Agriculture AP 10th Class Social Geography 4th Lesson Important Questions
AP 10th Class Social Geography 4th Lesson Important Questions: 8 Marks
Question 1.
Discuss the cropping patterns prevalent in India Why cropping pattern is important in India ?
Answer:
The cropping pattern in India is discussed as follows
- India has three main cropping seasons Kharif, Rabi and Zaid
- Kharif crops are sown during the onset of the mbnsoon season
- Rabi season begins with the onset of winter
- There is a short cropping season between Rabi and Kharif called Zaid
Importance of cropping pattern
- It increases soil fertility
- It increases crop yield
- It allows the land to regenerate and rejuvenate its self-nutrients, ie, increases soil nutrients
- Reduces soil erosion
- Improves the soil structure
- Diversification and Reduced cost of production, it helps the distribute the workload and resources used throughout the year for which cost of production of the crops decreases to a certain extent
Question 2.
Why is jute called the golden fibre, where is it grown in India and why ?
Answer:
- Jute is considered as the golden fibre because of its shiny brown colour
- It is most affordable natural fiber and is 100% biodegredable
- It is a cash crop and can be very profitable for the economy as its export can bring in a lot of money into the economy
- It is made of cellulose and lignin plant material
- Fertile region necessary for jute production is shared by India and Bangladesh
- It is the second most important natural fiber after cotton and now at present its demand has risen in India and also all around the world
Question 3.
What is the significance of Bhoodan and Gramdan ?
Answer:
- Vinoba Bhave was declared by Mahatma Gandhis spiritual heir He participated in Satyagraha and was a follower of Gandhis concept of Gram Swarajya
- After Gandhis death, Vinoba Bhave undertook a Padayatra to spread Gandhis message across India
- In Pochampalli, some poor landless villagers demanded land for their economic well-being and Vinoba Bhave suggested cooperate farming to the government as a solution
- Shri Ram Chandra Reddy stood up and offered 80 acres of land to be distributed among 80 landless villagers, which was known as Bhoodan
- Later, Vinoba Bhave traveled and introduced his ideas widely all over India and some Zamindars offered to distribute some villages among the landless, known as Gramdan
- This movement initiated by Vinoba Bhave is also known as the Bhoodan and Gramdan movement or the Blood-less Revolution
Question 4.
What is the Difference between Rabi and Kharif crops ?
Answer:
The difference between the Rabi and Kharif crop is as follows
| Rabi crop |
Kharif Crop |
| Rabi crops are sown during October / November the end of the monsoon |
Kharif crops are sown in Summer (June - July) |
| Harvested in Spring (March - April) |
Harvested in Autumn (September - October) |
| Warm and wet conditions, high rainfall |
Cooler temperatures, moderate moisture |
| Kharif crops are short-day plants |
Rabi Crops are long-day plants |
| Kharif crops are known as monsoon crops |
Rabi crops are known as Spring crops |
| Examples : Wheat, Peas, Gram, Mustard, Barley, etc |
Examples: Rice, Arhar, Maize, Blackgram etc |
Question 5.
Write the difference between Primitive Subsistence Farming and Intensive Subsistence Farming?
Answer:
| Primitive Subsistence Farming |
Intensive Subsistence Farming |
| 1) It is one of the earliest farming methods to be trained because it utilises primitive tools and is carried out on a small scale |
1) In this type of farming the farmer cultivates a small plot of land using simple tools and more labour |
| 2) primitive tools like a hoe, dow, digging sticks are used for cultivation |
2) Modern agricultural inputs like chemical fertilizers, HYV seeds, machines are used wherever suitable |
| 3) This agriculture is dependent on rainfall apd the natural fertility of the soil |
3) Means of irrigation like tube wells, canals, are used Soil fertility is also increased by the use of fertilizers |
| 4) Family members provide labour |
4) Labourers are hired |
| 5) Land productivity in this type of agriculture is low |
5) Land productivity in this type of agriculture is high as it is meant for commercial purpose |
Question 6.
What are the favourable climatic conditions required for the production of rubber?
Answer:
Rubber cultivation requires certain favourable conditions to ensure healthy growth of the rubber trees and high rubber yieTtlSome of these conditions include
- Rubber trees thrive in regions with a warm and humid tropical climate with an average temperature of 27 - 35 degree Celsius The annual rainfall should be between 1500- 3000 mm and evenly distributed throughout the year
- Soil type : Rubber trees grow best in well - drained, fertile soil with a pH of 45 to 60 They prefer sandy loam soils with good drainage and high organic content
- Altitude: Rubber trees can grow at an altitude of upto 1000 meters above sea level
- Sunlight: Rubber trees required full sunlight for optimal growth and yield Kerala, Tamilnadu, Karnataka, Tripura, Assam and other some other states such as Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland are the major producers of natural rubber in the world
Question 7.
