TS 10th Class Biology Important Questions 3rd Lesson Circulation
1 Mark Question
Question 1.
Two persons Blood Pressure is like this
| Ramaiah |
140/80 |
| Rangaiah |
110/90 |
Whose Blood Pressure is high ? What does It Indicate?
Answer:
The normal blood pressure is 120/80
The numerator 120 indicates systolic pressure.
The denominator 80 indicates diastolic pressure.
Ramaiah B.P. Is 140/80. So he has high blood pressure
Question 2.
How does lymph differ from blood?
Answer:
- RBC are present in blood, RBC are absent in lymph
- Blood is Red in colour, lymph is colourless
Question 3.
Name the largest artery in the body?
Answer:
Aorta is the largest artery in the body
Question 4.
What happens If platelets are absent in the blood?
Answer:
If platelets are absent in the blood, then
- blood doesnt clot
- blood flows continuously
Question 5.
Name the apparatus, shown in the figure below?
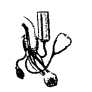
Answer:
Sphygmomanometer
Question 6.
List out the materials you have used to observe the goat heart in your laboratory?
OR
Write any two materials needed for an experiment to examine a mammal heart.
Answer:
- Freshly collected specimen of goats heart
- Soda straws
- Used pen refus
- Sharp and long blade
- Tray
- A jug of water
- Dissection scissors
- Forceps
- Gloves
Question 7.
Prepare two Questions, which you ask the doctor to know more details about high blood pressure?
Answer:
- How can we know that we have high blood pressure
- What are the adverse affects of high blood pressure
- How can we prevent high blood pressure
- What diet should you prescribe for high B.P patients
Question 8.
Name any two valves present in human heart?
Answer:
- The valve that is present between left atrium and left ventricle is mitral valve or bicuspid valve
- The valve that is present between right atrium and right ventricle is tricuspid valve
Question 9.
Siri injured while playing, and the blood is flowing continuously from wound, what may be the reason for this?
Answer:
- Vitamin - K is helpful for clotting of blood. Perhaps Sin might be suffering from deficiency of Vitamin - K. So, blood is flowing continuously from the wound
- He may be suffering from thalassemia
Question 10.
What is the size of our heart ?
Answer:
It is approximately size of our fist
Question 11.
What is the shape and structure of heart ?
Answer:
The heart is a pear shaped structure, triangle in the outline, wider at the anterior end and narrower at the posterior end
Question 12.
Which protects the heart from shocks ?
Answer:
The space between the two layers of pericardial membrane is filled with pericardial fluid, protects the heart from shocks
Question 13.
What is cardiac cycle ?
Answer:
One contraction and one relaxation of atria and ventricles is called one - cardiac cycle
Question 14.
In which organism protoplasm shows Brownian movements ?
Answer:
Amoeba
Question 15.
The digestive system is highly branched and supplies digested food to all the cells in ?
Answer:
Platyhelmenthes
Question 16.
Which has taken up the function of collection and distribution of materials in Nemafyhelmenthes ?
Answer:
Pseudocoelom
Question 17.
What is lymphatic system ?
Answer:
Lymphatic system is a parallel system to venous system which collects tissue fluid from tissues and transports it to the venous system
Question 18.
What is lymph ?
Answer:
Lymph is the substance that contains blood without solid particles
Question 19.
What is tissue fluid ?
Answer:
To supply nutrients to the cells the liquid portion of the blood with nutrients flows out of the capillaries. This is called tissue fluid
Question 20.
What is double circulation ?
Answer:
If the blood flows through the heart twice for completing one circulation, it is called double circulation
Question 21.
What is hypertension ?
Answer:
People who have B.P more than 120/80 during rest period are said to have hypertension
Question 22.
What is serum ?
Answer:
The straw coloured fluid portion after formation of the blood clot is called serum
Question 23.
Which vitamin is required for blood clot ?
Answer:
Vitamin - K
Question 24.
What is haemophilia ?
Answer:
Due to genetic defect, the blood may not coagulate or clot. This type of defect is called haemophilia
Question 25.
In root where was xylem tissue situated ?
Answer:
Xylem tissue was situated towards the centre of the root
Question 26.
Where do we find xylem in stems ?
Answer:
In stems, xylem was arranged in vascular bundles near the outside
Question 27.
Which process plays an important role in absorption of water by root hairs ?
Answer:
Osmosis
Question 28.
What is transpiration ?
Answer:
Evaporation of water through stomata of leaves is called transpiration
Question 29.
Which tissue transports food to all the other parts of the plant ?
Answer:
Phloem
Question 30.
Which tissue transports water to all the other parts of the plant ?
Answer:
Xylem
Question 31.
Which organ acts as a pump in the circulatory system ?
Answer:
Heart
Question 32.
Name two liquids which help in the transport of substances in the human body?
Answer:
Blood and lymph
Question 33.
Name the two types of transport systems in human beings?
Answer:
Circulatory system and lymphatic system
Question 34.
Name the two parts of a plant through which its gaseous waste products are released into the air?
Answer:
Stomata in leaves, lenticels in stem
Question 35.
