Resources and Development AP 10th Class Social Geography 1st Lesson Important Questions
Question 1.
Classify resources on the basis of ownership with example?
Answer:
- Individual Resources : These are owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is alloted to them by government against the payment of revenue. People own plots, houses and other property etc
- Community Owned Resources : There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons, public parks, burial ground, play ground in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there
- National resources: All the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal power to acquire even private property for public good. We have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land
- International Resources: There are international institutions which regulate som resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the exclusive Economic zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilize these without the concurrence of international institutions
Question 2.
Why is resource planning important in the context of a country like India ?
Answer:
- India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources
- There are regions which are rich in certain types of resources but are deficient in some other resources
- There are some regions which can be considered self sufficient in terms of the availability of resources and there are some regions which have acute shortage of some vital resources
- For example, the states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits. Arunachal Pradesh has abundance of water resources but lacks infrastructural development
- The state of Rajasthan is very well endowed with solar and wind energy but lacks in water resources
- The cold desert of Ladakh is entirely isolated from the rest of the country
Question 3.
Which type of soil is ideal for growth of cotton ? What are the main characteristics of this type of soil ? Name some areas where they found ?
Answer:
Black soil is ideal for the growth of cotton soil. Following are its characteristics
- Black soils are also known as regur soils or black cotton soils
- Such a soil is ideal for growing cotton and hence the name
- They have extremely good moisture retention capacity but become sticky when wet
- These Soils are difficult work upon unless tilled during pre-monsoon periods or just after the first shower
- Black soils are rich irt!S6il nutrients such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime but poor in phosphoric contents
- This soil is found in Deccan trap areas. This includes Maharashtra, Western Madhya Prattesli, Gujarat and Chhattisgarh, some parts of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Tamilnadu
Question 4.
What is meant by resources ? Mention the four basis to calssify the resources?
Answer:
Resource
- Everything that is available in otrr environment which can be used to satisfy our needs is called a Resource. Resouces are technological accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable. Examples are coal, minerals, forest, land, water, fossil fuels etc
- Resources are classified as follows
- On the basis of origin
- Biotic : Living resources like plants etc
- Abiotic : Non-living resources like solar energy, land etc
- On the basis of exhaustibility
- Renewable : Which can be recreated like soalr energy etc
- Non-Renewable : Which cannot be recreate like fossil fuels
- On the basis of ownership
- Individual (Personal): Owned by an individual person
- Community: Owned by the whole community
- National: Owned by a country
- International: Accessed by all nations
- On the basis of status of development
- Potential: Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilized
- Developed : Which are surveyed and quality and quantity shows the utilization
- Reserve : Which can be used for meeting future requierments
- Stock: Which can be used due to the lack of appropriate technology to used these resource
Question 5.
Provide a suitable classification for resources on the basis of ownership. Mention main features of any three types of such resources?
Answer:
On the basis of ownership, there are four types of resources
- Individual resources: Resources which are owned privately by individuals,
Ex: Farmers own pieces of land or houses. Plantation, pasture lands and water in wells are some resources owned by individuals
- Community owned resources: These resources are accessible to all the members of the community. Public parks, and playgrounds, ponds etc
- National resources : All the resources within the political boundary of a nation including the territorial water (oceanic area upto 12 nautical miles from the coast) extending into the ocean and resources therein belong to the nation. Ex: Minerals, forests, wildlife, land, etc
- International resources: There are international institutions which own and regulate some resources, Ex : The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to the open ocean. No individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of internatinoal institutions
Question 6.
What is the importance of resource planning, and how does it relate to sustainable development?
Answer:
- Resource planning is crucial for a country like India due to its diverse availability of resources across regions
- It involves identifying, inventorying, and quantifying resources, and aligning resource development plans with national development goals
- Resource planning helps in balanced development, considering areas with resource deficits and surpluses
- It contributes to sustainable development by ensuring resources are used judiciously
- Sustainable development means development without harming the environment and compromising future generations needs
- Resource planning plays a key role in achieving sustainable development goals
- Balanced resource utilisation helps prevent over-exploitation and ecological damage
- Sustainable development aims to address environmental, economic, and social concerns
Question 7.