Explain the features of intensive subsistence and plantation farming in India?
Answer:
Intensive farming: It is a type of farming in which the agricultural production is increased by using scientific methods and better agricultural inputs
Features:
- HYV seeds and modern inputs are used to increase the production
- More than one crop is cultivated during a year
- It is practised in thickly populated areas
- The per hectare yield is very high
Plantation farming:
This is a type of agriculture which involve growing and processing of a single cash crop purely meant for sale Rubber, tea, coffee, spices, coconut and fruits are some of the important crops which come under the category of plantation agriculture
Features:
- It is a single crop farming
- It is a capital intensive farming, ie, a huge amount of capital is required
- It needs vast estates, managerial ability, technical know-how, sophisticated machinery, fertilisers, good transport facilities and a factory for processing
- This type of agriculture has developed in areas of north-eastern India, Sub-Himalayan region, West Bengal and Nilgiri
Question 8.
Compare intensive subsistence farming;! with that of commercial farming Practiced in India?
Answer:
| intensive Subsistence farming |
commercial farming |
| i) Here, crops produced by the farmers are mainly consumed by their families Surplus production is sold in the nearby local markets |
i) Here, the farmers grow crops for the purpose of trade, it is called commercial farming |
| ii) More than one crop is cultivated in the agricultural field |
ii) One crop is cultivated in the field |
| iii) It is labour intensive farming |
iii) Farming is mechanised, and is prevalent in areas where farms are large and market economy is well developed |
| iv)It depends on monsoon |
iv) It uses modern irrigation methods |
| v) It is practiced in small area |
v) It ispracticed in large area |
| vi)Major crops are: Food grains, fruits and vegetables |
vi) Major crops are: cash crops and cereals |
Question 9.
Name the two major beverage crops grown in India Describe their growing areas?
Answer:
The two most important beverage crops of India are tea and coffee
- Tea:
Assam is a major tea producing state in India along with West Bengal, Kerala and Tamil Nadu The cropping season begins as early as March and extends almost to mid- December
- The tea plant grows in tropical and sub-tropical climates
- Tea bushes require moist, frost-free and warm climate all through the year
- It requires deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter
- Conditions required for tea cultivation
- Temperature 10-30 degrees Celsius
- Rainfall-average yearly rainfall of 200 cm
- Altitude ground level of between 600-2000 m above sea level
- Coffee:
It isa tropical plant grown in semi-tropical climate Coffee tree requires heat, humidity and abundant rainfall
In India, coffee is traditionally grown in the Western Ghats spread over Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu Karnataka is the largest producer accounting for about 70% of the total coffee production
- The temperature of the place is 23°C to 28°C
- Bright sunshine and warm weather are necessary for the harvesting
- Requires rainfall between 60-85 inches but water stagnation is very harmful for coffee plants
Soil requires presence of humus and other nitrogenous matter
AP 10th Class Social Geography 4th Lesson Important Questions: 4 Marks
Question 1.
Mention any three features of slash, and burn agriculture?
Answer:
The three features of slash and burn agriculture are as follows
- Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family
- When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation
- India has tropical climate with ample sunshine So, we have a long growing season
Question 2.
What is commercial farming Mention its major features?
Answer:
Commercial farming is a type of farming under which farmers grow crops to sell in the market
Features:
- Farmers use higher doses of modern inputs, eg High Yielding Variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides, etc
- Per hectare the productivity rate is very high
- Rice, sugarcane, tea, coffee are the major crops which are grown under this
Question 3.
Why is subsistence agriculture still practised in certain parts of the country ?
(Or)
What is primitive (subsistence) farming Write any four features of subsistence farming
Answer:
A farming in which the main production is consumed by the farmers household is known as subsistence farming
Features:
- Old technology and traditional implements are used
- Agricultural fields are smaff ancf farmers possess scattered land holdings
- Most of the farmers are poor and do not use fertilizers and HYV seeds
- The overall productivity is very low
Question 4.
What is intensive farming write some features of intensive farming ?
Answer:
Intensive farming : It is a type of farming in which the agricultural production is increased by using scientific methods and better agricultural inputs
Features:
- HYV seeds and modern inputs are used to increase the production
- More than one crop is cultivatedduring a year
- It is practised in thickly populated areas
- Per hectare the yield is very high
Question 5.
Name the most important beverage crop of India Describe the suitable climatic conditions required for its growth Also mention the major states producing that crop?
