AP 10th Class Physical Science 2nd Lesson Acids, Bases and Salts Important Questions
Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 2 Important Questions - 1 Mark
Question 1.
What are indicators ?
Answer:
Those substances which change their colour in different types of substances are called indicators.
Question 2.
Name an indicator which indicates the various levels of hydrogen ion concentration. ‘
Answer:
Universal indicator.
Question 3.
Name flowers whose colour or petals can be used as indicator.
Answer:
Hydrangea, Petunia, Geranium.
Question 4.
What are phenolphthalein and methyl orange ?
Answer:
Synthetic indicates.
Question 5.
What is the colour of methyl orange in NaOH ?
Answer:
Yellow.
Question 6.
What will be happen to blue litmus when it is added to soda water ?
Answer:
It changes to red.
Question 7.
What would be the colour of litmus in a solution of sodium carbonate ?
Answer:
The red litmus will change to blue in sodium carbonate solution.
Question 8.
Name an acid - base indicator prepared at.home.
Answer:
Beetroot extract.
Question 9.
What is the colour of litmus in a solution of ammonium hydroxide ?
Answer:
Red litmus will turn blue in ammonium hydroxide.
Question 10.
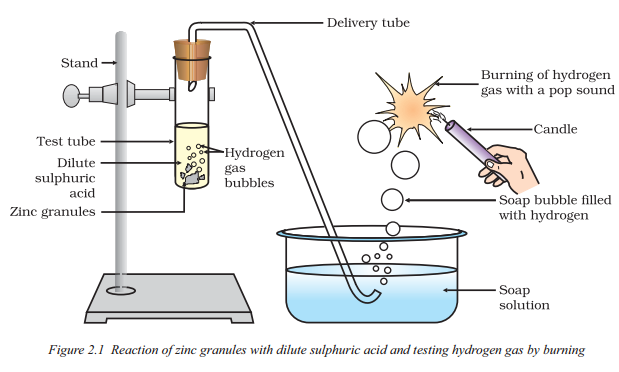
How will you test for the gas which is liberated when hydrochloric acid reacts with an active metal ?
Answer:
Bring a burning match-stick near the gas. It burns with ‘pop’ sound showing thai it is hydrogen.
Question 11.
Which gas is evolved when sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
Question 12.
A few drops of sulphuric acid is added to water before electrolysis, why ?
Answer:
It makes water better conductor.
Question 13.
What effect does the concentration of H+ (aq) have on the acidic nature of the solution?
Answer:
Acidic nature increases with increase in cone of H3O+ ion.
Question 14.
Which gas is Evolved when metal carbonates or metal hydrogen carbonate reacts with dilute acids ?
Answer:
CO2 (g).
Question 15.
Which acid is present in honey bee sting and hair of nettle leaves ?
Answer:
Formic acid.
Question 16.
Name the acid present in ant sting.
Answer:
Methanoic acid.
Question 17.
Which bases are called alkalies ? Give an example of alkalies.
Answer:
Soluble bases are called alkalies. Eg : Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Question 18.
What is cure for bee sting ? Why ?
Answer:
Baking soda, which is a mild base. It gives relief by neutralising the effect of formic acid.
Question 19.
Which remedy you will suggest if some one in family is suffering from problem of acidity and why ?
Answer:
Baking soda solution because it will neutralise excess of acid.
Question 20.
What is pH?
Answer:
pH is defined as negative logarithm of H+ concentration or H3O+ concentration.
Question 21.
What is meant of p and H in pH ?
Answer:
‘P’ stands for ‘Potenz’ in German meaning power ‘H’ stands for hydrogen. pH stand for power of hydrogen.
Question 22.
Why does bleaching powder act as bleaching agent ?
Answer:
It is because it is oxidising agent.
Question 23.
Write chemical equation representing the action of CO present in atmosphere on bleaching powder left in open.
Answer:
CaOCl2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + Cl2 (g)
Question 24.
What are antacids ? Give one example.
Answer:
those compounds which neutralise excess of acid in stomach, E.g. : NaHCO3.
Question 25.
State the purpose for which litmus is used in laboratories.
Answer:
The main purpose for which litmus is used in laboratories is to check whether a solution is acidic or basic.
Question 26.
Define neutralization reaction.
Answer:
The reaction in which a base reacts with are acid is called neutralization reactions.
Question 27.
Two solution X and Y are tested with universal indicator. Solution X turns orange whereas solution Y turns red. Which of the solutions is a stronger acid ?
Answer:
Solution Y is a stronger acid as strength of red colour is more than orange on the universal indicator scale.
Question 28.
If two solutions of different pH 2 and 5 are given, which will be stronger acid and why?
Answer:
pH = 2 as lower pH, strogner is the acid.
Question 29.
Name a salt which does not contain water of crystallisation.
Answer:
Baking soda.
Question 30.
Name two main constituent of baking powder ?
Answer:
Sodium hydrogen carbonate (sodium bicarbonate) and tartaric acid.
Question 31.
Give one word for water soluble base.
Answer:
Alkali.
Question 32.
Define alkalies and give an example.
Answer:
The bases soluble in water are called alkalies. E.g.: NaOH, KOH.
Question 33.
Mention the range of pH value for identification of a base.
Answer:
pH value for identification of a base is 7 - 14.
Question 34.
How chloride of lime differs chemically from calcium chloride ?
Answer:
Chloride of lime is CaOCl2 while calcium chloride is CaCl2.
Question 35.
Write the chemical name and chemical formula of washing soda. .
Answer:
Chemical Name : Sodium carbonate.
Chemical Formula: Na2CO3.10 H2O.
Question 36.
Name the gas evolved when dilute HCl reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. How is it recognised ? .
Answer:
The gas evolved is CO2. When this gas is passed through lime water, it turns it milky.
Question 37.
What are olfactory indicators ?
Answer:
The substances whose odour changes in acidic or basic media are called olfactory indicators.
Question 38.
At what pH rain water is said to be acidic.
Answer:
When pH of rain water is lessthan 5.6, then it is called acid rain.
Question 39.
Which gas is evolved when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc ? Write the molecular formula of this gas.
Answer:
Hydrogen gas. Molecular formula is H.
Question 40.
Show that non-metalic oxides are acidic in nature with the help of a chemical equation. j
Answer:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Calcium hydroxide is a base. So, to form salt and water it must react with an acid. It means CO2 is acidic in nature.
Question 41.
Two solutions A and B have pH values of 5 and 8 respectively. Which solution,will be basic in nature ?
Answer:
Solution B.
Question 42.
HCl is a stronger acid than acetic acid explain.
Answer:
HCl is a stronger acid than acid because it ionises completely in aqueous solution while acetic acid is only partially ionised in aqueous solution.
Question 43.
Arrange the following in the increasing order of acidic strength.
Gastric Juice, Milk, Lemon Juice
Answer:
Milk < Lemon Juice < Gastric Juice.
Question 44.
A white chemical compound becomes hard on mixing proper quantity of water. It is also used in surgery to maintain joints in a fixed position. Name the chemical compound.
Answer:
Plaster of Paris.
Question 45.
Which one of these has higher concentration of H+ ions ?
1M HCl or 1M CH3COOH
Answer:
1M HCl has a higher concentration of H+ ions because it is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
Question 46.
What is the commercial name of calcium sulphate hemihydrate ?
Answer:
Plaster of Paris.
Question 47.
Name the substance obtained by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime.
Answer:
Bleaching powder.
Question 48.
How many molecules of water of crystallisation are there in
i) Plaster of Paris
ii) Washing soda crystals ?
Answer:
i) 12
ii) 10.
Question 49.
i) What do you think will be pH in the stomach of a person suffering from indigestion ?
ii) What do you think will be pH of an antacid solution ?
Answer:
i) Less than 7
ii) More than 7.
Question 50.
Why is the electrolysis of a concentrated solution of sodium chloride known as chlor-alkali process ?
Answer:
It is because of the products formed. Chlor for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide.
Question 51.