How does technology and institutions influence resource development and utilisation?
Answer:
- Mere resource availability isnt sufficient for development; technology and institutions play vital roles
- Technology helps harness resources effectively, increasing their economic value
- Advanced technology allows for efficient resource extraction, processing, and utilisation
- Proper institutions, including regulatory bodies and governance structures, ensure fair and sustainable resource management
- Technology can enhance resource conservation and reduce waste
- Institutions create frameworks for resource allocation, preventing monopolisation and ensuring equitable distribution
- Technology and institutions together can transform resource-rich areas into economically developed regions
- Historical experiences and human resources also impact resource development
Question 8.
Why is resource conservation essential, and how has it been addressed in the past?
Answer:
- Resource conservation is vital to prevent resource depletion, socio-economic problems, and environmental damage
- Excessive resource consumption can lead to scarcity and ecological crises
- Resource conservation ensures resources are available for future generations
- Mahatma Gandhi emphasized resource conservation by promoting the idea of "enough for everybodys need, not for anybodys greed."
- The club of Rome, in 1968, highlighted the importance of resource conservation
- E.E Schumachers book "Small is Beautiful" reinforced the concept of responsible resource use
- The Brundtland Commission Report in 1987 introduced the concept of sustainable development, linking it to resource conservation
- International initiatives like the Earth Summit in 1992 at Rio de Janeiro emphasized resource conservation on a global scale
Question 9.
Discuss the significance of soil as a natural resource and its role in supporting life?
Answer:
Soil is an essential natural resource with significant importance
- Supports Life: Soil is crucial for plant growth, serving as a medium for plants to thrive. It supports various living organisms on Earth
- Formation : Soil formation is influenced by relief, parent rock, climate, vegetation, and time. Natural forces like temperature changes, running water, wind, and glaciers contribute to soil formation
- Composition: Soil comprises organic (humus) and inorganic materials. It contains nutrients like calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime, essential for plant growth
- Agriculture: Soil is the foundation of agriculture, providing a medium for crops to grow and contributing to food production
- Ecology: Soil supports different ecosystems and plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance
- Renewable Resource : While it takes millions of years to form, soil is a renewable resource that can be managed and conserved for sustainable use
Question 10.
Information Table: Land Use Pattern in India (1960-61 to 2014-15)?
| |
Net sown Area |
Forest Area |
Land under Permanent Pasture |
| 1960-61 |
Marginal |
Mariginal |
High |
| 2014-15 |
Marginal |
Marginal |
Decreased |
Read the above table and analyse
Answer:
- The land use pattern in India has shown marginal changes from 1960-61 to 2014-15. The net sown area has remained relatively unchanged, indicating a stable agricultural sector
- The forest area has also marginally changed, possibly due to deforestation and urbanisation, leading to the loss of forested land
- However, the land under permanent pasture has decreased significantly, which could be attributed to the conversion of pasture land into cultivation areas or other forms of land use
- It is important to note that the land under permanent pasture plays a crucial role in supporting the cattle population in India. The decline in this land could have adverse consequences for the agricultural and livestock sectors
- Overall, the land use pattern in India reflects the complex interplay between physical factors such as topography and human factors such as population density and cultural practices. It highlights the need for sustainable land use planning and conservation measures to ensure the equitable distribution of resources and prevent land degradation
Question 11.
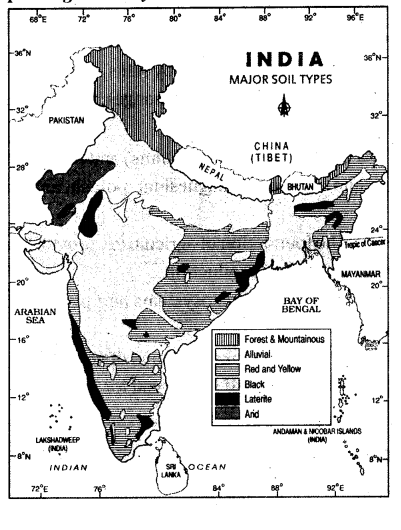
Answer:
- Alluvial soil: This type of soil is found in the Indo-Gangetic plains and other river valleys. It is a fertile soil that is well-suited for agriculture
- Black soil: This type of soil is found in the Deccan plateau region. It is a clay-rich soil that is known for its high fertility
- Red soil : This type of soil is found in the eastern and southern parts of the country. It is a sandy soil that is less fertile than alluvial soil and black soil
- Laterite soil: This type of soil is found in the Western Ghats region and other hilly areas. It is a highly acidic soil that is not suitable for agriculture
- Arid soil: This type of soil is found in the Thar Desert and other arid regions. It is a sandy soil that is low in fertility
- Saline soil: This type of soil is found in coastal areas and other saline regions. It is a soil that contains high levels of salt, which makes it unsuitable for agriculture
Question 1.