Answer:
Tea is the most important beverage crop of India
Climatic conditions
- Temperature : The tea plants grows well in tropical and sub tropical climate Tea bushes require warm and moist, frost free climate all through the year Tea bushes need temperature of more than 25° C
- Rainfall : Tea plant needs heavy rainfall ranging between 150 cm to 250 cm The rainfall should be well distributed throughout the year
- Soil: The plant requires a light loamy soil The soil should be rich in humus and iron content Tea is a soil exhausting crop, so frequent use of chemical fertilisers and manure is essential
Producers : Major tea - producing states are Assam, West Bengal, (Hills of Darjeeling and Japaigurf districts), Tamilnadu and Kerala Apart from these, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh and Tripura are also tea producing states in the country
Question 6.
Name one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced?
Answer:
- Rice is a staple food crop in India It grows in the Indo-Gangetic plain and north-east India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions
- The major rice producing areas are northern plain and coastal and deltaic regions while minof rice producing areas are Punjab plain and part of Deccan plateau
- Development of a dense network of canal irrigation and tube wells have made it possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall such as Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan
Question 7.
What are the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers ?
Answer:
The various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government for the benefit of formers are
- Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, fire disease etc
- Establishment of Gram een banks, cooperative societies and bank for providing loan facilities to the farmers at a lower rate of interest Government also announces minimum support price
- Subsidy on agricultural inputs and resources such as power and fertilisers
- Facilities of Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme
- Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers were introduced On radio and television
Question 8.
Explain any four factors which have hindered the pace of agricultural development in India?
Answer:
- Over crowding in agriculture : The real problem of Indian agriculture is that there are too many people who depend on agriculture Since 1901, the proportion of people dependent on agriculture has almost remained constant, ie, 70%
- Problem of inputs : Indian agriculture suffered because of the inadequacy of finance,, seeds, fertilizers, marketing, transportation etc
- Size of land holdings : The average size of land holding in India is very low, less than 2 hectares or 5 acres Not only agricultural holdings are small, but they are also fragmented Op certain parts of the country, plots of land have become so small that it is impossible to use modern machinery
- Over dependence on nature : Inspite of the development of sources of irrigation, most of the farmers in large parts of the country still depend upon monsoon and natural fertility in order to carry on their agriculture
Question 9.
The decline share of agriculture in the GDP is a matter of serious concern" Explain?
Answer:
- More than half the population of Indias work force is employed by the farm sector
- Any decline in the share of agriculture means low production of foodgrains this may lead to food shortage
- Any decline and stagnation in agriculture will lead to a decline in other spheres of the economy having wider implications for society
Question 10.
Give an account of soil-seeds in India State the importance of groundnut and name the states where it is grown?
Answer:
- India is the largest producer of oil-seeds in the world
- Different types of oilseeds are grown covering approximately 12 percent of the total cropped area of India
- India is an important producer of groundnut, mustard, coconut, sesamum, soyabean, castor seeds, cotton seeds, linseed and sunflower
- Most of these are edible and used as cooking medium and some of these are also used as raw materials in the production of soap, cosmetics and ointments
- Groundnut is a Kharif crop and accounts for about half of the major oilseeds produced in the country
- Andhra Pradesh is the largest producer of groundnut It is also grown in Tamilnadu, Karnataka, Gujarat and Maharashtra
Question 11.
What Is the importance of agriculture in Indian economy ?
Answer:
- Agricultureis the mainstay of Indian economy because about 60% of our population depends directly or indirectly on agriculture
- It provides raw materials to the industries
- India earns foreign exchange by exporting agricultural products
- It contributes about 29% to the Gross Domestic Product
- It provides food to over 12102 million population
Question 12.
What is plantation agriculture ?
Write some features of the plantation agriculture?
- This is a type of agriculture which involves growing and processing of a single cash crop purely meant for sale
- Rubber, tea, coffee, spices, coconut and fruits are some of the important crops which come under the category of plantation agriculture
Features:
It is a single crop farming
It is a capital intensive farming, ie, a huge amount of capital is required
It needs vast estates, managerial ability, technical know-how, sophisticated machinery, fertilisers, good transport facilities and a factory for processing
This type of agriculture has developed in areas of north-eartern India, sub-Himalayan - region, West Bengal and Nilgiri
Question 13.
Describe any four geographical conditions required for the growth of sugarcane?
Answer:
The following geographical conditions are required for the cultivation of sugarcane:
- It is a tropical as well as subtropical crop
- It grows well in hot and temperature of 21° C to 27° C It required an annual rainfall between 75 cm and 100 cm
- In areas of less rainfall, it requires irrigation
- It can be grown on a variety of soils It needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting and is a long duration crop
- The major sugarcane - producing states are Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamilnadu, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab and Haryana
- It is the main source of sugar, gur (jaggery), Khandsari and molasses
- India is the second largest producer of sugarcane only after Brazil
Question 14.
