Minerals and Energy Resources AP 10th Class Social Geography 5th Lesson Important Questions
AP 10th Class Social Geography 5th Lesson Important Questions: 8 Marks
Question 1.
Describe the importance of minerals in human life?
Answer:
- Minerals are an indispensable part of human life. Almost all things we use are made of minerals
- Human beings use minerals for their livelihood, decoration, festivities, religious and ceremonial rites
- Buildings, ships, railway lines, cars, buses, aeroplanes, various implements, etc., are manufactured from minerals and run on power resources derived from the earth
- Our food too contains minerals. Life processes cannot occur without minerals
- They are very important part of total food intake
- It is only 0.3 percent of the total intake of nutrients but they are so potent and so important that without them we would not be able to utilise the other 99.7 percent of the food stuff
- In toothpaste, fluoride which is used to reduce cavities, comes from a mineral fluorite
Question 2.
Explain the importance of conservation of minerals; Highlight any three measures to conserve them?
Answer:
Reasons for conservation
- The strong dependence of industry and agriculture upon minerals
- The process of mineral formation is slow
- They are non - renewable
Methods to conserve :
- Minerals should be used in a planned and sustainable manner
- Improved technology needs to be constantly evolved to allow use to low grade ore at low cost
- Recycling of metals using scrap metals
- Wastage in the mining and processing should be minimised
Question 3.
Differentiate between Metallic and Non-Metallic minerals with examples?
Answer:
| Metallic minerals |
Non-Metallic minerals |
| 1) Metallic minerals generally occur in igneous and Metamorphic rocks. Certain minerals may also occur as alluvial deposits in sands of valley floor and base of hills |
1) Non-metallic minerals occur in sedimentary rocks. They have been formed as a result of deposition, accumulation and concentration in the horizontal stra |
| 2) Metallic minerals comprise of ferrous minerals, non-ferrous minerals and precious metals. Ferrous minerals containing iron-ore, cobalt, account for strong development of metallurgical industries. Noil-ferrous minerals eg. copper, bauxite etc |
Non-metallic minerals comprise of mica, salt, limestone, granite, etc. Limestone is used as raw material in cement industries. Mica, salt and granite are indispensable minerals used in electric industries |
| 3) Metallic minerals are found in Odisha, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra |
3) Non-metallic minerals are found in Rajasthan, Jharkhand and Andhra Prad |
Question 4.
Differentiate between Ferrous and Non-Ferrous minerals with example?
Answer:
| Ferrous minerals |
Non-Ferrous minerals |
| 1) These minerals are magnetic |
1) These minerals are not magnetic |
| 2) Less resistant to corrosion |
2) More resistant to corrosion |
| 3) These minerals weight more |
3) These minerals weight loss |
| 4) Examples : Manganese (Mn) and Iron (Fe), etc |
4) Examples : Gold (Au), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), etc. |
Question 5.
Highlight the importance of petroleum. Explain the dccurrence of petrolum in India?
(Or)
Which is the next major source of energy after coal in India ? Describe any three advantages of it ?
Answer:
Importance of Petroleum:
- Petroleum is the major energy source in India
- Provides fuel for heat and lighting
- Provides lubricant for machinery
- Provides raw material for a number of manufacturing industries.
- Petroleum refinaries act as a nodal industry for synthetic, textile, fertilizer and chemical industries
Its occurrence:
- Most of the petroleum occurrences in India are associated with anticlines and fault traps
- In regions of folding, anticline or domes, it occurs. Where oil is trapped in the crest of £he unfold
- Petroleum is also found in fault traps between porous and non-porous rocks
Question 6.
What are the three major iron ore belts in India ?
Write the main features of each?
Answer:
Three major iron ore belts in India are
- Odisha, Jharkhand belt
- Durg-Bastar Chandrapur belt
- Ballari-Chitradruga-Chikkamagaluru-Tumakuru belt
- Odisha, Jharkhand belt : Odisha Jharkhand belt is famous for Hematite dre in Badampahar mines aftd Kendujhar districts. In the adjoining Singhbhum district of Jharkhand haematite ore is mined in Gua and Noamundi
- Durg-Bastar Chandrapur belt : High Grade Haematite ore. Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra. Bailadila range of hills the Bastar district of Chhattisgarh. Iron ore from these mines is exported to-Japan, S.Korea from Visakhapatnam port
- Bellary - Chlkkamagaluru - Chitradurga Belt: Kudremukh deposits in Karnataka are one of the largest in the Kudremukh mines are hundred percent export units
Question 7.
What are the two main ways of generating electricity ?
How are they different from each other ?
Answer:
The two main ways of generating electricity are by running water (hydro electricity) and by burning fules (thermal electricity).
Differences between these two are as follows
| Hydro electricity |
Thermal electricity |
| 1) It is produced from water |
1) It is obtained by using petroleum, coal and natural |
| 2) It is non-renewable resource |
2) It is renewable. |
| 3) It causes pollution. |
3) It does not cause pollution |
| 4) It is expensive in long run |
4) It is cheaper in long run |
Question 8.