What is the definition of a resource?
Answer:
- Everything available in the environment that can be used to satisfy needs
- It must be technologically accessible, economically feasible, and culturally acceptable
- Resources can be classified based on various factors
Question 2.
What are the criteria for something to be considered a resource?
Answer:
The resource must be technologically accessible, meaning it can be used with available technology
- It must be economically feasible, meaning it can be utilised without excessive cost
- It should be culturally acceptable, meaning it aligns with the values and practices of the society
Question 3.
Can anything in the environment be considered a resource?
Answer:
Yes, anything in the environment that fulfils the criteria of being technologically. accessible, economically feasible, and culturally acceptable can be termed as a resource
Question 4.
What factors determine whether something is classified as a resource?
Answer:
The classification of resources is based on various factors such as origin, exhaustibility, ownership, and status of development
AP 10th Class Social Geography 1st Lesson Important Questions: 4 Marks
Question 1.
Examine the three major problems created as a result of indiscriminate utilization of natural resources ?
Answer:
The three major problems created as a result of indiscriminate utilization of natural resources are as follows
- Depletion of resources at a faster rate
- Accumulation of resources in the hands of few creating a wide gap between the haves (rich) and have nots (poor)
- Increase in global crises like ozone layer depletion, global warming, pollution and land degredation
Question 2.
Mention some features of arid soil?
Answer:
The following are the features of arid soils
- The colour of the arid soil ranges from red to brown
- Arid soils are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature
- The soils lack humus and moisture because of dry climate, high temperature and fast evaporation
- The lower parts of the soils are occupied by Kankar because of high calcium content. It restricts the infiltration of water in lower layers
Question 3.
Explain the role of human in resource development ?
Answer:
- Human is at the centre of resource development
- Actually all resources become resource only when they are put to use by humans
- It is human who makes natural things usable with help of technology
- To enhance economic development the state constructs roads, buildings, bridges, dams, power houses, hospitals, etc., to run these units doctors, engineers, scientists, teachers, are required
- Human Resources development has an ample affect on the economy and society
Question 4.
What is meant by resource ? Mention the four basis to classify the resources?
Answer:
- Resource : Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable can be termed as resource
- Four basis to classify resources are as mentioned below
- On the basis of origin-biotic and abiotic
- On the basis of exhaustibility renewable and non-renewable
- On the basis of ownership- individual, community, national and international
- On the basis of status of development - potential, developed stock and reserves
Question 5.
Classify resources on the basis of exhaustibility. Write examples?
Answer:
- Renewable resources : The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable resources. For example : Solar and wind energy, water, forests.and wildlife etc
- Non Renewable resources: These occur over a very long geological time. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation.
For example : The resources like metals are recyclable and some like fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use
Question 6.
Define sustainable development ? What are their importance ?
Answer:
- Sustainable development means, development should take place without damaging the environment and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of the future generations
- It is essential for substained quality of life
- If the present trend of resource depletion by a few individuals and countries continues, the future of our planet is in danger
- So, sustainable development is very important to save our planet and ourself
Question 7.
Explain the three steps that involved in the complex process of resource planning ?
Answer:
- Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources
- Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans
- Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans
Question 8.
What type of relief covers most of Indias land ? Explain?