Assertion (A) : Reaction of Quicklime with water is an exothermic reaction.
Reason (R) : Quicklime reacts vigorously with water releasing a large amount of heat.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
a) Slaked lime is produced with the evolution of a great deal of heat when quick lime is treated with water. This reaction is therefore exothermic in nature.
Question 52.
Assertion (A) : It is advised that while diluting an acid one should add water to acid and not acid to water keeping the solution continuously stirred.
Reason (R) : The process of dissolving an acid into water is highly exothermic.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is. the correct explanation of (A).
Question 53.
The graph given depicts a neutralization reaction
(acid + alkali → salt + water). The pH of a solution changes as we add excess of acid to an alkali. PH
Which letter denotes the area of the graph where both acid and salt are present?
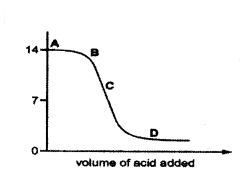
Answer:
From the graph, the pH is lessthan 7 at only part ‘D’.
Question 54.
What is the reason for the change in colour of the moist set up ?
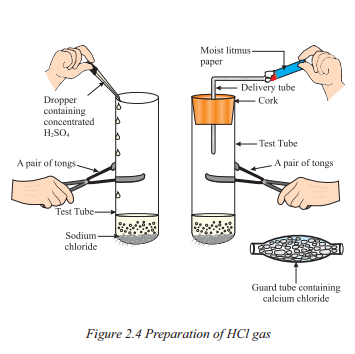
Answer:
Due to the presence of H+ (aq) in the solution.
Question 55.
Assertion (A) : The colour of aqueous solution of copper sulphate turns colourless when a piece of lead is added to it.
Reason (R) : Lead is more reactive than copper, and hence displaces copper from its salt solution .
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 56.
A colourles and odourless gas is liberated when hydrochloric acid is added to a solution of washing soda. What is the name of the gas ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide.
Question 57.
On adding a few drops of universal indicator to three unkown colourless solution (P), (Q) and (R) taken in three test tubes shown in the following diagrams. A student observed the changes in colour as green in (P), red in (Q) and violet in (R).
What is the decreasing order of pH of the solutions taken ?
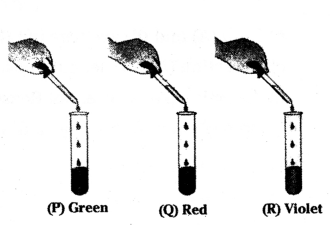
Answer:
The decreasing order of pH of the solutions P, Q, and R is R > P > Q.
Question 58.
Observe the diagram of an activity given below. What does it help to conclude, when the person exhales into the test-tube ?
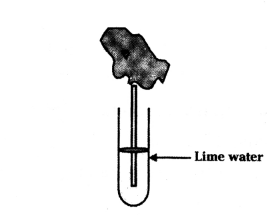
Answer:
Percentage of carbon dioxide is more in the exhaled air.
Question 59.
Assertion (A) : Fresh milk in which baking soda is added, takes a longer time to set. Reason (R) : Baking soda decreases the pH value of fresh milk to below 6.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false. d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
Question 60.
Write the name of gas A in the following experiment.
Answer:
Hydrogen
Question 61.
Observe the experimental setup carefully.
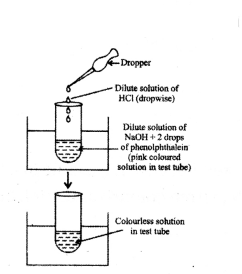
Which type of reaction is this ?
Answer:
Neutralisation
Question 62.
50.0 ml of tap water was taken in a beaker. Hydrochloric acid was added drop by drop to water. The temperature and pH of the solution was noted. The following graph was obtained. Write an observation related to this activity.
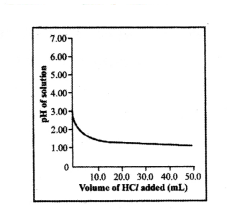
Answer:
The pH of the solution decreases rapidly on addition of acid, and the pH of tap water was around 7.0.
Question 63.
In which of the following set ups would the bulb glow ?
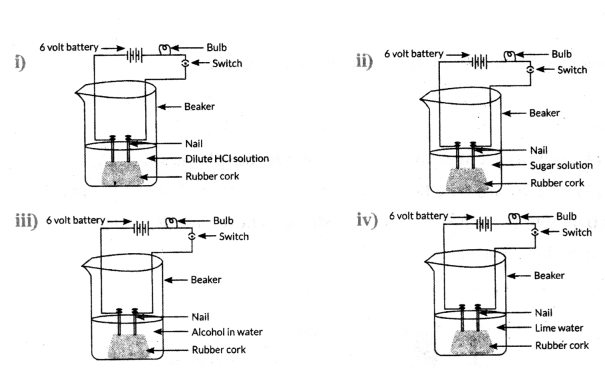
Answer:
In (i) and (iv)
Question 64.
Give any one use of Plaster of Paris other than for plastering or smoothening of walls.
Answer:
One use of Plaster of Paris is in the medical field for casting broken bones and making orthopedic casts.
Acids, Bases and Salts Class 10 Important Questions - 2 Marks
Question 1.
Two solutions X and Y have pH values of 3.0 and 9.5 respectively. Which of these will turn litmus solution from blue to red and which will turn phenolphthalein from colourless to pink?
Answer:
X will turn blue litmus to red because it is acidic in nature having pH value less than 7.
Y will turn phenolphthalein from colourless to pink because it is basic in nature having pH value greater than 7.
Question 2.
Three acidic solutions A, B and C have pH =0, 3 and 5 respectively.
i) Which solution has the highest concentration of H+ ions?
ii) Which solution has the lowest concentration of H+ ions?
Answer:
i) Solution ‘A’ with pH = 0 has highest concentration of H+ ions,
ii) Solution ‘C’ with pH = 5 has the lowest concentration of H+ ions.
Question 3.
What is meant by "Water of crystallisation" in a substance ? Explain with an example.
Answer:
Water of crystallisation is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt.
Example : Hydrated copper sulphate (CuSO4. 3H2O). Here, 5 H2O signify five molecules of water as water of crystallisation.
Question 4.
i) What is the pH range for a base ?
ii) How is strength of basic solution can be increased ?
Answer:
i) The pH range of a base is 7 - 14.
ii) The strength of bases depends on the number of OH- ions produced. So by adding OH- ions, the strength of basic solution can be increased.
Question 5.
Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in our body. Name the compound of which it is made up of. At what pH of the mouth it gets corroded ? State the role of bacteria present in the mouth. Suggests a method of prevent tooth decay.
Answer:
Calcium phosphate, below 5.5, bacteria produce acids by degradation of sugar and food particles remaining in the mouth after eating, using tooth pastes which are generally basic.
Question 6.
Acid do not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water but do so in water. Justify this statement with the help of a chemical equation.
Answer:
Acids ionise in aqueous mediums to form hydrogen ions. These hydrogen ions cannot exist alone, they exist after combining with water molecules. Thus, aqueous hydrogen ions which are responsible for acidic behaviour can exist in the presence of water only
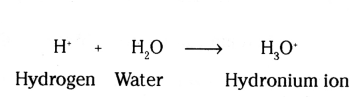
Question 7.
Crystals of copper sulphate are heated in a test tube for some time,
a) What is the colour of copper sulphate crystals
i) before heating, and
b) What is the source of liquid droplets seen on the inner upper side of the test tube during the heating process ?
Answer:
a) i) Blue
b) Crystals of copper sulphate (CuSO4.5 H2O) contain water of crystallisation-and on heating, these crystals loose water and become white. This lost water can be seen in the form of droplets on the inner upper side of the test tube.
Question 8.
Write the chemical name of Na2CO3.10H2O and Na2CO3 write the significance of 10H2O. Mention the terms used for water molecules attached with a salt.
Answer:
Na2CO3.10H2O - Hydrated salt / sodium carbonate with water of crystallisation (sodium carbonate decahydrate)
Na2CO3 - Anhydrous salt / sodium carbonate 10H2O means water of crystallisation. It imports colour and shape to the crystals.