What does the pulse rate show ?
Answer:
Pulse rate shows the number of heart beats, the mechanism of heart beating and also the flow of blood in the blood vessels
Question 36.
How many layers are covering the heart ?
Answer:
The heart is covered by two layers of membranes. They are called pericardial membranes
Question 37.
Which end of the heart is broader and which end is narrow ?
Answer:
Heart is wider at the anterior end and narrow at the posterior end
Question 38.
Why are the artery walls very strong and elastic ?
Answer:
Because they are carrying blood away from the heart to every cell of the body tissues and are doing with a lot of pressure. So the walls are thick to enable it to do its job and they are elastic
Question 39.
What is the function of Gastro vascular cavity ?
Answer:
Digestion and transportation of nutrients to each cell of the body in cnidarians
Question 40.
Which animals are encouraged by foresters to keep down the population of voles and rabbits ?
Answer:
Foxes, Badgers, Hawks, Owls
Question 41.
Which animals do great damage particularly to beech and sycamore ?
Answer:
Grey squirrels
Question 42.
When do you think that our pulse rate goes up ?
Answer:
Our pulse rate increases after jogging, running, strenuous exercise, during fear, anxiety, and suffering from fever
Question 43.
Sometimes barks of the tree damaged more than a half, even though tree is alive. How is this possible ?
Answer:
On the outside of cambium phloem is present. To the centre of the tree xylem is present.
There is no obstruction to flow of water in the damaged tree. Hence it survives
Question 44.
Which of the four chambers of the human heart has the thickest muscular walls?
Answer:
Right ventricle
Question 45.
Name the conducting tissue of plants which is made of sieve tubes along with companion cells?
Answer:
Phloem
Question 46.
What factors contribute to rate of transpiration ?
Answer:
Number of leaves, number of stomata, temperature of surroundings, wind, water supply, amount of light, etc
Question 47.
How does transpiration pull help in ascent of sap ?
Answer:
Water column build up as a result of cohesion and adhesion forces. The negative pressure in the upper tissues results in upward pull of water
Question 48.
What is translocation?
Answer:
The transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation
Question 49.
Sweating in animals is equivalent to what in plants ?
Answer:
Transpiration
2 Mark Question :
Question 1.
Neelima conducted an activity on her friends and got the following results?
Answer:
| S.No. |
Name |
Heart beat at rest/min |
Heart beat after jogging / min |
Pulse rate at rest / min |
| 1 |
Jeevan |
72 |
109 |
72 |
| 2 |
Raju |
75 |
110 |
74 |
| 3 |
Reshma |
73 |
111 |
73 |
- What is the relation between heart beat and pulse rate
- Why is the heart beat rate more after Jogging
Answer:
- Heart beat rate Is equal to pulse rate
- In the jogging muscles need more oxygen to produce high energy. To supply this oxygen heart beat is increased alter jogging
Question 2.
A person is injured while playing on the ground. Blood is flowing continuously. What might be the reasons?
Answer:
In this case blood is not clotting. Because
- He may be suffer from Haemophilia
- Blood platelets are less in number
- He may suffer from vitamin K deficiency
- Enzyme Thrombokinase may not release
Question 3.
Where are the valves located in human heart? Write their names?
Answer:
Valves present in human heart
| Name of the valve |
Location |
Allows blood to flow from |
| 1. Tricuspid Valve |
Right auriculoventricular septum |
Right atrium to right ventricle |
| 2. Bicuspid Valve (Mitral Valve) |
Left auriculoventricular septum |
Left atrium to left ventricle |
| 3. Pulmonary Valve |
At the origin of pulmonary aorta in the right ventricle |
Allows blood to flow from right ventricle into pulmonary ao |
| 4. Systemic Valves (Aortic Valves) |
At the origin of systemic- aorta |
Allows blood to flow from left ventricle into the systemic aorta |
Question 4.
What happens if there are no valves in veins?
Answer:
- If the valves are absent in veins blood will not flow in uni-direction and flows backward too
- Blood will not supplied to heart properly
- Bulging of veins may takes place
Question 5.
Which items do you take into consideration to explain the differences of arteries and veins?
Answer:
I would like to consider the following items to explain the difference between arteries and veins. They are thickness of walls, valves, capacity to retain shape when blood is absent, direction of blood flow, pressure in the vessels, type of blood transported, type of blood carried by pulmonary artery and type of blood carried by pulmonary vein
Question 6.
When you know the heart pumping method is circulatory system, which issue did you remember particularly ? Whats the reason for that ?
Answer:
The heart beats faster during and after an exercise remembered by me. Because at that time our body needs more energy under these conditions. The faster breathing of heart pumps blood more rapidly to the body organs which supplies more oxygen to the body cells for rapid respiration to produce more energy. That is a hefty job for a fist sized muscle
Question 7.
Classify different types of blood vessels in humans. On what bases you classify blood vessels ?
Answer:
- There are three types of blood vessels called arteries, veins and capillaries present in humans
- These blood vessels are classified on the basis of thickness of walls, valves, capacity to retain shape when blood is absent, direction of blood flow, pressure in the vessel, type of blood transported, type of blood carried by pulmonary artery or vein
Question 8.