Answer:
- India has land under a variety of relief features, namely; mountains, plateaus, plains and islands
- About 43 percent of land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry
- Mountains account for 30 percent of the total surface area of the country and ensure perennial flow of rivers, provides facilities of tourism and ecological aspects
- About 27 percent of the area of the country is the plateau region. It possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests
Question 9.
Why does the net sown area vary from one state to another ?
Answer:
- There are wide variations in the pattern of net sown area from one state to another state
- If we compare Haryana and Punjab with Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman and Nicobar Islands there is a great disparity
- In Punjab and Haryana the net sown area is 80% of the total area but in other mentioned states it is less than 10% of the total area
- The resources for this differences are many, e.g., climate, soil, relief, irrigation facilities
Question 10.
Explain the two types of water erosion?
Answer:
- Sheet Erosion: When the top layer of the soil is removed over a large area by the running water is called as sheet erosion. In such cases the top soil is washed away
- Gully erosion : The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. The land becomes unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land. In the Chambal basin such lands are called ravines
Question 11.
Write a brief notes on Laterite soil?
Answer:
- Laterite soil is commonly used as road pavement materials to provide a better sub base gravel for roads and base materials
- They are also good material for embankment construction
- Laterite-soils lack fertility due to intensive leaching
- Some laterites are suitable for growing plantation crops like tea, coffee, rubber, cinchona, coconut, arecaput, etc
Question 12.
Suggest some measures to control land degradation in India?
Answer:
Measures to control land degradation in India are
- Construction of terraces for farming and building of dams in hilly area to check soil erosion
- Proper discharge and disposal of industrial wastes after treatment
- Management of grazing by animals
- Planned management of forests, planting of shelter belts of plants and more plants can be planted to check soil erosion.
- Control on mining activities
Question 13.
What are the main causes of land degradation in India, and in which regions are they prominent?
Answer:
- Deforestation, overgrazing, mining, and quarrying contribute to land degradation
- States like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Odishaface degradation due to mining
- Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra witness overgrazing-related degradation
- Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh experience land degradation due to over-irrigation
- Industrial activities, like grinding minerals,and industrial effluents, also contribute to land and water pollution
Question 14.
Read the table and answer the given questions?
| Categories of Resources |
Characteristics |
| Origin
Biotic Resources
Abiotic Resources |
From living organisms.
From non-living substances |
| Exhaustibility
Renewable Resources
Non-renewable Resources |
Can be replenished naturally or through human intervention.
Cannot be replenished within a human lifetime |
| Ownership
Individual Resources
Community Resources
National Resources |
Owned and utilized by an individual.
Owned and utilized by a community or group.
Owned and utilized by a nation.
Shared and utilized by multiple nations |
| Status of Development
Potential Resources
Developed Stock Resources
Reserve Resources |
Identified but not yet utilized.
Currently being utilized.
Being stored for future use |
Question (i) What are the two categories of resources based on their origin?
Answer:
Biotic and abiotic resources
Question (ii) Name a renewable resource?
Answer:
Solar energy
Question (iii) Who owns community resources?
Answer:
A community or group
Question (iv) What are potential resources?
Answer:
Resources that are identified but not yet utilized
Question 15.
Read the given source and answer the following?
| Sustainable development is a key concept in resource planning and management, It emphasises the need for economic development without causing harm to the environment and compromising the needs of figure generations. The Rio Convention and Agenda 21, signed in 1992, amied atachieving global sustainable development through International cooperation and shared, responsibilities. These efforts recognize the interdependence between nature, technology, and institutions in transforming resources and promoting economic development. In India, the pattern of land resources and their utilisation is influenced by physical factors such as topography and human factors such as population density and tradition |
Questions and Answers:
Question (i) What is the concept of sustainable development?
Answer:
Sustainable development means economic development without harming the environment and compromising future needs
Question (ii) What were the goals of the Rio Convention and Agenda 21?
Answer:
The Rio Convention and Agenda 21 aimed at achieving global sustainable development through international cooperation and shared responsibilities
Question (iii) What factors influence the pattern of land resources in India?
Answer:
The pattern of land resources in India is influenced by physical factors such as topography and human factors such as population density and traditions
Question(iv) What is the relationship between nature, technology, and institutions in resource transformation?