Question 9.
2 ml of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a few pices of granulated zinc metal taken in a test tube. When the contents are warmed, a gas evolves which is bubbled through a soap solution before testing. Write the equation of the chemical reaction involved and the test to detect the gas. Name the gas which will be evolved when the same metal reacts with dilute solution of a strong acid.
Answer:
i) 2NaOH (aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2 (aq) + H2 (g)
ii) Test: Hydrogen gas burns with a pop sound.
iii) Zn(s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
Gas evolved is hydrogen
Question 10.
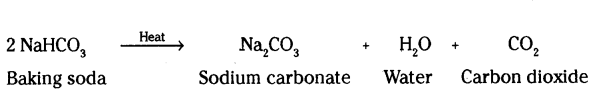
A compound ‘X’ is a constituent of baking powder. It is used as an antacid. When ‘X’ is heated it gives out a ‘Y’ which, when passed through lime water turns it’milky and salt ‘Z’ is formed which is the main constituent of washing powder. Identify X,
Y and Z. Write balanced chemical equations for the reaction involved.
Answer:
X - Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3)
Y - Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Z - Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3)
Question 11.
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for testing carbon dioxide. Identify ‘X’. What will be its reaction with carbon dioxide ? Write a balanced equation for the reaction.
Answer:
i) X is lime water Ca(OH)2
ii) Due to the formation of calcium carbonate lime water turns milky when carbon dioxide gas is passed through it.
iii) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O.
Question 12.
Give two practical applications of neutralisation reaction.
Answer:
- ntacids have been developed on the basis of neutralisation reaction.
- Tooth pastes are basic in nature which neutralise the excess of acid produced in our mouth.
Question 13.
i) Name the products obtained in chlor-alkali process.
ii) Name the gases liberated at anode and at cathode respectively.
Answer:
i) Chlorin gas, hydrogen gas and sodium hydroxide solution.
ii) Chlorin gas is given off at the anode and hydrogen gas at the cathode.
Question 14.
Give the chemical names of acids present in
i) ants
ii) lemon
iii) milk
iv) tomato
Answer:
i) formic acid / methanoic acid
ii) citric acid
iii) lactic acid
iv) oxalic acid
Question 15.
Write the chemical names of two salts belonging so sodium family.
Answer:
i) Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3)
ii) Sodium sulphate (Na2SO4)
Question 16.
Explain why
a) Colour of copper sulphate crystals changes on heating ?
b) Baking soda acts as an antacid ?
c) An acid should be added to water while diluting ?
Answer:
a) It loses its 5 molecules of water of crystallisation hence colour changes.
b) It is alkaline and neutralises excess acid to relieve pain.
c) As dilution of acids is an exothermic reaction and adding water to acids will splash and cause burns.
Question 17.
Write the balanced equation involved when
a) Chlorine is passed over dry slaked lime
b) Sodium bicarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid
c) Sodium bicarbonate is heated.
Answer:
a) Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
b) NaHCO3 + dil. HCl → NaCl + CO2 + H2O
c) 2 NaHCO3  Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
Question 18.
Write chemical names and formulae of Plaster of paris and gypsum.
Answer:
Calcium sulphate hemihydrate CaSO4. 1/2 H2O
Calcium sulphate dihydrate CaSO4.2H2O
Question 19.
What is the nature of the salt if the pH of its solution is greater than 7 ? Name the acid and base would be used to prepare the following salts.
i) Potassium sulphate
ii) Ammonium chloride
Answer:
Basic salt :
i) Base - KOH (Potassium hydroxide)
Acid - H2SO4 (Sulphuric acid)
ii) Base - NH4OH (Ammonium hydroxide)
Acid - HCl (Hydrochloric acid)
Question 20.
Study the following chemical equation
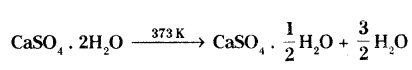
Name the reactant and the product. State one use of the product.
Answer:
Reactant - Gypsum
Product - Plaster of Paris
Use - Healing the fractured bones / casting moulds for statues or toys / dentistry.
Question 21.
State in tabif lar form the name of the acid and base from which is the following salts are formed. Also, mention the nature of the salt, whether it is acidic or basic ?
i) Sodium acetate
ii) Ammonium sulphate
| Salt |
Acid |
Salt |
Nature |
| Sodium acetate |
Acetic acid |
Sodium hydroxide |
Basic |
| Ammonium sulphate |
Sulphuric acid |
Ammonium hydroxide |
Acidic |
Question 22.
a) A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for testing carbondioxide. Write the equation . of the reaction ‘X’ with carbondioxide.
b) How is ‘X’ obtained ? Write chemical equation.
Answer:
a) Substance ‘X’ is lime water (Ca(OH)2)
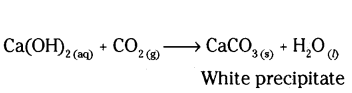
b) Lime water can be obtained from CaO (quick lime)
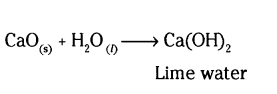
Question 23.
Give suitable reasons for the following statements "An aqueous solution of sodium chloride is neutral but an aqueous solution of sodium is basic".
Answer:
Aqueous solution of sodium chloride is neutral because it is formed from strong acid (HCl) and strong base (NaOH)
Aqueous solution of sodium forms sodium hydroxide, which is basic in nature
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
Question 24.
State the chemical property in each of the following cases, on which the following uses of baking soda are based.
a) Applied on an ant sting area.
b) In soda - acid fire extinguisher.
Answer:
a) As base, to neutralise the ant sting area,
b) To produce CO2 gas which extinguish the fire.
Question 25.
Write the chemical formula of bleaching powder. How is bleaching powder prepared? For what purpose is it used in drinking water ?
Answer:
CaOCl2
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
To kill germs or act as disinfectants.
Question 26.
What happens when nitric acid is added to egg shell ?
Answer:
Egg shells contain calcium carbonate. When nitric acid is added to it, carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
The reaction can be given as CaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2
Question 27.
A student prepared solutions of (i) an acid and (ii) base in two separate beakers. She forgot to label the solutions and litmus paper is not available in the laboratory. Since both the solutions are colourless, how will she distinguish between the two?
Answer:
Using chemical indicator like phenolphthalein or natural indicators like turmeric, china rose etc.
Question 28.
Identify the compound X on the basis of the reactions given below. Also, write the name and chemical formulae of A, B and C.
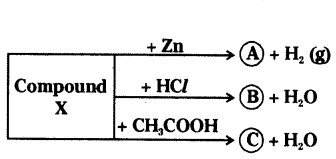
Answer:
X - NaOH (Sodium hydroxide)
A - Na2ZnO2 (Sodium zincate)
B - NaCl (Sodium chloride)
C - CH3COONa (Sodium acetate)
Question 29.
Dry ammonia gas has no action on litmus paper, but a solution of ammonia in water turns red litmus paper blue. Why is it so ?
Answer:
Ammonia dissolves in water, forms ammonium hydroxide which is base and turns red litmus blue
NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH-
Dry ammonia gas does not change into OH- ions.
Question 30.
Classify the following into strong acids and weak acids
CH3COOH. H2SO4, H2CO3, HNO3
Answer:
H2SO4 and HNO3 are strong acids
CH2COOH, H2CO3 and H2S2O3 are weak acids.
Question 31.
Explain how is pH changes in the river water can endanger the lives of aquatic animals like fish ?
Answer:
If pH of river water changes, amount of oxygen dissolved in water may decrease. Acidic and basic water is harmful for skin of aquatic animals like fish.
Question 32.
What happens when sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) and sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) react with dilute HCl, and what is the gas produced ?
Answer:
- When sodium carbonate reacts with, dilute HCl, it produces a salt, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water.
- When sodium hydrogencarbonate reacts with dilute HCl, it also produces a salt, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water.
- The gas produced in both cases is carbon dioxide (CO2).