Anil fell down in going to school got knee injury, start bleeding after some time he was wondered by seeing blood clot ? Why blood clotted ?
Answer:
Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to blood vessel. Platelets immediately begin to adhere to the cut edges of the vessel and release chemicals to attract even more platelets. A platelet plug is formed and the external bleeding stops
Question 9.
Describe the blood vessels that carry away blood from human heart?
Answer:
- The rigid vessels called arteries which originate from the heart supply blood to various organs in the body
- From the upper part of the left ventricle a thick blood vessel called aorta arises. It supplies oxygenated blood to the body parts
- From the upper part of the right ventricle pulmonary artery arises that supplies deoxygenated blood to the lungs
- A pair of coronary arteries (vessels) carry oxygenated blood to the muscles of heart
- All the arteries carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery
Question 10.
How is the human heart protected from shocks or injuries ?
Answer:
- Heart is located between the two lungs protected by rib cage
- The human heart is covered by two layers
- These membranes are called pericardial membranes
- The space between the two layers is filled with pericardial fluid
- The pericardial fluid protects the heart from physical shocks or injuries
Question 11.
When do we hear the sounds of lubb and dubb from the heart ?
Answer:
- On ventricular contraction due to pressure, the blood moves into the aorta and pulmonary artery
- The aperture between the atria and ventricles is closed by valves
- When the valves are closed forcibly, we can listen to the first sharp sound of the heart lubb
- When the ventricles start relaxing the pressure in the ventricles is reduced
- The valves which are present in the blood vessels are closed to prevent backward flow of blood into the ventricles
- Now we can listen to a dull sound of the heart dubb
Question 12.
What is cardiac cycle ? How does it occur ?
OR
Blood is /towing in blood vessels continuously from heart to all parts of body.
What is cardiac cycle ? Explain different phases of cardiac cycle.
Answer:
- The sequential events in the heart which are cyclically repeated are called cardiac cycle
- The cardiac cycle includes an active phase systole and a resting phase the diastole of atria and ventricles
- The contraction phase of the heart beat is called systole and the relaxation phase of heart beat is diastole
- The whole process of cardiac cycle is completed in approximately 0.8 seconds
- The time needed for atrial contraction is 0.11-0.14 seconds
- The time needed for ventricular contraction is 0.27-0.35 seconds
Question 13.
Write the differences between single circulation and double circulation?
Answer:
| Single circulation |
Double circulation |
| 1. Blood flows through the heart only once for completing one circulation |
1. Blood flows through the heart twice for completing one circulation |
| 2. Pulmonary circulation is absent |
2. Pulmonary circulation is absent |
| 3. Heart consists of two chambers |
3. Heart consists of three or four chambers |
| 4. Single circulation is seen in fishes |
4. Double circulation occurs in frogs, reptiles, birds and mammals |
Question 14.
What are the components of the transport system in highly organised plarts ?
Answer:
- The transport system of organised plants consists of xylem and phloem
- Xylem which has vessels and trachieds transports water and minerals from root to other parts of the plant
- Phloem which consists of sieve tubes, sieve cells and companion cells transports food from leaves to storage organs and other parts of the plants
- In xylem the transport is unidirectional i.e., from root upward while in phloem it is bidirectional
Question 15.
State the role and function of lymph in human transport system?
Answer:
Lymph is a circulatory fluid. It flows in lymph vessels
- Lymph (is also called tissue fluid. is colourless
- It consists of lymphocytes which kill germs and protect the human body from infections
- Lymph carries digested and absorbed fat from intestine
- It drains excess fluid from extra cellular space back into the blood
- Its flow is unidirectional i.e., from tissues ? lymph capillaries ? vein ? heart
Question 16.
Write the differences between blood and lymph?
Answer:
| Blood |
Lymph |
| 1. Reddish in colour |
1. Pale yellow in colour |
| 2. Red blood cells are present |
2. Red blood cells are absent |
| 3. Bidirectional flow |
3. Unidirectional flow |
| 4. Flow is rapid |
4. Flow is slow |
| 5. Leucocyte count relatively less |
5. High leucocyte count |
| 6. Platelets present |
6. Platelets absent |
Question 17.
A certain tissue in a green plant somehow gets blocked and the leaves wilted. What was the tissue that got blocked ?
Answer:
- The tissue that got blocked may be xylem. It is through the xylem that water and minerals absorbed by roots from the soil are transported to the leaves and other parts of the plant
- So if xylem is blocked, the leaves will not get the nourishment and will get wilted
Question 18.
How does transpiration help plants ?
OR
Transpiration is necessary evil. Explain.
Answer:
- During transpiration the evaporating water carries away heat energy. Thus it cools the temperature of plants
- Due to water loss the osmotic pressure inside leaves decreases. Due to which water and other minerals are able to reach leaves from roots and stem
4 Mark Question :
Question 1.
What is a Cardiac cycle? Explain the steps involved in it?
Answer:
Cardiac cycle : One contraction and one relaxation of atria and ventricles is called one cardiac cycle
(Or)
The sequential events in the heart which are cyclically repeated are called cardiac cycle.