Answer:
Human beings interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate economic development
Question 16.
Read the given map and answer the following questions?
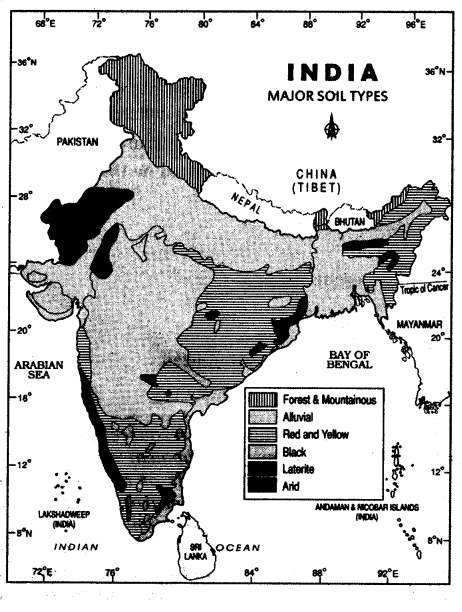
Question (i) Where is the forest and mountainous region ?
Answer:
In the Himalayan region
Question (ii) Name red and yellow soil state?
Answer:
Orissa
Question (iii) Name the arid soil region?
Answer:
Rajasthan
Question (iv) Name any alluvial soil region?
Answer:
The Krishna and Godavari delta
Question 17.
What is soil erosion ? Explain the major types of soil erosion?
Answer:
Soil Erosion : Soil erosion is the removal of soil by the forces of nature like wind and water is called soil erosion. This can also be described as denudation of soil cover and subsequent washing down. Following are its two types
- Wind Erosion : Wind blows loose soil off flat or slopping land. This is known as wind erosion
- Water Erosion : When running water is responsible for the removal of the top most layer of the earth that is known as water erosion
Question 18.
Explain any three human activities which are mainly responsible for land degradation in India?
Answer:
- Some human activities such as deforestation, over grazing, mining and quarrying too have contributed significantly in land degradation
- Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep sears and traces of over-burdening
- Deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation
- Over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil
Question 19.
How is red soil formed ? Mention its features ?
Answer:
- Formation : Most of the red soils have come into existence due to weathering of ancient crystalline igneous rocks
- Soils are loamy in deep depressions and in upload. They consist of loose gravels and highly coarse materials
- These soils develop a reddish colour due to diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks
- If looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form
- This soil is found in the areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau
Question 20.
Read the given para and answer the following questions?
| Resources are vital for any developmental activity. But irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to socioeconomic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at variopslevels is important This had been the main concern Of the leaders and thinkers in the past. For example, Gandhiji was very apt in voicing his concern about resource conservation in these words: "There is enough for everybodys weed ariUhbt for any bodys greed." |
Question (i) Resources are vital for?
- Developmental activity
- Commercial activity
- Social activity
- Environmental activity
Answer:
Developmental activity
Question (ii) Irritional consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to?
- Social problems
- Commercial problems
- Environmental problems
- All the above
Answer:
All the above
Question (iii) There is enough for everybodys need and not for anybodys greed." Who said this?
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Mahatma Gandhi
- Raj endra Prasad
- Vinoba Bhave
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi
Question (iv) What had been the main concern of the leeders and thinkers in the past ?
- Ocean conservation
- Soil conservation
- Biodiversity conservation
- Resource conservation
Answer:
Resource conservation
Question 21.
Read the given para and answer the following questions?
| Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaning deep SCdtis and traces of over-burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhtittisgarh, Madhya fradesh and (Misha deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation. In the states of Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading ! to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil |
Question (i) In which states deforestation due to mining has caused several land degradation ?
Answer:
Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh
Question (ii) What is the main reason of land degradation in Punjab and Haryana ?
Answer:
Over irrigation
Question (iii) In which states over-grazing is the main reason for land degradation ?
Answer:
Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra
Question (iv) What is the main reason for land degradation in Jharkhand ?
Answer:
Deforestation is the reason for land degradation in Jharkhand
Question (v) Which is the main reason for land degradation in Rajasthan ?
Answer:
Over-grazing
Question 22.