Describe any three main features of Rabi crop season?
Answer:
Features of Rabi crop season :
- Rabi crops are sown in the winter months of October through December
- At the time of harvesting, it requires bright sunshine and is harvested is summer from April to June
- Crops depend on sub-soil moisture
- Requires less rainfall between 50-75 cm Availability of precipitation during winter months due to western temperate cyclones help in success of these crops
- Major Rabi crops are wheat, gram, peas, barley etc
Question 15.
Describe any three main features of Kharif crop season?
Answer:
Features of Kharif crop season :
- It was sown with the onset of the monsoon in May
- Crops are harvested in September-October
- Requires more rainfall between 100-110 cm and requires a lost of water and hot weather to grow
- It requires loamy or alluvial soil
- Rice, maize, pulses such as urad, moong dal and millets are among the key kharif crops
Question 16.
Explain any three institutional reforms taken for the development of India agriculture?
Answer:
Institutional reforms are the term used to describe the governments efforts to alter the agricultural industry These are as follows
- The government introduced various land reforms, such as collectivization, holding consolidation, cooperation, and zamindari abolition
- Land development programmes such as the construction of Grameen banks, cooperative societies, and banks to offer farmers lending opportunities at cheaper interest rates
- Providing crop insurance to protect farmers from damages brought on by natural calamities like fires, cyclones, fires, and droughts
- Specific radio and radio weather reports, as well as agricultural programmes, have been introduced
Question 17.
Read the source given below and answer the following Questions?
| Jhumming: The slash and burn agricultures known as Milpa in Central America, Conucoin Venzuela, Roca in Brazil, Masola in Central Africa, LadangiftMdonesia, Royin Vietnam
In India, this primitive form of cultivation is called Bewaror Dahiya in Madhya Pradesh, Podu or Penda in Andhra Pradesh, Pama Dabi or Koman or Bringa in Odisha, Kumari in Western Ghats, Valre of Waltre in South-eastern Rajasthan, Khil in the Himalayan belt, Kuruwa in Jharkhand, and Jhummmg in the North-eastern region |
Question(1) How is Primitive Subsistence Agriculture related with Jhumming ?
Answer:
Primitive subsistence agriculture is also known as shifting cultivation or slash and burn cultivation A patch of land is cleared and then set on fire This patch of land is used to sow seeds and grow crops
Question(2) The slash and burn agriculture is known as Conuco in which country ?
Answer:
The slash and burn agriculture is known as Conuco in Venezuela
Question(3) The slash and burn agriculture is known as Roca in which country ?
Answer:
The slash and burn agriculture is known as Roca in Brazil
Question(4) What is the major problem of Jhumming cultivation ?
Answer:
Low production is the major problem of Jhumming cultivation
Question(5) In India slash and burn agriculture is known as Bewar, in which state ?
Answer:
The Slash and burn agriculture is known as Bewar in Madhya Pradesh
Question(6) Match Column I with Column II?
| Column - I |
Column - II |
| I) Andhra Pradesh |
A) Kuruwa |
| II) Odisha |
B) Valre |
| III) Rajasthan |
C) Penda |
| IV) Jharkhand |
D) Pama Dabi |
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh - Penda
Odhisa - Pama Dabi
Rajasthan - Valre
Jharkhand - Kuruwa
Question 18.
What are some traditional practices of water conservation in agriculture?
Answer:
Traditional practices of water conservation
- Earthen bunds and properly lined canals
- Watershed management and check dams
- Bamboo drip irrigation, in Meghalaya
- Kulhs in hill slopes to collect water
- Community participation and indigenous systems
Question 19.
What are the major challenges faced by Indian agriculture?
Answer:
Challenges Faced by Indian Agriculture
- Small and fragmented landholdings with poor mechanization
- Dependence on monsoons and lack of irrigation facilities
- Low productivity of crops compared to global standards
- Lack of access to formal institutional credit, leading to indebtedness
- Overuse of chemical inputs leading to environmental sustainability issues
- Lack of storage, processing, and marketing infrastructure
- Distress migration and farmer suicides in some regions
Question 20.
How can the rural credit system be strengthened for provision of credit to farmers?
Answer:
Strengthening Rural Credit System
- Expanding outreach of cooperative and rural banks
- Simplifying lending procedures and relaxing collateral requirements
- Introducing and expanding Kisan Credit Card scheme
- Providing crop insurance against disasters and loan waivers
- Promoting Self-Help Groups and microfinance initiatives
- Developing financial literacy and marketing skills of farmers
Question 21.
How can agriculture be made ecologically sustainable?