Steps:
- Relaxation of atila and ventricles: AH the tour chambers of the heart are in relaxed state (diastole)
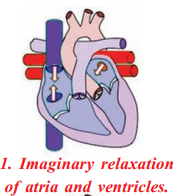
- Blood flows into atila : Blood from venacava and pulmonary veins enters the right and left atria respectively
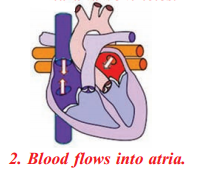
- Contraction of atila and flow of blood into ventricles: The atria contract, forcing the blood to enter into the ventricles
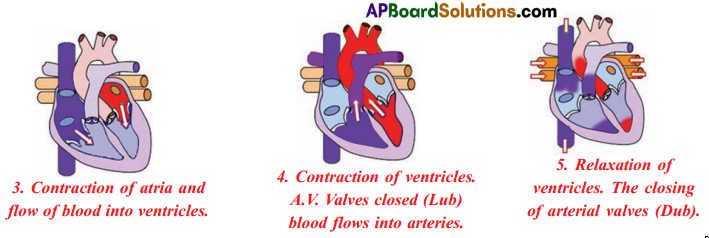
- Contraction of ventricles (Lub) : When the ventricles are filled with blood they start contracting and atria start relaxing. The aperture between the atria and ventricLes is closed by valves
- Relaxation of ventricles (Dub): When the ventricles start relaxing the pressure in the ventricles reduced. The blood which has entered the arteries tries to come back into the ventricles. The valves which are present in the blood vessels are closed to prevent backward flow of blood into the ventricles
Question 2.
What Questions do you ask your teacher to know about the coagulation of the blood?
OR
What Questions do you pose to your teacher to understand blood clotting?
Answer:
- What is coagulation
- How blood coagulates
- What are the factors responsible for coagulation
- What happens if coagulation occurs in blood vessels
- Which substance prevents coagulation of blood in blood vessels
- Which vitamin is required for coagulation of blood
- What happens if coagulation of blood does not occur when we meet with accidents
- Which cells present in blood help in coagulation of blood
Question 3.
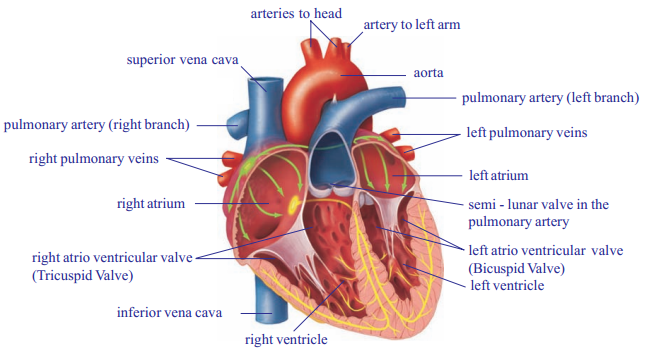
Describe the internal structure of heart with a neat labelled diagram?
OR
What is called pumping station in human body? Explain its structure with suitable diagram.
Answer:
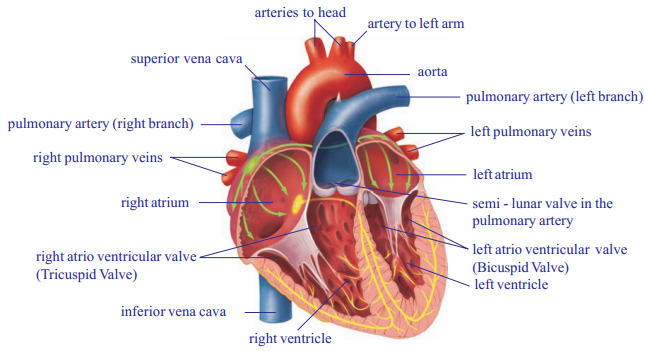
- Heart is called pumping station in human body
- Internally heart is divided into four parts by grooves
- Two upper parts are called atria, and the lower ones are called ventricles
- The two atria are separated from each by inter-atriolar septum and the right and
left ventricles are separated from each other by inter-ventricular septum
- The inter-atriolar septum and inter-ventricular septum prevent mixing of deoxygenated blood in the right side of the heart with oxygenated blood in the left side of the heart
- The walls of the ventricles are relatively thicker than atrial walls
- The largest artery is the aorta which arises from the left ventricle supplies blood to all the body parts except lungs
- Pulmonary artery that arises from the right ventricle carries deoxygenated blood to lungs
- The right atrium and right ventricle are connected to each other by right atrioventricular aperture
- The left atrium and left ventricle are connected to each other by left atrioventricular aperture
- Tricuspid valve guards the right auriculoventricular aperture and mitral valve or bicuspid valve guards the left atrioventricular aperture
- Blood from the anterior parts of the body is collected by superior venacava which opens into right atrium
- Blood from the posterior parts of the body is collected by inferior venacava or post-cava vein which also opens into right atrium
- Coronary arteries supply blood to the muscles of the heart whereas coronary veins collect blood from the heart. It also opens into right atrium
Question 4.