Read the given para and answer the following questions?
| Arid soils range from red to brown in colour. They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas the salt content is very high and Common gait is obtained by evaporating the water. Due to the dry climate, high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture. The lower horizons of the soil are occupied by Kankar because of the increasing calcium content down-war. The Kankar layer formations in the bottom horizons restrict the infiltration of water |
Question (i) What does the Kankar layer formation restrict in the bottom horizons ?
Answer:
The Kankar la/er formation restrict the infilterat.ion of water
Question (ii) What are the two components lacking by dry climate and high temperature ?
Answer:
Humus and moisture
Question (iii) Why are the lower horizons of the soil occupied by Kankar ?
Answer:
The bottom horizon of the soil is occupied by Kankar because of the high content of calcium
AP 10th Class Social Geography 1st Lesson Important Questions: 2 Marks
Question 1.
What do you understand by international resources ? Give example?
Answer:
- These resources are regulated by international institutions
- Examples are the Oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilize there without the concurrence of international institutions
Question 2.
What are developed resources ?
Answer:
- Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation
- The development of resources depends on technology and level of their feasibility
Question 3.
What is Agenda 21 ?
Answer:
Agenda 21 is the plan of action to achieve sustainable development that was adopted by the world leaders at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held in Rio-de-Janeiro, Brazil, in June 1992
Question 4.
How much area of land in India is plain and what is its importance ?
Answer:
- About 43 percent of the land area is plain
- It provides facilities for agriculture and industry
Question 5.
How are mining activities responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand ?
Answer:
- Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars in states such as Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha
- Deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation
Question 6.
In which states is over irrigation responsible for land degradation ?
Answer:
In the states of Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation
Question 7.
We need sustainable development because resource exploitation is leading to inequality. Explain the inequality of resources in two points?
Answer:
- Accumulation of resources in the hands of a few
- Division of society into haves and have nots
- Effects of climate change and resources storage faced by marginalised communities
Question 8.
Classify resources on the basis of origin?
Answer:
Resources classification on the basis of origin
- Biotic resources : All living organisms in our environment are knowrt as biotic re-sources. Example : Tree, animal, insects etc
- Abiotic resources: All non-living present in our environment are known as abiotic resources. Example : Earth, air, water, metals, rocks etc
Question 9.
How is over irrigation responsible for land degradation in Punjab ?
Answer:
- Over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging which leads to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil
- Over irrigation without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage land has resulted in land degradation in Punjab
Question 10.
Haw is cemeht industry responsible for land degradation ?
Answer:
- Cement Industries generates heavy amount of dust which is released in the of atmosphere
- Later, it settles down in the surrounding areas which slows the process of infiltration of water into the soil
Question 11.
Look at the map given below and answer the question?
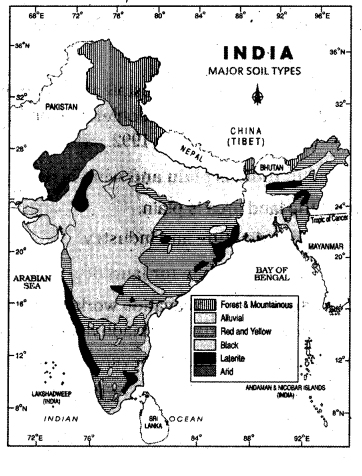
Observe the regions where laterite soil is present using the map, explain the sintilarities between areas that have laterite soil.
Answer:
- Laterite soil develops in hot, humid tropical regions
- It is rich in iron and aluminium
- Laterite is a type of soil and rock formation that is commonly found in tropical regions around the world
Question 12.
What factors contribute to the formation of soil, and why is soil considered a vital renewable resource?
Answer:
- Soil formation involves factors like relief, parent rock, climate, vegetation, and time
- It takes millions of years to form even a few centimeters of soil
- Soil supports plant growth and various life forms, making it crucial for ecosystems and agriculture
Question 13.
How are alluvial soils classified based on age and why are they important in India?
Answer:
- Alluvial soils are classified as old alluvial (Bangar) and new alluvial (Khadar) based on age
- Bangar soil is older, has more kanker nodules, finer particles, and is more fertile than Khadar
- Alluvial soils are important for agriculture, particularly in densely populated regions like the northern plains
Question 14.