Explain
Answer:
Making Agriculture Ecologically Sustainable
- Reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers and pesticides
- Promoting organic manures, biofertilizers, and natural pest control
- Crop diversification and rotation techniques
- Water conservation through rainwater harvesting
- Integrated farming systems with horticulture and livestock rearing
- Conserving indigenous crop varieties and livestock breeds
- Community-managed sustainable agricultural practices
Question 22.
How can the credit needs of farmers be served in a better manner?
Answer:
Serving Credit Needs of Farmers
- Strengthening cooperative and rural banking institutions to enhance outreach
- Simplifying lending procedures and relaxing collateral requirements
- Expanding Kisan Credit Card scheme tomeet short term credit needs
- Crop insurance to safeguard against weather risks and loan waivers
- Promoting SHGs and microfinance for small and marginal farmers
- Developing financial literacy and marketing skills of farmers
Question 23.
Read the given para and answer the following Questions?
| India has a diverse climate that allows for cultivation of a wide variety of crops The northern plains and central parts of the country are important far growing wheat, while rice is a major crop grown in the northeast, coastal and southern regions Maim is cultivated in several states including Karnataka Madhya Pradesh and Bihar among others Pulses like tur, grad and moong are grown in the dry regions of central and northern India |
Question(i) Which parts of India are important for wheat cultivation?
Answer:
The northern plains and central parts of India are important for wheat cultivation
Question(ii) Which region is a major producer of rice in India?
Answer:
Rice is a major crop grown in the northeast, coastal and southern regions of India
Question(iii) Name three states where maize is cultivated?
Answer:
Some states where maize is cultivated are Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Bihar
Question(iv) Where are pulses like tur, urad and moong mainly grown in India?
Answer:
Pulses like tur, urad and moong are mainly grown in the dry regions of central and northern India
Question 24
Read the given para and answer the following Questions?
| India is the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables fa the warty after China It is a leading producer of tropical fruits like mangoes, bananas, guavas and citrus fruits SubtrbpicatfafafatiUegrapes, apples, peachei, plums and almonds are also grown in parts of the Himnlayas and Nitgirls Major vegetable crops are potatoes, onions, tomatoes, cauliflower, cabbage and peas |
Question(i) Which country is the largest producer of fruits and vegetables in the world?
Answer:
China is the largest producer of fruits and vegetables in the world
Question(ii) Name two tropical fruits grown in India?
Answer:
Mangoes and bananas are two major tropical fruits grown in India
Question(iii) Which hill regions are important for growing apples in India?
Answer:
Apples are grown in parts of the Himalayas and Nilgiris
Question(iv) Name any two major vegetable crops of India?
Answer:
Major vegetable crops of India include potatoes, onions, tomatoes and cauliflower range of benefits such as irrigation, flood control, hydropower production, and water supply
Question 25.
Mark and colour the rice growing areas in the given map of India?
Answer:
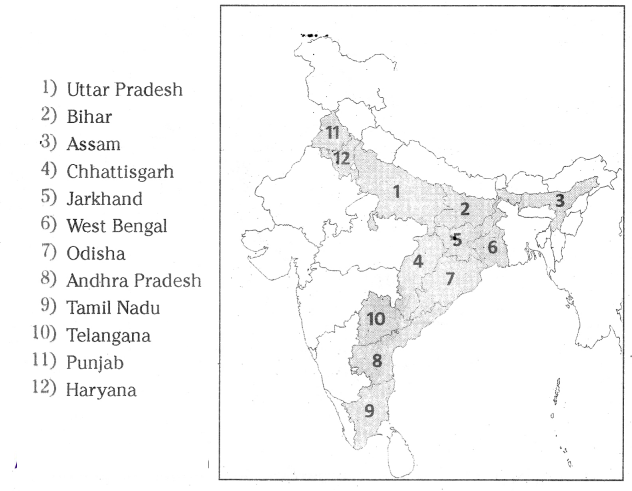
Question 26.
Locate wheat growing states and color them in the given map of India?
Answer: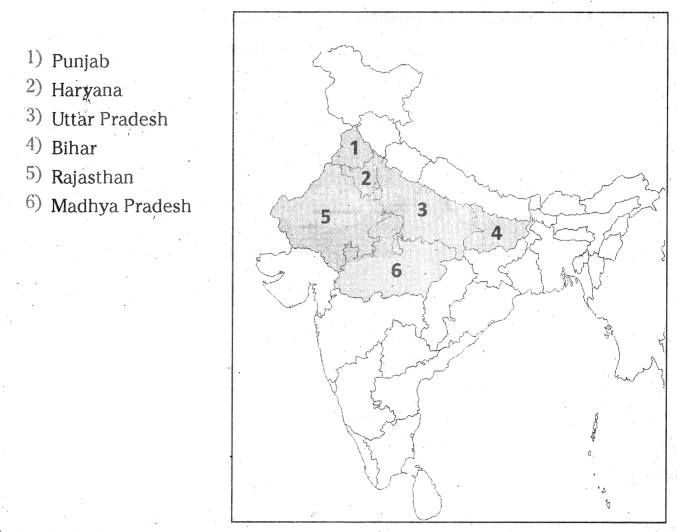
Question 27.