"Minerals are an indispensable part of our level." Justify the statement with suitable examples?
Answer:
Minerals are an indispenable part of our lives. This can be understood through the following examples
- Almost everything we use from a tiny pin to a towering building or a big ship, all are made from minerals
- The railway lines and the tarmac (paving) of the roads, our implements and machinery too are made from minerals
- Cars, buses, trains, aeroplanes are manufactured from minerals and run on power resources derived from the earth. Even the food that we eat contains minerals
Thus, in all the stages of development, human beings have used materials for their livelihood, decoration, festivities, religious and ceremonial rites. So correctly said- minerals are an indispensable part of our lives
Question 9.
"Nuclear energy is expected to play an increasingly Important role in India." Give arguments to support this statement?
Answer:
Nuclear energy is expected to play an increasingly important role in India due to following reasons
- India has limited reserves of coal and petroleum. Nuclear energy minerals like thorium is found in plenty in India
- Hence, nuclear energy can compensate for deficiency of fossil fules
- Nuclear power stations can be established easily and conveniently in those areas where other sources are not available
- Nuclear power releases tremendous amounts of energy. India can utilise this energy for peaceful purposes such as generation of electricity that can be used to run machines in industries
- It is a non-conventional source of energy. After the initial expenses. It becomes very economical
Question 10.
Consumption of energy in all forms has been rising all over the country. These is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development and energy saving. Suggest and explain any three measures to solve this burping problem?
Answer:
The rapid consumption of energy in all forms has given rise to an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development and energy saving. This can be done by adopting the following measures
- The use of public transport systems instead of individual vehicles can help in minimising the usage of resources such as petroleum or diesel. Pooling is a very sustainable option in this regard as well
- The use of electricity needs to be regulated carefully. Switching off power points and plugs and other electrical appliances when not in use can positively help in this direction
- Technology has also added to mechanisms wherein use can use as well as save energy at the same time
- For example - the use of power saving devices available in the market. Additionally, the use of various non-conventional sources of energy can help in minimising the amount of energy used
Question 11.
What is natural gas ?
Explain natural gas as a source of energy in India and also give the distribution?
Answer:
- Natural gas is a natural hydrocarbon gas mixture primarily consisting of methane
- Usually accompanies the petroleum accumulation
- It is formed when layers of decomposed plants and animals are exposed to intense heat and pressure over thousands of years
- Natural gas a source of energy
- Natural gas is a cleaner fuel
- It is less harmful to the environment than coal, petrol or diesel as it has less carbon dioxide emissions
- It can be easily stored and transferred through pipelines
- Distribution:
- Large reserves of natural gas are found in Krishna Godavari basin
- Along the west-coast the reserves of the Mumbai High and allied fields are supplemented by finds in the Gulf of Cambay
- Andaman and Nicobar islands are also important areas having large reserves of natural gas
Question 12.
"Minerals are an indispensable part of our lives." Support this statement with examples?
Answer:
- In igneous and metamorphic rocks, mineral is may occur in the cracks, crevices faults or joints. Zinc is mixed in, this way. They are formed when minerals in their liquid / gaseous forms are forced upwards to the Earth
Questions surface through cavities. They cool and solidify as they rise. Major metallic minerals we formed iri this way
- In sedimentary rocks, they occur in beds and layers as a results of decomposition, accumulation and concentration in horizontal straza coal and iron ore are formed in this way Gypsum, potash and sodium salt are another class of sedimentary satisfy which are obtained through evaporation in acid areas
- Bauxite is formed by the decomposition of surface rocks and removal of soluble constituents leaving a residual mass of weathered material containing ores
- Gold and silver are found as places deposits in the sands of valley floors and base of hills
- Seawater contains magnesium and bromine salts. Managenese modules are also found in the seabeds
Question 13.
Write a brief note on crude oil?
Answer:
- Crude oil is a type of fossil fuel which occurs naturally
- It is an unrefined petroleum product composed of hydrocarbon deposits and other organic materials
- It is a non-renewable resource of energy
- It takes millions of years for the formation of this fuel
- It is used to propel vehicles, to heat buildings, and to produce electricity
- This type pf fuel is being used at a faster rate than they are being produced
- This causes depletion and scarcity of crude oil
- Saudi Arabia is the world
Questions largest oil producer
- The country produces 13.24% of the oil consumed in the entire world daily
- Saudi Arabia has the second-largest reserves of naturally occurring oil in the world after Venezuela
Question 14.
What are the various types of conventional energy sources in India?
Discuss their distribution and utilization?
Answer:
Various types of conventional energy sources in India
- Firewood, cattle dung cakes used traditionally in rural areas
- Coal major source, mainly found in Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh
- Lignite in Tamil Nadu used for power generation
- Petroleum along western offshore and Assam
- Natural gas with petroleum reserves and Assam
- Hydropower from dams like BhakraNangal, Tehri, Mettur
- Thermal power plants use coal, gas, diesel to generate electricity
- Major industries and urban centers utilize these sources
- Rural areas still dependent on firewood, chips causing deforestation
- Commercial energy consumption rising rapidly with economic growth
- Need for shift to renewable energy to reduce environmental impact
- Minimize wastage and increase efficiency of energy usage
Question 15.