Explain the characteristics and distribution of red and yellow soils in India and their suitability for agriculture?
Answer:
- Red soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in regions with low rainfall
- Yellow and red soils are found in parts of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, the Ganga plain, and along the Western Ghats
Question 15.
What are shelter belts ? How have they proved helpful ?
Answer:
- Rows of trees which are planted in between the crops are called shelter belts
- These shelter belts have proved helpful in the stabilisation of sand dunes and in stabilising the desert in Western India
Question 16.
How does the contour farming help in the soil conservation ?
Answer:
Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes and thus helpful in the soil conservation
Question 17.
What are the important factors in the formation of soil ?
Answer:
The important,factors in the formation of soil include relief, parent rock or bed.rock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time
Question 18.
Why is resource planning essential ?
Answer:
Resource planning is essential because
- Resources are limited in supply
- Resources are unevenly distributed over the surface of the earth
- Exploitation and over utilization of resources must be checked
Question 19.
What ajre biotic and abiotic resources ? Give two examples for each?
Answer:
- Biotic resources: These are obtained from biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries and livestock
- Abiotic resources : All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources eg., rocks and metals
Question 20.
What is resource planning ? Why is it essential ?
Answer:
- Resource Planning
- Resource Planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources
- Resource planning is essential for sustainable existence of all forms of life
- Sustainable existence is a component of sustainable development
Question 21.
What are the different factors that determine land use ?
Answer:
- Both physical and human factors determine the land use pattern of any area
- Physical factors include topography, climate, and soil types
- Human factors include population density, technological capability and cultural traditions
AP 10th Class Social Geography 1st Lesson Important Questions: 1 Mark
Question 1.
What do you understand by Resource ?
Answer:
Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable, can be termed as Resource
Question 2.
Which states in India are rich in minerals and coal deposits ?
Answer:
Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh.
Question 3.
Which report in 1987 introduced the concept of Sustainable Development ?
Answer:
Brundtland Commission Report
Question 4.
What is total geographical area of India ?
Answer:
3.28 million sq.km
Question 5.
How much degraded land is in India ?
Answer:
At present there are about 130 million hectares of degraded land in India
Question 6.
Classify resources on the basis of exhaustibility?
Answer:
Renewable and non-renewable resources
Question 7.
Classify resources on the basis of development?
Answer
Potential, developed stock and reserves
Question 8.
Give an example of biotic resources?
Answer
Human beings, flora and fauna are examples of biotic resources
Question 9.
What type of resources are solar and wind energy ?
Answer
Solar and wind energy are renewable resources
Question 10.
Mention a non-renewable source that cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use?
Answer
Fossil fuel
Question 11.
How did Gandhijl voice his concern about resource conservation ?
Answer
Gandhiji said, "There is enough for everybodys need and not for anybodys greed."
Question 12.
What was the,main reason for the colonial countries to exploit resources of countries under their control ?
Answer
High level of technological development
Question 13.
Historically, colonising countries took advantage of Indias rich resources to gain supremacy. Why was India not able to resist the exploitation of her resources ?
Answer
Due to the colonising countries superior technology
Question 14.
In a village, the grazing ground can hold up to 10 cows per day. Beyond this, it cannot replenish itself. The villagers did not pay attention to this information and brought 50 cows to graze in the ground and soon the grazing ground ceased to exist. What kind of resources is being depleted here ?
Answer
Community-owned resource
Question 15.
M gave his friend cities about a type of soil that suits for growing cotton. Which clues provided by "M" would he most useful in identifying the ideal type of soil ? (a)?
Answer
- It is well-known for its capacity to hold moisture
- It turns yellow when it is hydrated
- It is rich in kankur and bhangar nodules
- It is a Well-drained loamy soil
- clue i
- clue i and iii
- clue i and ii
- clue iv
Question 16.
Which of the following is correctly matched ?
| (a) Alluvial Soil |
Consist of sand and silt |
| (b) Black Soil |
Salt content is high |
| (c) Arid Soil |
Diffusion or iron in crystalline |
| (d) Laterite Soil |
Made up of lava flows |
Answer
Alluvial Soil - Consist of sand and silt
Question 17.