Question 33.
For making cake, baking powder is taken. If at home your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake.
a) How will it affect’the taste of the cake and why ?
b) How can baking soda be converted into baking powder ?
c) What is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda ?
Answer:
a) If baking soda is used for making cake in place of baking powder, then cake will taste bitter since there is no tartaric acid available to neutralise sodium carbonate formed.
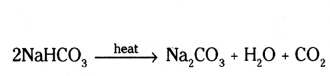
b) By adding appropriate amount of tartaric acid.
c) Tartaric acid as pointed above will react with sodium carbonate which makes cake bitter. This means that the cake will not taste bitter.
Question 34.
a) Identify the gasses evolved at the anode and cathode in the given experimental set up.
b) Name the process that occurs. Why is it called so ?
c) Illustrate the reaction of the process with the help of a chemical equation.
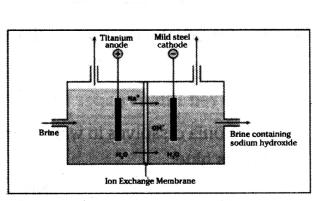
Answer:
a) Chlorine gas is off at the anode, and hydrogen gas at the cathode.
b) Chlor - alkali process because of the products formed chlor for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide.
c) 2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g).
Question 35.
The industrial process used for the manufacture of caustic soda involves electrolysis of an aqueous solution of compound ‘X’ .In this process, two gases ’Y’ and ‘T are liberated. ‘Y ’ is liberated at cathode and ‘Z’,which is liberated at anode, on treatment with dry slaked like forms a compound ‘B’. Name X, Y, Z and B.
Answer:
Compound X : Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Gas Y : Hydrogen gas (H2)
Gas Z : Chlorine gas (Cl2)
Compound B : Bleaching powder (calcium hypochlorite, Ca(ClO)2)
Question 36.
The following observations were made by a student on treating four metals P, Q, R, and S with the given salt solutions :
| Sample |
MgSO4(aq) |
Zn(NO3)2(aq) |
CaSO4(aq) |
Na2SO4(aq) |
| p |
No reaction |
Reaction occurs |
Reaction occurs |
No reaction |
| Q |
Reaction occurs |
Reaction occurs |
Reaction occurs |
Reaction occurs |
| R |
No Reaction |
Reaction |
No Reaction |
No Reaction |
| S |
No Reaction |
No Reaction |
No Reaction |
No Reaction |
Based on the observations answer the following questions :
a) Arrange the given samples in the increasing order of reactivity.
b) Write with the chemical formulas of products formed when Q reacts with CuSO4 Solution.
Answer:
a) S > R > P > Q
b) When sample Q reacts with CuSO4 solution, the chemical formula of the product formed is CuQSO4.
Question 37.
On adding a few drops of universal indicator in three colourless solutions X, Y and Z taken separately in three test tubes, a student observed the changes in colour as green in X, red in Y and blue in Z,
a) Arrange X, Y and Z in increasing order of their pH values.
b) Which one of the three X, Y and Z, will change the colour of phenolphthalein? Why?
Answer:
a) The increasing order of pH values for solutions X, Y, and Z is Y < X < Z.
b) Solution Z will change the colour of phenolphthalein because it is a basic solution that changes the colour of phenolphthalein from colourless to pink.
Question 38.
Rahul found that the Plaster of Paris, which he stored in a container, has become very hard and lost its binding nature. What is the reason for this ? Also, write a chemical equation to represent the reaction taking place.
Answer:
The Plaster of Paris becomes hard and loses its binding nature when exposed to moisture because it undergoes a chemical reaction called hydration. The chemical equation for the reaction is :
CaSO4 . 0.5H2O + 1.5H2O → CaSO4 . 2H2O
Important Questions on Acids, Bases and Salts Class 10 - 4 Marks
Question 1.
a) What is pH value of salt formed by a
i) Weak acid and strong base ?
ii) Strong acid and strong base ?
b) 15 ml of water and 10 ml of sulphuric acid are to be mixed in a beaker
i) State the method that should be followed with reason,
ii) What is this process called ?
Answer:
a) i) The pH value will be greater than 7
ii) The pH value will be less than 7
b) i) The acid is to added slowly in water to prevent the mixture to be splashed. The reaction is highly exothermic, therefore constant codling should be done.
ii) The process is called dilution.
Question 2.
a) The soil in a field is highly acidic. List any two materials which can be added to this soil to reduce its acidity. Give the reason for four choice.
b) A gas produced in a laboratory is highly soluble in water. Its colourless solution turns pink when a few drops of phenolphthalein is added to it. What is the nature of this gas ?
Answer:
a) i) Lime, (CaO) can be added to neutralise acidity.
ii) Chalk, (CaCO3) can also be added to neutralise acidity.
It is because CaO and CaCO3 are basic in nature which neutralize acid present in soil.
b) The nature of gas is basic because it turns phenolphthalein pink. The following reaction takes place in aqueous solution.
Eg : NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH-
Question 3.
a) The pH of soil A is 7.5 while that of soil B is 4.5. Which of the two soils A or B should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH and why ?
b) Name the chemical which is injected into the skin of a person.
i) During an ant’s sting
ii) During the nettle leaf sting.
How can the effect of these stings be neutralised.
Answer:
a) Soil ‘B’ is acidic. It should be treated with powdered chalk which is basic so as to adjust its pH.
b) i) Formic acid (HCOOH)
ii) Formic acid (HCOOH)
The effect of these stings neutralised by rubbing the skin with mild base like baking soda (NaHCO3).
Question 4.
What is observed when sulphur dioxide is passed through
i) water
ii) lime water
Also write chemical equation for the reactions that take place.
Answer:
i) Sulphurous acid is formed
SO2 + H2O → H2SO2 (sulphurous acid)
ii) 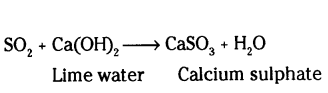
Lime water turned milky due to formations of calcium sulphate.
Question 5.
On passing excess carbon dioxide gas through lime water, it first turns milky and then becomes colourless. Explain why ? Write all the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Answer:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 (s) + H2O
CaCO3 (s) + CO2 (g) + H2O(l) → Ca(HCO3)2
Lime water turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate. It becomes colourless , when excess of CO2 is passed due to formation of CaCa(HCO3)2 which is soluble in water.
Question 6.
a) For the preparation of cakes, baking powder is used. If at home your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder. How will it affect the taste of the cake and why ?
b) How is baking soda be converted into baking powder ?
c) What makes the cake soft and spongly ?
Answer:
a) Baking powder consists of sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) and tartaric acid. If only baking soda is used in making cake, then sodium carbonate is formed on heating which will give a bitter taste to cake.
b) Baking soda can be converted into baking by adding starch can tartaric acid.
c) Sodium hydrogen carbonate gives CO2 gas which makes the cakes soft and spongy.
Question 7.
What are strong and weak acids ? In the following list of acids, separate strong acids from weak acids.
Hydrochloric acid, citric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, formic acid, sulphuric acid.
Answer:
Strong acids are those acids which are completely ionised in aqueous solution.
E.g. H2SO4 weak acids are those which do not ionise completely in aqueous solution. E.g. CH3COOH
Strong acids ; HCl, HNO3, H2SO4
Weak acids: Citric acid, acetic acid, formic acid.
Question 8.
A metal carbonate X on reacting with an acid gives a gas which when passed through a solutions Y gives the carbonate back. On the Other hand, a gas G that is obtained at anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry Y, it gives a compound Z, used for disinfecting drinking water. Identify X, Y, G and Z.
Answer:
‘X’ is calcium carbonate
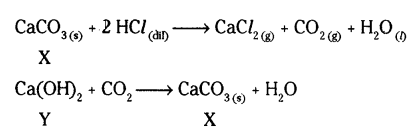
Y is calcium hydroxide
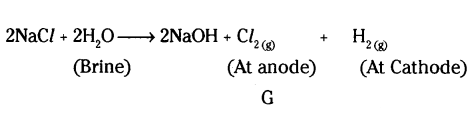
The gas G is chlorine gas which is obtained at anode.