How do mining activities negatively impact the environment?
What measures should be taken to mitigate these impacts?
Answer:
- Land degradation and landscape alteration due to open cast mining
- Air and water pollution due to waste dumping and slurry discharge
- Surface and ground water contamination due to water use in mining
- Noise and vibration affect wildlife and human habitats nearby
- Deforestation and biodiversity loss as forests cleared for mining
- Health hazards for mine workers due to dust, toxins and hazards
- Should follow best practices and mining regulations
- Minimize waste dumping through recycling and safe disposal
- Reclaim and replant mined out areas to revive ecology.
- Iristall pollution control equipment to reduce emissions
- Proper safety gear and facilities for workers
Question health and safety
- Community awareness and preparedness for disasters like landslides
Question 16.
What are the environmental impacts of using fossil fuels like coal and petroleum Suggest someQuestion methods for mitigating these effects?
Answer:
- Burning fossil fuels emits air pollutants like SOx, NOx, fly ash
- Causes respiratory health hazards for people
- Contributes to acid rain, smog and greenhouse effect
- Strip mining of coal destroys soil, forests and landscapes
- Thermal effluents from power plants affect aquatic ecosystems.
- Oil spills, leakages contaminate terrestrial and marine ecosystems
- Greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels leading to climate change
- Air pollution control equipment like scrubbers reduce emissions
- Reclaiming and reforesting mined areas to restore ecology
- Switching to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, biogas
- Increasing share of hydro and nuclear power generation
- Energy efficiency and conservation measures in industry, transport etc
Question 17.
What are the various problems associated with nuclear energy as a major source of power generation in India?
Suggest some safety measures to be followed?
Answer:
- Risk of nuclear radiation hazards and contamination
- Radioactive waste disposal is an environmental challenge
- High capital costs and technological constraints
- Limited domestic fuel reserves - mostly dependent on imports.
- Concerns regarding weapons proliferation
- Needs abundant water for cooling leading to thermal pollution
- Exposure to radiation can cause health effects like cancer
- Must follow highest safety standards in reactor design and operation
- Waste disposal in deep geological repositories to isolate radiation
- Strict regulations on waste transportation and nuclear material transfers
- Emergency preparedness plans for accidents/natural disasters
- Transparent siting policies considering ecological factors and community acceptance
Question 18.
How is mining activity regulated in India?
Discuss the objectives and major provisions of the Mines Act, 1952?
Answer:
- Mineral concessions granted through Ministry of Mines under MMDR Act 1957
- Environmental clearances needed from Ministry of Environment and Forests
- Mines Act 1952 deals with health, safety and welfare of mine workers
- Ensures adequate ventilation, lighting, safe machinery, protective gear
- Stipulates maximum work hours, rest intervals, paid leave, creches if women employed
- Mine closure plans mandatory for underground mines
- Tripartite safety committees with worker representation
- Mandatory disaster management plans and relief funds
- Prescribes qualifications of mine managers and engineers
- Provisions for inspection, penalties for violations
- Key objective is safety, welfare and health of workers
- Also ensures systematic and scientific mining to conserve resources
Question 19.
Analyze the factors responsible for growing energy demand in India and its implications on the environment?
Answer:
- Economic growth, rising incomes increasing energy demand
- Expanding industry, transport Infrastructure, urbanization
- Growing population needing more residential energy
- Lower energy access, affordability in rural areas
- Increasing commercial energy and reducing dependence on traditional sources
- High emission intensity of energy usage in India
- More than half of commercial energy from coal having high carbon and particulate emissions
- increased private vehicles, congestion instead of public transport
- Subsidies on conventional energy lead to wasteful consumption
- Need for energy efficiency, optimization in all sectors - residential, industry, transport etc
- Shift to lower emission fuels like natural gas and renewable sources
- Promote transition to electric vehicles, public transport
- Environmental regulations on pollution control, standards
- Raising awareness and incentives for efficient technology adoption
Question 20.
How is sustainable development achieved with respect to availability of energy resources in India?
Explain?
Answer:
- Efficient extraction and use of conventional energy resources
- Adopting renewable energy like solar, wind, biogas on large scale
- Reducing transmission losses and wastage in distribution
- Upgrading technology in industry, transport, buildings for energy optimization
- Promoting energy conservation awareness and practices
- Reducing dependence on imported fuels by finding domestic alternatives
- Making energy affordable and accessible especially in rural areas
- Constant R&D into new clean technologies and energy security
- Frameworks for transparent and participatory environmental impact assessments
- Switching over time to a less energy-intensive economic structure
- Promoting decentralised distributed energy model for self-reliance
- Following intergenerational and intragenerational equity for energy use
AP 10th Class Social Geography 5th Lesson Important Questions: 4 Marks
Question 1.