Most of the alluvial seal found in India is formed from the silt deposited by the Indo- Gangetic-Brahmaputra rivers.
Which regions contains the parent rock that forms this silt ?
Answer
Himalayas
Question 18.
Write the name of the soil with the help of clues given below?
- Develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall
- Is low in humus content
- Found in the hilly areas of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu
Answer
Laterite soil
Question 19.
Write the name of the soil which ranges from red to brown in colour and saline in nature?
Answer
Arid soil
Question 20.
Two statements are given below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Read the statements and choose the correct option :
Assertion (A) T Soil formation and erosion go hand in hand but sometimes this balance is disrupted by human activities.
Reason (R) : The formation of soil takes millions of years while soil erosion takes much less time?
Answer
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) ( b )
- Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
- (A) is true but (R) is false
- (A) is false but (R) is true
Question 21.
Which factor is mainly responsible for maximum land degradation in India ?
Answer
Overgrazing is one of the main reason for land degradation. States, where overgrazing has resulted in land degradation are, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra
Question 22.
Aaron gave his friends three clues about a type of soil?
- It is found in Maharashtra, the largest producer of cotton in India
- During summers, the soil exhibits self-aeration capacity
- It is rich In nutrients
What soil is being referred to by Aaron
Answer
Black soil is being referred to by Aaron.
Question 23.
Read the following features of a soil and name the related soil?
- Develops in high rainfall area
- Intense leaching process takes place
- Humus content is low
Answer
Laterite soil
Question 24.
What is the definition of a "resource" in the context of the environment?
Answer
Resources are things in our environment that can satisfy human needs, provided they are technologically accessible, economically feasible, and culturally acceptable
Question 25.
How do human beings interact with nature?
Answer
Human being& interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development
Question 26.
What does "sustainable economic development" mean according to the Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit?
Answer
Sustainable economic development means that development should take place without damaging the environment and should not compromise the needs of future generations
Question 27.
What key factors, besides the availability of resources, are essential for development?
Answer
Besides resource availability, appropriate technological development, quality of human resources, and historical experiences of the people are essential for development
Question 28.
Why is land use data not available for the entire geographical area of India?
Answer
Land use data is missing for certain regions, including some north-eastern states, due to incomplete-reporting
Question 29.
Why is the forest area in India lower than the desired 33% of geographical area?
Answer:
Forest area falls short due to factors like land use changes, which have ecological and livelihood consequences
Question 30.
What factors contribute to land degradation, and Jtiow has it affected India?
Answer:
Land degradation results from activities like deforestation, overgrazing, mining, and over-irrigation, leading to environmental and societal issues in India
Question 31.
Which type of soil is ideal for cotton cultivation and is also known as black cotton soil ?
Answer:
Black soil, also known as regur soil, is ideal for cotton cultivation
Question 32.
Give two examples of resources conservation practices in our daily lives that make way for sustainable development?
Answer:
- Turn off lights and other electronics when you are not using them
- Purchase energy-efficient appliances and weatherproof your home
Question 33.
Why was Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit convened in 1992 ?
Answer:
The summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
Question 34.
Which is the most widespread relief feature of India ?
Answer:
Plains are the most widespread relief features of India.
Question 35.
State any reason for over use of resources?
Answer:
Rapid increase in population is a reason for over use of resources
Question 36.
In which Five Year Plan period, resource planning was introduced in India ?
Answer:
Resource planning was introduced in the First Five Year Plan in India after independence
Question 37.
Which type of soil is most suitable for growing the crop of cashew nut ?
Answer:
Red laterite soil is most suitable for growing the crop of cashew nuts
Question 38.
Which type of soil in India is most widespread and important ?
Answer:
Alluvial soil is the most widely spread and important soil in India?
Question 39.
What is bad land ?
Answer:
Bad land is the land unfit for cultivation due to gully erosion?
Question 40.
Define ravine?
Answer:
Ravines are geographical features that are characterized by steep-sided narrow valleys or gorges that are formed by the erosion of water