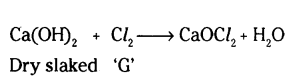
‘Z’ is calcium oxychloride used for disinfecting drinking water.
Question 9.
A dry pellet of a common base B, when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns stickly. The compound is also a by product of chlor-alkali process. Identify B. What type of reaction occurs when B is treated with an acidic oxide ? Write a balanced chemical equation for one such solutions.
Answer:
‘B’ is NaOH. It obsorbs from atmosphere because it is hydroscopic in nature. It is obtained by product of chlor-alkali process
2NaCl + 2H2O → 2NaOH + Cl2 + H2
2NaOH + CO2 →Na2CO3 + H2O
‘B’ reacts with acidic oxide (CO2) to form salt and water. This reaction is called neutralisation reaction.
Question 10.
a) A salt is produced by the reaction between an acid and a base. Identify the acid and the base from which the following salts have been formed.
i) Na2SO4
ii) NH4Cl
iii) KNO3
iv) NaCl
b) Which of the above salts has a pH less than 7 ? Why ?
Answer:
a)
| Formula of the salt |
Acid from which it is formed |
Base from which it is formed |
| i) Na2SO4 |
H2SO4 |
NaOH |
| ii) NH4Cl |
HCl |
NH4Cl |
| iii) KNO3 |
NHO3 |
KOH |
| iv) NaCl |
HCl |
NaOH |
b) NH4Cl will have pH less than 7, because.it is formed from strong acid and weak base.
Question 11.
a) Write the chemical name and chemical formula of washing soda.
b) Why is it called a basic salt ? Give its uses.
Answer:
a) Chemical name - sodium carbonate Formula - Na2CO3.10H2O
b) It is a basic salt because when dissolves in water it gives a strong base NaOH
i) In glass, paper industry
ii) As cleansing agent
iii) For removing permanent hardness.
Question 12.
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbon are taken in two test tubes A and B. H2SO4 is added to test tube A and H2CO3 in test tube B in equal amounts.
a) Identify the test tube showing vigorous reaction.
b) Give reason to support your answer.
c) Name the gas liberated in both the test tubes. How will you prove its liberation ?
d) Write the chemical equations for both the reactions.
Answer:
a) Vigorous reaction will be seen in test tube A.
b) It is because H2SO4 is stronger acid than H2CO3.
c) i) Hydrogen gas is liberated in both the test tubes.
ii) When we bring a burning candle near the evolving gas, it burns with a pop sound. This proves that the produced gas is hydrogen gas.
d) Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2
Mg + H2CO3 → MgCO3 + H2
Question 13.
How do metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates react with acids ? Give there chemical equations. Name the gas evolved during the reaction what will happen when this gas is passed through lime water ?
Answer:
a) Metal carbonate and hydrogen carbonate react with acids to give corresponding salt, carbon dioxide and water,
b) i) Metal carbonate
Na2CO3(s) 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
ii) Metal hydrogen carbonate
NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
c) Gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO2)
d) When this gas is passed through lime water, it turnes milky.
Question 14.
Write chemical equation when zinc granules react with : .
a) Sulphuric acid
b) Hydrochloric acid
c) Aluminium chloride
d) Sodium hydroxide
Answer:
a) Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
b) Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
c) Zn + AlCl3 → ZnCl3 + Al
d) Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2
Question 15.
Explain how changes in pH can lead to tooth decay, and how proper dental hygiene can prevent it.
Answer:
1) Tooth decay and pH :
a) Tooth enamel is made of calcium hydroxyapatite, which is corroded when the mouth’s pH falls below 5.5.
b) Bacteria in the mouth produce acids when degrading sugar, leading to low pH.
2) Preventing tooth decay :
a) Cleaning the mouth after eating removes food particles and bacteria.
b) Toothpaste, generally basic, neutralizes excess acid and helps prevent decay.
c) Maintaining good dental hygiene by brushing and flossing is essential to prevent pH-related tooth problems.
Question 16.
What is the common factor among all acids, and how can you demonstrate it with an experiment ?
Answer:
- The common factor among all acids is the presence of hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
- Demonstrated by an experiment:
- Using a setup with a bulb, battery and solutions of various substances, only acids
(e.g., HCl, H2SO2 allow the bulb to glow.
- Glucose and alcohol solutions, which don’t contain H ions, do not conduct electricity.
Question 17.
How is HCl gas prepared according to Figure ?
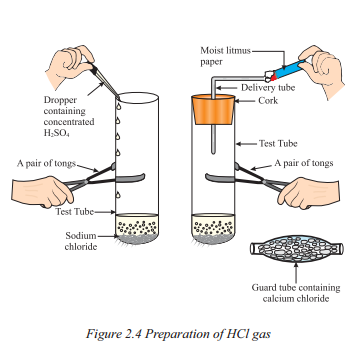
Answer:
- Take about 1 g solid NaCl in a clean and dry test tube.
- Add some concentrated sulphuric acid to the test tube.
- Observe if a gas is coming out of the delivery tube.
- Test the gas evolved with dry and wet blue litmus paper.
- Check which case causes a change in the litmus paper’s colour.
- Based on the activity, infer the acidic character of dry HCl gas and HCl solution.
Question 18.
Observe the following diagram and answer the following questions.
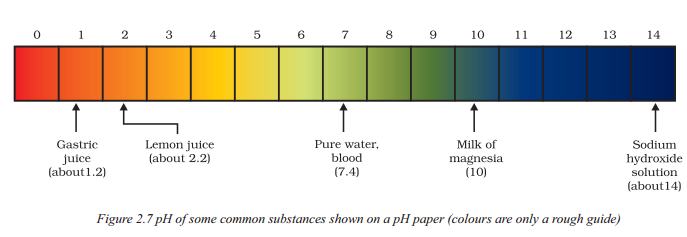
i) What does the pH paper in Figure show ?
Answer:
The pH paper in Figure shows the pH values of some common substances. The colours on the pH paper are only a rough guide to indicate the pH range of each substance.
ii) How can the pH values of substances be determined using the pH paper shown in Figure ?
Answer:
To determine the pH values of substances using the pH paper shown in Figure, a small portion of the substance should be placed on the pH paper. The paper will change colour based on the pH of the substance, indicating whether it is acidic, basic, or neutral.
iii) What is the importance of knowing the pH of substances using the pH paper shown in Figure ?
Answer:
Knowing the pH of substances is important as it allows us to understand their acidic, basic, or neutral nature. This information is useful in various applications, such as determining the ideal pH range for plant growth, testing the pH of soil, analyzing the acidity of our digestive system, and monitoring the pH levels of common substances in everyday life.
Question 19.
Observe the following table and answer the following questions.
| Natural source |
Acid |
Natural source |
Acid |
| Vinegar |
Acetic acid |
Sour milk (Curd) |
Lactic acid |
| Orange |
Citric acid |
Lemon |
Citric acid |
| Tamarind |
Tartaric acid |
Ant sting |
Methanoic acid |
| Tomato |
Oxalic acid |
Nettle sting |
Methanoic acid |
i) What acids are naturally found in vinegar and sour milk ?
Answer:
Acetic acid is found in vinegar, while lactic acid is found in sour milk (curd).
ii) Which acids can be found in oranges, lemons, tamarinds, and ant stings ?
Answer:
Oranges and lemons contain citric acid, while tamarinds contain tartaric acid. Ant stings inject methanoic acid.
iii) What acids are present in tomatoes and nettle stings ?
Answer:
Tomatoes contain oxalic acid, while nettle stings inject methanoic acid.
Question 20.
How do acids and bases behave in water solutions, and what ions do they produce? Provide examples and equations to illustrate their behaviour.
Answer:
1) Acids in water: Acids generate H+ (hydronium) ions when dissolved in water.
Example : HCl in water forms H3O+ ions.