How is the mining activity injurious to the health Of the miners and environment ?
Explain?
Answer:
Mining activity is injurious to the health of miners due to the following reasons
- Inhalation of poisonous gases and dust make them vulnerable to pulmonary diseases
- The risk of collapse of mine roofs may risk the life of miners
- Inundation and fires in coal mines are a constant threat to the mines
The following points
Questionshow how mining affects the environment
- It results in contamination of water
- Dumping of waste and slurry leads to degredation of land and soil
- It results in air and water pollution
Question 2.
How can biogas solve the energy problem mainly in rural India ?
Give your suggestions>
Answer:
Biogas is produced from shruhs, farm waste, animal and human waste mainly for domestic consumption in rural areas. It can solve the energy problem in rural India as follows
- Decomposition of organic matter yields gas, which has higher thermal efficiency than kerosene, dung cake and charcoal
- It provides the farmers with energy and improved quality of manure
- It prevents the loss the trees and manure due to burning of fuel coal and cowdung cakes
Question 3.
Why should non-conventional energy be used more Explain?
Answer:
The reasons for using renewable energy sources or non-conventional energy such as solar, wind, water are as mentioned below
- Use of fossil fuels has caused serious environmental problems
- Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainities about energy resources in the future
- India has abundance of sunlight, water, wind and biomass
- Rising prices of oil etc., has serious repercussions on the growth of the national, economy as we have to make payment for import of oil in foreign exchange
Question 4.
Which is the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India ?
Mention its different forms?
Answer:
The most abundantly available fossil fuel in India is coal
- Peat has low carbon and high moisture content and low heating capacity
- Lignite is a low-grade brown coal which is soft with high moisture content. It is used for generating electricity
- Bitufninous is the most popular coal of commercial use. It has a special value of smelting iron in blast furnaces
- Anthracite is the highest quality hard coal
Question 5.
Explain any three types of formations in which Minerals occur?
Answer:
The main types of formations in which minerals occur are
- Veins and lodes : In igneous and metamorphic rocks, minerals may occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints. Smaller occurrences are called veins and larger ones are called lodes
- Beds or layers : In sedimentary rocks, minerals occur in bed or layers. They are formed as a result of
Questiondeposition, accumulation and concentration in horizontal strata (layers)
- Placer Deposits: Certain minerals occur as alluvial deposits in sands of valley floors and the base of hills as placer deposits
Question 6.
What is mineral ?
Classify minerals with examples?
Answer:
Mineral is a naturally occurring substance, having definite chemical composition. Its outer layer is rigid and hard
Classification of Minerals :
- Metallic minerals : Those minerals from which we obtain metals like iron, gold, copper, silver, aluminium etc. They are two types
- Ferrous Non-Ferrous
- Ferrous: Iron ore manganese, etc
- Non-Ferrous : does not contain iron but may contain some other metals like - . gold, silver, copper, etc
- Non-metallic minerals: They do not contain metals like coal, mica, sulphur, potash, etc
Question 7.
How can solar energy solve the energy problem to some extent in India ?
Give your opinion?
Answer:
Following are the reasons why solar energy solves the energy problem
- It will reduce the dependence of rural households on firewood.
- Use of Solar Energy will reduce the pressure on conventional sources of energy
- Since the sun shines across the globe, it makes every country a potential energy producer, thus allowing for greater energy independence and security
- As India has been blessed with abundance of sunlight, water, wind and biomass, we must use these to overcome present day energy crisis
Question 8.
Analyse any three ways to conserve energy resources?
Answer:
Energy Resources are very important so we should conserve them
- Instead cars and bikes a bicycle should be used to conserve fuel
- We can do car Pooling too with our colleages
- Using renewable resources like solar energy instead of electricity whenever possible
- Clean or replace air fiters when required
Question 9.
QuestionConsumption of energy in all forms has been rising all over the country, There is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development and energy saving.Question Suggest and explain any three measures to solve this burning problem?
Answer:
Consumption of energy in all forms has been rising. To take care of this concern various measures that need to be adopted are as follows
- Increase in the use of renewable energy resources like-solar, wind, biogas, tidal and geothermal energies
- This will decrease the dependence on non-renewable sources.
- Judicious use of limited energy resources
- Use of public transport system in place of individual vehicle
- Energy conservation, through switching off electrical devices when not in use, using power saving devices etc
Question 10.
What are the environmental effects of mining?
Answer:
Land degradation and soil erosion
- Air and water pollution due to wastes
- Loss of biodiversity and deforestation
- Health hazards for miners
- Aesthetic degradation of landscape
Question 11.
Why is it necessary to conserve mineral resources ?
Answer:
Conservation
- The geological process of mineral formation is quite slow
- The rate of replenishment is infinitely small whereas the rate of consumption is quite high
- Mineral resources found on the earth surface are limited in number and are exhaustible
- Minerals are a non-renewable resource and finite. So it is necessary to conserve mineral resources
Question 12.
Read the following passage and answer the Questions?