Mark the major coffee grown states in India map?
Answer:
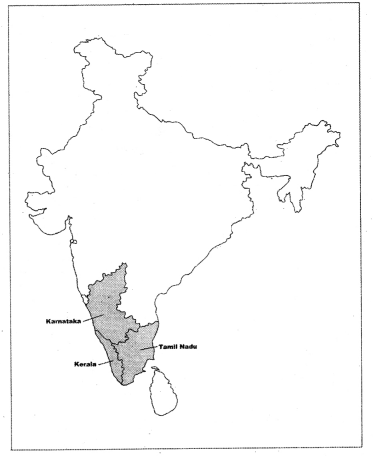
Question 28.
Locate the largest produce states of surgarcane, tea, rubber and jute on the outline map of India
Sugarcane : Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra
Tea : Assam, West Bengal
Rubber : Kerala, Karnataka
Jute : West Bengal, Bihar?
Answer:
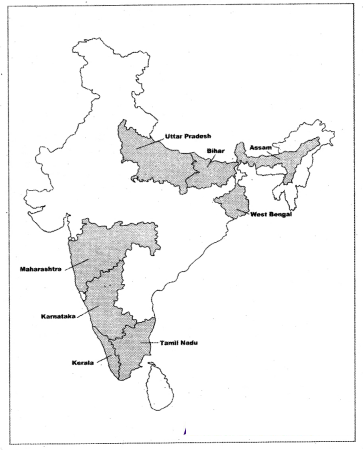
Question 29.
Locate the following points in the India map
Iron ore mines ; Mayurbhanj, Durg, Baiiadila, Bellary, Kudremukh
Mica mines : Ajmer, Beawar, Nellore-, Gaya, Hazaribagh?
Answer:
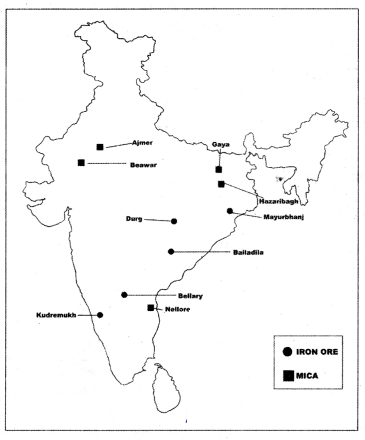
Question 30.
Read the given source and answer the following Questions?
| Plantation is also a type of commercial farming In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area The plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry Plantations cover large tracts of lands Using capital intensive inputs with the help migrant labourers All the produce is used as raw-material in respective industries |
Question(i) What is plantation agriculture ?
Answer:
Plantation is a type of commercial farming, in which a single crop is grown on large area
Question(ii) Explain the three important features of plantation agriculture in India?
Answer:
The three important features of plantation agriculture in India
- In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area
- The plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry
- Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers
Question(iii) Why are plantation crops essential ?
Answer:
These plantations crops are essential because these crops are high; value commercial crops of greater economic importance
Question 31
Read the given source and answer the following Questions
Primitive Subsistence agriculture is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks, and family community labour This type of farming depends upon monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown It is a slash and burn agriculture Farmers clear a patch of land produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family?
Question(i) What is Primitive Subsistence agriculture ?
Answer:
Primitive subsistence agriculture is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks and family community labour
Question(ii) Why Primitive Subsistence farming is also called as slash and burn agriculture ?
Answer:
Primitive subsistence farming is also called slash and burn agriculture or shifting cultivation In this farming a patch of land is cleared by slashing the vegetation and then the slashed plants are burnt
Question (iii) What is slash and burn method ?
Answer:
Slash and burn is a method of farming that involves cleaning land by destroying and burning all the trees and plants on it for a short time and then moving on to clear a new piece of land
Question 32.
Read the given source and answer the following Questions
Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June Some of the important rabi crops are wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard Though these crops are grown in large parts of India, states, from the north and north-western parts such as Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are important for the production of wheat and other rabi crops
Availability of precipitation during winter months due to the western temperature cyclones helps in the success of these crops However, thesuccess of the green revolution inPunjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan has also been an important factor in the growth of the above mentioned rabi crops?