Equation : HCl + H2O → H3O + Cl-
2) Bases in water: Bases produce OH- (hydroxide) ions when dissolved in water.
Example : NaOH in water forms Na+ and OH- ions.
Equation : NaOH(s) → Na+ + OH-
3) The behaviour of acids and bases in water solutions is essential for understanding neutralization reactions.
Question 21.
Self defence by animals and plants through chemical warfare Have you ever been stung by a honey-bee? Bee-sting leaves an acid which Causes pain and irritation. Use of a mild base like baking soda on the stung area gives relief. Stinging hair of nettle leaves inject methanoic acid causing burning pain.
i) What causes pain and irritation when stung by a honey-bee ?
Answer:
The acid in the bee-sting causes pain and irritation.
ii) How can relief be obtained from a bee sting ?
Answer:
Relief can be obtained by applying a mild base like baking soda to the stung area.
iii) What substance is injected by the stinging hair of nettle leaves?
Answer:
Methanoic acid is injected by the stinging hair of nettle leaves, causing burning pain.
iv) How does a mild base help in relieving the pain caused by nettle leaf stings ?
Answer:
The use of a mild base can help neutralize the effects of the methanoic acid and provide relief from the burning pain caused by nettle leaf stings.
Question 22.
Acids are substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. They are known for their sour taste and can corrode metals. Examples of common acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). On the other hand, bases are substances that release hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water. They have a bitter taste and a slippery feel Common bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and ammonia (NH3). Salts, which are typically formed from the neutralization of an acid and a base, are ionic compounds consisting of positive and negative ions. Common table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), is an example of a salt.
Now answer the questions:
i) What is the defining characteristic of an acid when it is dissolved in water ?
Answer:
The defining characteristic of an acid is its ability to release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
ii) Can you name a common acid used in laboratories and industrial processes ?
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a common acid used in laboratories and industrial processes.
iii) How do bases feel when touched, and what ions do they release in water ?
Answer:
Bases have a slippery feel, and they release hydroxide ions (OH-) in water.
iv) What is the primary component of salts, and how are they typically formed ?
Answer:
Salts are primarily composed of positive and negative ions. They are typically formed by the neutralization of an acid and a base.
Question 23.
Case : The Salt Story
From: The New Indian Express 9 March 2021
The salt pans in Marakkanam, a port town about 120 km from Chennai are the third largest producer of salt in Tamil Nadu. Separation of salt from water is a laborious process and the salt obtained is used as raw materials for manufacture of various sodium compounds.
One such compound is Sodium hydrogen carbonate, used in baking, as an ant¬acid and in soda acid fire extinguishers.
The table shows the mass of various compounds obtained when 1 litre of sea water is evaporated
| COMPOUND |
FORMULA |
MASS OF SOLID PRESENT /g |
| Sodium Chloride |
NaCl |
28.0 |
| Magnesium Chloride |
MgCl2 |
8.0 |
| Magnesium Sulphate |
MgSO4 |
6.0 |
| Calcium Sulphate |
CaSO4 |
2.0 |
| Calcium Carbonate |
CaCO3 |
1.0 |
| TOTAL AMOUNT OF SALT OBTAINED |
45.0 |
i) Which compound in the table reacts with acids to release carbon dioxide ?
Answer:
CaCO3, which reacts with acids to release carbon dioxide
ii) How many grams of Magnesium Sulphate are present in 135g of solid left by evaporation of sea water ?
Answer:
18g.
iii) What is the saturated solution of Sodium Chloride called ?
Answer:
Brine.
iv) What is the pH of the acid which is used in the formation of common salt ?
Answer:
Between 1 to 3
Question 24.
Write balanced acid-base neutralization reactions that would lead to formation of the following salts or acid salts.
i) CaBr2
ii) Sr(ClO2)2
iii) Ba(HS)2
iv) Li2S
Answer:
i) CaBr2 Ca(OH)2 + 2HBr → CaBr2 + 2H2O
ii) Sr(ClO2)2 Sr(OH)2 + 2HClO2 → Sr(ClO2)2 + 2H2O
iii) Ba(HS)2 Ba(OH)2 + 2H2S → Ba(HS)2 + 2H2O
iv) Li2S 2LiOH + H2S → Li2S + 2H2O
Question 25.
A compound which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with a proper quantity of water. Identify the compound and write its chemical formula. Write the chemical equation for its preparation. Mention any one use of the compound.
Answer:
- The compound prepared from gypsum that hardens when mixed with water is called calcium sulphate hemihydrate, commonly known as Plaster of Paris.
- Its chemical formula is CaSO4 . 1/2H2O.
- The chemical equation for its preparation is :
CaSO4 . 2H2O + heat → CaSO4 . 1/2 H2O + 3/2 H2O
- One use of Plaster of Paris is for making toys or molds for medical purposes, such as setting broken bones.
- It is also used in art and construction for creating decorative elements or repairing damaged surfaces.
Question 26.
The pH of a salt used to make tasty and crispy pakoras is 14. Identify the salt and write a chemical equation for its formation. List its two uses.
Answer:
- The salt with a pH of 14 that is used to make tasty and crispy pakoras is sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- The chemical equation for its formation is :
NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
- Two uses of sodium hydroxide are :
i) It is used in food preparation, such as in the curing of olives, softening pretzels, and making caramel.
ii) It is used in soap and detergent production for saponification, which is the process of converting oils and fats into soap.
Question 27.
What do you observe when you drop a few drops of acetic acid to a test tube containing :
i) Phenolphthalein
ii) Distilled water
iii) Universal indicator
iv) Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Answer:
When you drop a few drops of acetic acid to a test tube containing:
i) Phenolphthalein : The pink colour of phenolphthalein will turn colourless.
ii) Distilled water : There will be no visible change.
iii) Universal indicator : The universal indicator will turn orange or red, depending on the concentration of the acetic acid.
iv) Sodium hydrogen carbonate : There will be brisk effervescence due to the forma¬tion of carbon dioxide gas.
Question 28.
i) A compound X which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening
when mixed with proper quantity of water.
Identify ‘X’ and write its chemical formula.
ii) State the difference in chemical composition between baking soda and baking powder,
Answer:
i) The compound X that is prepared from gypsum and has the property of hardening when mixed with a proper quantity of water is Plaster of Paris. Its chemical formula is CaS04 . 1/2 H2O.
ii) The chemical composition difference between banking soda and baking powder.
| Baking Soda |
Baking Powder |
| 1) A single compound |
1) A mixture |
| 2) It consists of sodium carbonate (NaHCO3) |
2) It consists of baking soda, an acid (usually cream of tartar), and a moisture absorbent |
Question 29.
On heating X’ at 373 K, it loses water molecules and becomes Y. Y is a substance which doctors use for supporting fractured bones in the right position.
i) Identify X and Y.
ii) How can X be reobtained from Y ?
Answer:
i) X is gypsum (CaSO4 . 2H2O) and Y is Plaster of Paris (CaSO4 . 0.5H2O). Y is the substance doctors use for supporting fractured bones in the right position.
ii) X can be re-obtained from Y by adding water to Plaster of Paris, which will convert it back to gypsum.
The reaction is as follows : CaSO4 . 0.5H2O + 1.5H2O → CaSO4 . 2H2O
Question 30.
How is sodium hydroxide manufactured in industries? Name the process. In this process a gas X is formed as by - product. This gas reacts with lime water to give a compound Y, which is used as a bleaching agent in the chemical industry. Identify X and Y and write the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
Answer:
- In the manufacturing of sodium hydroxide in industries, it is produced by the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride (brine) in a process called the chlor-alkali process.
- The gas X formed as a by-product is chlorine gas (Cl2).
- This chlorine gas reacts with lime water (calcium hydroxide solution) to give a compound Y, which is bleaching powder (calcium hypochlorite, Ca(ClO)2).
- The chemical equations involved are :
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g);
Cl2(g) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → Ca(ClO)2(s) + H2O(l)
Question 31.
How is washing soda prepared from sodium carbonate ? Give its chemical equation, State the type of this salt. Name the type of hardness of water which can be removed by it ?