IndiaQuestions Mineral Resources India is rich in mineral resources, with significant reserves of coal, iron ore, manganese, bauxite, and copper. These minerals are essential for economic development and industrialization. However, mining activities can have negative environmental impacts, including land degradation, soil erosion, air and water pollution, loss of biodiversity, and deforestation. It is important to regulate mining practices to minimize environmental damage and ensure that the benefits of mining are shared equitably among all stake holders |
Question 1.
Which mineral is not found in significant quantities in India?
Answer:
Uranium
Question 2.
What are some of the negative environmental impacts of mining?
Answer:
- Land degradation
- Soil erosion
- Air and water pollution
Question 3.
Why is it important to regulate mining practices?
Answer:
To minimize environmental damage
Question 4.
How can the benefits of mining be shared equitably among all stakeholders?
Answer:
By improving transparency and accountability in the mining sector
Question 13.
Read the following passage and answer the Questions?
| Non-Conventional Sources of Energy including solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, and biogas, are becoming Increasingly important as countries seek to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and address environmental concerns such as air pollution and climate change. These sources of energy are renewable and do not produce emissions or waste like fossil fuels. However, they also face challenges such as intermittency, grid integration, and high costs |
Question 1.
Which is a non-conventional source of energy?
Answer:
Solar
Question 2.
Why are non-conveuth»nal sources of energy becoming increasingly important?
Answer:
To address environmental concerns
Question 3.
What are some of the challenges faced by non-conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
- High costs
- Intermittency
- Grid integration
Question 4.
What-is the advantage of renewable energy sources over fossil fuels?
Answer:
They do not produce emissions or waste like fossil fuels
Question 14.
Locate and label the following with appropriate symbols on the same given outline political map of India?
- Bokaro - Iron and Steel Plant
- Gandhinagar - Software Technology Park
- Tarapur - Nuclear Power Plant
- Salal - Dam
Answer:
![]()
Question 15.
Locate and label the following with appropriate symbols on the same given outline political map of India?
- Kalpakkam - Nuclear Power Plant
- Vijayanagar - Iron and Steel Plant
- Noida -Software Technology Plant
- Paradeep - Sea Port
Answer:
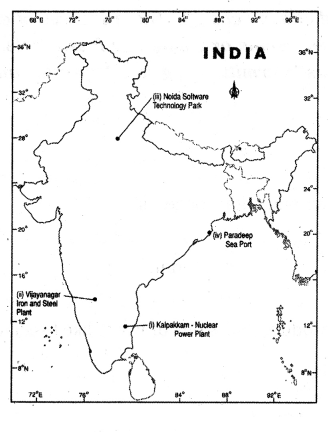
Question 16.
On the given map of India, locate the label the following features with appropriate marking?
- Kaiga - Nuclear Power Plant
- Bhilai - Iron and Steel Centre
- Kandla - Major Sea Port
- Kakrapara - Nuclear Power Plant
Answer:
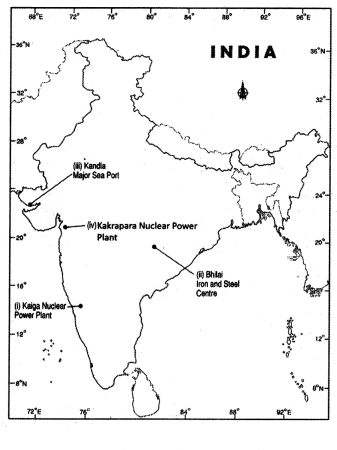
Question 17.
On the political map of India, locate the label the following with suitable markings?
- Tehri -Dam
- Bakaro - coal mines
- Pune - Software Technology Park
- Tuticorin - sea Port
Answer:

Question 18.
On the given map of India, located and label the following with appropriate markings?
- Sardar Sarovar - Dam
- Bhilai - Iron and Steel Plant
- Hyderabad - Rajiv Gandhi International Airport
- Ennore port (Kamarajar port)
Answer:
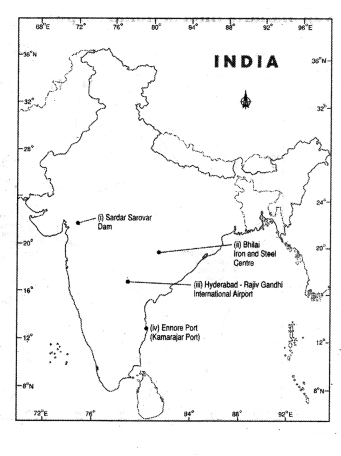
Question 19.
On the given map of India, located and label the following with appropriate markings?
- Ramagundam Thermal Plant
- Pune Software Technology Paris
- Chennai (Meenambakkam) International Airport
- Thiruvananthapuram - International Aiiport
Answer:
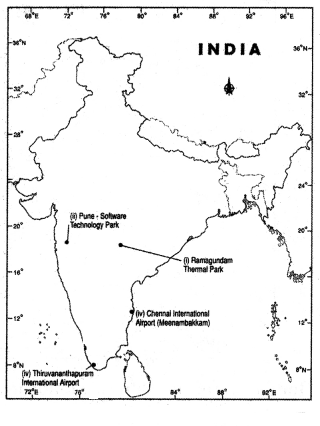
Question 20.