Read the table and answer the following Questions?
Answer:
| S.No. |
Name of the Phylum |
Type of transport system |
| 1 |
Cnidarians |
Gastro vascular cavity |
| 2 |
Platyhelminthes |
Digestive system |
| 3 |
Nematyhelminthes |
Digestive system |
| 4 |
Annelida |
Blood vessels |
| 5 |
Arthropoda |
Open circulatory system |
- In which phylum, blood vessels are first formed
- In which phylum, organisms have haemoglobin in their blood
- In which phylum, digestive system helps in transportation
- Why do Arthropods have open circulatory system
Answer:
- Blood Vessels first formed in Annelida phylum
- Organisms in Annelida phylum have haemoglobin in plasma
- Cnidarian phylum of digestive system helps in transportation
- In Arthopods blood vessels are absent, sinuses are present. So they have open circulatory system
Question 5.
Write about the valves, their positions, their functions in human heart. How many blood vessels are attached to heart ? Write about their positions and functions?
Answer:
Valves and their positions in Human heart:
- The valve present in between Right artery and Right ventricle is Tricuspid valve
- The valve present in between Right atrium and Right ventricle is Bicuspid valve
- The valves present at the region of pulmonary arota is called Pulmonary valves
- The valves present at the region of systemic arota is called systemic valves
Blood vessels attached to the heart their positions and functions :
- The blood vessels found in the walls of the heart are coronary vessels which supply blood to muscles of the heart
- From the upper part of the left ventrical arota arises it supplies oxygenated blood to the body parts
- From the upper part of the right ventricle pulmonary artery arises which supplies oxygenated blood to the lungs
- The vein which is right side of the heart is superior venacava
- The vein which is coming from the posterior part of the heart is inferior venacava which collects blood from posterior part of the body
Question 6.
Write a short note on Human Lymphatic System and its functions?
(OR)
What is lymph ? What are the functions of it ?
Answer:
- Lymphatic system consists of lymph capillaries, lymph vessels, lymph nodes and lymph glands
- To supply nutrients to the cells (tissues), the liquid portion of the blood with nutrients flows out of the capillaries. This is called tissue fluid
- This fluid flows through a system called as lymphatic system. The fluid mainly returns back into the blood stream
- Lymph is the vital link between blood and tissues by which essential substances pass from blood to cells and excretory products from cells to blood
- Lymph is the substance that contains blood without solid particles
- From intercellular spaces, lymph goes into lymphatic capillaries
- Lymphatic capillaries join to form large lymph vessels which finally open into larger veins
- Lymph flows only in one direction, that is from tissues to heart through veins
 Functions of Lymph :
Functions of Lymph :
- Lymph carries digested and absorbed fats from small intestine to different tissues of the body
- It helps in removing waste materials from the cells in the body to drain into blood
- Lymph protects cells in the tissues from infection
Question 7.
Explain the process of coagulation of blood?
Answer:
- When the blood flows out from injuries, the platelets release an enzyme called thrombokinase
- Thrombokinase acts on another substance present in the blood called prothrombin converting it into thrombin
- Thrombin acts on another substance called fibrin, that is present in dissolved state converting it into insoluble fibrin
- The blood cells entangle in the fibrin fibers forming the clot
- The fibrin fibers are attached to the edges of the wound and pull them together
I. Conceptual Understanding:
Question 1.
Observe the given diagram. Which type of cardiac cycle it indicates? Explain the process that happens here?
Answer:
- It indicates double circuit circulation. It includes pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation
- Here blood flows through the heart twice for completing one circulation. Hence it is called double circulation
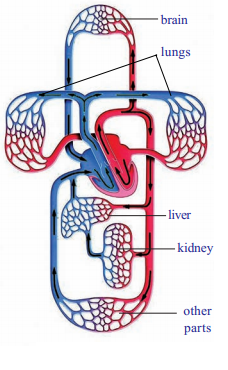
- In this circuit deoxygenated blood from organs of body is collected into the right auricle and then sent into right ventricle. From right ventricle blood is pumped to the lungs. In the lungs blood is oxygenated and is returned to the left auricle by pulmonary vein. This circulation is known as pulmonary circulation
- In systemic circulation the oxygenated blood from the left auricle is pumped into the left ventricle. From the left ventricle blood is pumped into the systemic aorta. This aorta supplies blood to various organs of the body
Question 2.
In human body "A" is a pumping organ. From lungs blood vessel "B" with oxygenated blood enters upper "C" part of left chamber of the organ. When "C" chamber contracts blood flows into "D" lower left chamber. "D" chamber contracts blood is pumped to all parts of the body except lungs through blood vessel E. Deoxygenated blood from body parts is collected by blood vessel "F and opens upper "G" right chamber. This chamber contracts blood flows "H" lower chamber. Lastly "H" contracts Deoxygenated blood sent to lungs by blood vessel "I"?