Answer:
- Washing soda is prepared from sodium carbonate by recrystallization.
- The chemical equation for the preparation of washing soda is :
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3 . 10H2O
- Washing soda is a hydrate of sodium carbonate.
- It can remove permanent hardness of water.
Question 32.
What would a student report nearly after 30 minutes of placing duly cleaned strips of aluminium, copper, iron and zinc in freshly prepared iron sulphate solution taken in four beakers ?
Answer:
- Aluminium and zinc will able to displace iron from iron sulphate solution.
- Copper is less reactive than iron will not give any reaction.
- Cu + FeSO4 → no reaction
- Fe + FeSO4 → no reaction
- Zn + FesO4 → Fe? + ZnSO4
- Al + FesO4 → Fe? + Al2(SO4)3
Question 33.
Complete the following table ;
| Sample solution |
Red litmus solution |
Blu litmus solution |
Phenolphthalein solution |
| Acetic acid |
|
|
|
| Sodium hydroxide |
|
|
|
| Baking soda |
|
|
|
Answer:
| Sample solution |
Red litmus solution |
Blu litmus solution |
Phenolphthalein solution |
| Acetic acid |
no colour change |
turns red in colour |
colourless |
| Sodium hydroxide |
turns blue in colour |
no colour change |
turns pink |
| Baking soda |
turns blue in colour |
no colour change |
turns pink |
Question 34.
A white coloured powder is used by doctors for supporting fractured bones.
a) Write chemical name and formula of the powder.
b) When this white powder is mixed with water a hard solid mass is Obtained. Write balanced chemical equation for this change.
Answer:
a) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate: CaSO4 . 12H2O
b) CaSO4 . 12 H2O + 32H2O → CaSO4 . 2H2O
Question 35.
Blue litmus solution is added to two test tubes A and B containing dilute HCl and NaOH solution respectively. In which test tube a colour change will be observed? State the colour change and give its reason.
Answer:
- When blue litmus solution is added to two test tubes A and B containing dilute HCl and NaOH solutions respectively, a colour change will be observed in test tube A
- The blue litmus solution will turn red in test tube A
- This colour change is due to the acidic nature of the HCl solution.
- HCl is an acid and it reacts with the blue litmus solution, causing it to change its colour to red.
Question 36.
From an experiment to study the properties of acetic acid. Answer the following questions.
i) Name the substances which on addition to acetic acid produce carbon dioxide gas. Give relevant chemical equation for the above.
ii) How is CO2, gas tested is the laboratary ?
Answer:
i) Acetic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate to produce carbon dioxide gas. , The chemical equation for this reaction is
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O.
ii) Carbon dioxide gas can be tested in the laboratory using lime water. When carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate, which is insoluble in water. The chemical equation for this reaction is CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O.
Question 37.
A teacher provided acetic acid, water, lemon juice, aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate and sodium hydroxide to students in the school laboratory to determine the pH values of these substances using pH papers. One of the students reported the pH values of the given substances as 3, 12, 4, 8 and 14 respectively.
Which one of these values is not correct? Write its correct value stating the reason.
Answer:
- The pH value reported by the student as 12 for sodium hydroxide is not correct.
- The correct pH value for sodium hydroxide is 14.
- Sodium hydroxide is a strong base, and strong bases have a pH value of 14.
- The reason for this is that strong bases completely dissociate in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH-) which contribute to the basic nature of the solution.
Question 38.
On burning Sulphur in oxygen a colourless gas is produced.
i) Write chemical equation for the reaction.
ii) Name the gas formed.
iii) State the nature of the gas.
iv) What will be the action of this on a dry litmus paper ?
Answer:
i) When sulphur is burned in oxygen, sulphur dioxide gas is produced. The chemical equation for this reaction is S + O2 → SO2.
ii) The gas formed is sulphur dioxide gas (SO2).
iii) Sulphur dioxide gas is acidic in nature.
iv) When sulphur dioxide gas is passed over a dry litmus paper, it will have no effect as it is a non-reactive gas in this context.
Extra Questions on Acids, Bases and Salts Class 10 - 8 Marks
Question 1.
a) Given below are the pH values of four different liquids 7.0, 14.0, 4.0, 2.0 Which of these could be that of
i) lemon juice
ii) distilled water
iii) 1 M sodium hydroxide solution
iv) tomato juice ?
b) i) What is the role of tooth pastes in preventing cavities ?
ii) How washing soda is prepared from baking soda ?
Answer:
a) i) Lemon juice pH = 2.0
ii) Distilled water pH = 7.0
iii) 1M NaOH pH = 14.0
iv) Tomoto Juice pH = 4.0
b) i) Bacteria present in the mouth produce acids which degrade the mouth and cause, cavities. Toothpastes are basic in nature. Using tooth paste neutralise the excess acid and prevent tooth decay.
ii) On heating baking soda, NaHCO3 it decomposes to sodium carbonate above 100°C.
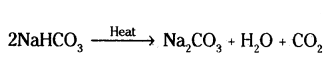
Washing soda is obtained by recrystallisation of sodium carbonate. Sodium carbonate is recrystallised by dissolving in water.
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3 . 10H2O
Question 2.
Explain the safety precautions and exothermic nature of mixing concentrated acids or bases with water.
Answer:
Safety precautions for mixing concentrated acids or bases with water :
- Always add acid/base slowly to water, not the other way around.
- Stir continuously while adding.
- Use appropriate safety gear like goggles and gloves.
- Be cautious of splashes, as they can cause burns.
- Handle concentrated nitric or sulfuric acid with extra care.
Exothermic nature :
- Mixing concentrated acids/bases with water releases heat.
- This process is highly exothermic.
- If not done carefully, it can lead to splashing, container breakage, and burns.
- Dilution reduces the concentration of ions and is important for safety.
Question 3.
How do you determine the pH of substances using a universal indicator, and what can you infer about the nature of these substances based on their pH ?
Answer:
To determine pH using a universal indicator :
- Apply the indicator to the substance.
- Observe the colour change and match it to the pH scale.
Nature of substances:
- pH values less than 7 indicate acidity.
- pH values greater than 7 indicate alkalinity.
- pH 7 is neutral.
- Substances with lower pH values have higher H+ ion concentrations and are stronger acids.
- Substances with higher pH values have higher OH- ion concentrations and are stronger bases.
Question 4.
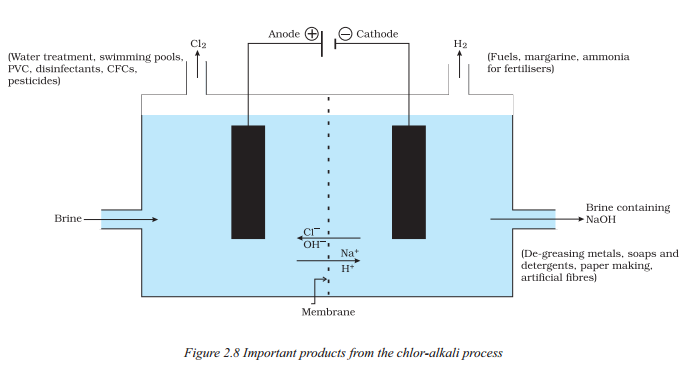
What are the important products obtained from the chior-alkali process illustrated in Figure ?
Answer:
- The important products obtained from the chior-alkali process are chlorine gas, sodium hydroxide solution, and hydrogen gas.
- Chlorine gas is given off at the anode, while hydrogen gas is produced at the cathode. Sodium hydroxide solution is formed near the cathode.
These products have various uses, such as :
- Chlorine gas is used for the manufacture of bleaching powder.
- Sodium hydroxide solution is an important raw material for various substances like sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Bleaching powder is used in textile industries for bleaching cotton and linen, in paper factories for bleaching wood pulp, and in laundry for bleaching washed clothes. It is also used as an oxidizing agent and for making drinking water free from germs.