On the given map of India, located the following?
- Namrup ThermaPlant
- Noida Software Technology Park
- Raja Sansi (Sri Ram Dass Jee) International Aiiport
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj International Aiiport
Answer:
Question 21.
On the outline map of India, locate and label any four of the following with appropriate markings?
- Haldia - Major sea port
- Mohali - Software Technology Park
- Rana Pratap Sagar
- Naraura - Nuclear Power Plant
Answer:
Question 22.
Locate and label any four of the following with appropriate markings on the same given political outline map of India?
- Tungabhadra
- Kochi - Major Sea Port
- Indore - Cotton Textile Industry
- Kudankulam - Nuclear Power Plant
Answer:
Question 23.
Locate the following coal mines in the outline map of India?
- Raniganj
- Bokaro
- Talcher
- Neyveli
Answer:
Question 24.
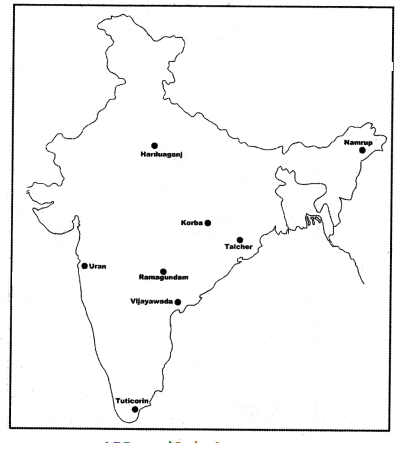
Locate the following Thermal Power Plants in the outline map of India?
- Harduaganj
- Uran
- Tuticorin
- Vijayawada
- Ramagundam
- Talcher
- Korba
- Namrup
Answer:
Question 25.
Mention any three factors that determine the economic viability of reserve ?
Answer:
The three factors that determine the economic viability of a reserve are as follows
- The quality and quantity of mineral concentration in the ore. For example, magnetite is regarded better than haematite as it has more concentration of iron
- The cost of extraction. If the cost of extraction is high than mining is not profitable
- Location of mines near the industries
Question 26.
State uses of limestone. Also mention the states where it is produced?
Answer:
- Limestone is the basic raw material for the cement industry and essential for smelting iron ore in the blast furnace
- It is found in association with rocks composed of calcium carbonates or calcium and magnesium carbonates
- It is found in sedimentary rocks of most geological formations
- It is produced in states like Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Tamilnadu
Question 27.
Explain the formation of Bauxite and name the metal obtained from it?
Answer:
- Bauxite is formed by the decomposition of a wide variety of rocks that are rich in aluminium silicates
- Intense weathering of the surface rocks helps in their decomposition thus forming bauxite deposits
- The metal obtained from bauxite is aluminium
Question 28.
Read the Paragraph and answer the following Questions?
| Energy can be generated from fuel minerals like coal, petroleum, natural gas, uranium and from electricity. Energy resources can be classified as conventional and non-conventional sources. Conventional sources include, firewood, cattle, dung cake, coal, petroleum, natural gas and electricity (both hydel and thermal). Non- conventional sources include solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, biogas and atomic energy. Firewood and cattle dung cake are most common in rural India |
Question(i) How can energy be generated ?
Answer:
Energy can be generated from fuel minerals like coal, petroleum, natural gas, uranium and from electricity
Question(ii) How are the sources of energy classified based on their usability ?
Answer:
The energy sources can be classified into two categories
Conventional source of energy
Non-conventional source of energy
Question(iii) What are conventional sources of energy ?
Answer:
Firewood, cattle dung cake, coal, petroleum, natural gas and electricity are the examples of the conventional sources of energy. They are non-renewable by any natural process
Question(iv) What are non-conventional sources of energy ?
Answer:
Non-conventional sources of energy are renewable energy sources that are continuously produced in nature and are limitless. Solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, biogas and atomic energy are the examples of the non-conventional sources of energy
Question 29.
Read the Paragraph and answer the following Questions?
| India is fortunate to have fairly rich and varied mineral resources. However, these are unevenly distributed. Broadly speaking penisular rocks contain most j of the reserves of coal, metallic minerals, mica and many other non-metallic minerals. Sedimentary rocks on the western and eastern flanks of the peninsula in Gujarat and Anam have most of the petroleum deposits. Rajasthan with the rock systems of the peninsula, has reserves of many non-ferrous minerals |
Question(i) Where are most of the reserves of coal, metallic minerals, mica and many other non-metallic minerals found ?
Answer:
Peninsular rocks contain most of the reserves of coal, metallic minerals, mica, etc
Question(ii) Which mineral resources are found in abundance in the sedimentary rocks on the western and eastern flanks of the peninsula ?
Answer:
Petroleum deposits
Question(iii) In which places most of the petroleum deposits are found ?
