer zone is called cortex and inner dark zone is called medulla. Triangular calyces are present in medulla
- These medulla lead into ureter
- Ureters are whitish tube like structures
IV. Information Skills and Projects
Question 1.
Observe the below flow chart. Fill the boxes. Explain to which system this be longs to?
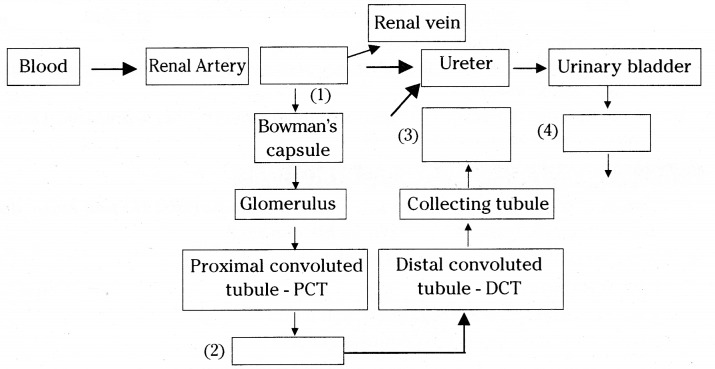
Answer:
- Kidney
- Loop of Renie
- Pelvis
- Urethra
This flow chart belongs to excretory system in human beings. It shows the way how the blood in the kidney moves filtered and urine is excreted. The blood is supplied to kidney by renal artery. After entering the kidney renal artery forms number of afferent arterioles. This afferent arteriole forms network of blood capillaries in Bowmans capsule of nephron. Blood gets filtered in Glomerulus of Bowmans capsule
The filtered blood is known as primary urine. it passes into PCT, loop of Henle and listen to convoluted tubule. After necessary reabsorption filtrate enters collecting tubule of nephron. Later filtrate enters pelvis from there it enters ureter and finally reaches urinary bladder. From urinary bladder urine is sent out of the body through urethra
Question 2.
Observe the following table and answer the following Questions?
Answer:
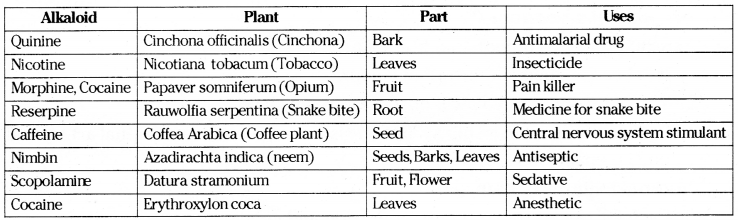
Questioni.
Name the alkaloid which is used as medicine for snake bite?
Answer:
Reserpine used as medicine for snake bite
Questionii.
Why do we feel much relief when we drink coffee?
Answer:
Caffeine present in coffee stimulates central nervous system. Hence we feel much relief
Questioniii.
What are different kinds of alkaloids which cause harm to us?
Answer:
Cocaine. Scopolamine, Nicotine, Strychnine and Ganja are different alkaloids which cause harm to us
Questioniv.
Name the alkaloid which acts as cancer causing agent (carsinogenic agent)?
Answer:
Nicotine which is present in tobacco
Questionvii.
Name the plant which gives antimalarial drug?
Answer:
Cinchona officitialis plant
Questionvi.
Why do we add neem leaves to bathing water when a person suffering from skin disease?
Answer:
Because Nimbin present in neem leaves acts as antiseptic
Questionvii.
What is the use of turmeric?
Answer:
Turmeric used as antiseptic
V. Communication Throught Drawing, Model Making:
Question 1.
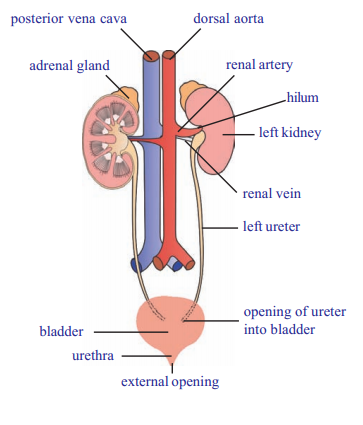
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Human main excretory system. Write the function of urinary bladder?
Answer:
The main function of urinary bladder is to store the urine.
Question 2.
Draw neat labelled diagram of the functional unit of kidney. Write main function of Glonierulus?
Answer:
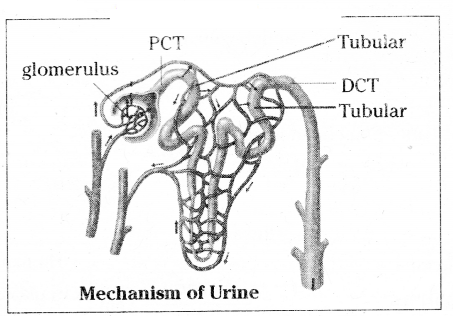 The main function of Glornerulus is filteration of blood and formation of primary urine
The main function of Glornerulus is filteration of blood and formation of primary urine
Question 3.
Label the parts for given diagrams?
Answer:
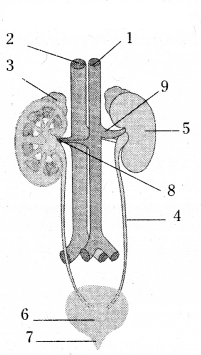
- dorsal aorta
- posterior venacava
- adrenal gland
-
- ureter
- left kidney
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- renal vein
- renal artery
-
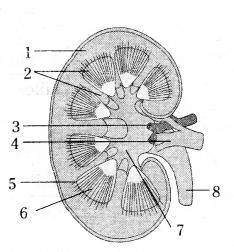
- cortex
-
- medulla
-
- renal artery
- renal vein
- nephron
- calyces
- pelvis
- Ureter
Question 4.