Question(i) What is the sowing period of rabi crops ?
Answer:
Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June
Question(ii) Where are Rabi crops grown in India ?
Answer:
Rabi crops are grown in Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh etc
Question(iii) What are the Rabi crops grown in India ?
Answer:
Some of the rabi crops grown in India are wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard
AP 10th Class Social Geography 4th Lesson Important Questions: 2 Marks
Question 1.
Name the cropping seasons of India with examples?
Answer:
- Rabi- Wheat
- Kharif - Paddy
- Zaid - Watermelon
Question 2.
List two characteristics of Green Revolution?
Answer:
- Increase in production of wheat and rice
- Use of high yielding varieties of wheat and rice
Question 3.
What is wet land farming ?
Answer:
It is a type of farming which is practised in high rainfall and irrigated areas, eg cultivation of rice and sugarcane
Question 4.
What is dry land farming ?
Answer:
It is a type of farming which is practised in scanty rainfall areas and where irrigation facilities are inadequate, eg cultivation of jowar and bajra
Question 5.
Name two schemes introduced by the Government of India for the benefit of the farmers?
Answer:
- Kissan Credit Card (KCC) were introduced
- Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) was also introduced
Question 6.
Why should the production of pulses be increased ?
Give two reasons?
Answer:
- These are the major sources of protein for most of the people
- These plants help in restoring the fertility of the soil
Question 7.
What is the period of Kharif crop ?
Answer:
Kharif season starts with the onset of the monsoon ie, June - July and continues till the beginning of winter ie, October - November For example, rice, millets, etc
Question 8.
What is primitive subsistence farming ?
Answer:
It is a type of agriculture which is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools like hoe, doa, digging sticks and family or community labour
Question 9.
What is agriculture ?
Answer:
The art and science of cultivating soil, raising crops and rearing livestock including animal husbandry and forestry
Question 10.
What is slash and burn agriculture ?
Answer:
Under slash and burn agriculture, farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family
Question 11.
What are rabi crops ?
Give four examples?
Answer:
The crops which are grown in Winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June Wheat, Barley, Peas, Gram are some examples of rabi crops
Question 12.
What are Zaid Crops ?
Answer:
These are crops which are sown between the rabi and kharif crops Watermelon, musk- melon, cucumber and vegetables are some examples of zaid crops
Question 13.
What is package technology ?
What was its result ?
Answer:
Under package technology combination or package of many improved methods of cultivation are adopted simultaneously in order to increase agricultural production This lead to Green Revolution
Question 14.
Name the two most important food crops of India Name any states where they are produced ?
Answer:
- The most important food crops of India are rice and wheat
- Major areas where rice is grown are: Bengal, Bihar, Assam, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh
- Major areas where wheat is grown are - Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh
Question 15.
Traders and travelers introduced new crops to lands they travelled" Substantiate this statement with illustrations?
Answer:
- Traders who travelled across the countries introduced new crops from their own places
- Best example which shows this is noodles which travelled from China through Arab traders to Sicily and potato reached the West through travellers and became the staple diet of the poor
Question 16.
Mr Palani is from Tamil Nadu, wishes to cultivate either Tea or Wheat Which one of the crops out of the two can he cultivate in his state Substantiate your answer with any two reasons?
Answer:
Mr Palani can grow tea in Tamil Nadu because of the following reasons
- Tamil Nadu does not cultivate wheat Because the temperature in these areas does not fall to the required level, the temperature should not rise beyond 10° to 15° C from proper growth
- Tamil Nadu has all the things required for the cultivation of tea, such as well-drained soil with a high amount of organic matter bond a pH of 45 to 55 The performance of tea is excellent at elevations ranging from 1000 to 2500 m Optimum temperature: 20-27° C
Question 17.
Write the amount of annual rainfall required for the cultivation of wheat?
Answer:
- Wheat requires rainfall of about 50 cm to 90 cm is most ideal
- The optimum temperature range for ideal germ in ation of wheat seed in 20-25°C though the seeds can germinate in the temperature range 35 to 35°C
- Rains just after sowing hamper germination and encourage seedling blight
- Areas with a warm and damp climate are not suited for wheat growing
Question 18.
Complete the following table with correct information for A and B?
| Annual Rainfall required |
Climate |
Temperature required for its growth (in degrees) |
| Sugar Cane crop |
A - ? |
Hot and Humid |
B - ? |
Answer:
A-75-100 cm
B-About 21-27° above 25°
Question 19
Name some important fibre crops of India and their uses?
Answer:
Important fiber crops and their uses:
- Cotton : used in the textile industry, leader in Gujarat
- Jute : used for packaging and sacks, leader in West Bengal
- Hemp : used for ropes and sacking
- Silk : used for fabric and sarees
Question 20.