Answer:
Gujarat, Assam and Western and Eastern flanks
Question(iv) Which state has reserves of non-ferrous minerals ?
Answer:
Rajasthan is known for reserves of non-ferrous minerals
AP 10th Class Social Geography 5th Lesson Important Questions: 2 Marks
Question 1.
Which is most abundently available fossil fuel in India ?
Answer:
Coal is most abundently available fossil fuel.
The four forms are : Anthracite, Lignite, Bituminous, Peat
Question 2.
Where are a number of minerals found in sedimentary rocks ?
Give example.
Answer:
In sedimentary rocks a number of minerals occur in beds or layers. Example are coal and some forms of iron ore
Question 3.
How do minerals occur in igneous and metamorphic rocks ?
Answer:
- In igneous and metamorphic rocks minerals occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints
- The smaller occurrences are called veins and the larger ones are called lodes
Question 4.
Why is there a pressing need to use non-conventional energy resources ?
Explain.
Answer:
- Renewable energies do not require many years for formation under the earth
Questions crust and are therefore renewable in nature
- Renewable energy sources do not cause environmental pollution with their use, and so, to preserve our environment, we must switch to using more of such sources
Question 5.
How are minerals formed in igneous and metamoiphic rocks?
Answer:
Minerals crystallize and accumulate in cracks, crevices, faults during these processes
- Molten magma cools and solidifies Into igneous rocks
- Pre-existing rocks undergo heat and pressure to form metamorphic rocks
Question 6.
What are the main petroleum reserves in India?
Answer:
Mumbai High fields off Mumbai coast
- Bassein field near Mumbai
- Ankelshwar in Gujarat
- Assam fields
- Digboi, Naharkatiya, Moran-Hugrijan
Question 7.
How does biogas help farmers?
Answer:
- Produced from cattle dung and farm waste
- Used as cooking fuel reducing wood usage
- Slurry used as manure enriching soil fertility
Question 8.
How does nuclear fission release energy?
Answer:
Unstable nuclei of heavy elements like uranium split
- Releases tremendous amount of heat energy used to generate electricity
- Very high energy output from small amounts
Question 9.
Why are fossil fuels called non-renewable?
Answer:
Formed over millions of years ago and limited reserves
- Being depleted much faster than being replenished
- Once exhausted, cannot be reused
- Unlike renewable energy derived continuously from sun, wind, water
Question 10.
Why should fossil fuel usage be reduced?
Answer:
Finite reserves, being depleted faster than formation
- Cause air pollution and greenhouse gases
- Alternative renewable energy options available
- Need for conservation and reducing carbon footprint
Question 11.
What are the features of sustainable development with respect to energy resources?
Answer:
Reduce wastage and increase efficiency of energy usage
- Minimize environmental impact
- Use renewable and non-conventional sources
- Equitable distribution and affordable access to energy
Question 12.
Why is fly ash produced in thermal power plants an environmental concern?
Answer:
Toxic heavy metals present
- Pollutes air if emitted, water if dumped in ash ponds
- Health hazards like respiratory issues
- Destroys soil fertility on deposition
Question 13.
Describe any three features of ferrous minerals found in India?
Answer:
Three features of ferrous minerals are as follows
- Ferrous minerals account for about three-fourths of the total value of the production of metallic minerals
- They provide the base for the development of metallurgical industries
- India is rich in ferrous minerals and exports substantial quantities after meeting the local demands
AP 10th Class Social Geography 5th Lesson Important Questions: 1 Mark
Question 1.
Which minerals are found in ocean water ?
Answer:
Salt and Magnesium
Question 2.
Sparkles in the toothpaste come from which mineraT?
Answer:
Mica
Question 3.
Name any two minerals which are found in veins and lodes?
Answer:
Zinc and lead
Question 4.
Which rock consists of single mineral only ?
Answer:
Limestone
Question 5.
Give some examples of energy minerals?
Answer:
Coal, petroleum and natural gas are energy minerals
Question 6.
State two types of electricity?
Answer:
Hydro-electricity and Thermal electricity
Question 7.
Which nuclear plant is situated in Tamil Nadu ?
Answer:
Kalpakkam nuclear power plant is located in Tamil Nadu
Question 8.
How do minerals occur in sedimentary rocks ?
Answer:
In beds or layers
Question 9.
Name some minerals formed in beds and layers?
Answer:
Coal and some forms of iron ore
Question 10.
Name, the minerals formed as Questionplacer depositsQuestion?
Answer:
Gold, silver, tin, platinum, etc., are formed as placer deposits
Question 11.
How is the nuclear energy obtained ?
Answer:
Nuclear energy is obtained by altering the structure of atoms
Question 12.
Which type of coal is for commercial use ?
Answer:
Bituminous coal
Question 13.
Which coal is most pure ?
Answer:
Anthracite
Question 14.
What is the general interest of geologists towards minerals ?
Answer:
geologists is mainly interested in the formation of minerals, their age and physical and chemical composition
Question 15.
What are ferrous minerals ?