- "A" represent what organ
- (i) B (ii) E (iii) F and (iv) I are what blood vessels ? Write their names
- (i) C (ii) D are what chambers
- (i) G (ii)Hare what chambers ? Write their names
Answer:
- Heart
- B - Pulmonary vein
- E - Systemic aorta
- F - Superior or Inferior venacava
- I - Pulmonary artery
-
- C - Left atrium
- D - Left ventricle
- G - Right atrium
- H - Right ventricle
Question 3.
Write about the blood vessels that bring blood to human heart?
Answer:
- The less rigid vessels called veins bring blood from body parts to the heart.
- There are three large blood vessels or veins that carry blood to heart from all the
body parts
- The vein that collects blood from the upper parts of the body is called superior venacava. These caval veins open into right atrium
- The vein that collects blood from the lower or posterior part of the body is called post caval vein or inferior venacava
- The third vein called pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from the lungs and open into left Auricle
- The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from lungs
- In addition to these veins a pair of veins called coronary veins brings deoxygenated blood from the walls of the heart. They also open into right atrium
Question 4.
What is blood pressure ? How is it measured ?
Answer:
- The pressure with which the blood flows in the blood vessels is known as blood pressure
- Blood pressure is measured in the upper arm artery
- There are two pressure readings
- One measures the strongest pressure during the time blood is forced out of the ventricles. This is called systolic pressure
- For a healthy young adult it will be 120 mm of Hg
- The second reading is taken during the rest period, as the ventricles refill with blood. This is called diastolic pressure
- The diastolic pressure will be 80 mm of Hg
- Doctors measure the blood pressure with a device called sphygmomanometer
Question 5.
What is the need of special tissues or organs for transport of substances in plants and animals ?
Answer:
- The body of plants and animals is made of cells
- In order to survive and maintain themselves, all cells require oxygen, water and food
- They need certain other substances to carry out various life processes
- Oxygen, water, food or any other substances may be picked up at one end of the body of an organism and transported to other parts
- Thus transportation is a life process in which a substance absorbed or synthesised in one part is moved to other parts of the body
- The methods of transportation of substances are different in plants and animals
- Therefore there is a need of special tissues or organs for transport of substances in plants and animals
Question 6.
Explain the process of transport of mineral salts?
Answer:
- Mineral salts are necessary for plant nutrition and that they are obtained from the soil in solution through the root hairs
- The salts are in the form of electrically charged ions
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) is in the form of Na+ and Cl- and Magnesium Sulphate (MgSO4 occurs as Mg2+ and SO42-.
- But, they are not absorbed into the root hairs by the simple process of diffusion, but it must involve the use of energy by the cytoplasm
- Once ions are absorbed, the ions travel with water in the xylem vessels and pass to the growing parts of the plants where they are used for growth
- They may also pass laterally from xylem to phloem
Question 7.
Write about the changes in the evolution of transport system in animals?
Answer:
- In Amoeba due to Brownian movements nutrients and oxygen are distributed throughout the protoplasm equally
- The parazones like sponges, use sea water for transportation. Sponges create their own currents by beating of flagella that are present in their body
- Cnidarians developed blind sac like gastrovascular cavity, which has taken up the function of digestion and transportation of nutrients, e.g.: Hydra and jelly fish
- In platyhelmenthes, the digestive system supplies digested food to all the cells directly, excretory system collects wastes from each cell individually
- In animals belonging to Nematyhelmenthes the pseudocoelom has taken up the function of collection and distribution of materials
- In Annelids, animals have developed a pulsative vessel to move the fluid and the transporting medium is blood
- In Arthropods have developed a pulsative organ to pump the blood. The blood floods the tissues, directly supplying the nutrients to the tissues
- Transportation system which supplies nutrients to the tissues directly is called open type of circulatory system. e.g.: Arthropods, many mollusks and lower chordates
- The other type of transportation system where the blood takes the responsibility of delivering the materials, which flows in the blood vessels is called closed type of circulatory system
- Such type of closed circulatory system is present in annelids, echinoderms, cephalopod mollusks and all the higher animals
Question 8.
How are water and minerals transported in plants ?
Answer:
- Xylem tissue transports water and mineral salts in plants
- Xylem vessels and tracheids of root, stem and leaves are interconnected to form a continuous system of water and minerals conducting channels to each part of the plant
- The cells of root hair present in the soil absorb water from the soil by osmosis
- The entry of water dilutes the contents of the root hair vacuole so that it becomes weaker than its neighbour
- Therefore water passes into the neighbouring cell which in turn becomes diluted, finally water enters the xylem vessel
- This creates a column of water that is steadily pushed upward, called root pressure
- Root pressure is not enough to push water and dissolved minerals to leaves in the tall trees
- There is a continuous loss of water through stomata of the leaves in the form of water vapour. This process is called transpiration
- The water lost due to transpiration is taken up from the xylem vessels and tracheids
in the leaves
- This loss of water during transpiration creates a suction pressure which pulls water from the xylem cells of roots
- This results in enhanced absorption and upward movement of water and dissolved minerals from roots to the leaves due to transpiration
- At night when stomata are closed root pressure has an effect on transportation of water
- Transpiration pull is the major force in the movement of water and dissolved minerals in the xylem during daytime
Question 9.