- Baking soda, sodium hydrogencarbonate, is commonly used in the kitchen for cooking purposes and can be used to neutralize acids due to its mild non-corrosive basic nature.
Question 5.
On diluting an acid, it is advised to add acid to water and not water to acid. Explain why it is so advised ?
Answer:
Exothermic reaction :
- It is a reaction in which energy is emitted in the form of light or heat.
- Energy is released to the environment as the reaction proceeds.
- The reaction of acid and water is an exothermic reaction since a lot of heat is liberated during the reaction.
- This heat changes some water to steam explosively which can splash the acid on our face or clothes and cause acid burns. Therefore,
i) While diluting an acid, it is preferred that the acid is added to water rather than the water being added to the acid.
ii) Adding water to a concentrated acid releases a large amount of heat, which can cause an explosion and acid burns on the skin, clothing, and other body parts.
- Hence, adding acid to water is safe, but adding water to acid is not.
Question 6.
A metal carbonate X’on reacting with an acid gives a gas which when passed through a solution Y gives the carbonate back. On the other hand, a gas G that is obtained at anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry Y, it gives a compound Z, used for disinfecting drinking water. Identify X, Y, G and Z.
Answer:
- The metal carbonate X is likely calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
- When calcium carbonate reacts with an acid, it produces carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
- The solution Y is likely calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
- When carbon dioxide gas is passed through calcium hydroxide solution, calcium carbonate is regenerated.
- The gas G obtained at the anode during the electrolysis of brine is likely chlorine gas (Cl2). ;
- When chlorine gas is passed through dry calcium hydroxide, it forms calcium hy¬pochlorite (CaClO2), which is used for disinfecting drinking water.
- Therefore, X = calcium carbonate, Y = calcium hydroxide, G = chlorine gas, and Z = calcium hypochlorite.
Question 7.
i) Draw a labelled diagram to show the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas in
laboratory.
ii) Test the gas evolved first with dry and then with wet litmus paper. In which of the two cases, does the litmus paper show change in colour ?
iii) State the reason of exhibiting acidic character by dry HCl gas / HCl slolution.
Answer:

ii) The litmus paper does not show any change in colour when tested with dry blue litmus paper. However, when tested with moist blue litmus paper, it turns red. This indicates that hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas does not exhibit acidic behaviour in the absence of water but shows acidic behaviour in the presence of water.
iii) When hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas dissolves in water, it forms hydrochloric acid solution (HC/(aq)). In the solution, HCl dissociates and produces H+ or H3O+ ions. The presence of these ions makes HCl solution acidic.
The reaction can be represented as : HCl(g) + H20(l) → H3O + (aq) + Cl-(aq)
Question 8.
a) A compound X of sodium forms a white powder. It is a constituent of baking powder and is used in some antacid prescriptions. When heated, X gives out a gas and steam. The gas forms a white precipitate with limewater. Write the chemical formula and name of X and the chemical equation for its decomposition on heating. What is its role in baking powder and in antacids ?
b) Name the constituents of baking powder. What is the function of each constituent of baking piowder in the manufacture of cake.
Answer:
a) The compound X of sodium is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). On heating, it decomposes into carbon dioxide gas (CO2), water (H2O), and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3).
The chemical equation for its decomposition is :
2NaHCO3(s) → Na2CO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g).
In baking powder, sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) plays a role as a leavening agent. It releases carbon dioxide gas when heated and helps the dough or batter to rise.
In antacid prescriptions, sodium hydrogen carbonate is used to neutralize excess stomach acid, providing relief from indigestion and heartburn.
b) The constituents of baking powder are sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda), an acidic salt (such as cream of tartar, sodium aluminium sulphate), and a . moisture-absorbing agent (such as cornstarch). The function of baking soda is to release carbon dioxide gas when heated, causing the dough or batter to rise. The acidic salt reacts with baking soda to activate it, and the moisture-absorbing agent helps to prevent caking and maintain the stability of the baking powder.
Question 9.
Write the main difference between an acid and a base. With the help of suitable examples explain the term neutralization and the formation of
i) acidic,
ii) basic and
iii) neutral salts.
Answer:
The main difference between an acid and a base is their chemical properties. Acids are substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water, while bases are substances that release hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water. Acids have a sour taste, turn blue litmus paper red, and have a pH value less than 7. Bases have a bitter taste, turn red litmus paper blue, and have a pH value greater than 7.
Neutralisation is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base that results in the formation of a salt and water. The H+ ions from the acid react with the OH- ions from the base to form water, while the remaining ions combine to form a salt. The type of salt formed depends on the acid and base used.
i) Acidic salts : These are salts that are formed when a strong acid reacts with a weak base. Example : Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is formed when hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with ammonia (NH3).
HCl + NH4OH → NH4Cl + H2O
ii) Basic salts : These are salts that are formed when a weak acid reacts with a strong base. Example : Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is formed when carbonic acid (H2CO3) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
iii) Neutral salts : These are salts that are formed when a strong acid reacts with a
strong base. Example : Sodium chloride (NaCl) is formed when hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
CH3COOH + NH4OH → CH3COONH4 + H2O
Question 10.
Match the following pH values 1,7, 10, 13 to the solutions given below :
. Milk of magnesia
. Brine
. Gastric juices
. Aqueous Sodium hydroxide.
Amit and Rita decided to bake a cake and added baking soda to the cake batter.
Explain with a balanced reaction, the role of the baking soda. Mention any other use of baking soda.
Answer:
The pH values can be matched to the solutions as follows :
Milk of magnesia : pH = 10
Gastric juices : pH = 1
Brine : pH = 7
Aqueous Sodium hydroxide : pH = 13
Amit and Rita added baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO3) to the cake batter. Baking soda acts as a leavening agent in baking by releasing carbon dioxide gas when it reacts with an acid.
The balanced reaction can be represented as :
2 NaHCO3 + 2 CH3COOH → 2 CH3COONa + H2O + CO2.
Another use of baking soda is as a household cleaner and deodourizer due to its ability to neutralize odours and remove stains.
Question 11.
A cloth strip dipped In onion jiiice is used for testing a liquid ‘X’. The liquid ‘X’ changes its odour. Which type of an indicator is onion juice ? The liquid ’X’ turns blue litmus red. List the observations the liquid ‘X’ will show on reacting with the following:
a) Zinc granules
b) Solid sodium carbonate Write the chemical equations for the reactions involved.
Answer:
Onion juice is an of factory indicator. Olfactory indicators give one type of odour in acidic medium and a different odour in basic medium. As the liquid ‘X’ turns blue litmus red, hence it is an acidic solution.
a) Acids react with active metals such as zinc, magnesium, etc. and evolve hydrogen gas. The observation with zinc granules will be the evolution of hydrogen gas.
The chemical equation for the reaction is :
Zn(s) + dil.H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
b) Acids react with metal carbonates to give carbon dioxide with brisk effervescence. The observation with solid sodium carbonate will be the release of carbon dioxide gas. The chemical equation for the reaction is :
2HCl(aq) + Na2CO3(s) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Question 12.
Almost all metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxides. Metal oxides are generally basic in nature. But some metal oxides show both basic as well as acidic behaviour. Different metals show different reactivities towards oxygen. Some react vigorously while some do not react at all.
a) What happens when copper is heated in air ? (Give the equation of the reaction involved).
b) Why are some metal oxidos categorized as amphoteric ? Give one example.
c) Complete the following equations:
i) Na2O(a) + H2O (l) →
ii) Al2O3 + 2 NaOH →
Answer:
a) When copper is heated in air, it reacts with oxygen to form copper oxide. The chemi-cal equation for this reaction is 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO.
b) Some metal oxides are categorised as amphoteric because they can react with both acids and bases, exhibiting both acidic and basic behaviour. An example of an am-photeric metal oxide is aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
c) i) Nitrogen dioxide reacts with water to form nitric acid. The chemical equation for
this reaction is 3NO2 + H2O → 2HNO3 + NO.
ii) Aluminium oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium aluminate. The chemical equation for this reaction is Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O.