Answer:
Ferrous minerals are metallic minerals containing iron. Ferrous minerals are magnetic
Question 16.
What are non-ferrous minerals ?
Answer:
Non-ferrous minerals do not contain iron and are non-metallic in nature
Question 17.
Which mineral is found in Kudremukh mines ?
Answer:
Iron - ore is found in Kudremukh mines
Question 18.
Which place is well known for effective use of wind energy ?
Answer:
Jaisalmer
Question 19.
In which form are minerals found ?
Answer:
Minerals are found in ores
Question 20.
Where are the minerals found ?
Answer:
Minerals occur in different types of rocks
Question 21.
Match the column - 1 with column - 2. [d]?
| Column - 1 (Resources) |
Column - 2 (Examples) |
I) Biological |
1. Coal |
| II) Renewable |
2. Wildlife |
| III) Non-renewable |
3. Solar Energy |
Answer:
I - 2 , II -3 , III -1
Question 22.
Match the following: [a]?
| Resources |
Examples |
| a. Renewable Resources |
I. Forests and wildlife |
| b. Non-renewable Resources |
II. The oceanic resources |
| c. National Resources |
III. Roads, canals and railway |
| d. International Resources |
IV. Minerals and fossil fuels |
Answer:
a-I, b-IV, c-III, d - II
Question 23.
Choose and write the correct option from Column A and B?
| Column- A |
Column- B |
| (a) Chandrapur Thermal power plant |
(i) Odisha |
| (b) Mayurbhanj iron ore mines |
(ii) Amarkantak |
| (c) Kalol oil fields |
(iii) Gujarat |
| (d) Bauxite mines |
(iv) Jharkhand |
Answer:
| Column- A |
Column- B |
| (a) Chandrapur Thermal power plant |
(iv) Jharkhand |
| (b) Mayurbhanj iron ore mines |
(i) Odisha |
| (c) Kalol oil fields |
(iii) Gujarat |
| (d) Bauxite mines |
(ii) Amarkantak |
Question 24.
Why should the use of cattle cake as fuel be discouraged ?
Answer:
The use of cattle cake as fuel is undesirable because, it releases harmful gases like carbon monoxide which is toxic in nature
Question 25.
What is the correct sequence of soils formed in India from north to south?
Answer:
Red soil - Laterite soil - Alluvial soil - Black soil
Question 26.
Arrange the following states in order of decreasing iron ore reserves in India:
Oddisha- Chhattisgarh. Karnataka. Jharkhand?
Answer:
Jharkhand, Odisha, Choha Hisgarh, Karnataka
Question 27.
Arrange the following states in increasing order of bauxite production.
Odisha, Jharkhand, Gujarat, Ghhattisgarh?
Answer:
Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Gujarat
Question 28.
Arrange the following industries in order of decreasing employment generation.
Jute, Textiles. Tea. Iron and Steel?
Answer:
Tea, jute, iron and steel, textiles
Question 29.
Write the correct sequence of human evolution?
Answer:
Australopithecus - Homohabilis - Homoerectus - Homosapiens
Question 30.
Define the term mineralQuestion?
Answer:
Geologists define mineral as a "homogeneous naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure"
Question 31.
How are QuestionGobar gas plantsQuestion beneficial to the farmers ?
Answer:
"Gobar gas plants
Question are beneficial to the farmers in the form of energy and improved quality of manure
Question 32.
State some product/things we use that are made of metals?
Answer:
Railway lines, a tiny pin, machinery, cars, etc., are all made of metals
Question 33.
Name the minerals which do the cleaning work?
Answer:
Silica, oxide and phosphate minerals do the cleaning work
Question 34.
How do Geographers study minerals ?
Answer:
Geographers study minerals as part of the earth
Questions crust for a better understanding of land forms
Question 35.
State some of the non-metallic minerals?
Answer:
Non-metallic minerals are mica, salt, potash, sulphur, granite, limestone, marble sand stone, etc
Question 36.
What is an QuestionoreQuestion ?
Answer:
The term
QuestionoreQuestion is used to describe an accumulation of any material mixed with other elements
Question 37.
Which minerals are formed as a result of evaporation ?
Name any two?
Answer:
Potash salt and sodium salt
Question 38.
Which reserves of minerals are-found in peninsular rocks?
Answer:
Peninsular rocks contain most of the reserves of coal metallic minerals mica and many other non-metallic minerals
Question 39.
What is the advantage of copperQuestions use in electrical cables ?
Answer:
The copper is malleable, ductile - and good conductor and therefore its use is advantageous in electrical cables
Question 40.
How are bauxite deposits formed ?
Answer:
Bauxite deposits are formed by the decomposition of a wide variety of rocks rich in aluminium silicates
Question 41.
Which are non-conventional source of energy ?
Mention any three.
Answer:
Non-conventional source of energy are solar, wind, biogas, tidal energy
Question 42.
What is geothermal energy ?
Answer:
Geothermal energy refers to the heat and electricity produced by using the heat from the interior of the earth