How is manufactured food in leaves transported to other parts of the plant ?
Answer:
- Food such as sugar is synthesised in the green parts of plants mainly leaves to be transported to actively growing and those which stores food
- Phloem is the tissue responsible for transport of food material
- The transport of soluble product of photosynthesis through phloem is known as translocation
- The transport of prepared food and other substances takes place both in upward and downward directions
- The translocation is an active process and utilizes energy
- Entry of food material into phloem tissue causes increase in osmotic pressure, as a result water from outside moves into phloem
- The osmotic pressure moves the dissolved material in the phloem to tissues which have less pressure
- Thus material moves in phloem, mainly in sieve tubes, to place of need in the plant body
- In plants sugar is translocated from its storage organs like root or stem to growing regions which need energy
II. Asking Questions And Making Hypothesis:
Question 1.
If you get chance to meet a cardiologist / cardiovascular surgeon, what Questions you will ask about the problems related to heart ?
Answer:
I will ask following
Questions to clarify my doubts about problems related to heart
- Why heart is very vital organ
- If we do strenous exercise, will it tired quickly
- Why do we get heart attack
- What are causes for heart attack
- What precautions shall we take, to prevent heart attack
- What is stunt
- When do a person need stunt
- What is by-pass surgery
- What is pace maker
- What type of food habits prevent heart related problems
- Why heart beat always not stable
Question 2.
What happens if valves between left auricle and left ventricle does not work properly ?
Answer:
- Pumping of oxygenated blood to different parts of body from the left ventricle may not occur properly
- Blood may re-enter into left auricle hence systolic pressure may not maintain properly
Question 3.
What happens the concentration of solution in root hair cell is less than the soil water ?
Answer:
- Water from root hair cell comes out in to soil water
- Water may not enter into the root hair cell and pass on to xylem
Question 4.
What would happen if cell sap in the cells of root hair contain high concentration of ions ?
Answer:
- Cell sap of root hair cells contain high concentration of ions pass from cell to cell by osmosis through the epidermis, root cortex, endodermis and reach the root xylem
- The xylem vessels of the root of the plant are connected to the xylem vessels of its stem
- The water containing dissolved minerals enter from the root xylem vessels into stem xylem vessels
- So the cell sap containing water and minerals carried by the xylem vessels in the stem reach the leaves through the branched xylem vessels which enter from the petiole into each and every part of the leaf
- In this way the cell sap of root hair cells containing high concentration ions reach through the root and stem to the leaves of the plant
III. Experimentation And Field Investigation:
Question 1.
Write briefly about the work done by William Harvey on circulation of blood?
Answer:
- William Harvey was an Englishman who after became a doctor went to Italy for further education
- Harvey dissected the hearts of dead people and studied the valves between each atrium and its ventricle
- Harvey noticed that they were one way valves which allow blood to flow from atrium to the ventricle, but not from ventricle into the atrium
- He also noticed that all the veins in the human body allows blood to flow towards heart
- Harvey also identified that the blood flows through the heart twice in human beings. Hence it is called double circulation
- Harvey also showed that it was impossible to suppose that the blood was used up in the body and that new blood was formed
- He found that in one hour, the heart pumped out a quantity of blood that was three times the weight of a man
- The same blood had to circulate and be used over and over again
Question 2.
What was the classical experiment conducted by William Harvey to demonstrate movement of blood in veins ?
OR
How do you repeat the classical experiment to demonstrate the movement of blood in veins ?
Answer:
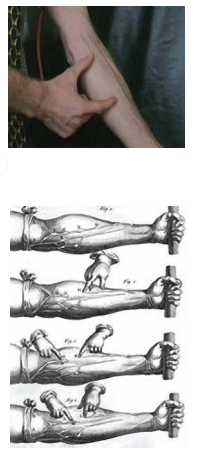
- In early 17th century William Harvey conducted an experiment to demonstrate the movement of blood in veins
- Tie a tornquit just above the elbow of a person, whose blood vessels are prominent in the hand
- Ask him/her to hold a firm support as shown in the figure. Now the blood vessels can be seen more prominently
- Locate a prominent bluish blood vessel
- At the end of the vessel farthest from the elbow apply steady pressure, so as to close its cavity
- Now apply pressure from elbow towards the palm slowly and observe the changes in the blood vessels
- Remove the pressure
- Apply pressure from palm to wards elbow and see what happens
Question 3.
Write an experiment to illustrate the conduction of sugars by phloem?
Answer:
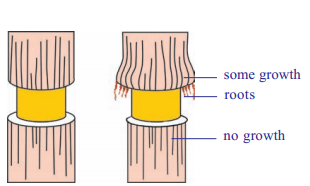
- Experiments to illustrate the conduction of sugars by the phloem have been done by removing a ring of bark from a shoot to expose the wood
- Remove all tissues from the cambium outwards including the phloem
- After a few days, when the tissues above and below the ring were analyzed
- it was shown that food had accumulated above the ring but was not present below it
- If it is left for sometime, the stem increases in thickness immediately above the ring, but no growth occurred below it
- So, any damage to the phloem all around the stem will prevent food from passing down to the roots and the tree will eventually die
V. Information Skills And Projects:
Question 1.