Draw the flow chart of process of haemodialysis?
Answer:
VI. Apprciation and Aesthetic Sense, Values
Question 1.
Write an essay stating the advantages of by -products of plants in our real life?
OR
What are secondary meto balites ? Briefly explain their uses.
Answer:
- The materials which do not require for normal growth and development are called secondary metabolites. These are the by - products of plants. eg : Alkaloids, Tannins, Resins, Gums and Latex etc. Though plants produce these chemicals for their own use man found the usage of these chemicals for own benefits. They are generally coloured and fragrant
- Alkaloids: These are nitrogenous by - products and poisonous. These are stored in different parts of the plants. Common alkaloids in plants and their uses are given in the table
- Tannins: Tannins are carbon compounds. These are stored in different parts of the plant and are deep browii in colour. Tannins are used in tanning of leather and in medicines. e.g. Cassia, Acacia
- Resin: Occur mostly in Gymnosperms in specialized passages called resin passages. These are used in varnishes. e.g. Pinus
- Gums: liants like Neem, Acacia oozes out a sticky substance called gum. When branches are cut. The gum swells by absorbing water and helps in the healing of damaged parts of a plant. Gums are economically valuable and used as adhesives and binding agents in the preparation of the medicines, food, etc
- Latex: Latex is a sticky, milky white substance secreted by plants. Latex is stored in latex cells or latex vessels. From the latex of Flevea braziliensis (Rubber plant) rubber is prepared. Latex from Jatropa is the source of bio-diesel
- Modern chewing gum originally made of chick natural latex from plant
Question 2.
Blood is purified in kidneys. So many wastes are removed from the blood in nephron of the kidney. Which issue make you surprise in excretory system ?
Answer:
- Kidneys remove garbage from our body. They also work towards balancing the amount of vitamins, minerals, fat and protein that are found in the blood. They do this so that our body can easily perform day to day activities
- The right and left kidneys are assisted by a number of organs in the body which help in disposing waste products
- Our intestine makes solid waste materials and is excreted through digestive tract
- Each day our body eliminates around 1.6 to 1.8 liters of urine which contains liquids, minerals and vitamins that are of no use of the body
- The bladder of a human body is nearly the same size as the average of human brain
- In one individuals life span the liver can produce around 184.275 kgs of bile (6500 ounces)
- In our lifetime an individual could urinate close to 7,850,000,000 gallons of fluid
- There are two kidneys in the human body. The left kidney is always found higher than the right kidney
- A really extraordinary fact regarding the excretory system is that upto 400 ml of urine can be held in human bladder
- Urine contains a high amount of urea which can be used by plants as a source of nitrogen. Because of this diluted urine can be used in gardens and potted plants
- It is amazing to see that each kidney is made up of approximately more than one million microscopic tubular functional units called nephrons or uriniferous tubules
Question 3.
In recent days many people are coming forward to donate organs of brain dead people, who met accidents. How will you appreciate the family members of organ donor?
Answer:
- In recent days many families are willing to donate organs of brain dead persons. This is truely significant change in attitude of people
- Most of the people are burning or burying body after death. Very a few people are would like to see their very dear ones in other people by donating organs like heart, liver, kidneys, cornea, spleen and bone marrow etc
- The family members of brain dead are already in great sorrow. They need great courage and so much kindness toward needy patients
- With nobel decision of that family giving new life to 5 - 7 persons, who has no alternate treatment, other than organ transplantation. In society every one must appreciate their courage, kindness and sympathy. They stood role model to others
VII. Application To Daily Life, Concern To Biodiversity
Question 1.
Which plants can you get in your village. Among these by products of which plants do you use in your real life ?
Answer:
- The plants? grow or available in our village are Sapota, Coconut, Cassia, Mango, Guava, Borassus plantain, Tobacco, Rauwolfia, Coffee, Neem, Datura, Chrysanthemum, Acacia, Pinus, Vallisneria, Teak, etc.,
- Out of these plants alkaloids are available from the plants like Tobacco, Rauwolfia, Coffee, Neem, Datura and Chrysanthemum. The by-products from these plants are utilised in my real life
| Plant |
Use |
| Tobacco
Rauwolfia serpentina
Coffee
Neem
Datura
Chrysanthemum |
Insecticide
Medicine for snake bite
Central nervous system stimulant
Antiseptic
Sedative
Insecticides |
- Tannins are the by - products of cassia, acacia. These are used in tanning of leather and in medicines
- Resin the by-product of Pinus is used in varnishes
- Gums are extracted from neem and acacia. They are used as adhesives and binding agents in the preparation of food, medicines
Question 2.
How secondary metabolites of plants are useful to us?
Answer:
- Secondary metabolites are which do not required for normal growth.Eg. Alkaloids, Tannins, Resins, Gums and Latex etc
- Alkaloids like Quinine, Reserpine, Morphine and Scopolamine are useful as medicines or different problems
- Nicotine, Pyrethroids, Turmeric and Nimbin are useful as Insecticides
- Tannins are useful in tanning leather and preparation of medicines
- Resins are used in varnishes
- Gums are used as adhesives and binding agents and preparation of food, medicines
- Latex is used in preparation of rubber and biodiesel