What are some geographical requirements for growth of sugarcane?
Answer:
Geographical requirements for growing sugarcane
- Tropical crop, needs warm and humid climate
- Rainfall between 75-100 cm and temperature between 21°C to 27°C
- Well-drained fertile soils, irrigation
- Largest producer in Uttar Pradesh
Question 21.
Which are some major oilseed crops of India?
Answer:
Major oilseed crops:
- Groundnut : Leader in Gujarat and Tamil Nadu
- Rapeseed : Produced after Canada and China
- Sesamum : Kharif crop in north and rabi crop in South India
- Soyabean : Leader in Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra
Question 22.
What are some institutional reforms introduced in agriculture?
Answer:
Institutional reforms
- Collectivization and consolidation of land holdings
- Cooperatives and rural banks for credit access
- Regulated markets, minimum support price
- Crop insurance against droughts, floods, etc
AP 10th Class Social Geography 4th Lesson Important Questions: 1 Mark
Question 1.
Which is the Kharif crop account for about half of the major oilseeds produced in the country?
Answer:
Groundnut
Question 2.
Who offered 80 acres of land to landless villagers ?
Answer:
Shri Ram Chandra Reddy
Question 3.
Which crop is used both as food and fodder ?
Answer:
Maize
Question 4.
Name some primitive tools used in slash and bum agriculture?
Answer:
Tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks
Question 5.
What are called coarse grains ?
Answer:
Millets are called coarse grains
Question 6.
What is horticulture ?
Answer:
Cultivation of fruits, vegetables and flowers is called horticulture
Question 7.
Which fibre crop is called as the Golden Fibre ?
Answer:
Jute is known as the golden fibre
Question 8.
Which state is the largest producer of bajra ?
Answer:
Rajasthan
Question 9.
Which crop is a major source of protein in a vegetarian diet ?
Answer:
Pulses
Question 10.
What percentage of our cropped area is covered by oilseeds ?
Answer:
12%
Question 11.
Which crop is an important raw material for automobile industry ?
Answer:
Rubber
Question 12.
Which is the most important occupation of the people of India ?
Answer:
Agriculture
Question 13.
What is Primitive Subsistence Farming known as in north-eastern states like Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland ?
Answer:
Jhumming
Question 14.
Name any two states where commercial farming is practised?
Answer:
Punjab and Haryana
Question 15.
Mention any four plantation crops produced in India?
Answer:
Tea, Coffee, Rubber and Sugarcane
Question 16.
Choose the correctly matched pair [c]?
Answer:
- Primitive subsistence farming - practised on large patches of land
- Intensive subsistence farming - single crop production farming
- Commercial farming - use of higher doses of modern inputs
- Plantation farming - practised on small patches of land
Question 17.
Write name of the crop with the help of the following information
It is a crop which is used both as food and fodder
It is a Kharif crop which requires temperature between 21°C to 27°C
It grown well in old alluvial soil
Use of modern inputs have contributed to the increasing production of this crop?
Answer:
Maize
Question 18.
Choose the correctly matched pair about the crops and the areas they are grown in (c)?
- Groundnut-Assam
- Tea-Gujarat
- Coffee-Karnataka
- Sugarcane-Chhattisgarh
Question 19.
Two statements are given below as Assertion (A) and Reasoning (R)
Assertion (A) : Indian farmers should diversify their cropping pattern from cereals to high value crops
Reason (R) : This will increase income and reduce environmental degradation simultaneously
Read the statements and choose the correct option ?
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
- (A) is true but (R) is false
- (A) is false but (R) is true
Answer:
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Question 20.
Why do MNCs set up their offices and factories in those regions where they get cheap labour and other resources ?
Answer:
MNCs set up their offices and factories in those regions where they get cheap labour and other resources to minimise the cost of production and maximise profit earning
Question 21.
What may be a developmental goal of farmers who depend only on rain for growing crops ?
Answer:
To have access to better water harvesting and irrigation techniques or be compensated in the absence of rain
Question 22.
What is sericulture?
Answer:
It is the process of rearing silkworms for silk production
Question 23.
Which crop requires warm and humid climate?
Answer:
Sugarcane, which also requires irrigation
Question 24.
Which crop saw the Green Revolution?
Answer:
Wheat and high-yielding varieties of seeds
Question 25.
What is White Revolution ?
Answer:
Increase in production of milk is known as white revolution It is also known as operation flood
Question 26.
What is sericulture ?
Answer:
Rearing of silkworms for the production of silk fibre is known as sericulture
Question 27.
What is intensive subsistence farming ?
Answer:
It is a type of farming practised in areas with high density of population using modern inputs