Observe following table and answer Questions given below?
| Name of the animal |
Weight of the body |
Weight of tine heart |
No, of beats/min |
| Blue whale |
1,50,000 kg |
750 kg |
7 |
| Elephant |
3000 kg |
12-21 kg |
46 |
| Man |
60 - 70 kg |
300gm |
76 |
| Coaltit (Bird) |
8gm |
0.15gm |
1200 |
Questioni.
In which animal the heart beat rate is very slow ?
Answer:
In Blue whale heart beat rate is slow
Questionii.
What is weight of human heart and heart beat rate ?
Answer:
Weight of human heart is 300 gms and heart beat rate is 76/min
Questioniii.
Which animal has highest heart beat rate ?
Answer:
Coaltit (Bird)
Questioniv.
Is there any relation between weight of the body and heart beat rate ?
Answer:
Yes, there is a relation between body weight and heart beat rate. If the body weight is more heart beat rate is less. If the body weight is less, the heart beat rate is more
Question 2.
Group of students conducted an activity and got following results?
| S.No. |
Name of the student |
At rest |
After jogging |
Heart beat/ minute |
Pulse rate/ minute |
Heart beat/ minute |
Pulse rate/ minute |
| 1 |
Raju |
76 |
76 |
118 |
| 2 |
Rama |
78 |
77 |
120 |
| 3 |
Manjula |
78 |
76 |
121 |
| 4 |
Shankar |
77 |
78 |
132 |
| 5 |
Rajasekhar |
77 |
77 |
135 |
Questioni.
What is the relation between heart beat and pulse rate at rest ?
Answer:
Pulse rate and heart beat always equal at rest
Questionii.
Why heart beat rate is more after jogging ?
Answer:
After jogging body cells need more energy. It need more respiration (oxygen).
Through heart, blood flows at high speed ultimately rate of breathing, heart beat and pulse rate increases rapidly
V. Communication Throught Drawing, Model Making:
Question 1.
Draw T.S. of flow of blood in arteries and veins. Write flow of blood in between them?
OR
Write the differences between T.S. of artery, T.S. of vein and T.S. of blood capillary.
Answer:
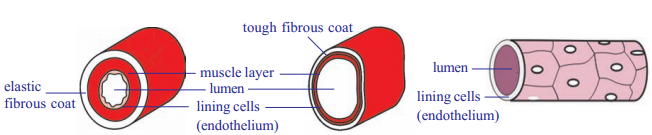
- Arteries carry blood from the heart to body parts. Veins carry blood from body organs to heart
- Veins collects deoxygenated blood from all body parts into the right atrium. Pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from lungs into left atrium
- Blood capillaries are the microscopic vessels that connect smallest arteries and veins
Question 2.
Draw neat labelled diagram of L.S of human heart. What is the function of pulmonary artery ?
Answer:
Question 3.
The diagrams given below shows cross-section of two kinds of blood vessels?
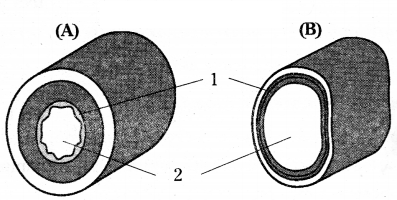
Questioni.
Identify the blood vessels A and B. In each case, give reasons to support your answer?
Answer:
A is T.S. of artery and B is T.S. of vein.
Artery walls are thick, the shape of its wall is retained when blood is absent.
Veins walls are thin, and the shape of its wall is collapsed
Questionii.
Name the parts numbered 1 and 2?
Answer:
Name of part 1 is muscle layer and 2 is lumen
Question 4.
Draw the diagrams of single and double circulation blood systems?
Answer:
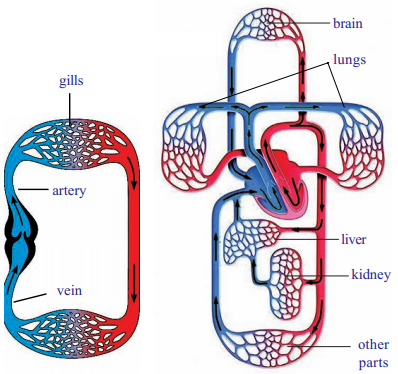
VI. Appreciation and Aesthetic Sence,Value
Question 1.
How will you appreciate function of Human heart since 21st day of embryonic stage to till death ?
Answer:
- Heart beat starts since 21st day of conception and by the day of birth it function fully
- Heart beat denotes state and condition of human body
- Heart is most amazing organ of human body which works even if you take rest
VII. Application to Daily Life, Concern to Biodiversity:
Question 1.
After learning about circulatory system, what changes would you like to bring in your life style ?
Answer:
I will bring following changes in my life style
- I will avoid heavy fat food and junk food
- Try to spend stress free life as stress leads where to cardiac problems
- I will do regular physical exercise or work to keep my self fit
- Keep away from bad habits like smoking and alcohol consumption
- After 40 years, yearly twice I will consult cardialogist
Question Papers / Notes Download