AP 10th Class Physical Science 1st Lesson Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions
Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 1 Important Questions - 1 Mark
Question 1.
What does the word aqueous (aq) represent in a chemical reaction ?
Answer:
It represents that the compound is present as a solution in water.
Question 2.
What is wrong with the following equation ?
Mg + O → MgO
Identify the mistake and balance the equation.
Answer:
In this equation, Oxygen should be in molecular form (02)
2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO
Question 3.
What is meant by skeletal equation ?
Answer:
The equation where the number of atoms of each element on both the sides of a chemical equation are not equal is called skeletal equation.
Question 4.
Potassium chlorate (KClO2) on heating forms potassium chloride and oxygen. Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
Answer:
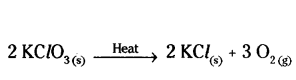
Question 5.
What do you observe when magnesium ribbon is burnt ?
Answer:
When magnesium ribbon is burnt, formation of white powder is observed along with white dazzling flame.
Question 6.
Convey the following information in the form of a balanced chemical equation.
"An aqueous solution of ferrous sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide to form a precipitate of ferrous hydroxide and sodium sulphate remains in solution".
Answer:
FeSO4(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Fe (OH)2(s) + Na2SO4(aq)
Question 7.
Balance the following chemical equation.
Answer:
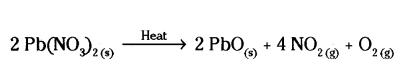
Question 8.
What is the difference between the following two types of reactions ?
AgNO3 + HCl → AgCl + HNO3
Mg + HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Answer:
The first reaction is a dou ble displacement reaction whereas second reaction is a single displacement reaction.
Question 9.
Why is hydrogen peroxide kept in coloured bottles ?
Answer:
This is done in order to cut off light because hydrogen peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen in the presence of light.
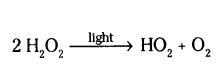
Question 10.
Give one example of a reaction which is a double displacement reaction as well as a precipitation reaction.
Answer:
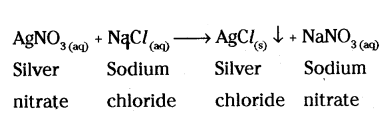
Question 11.
Why is Photosynthesis considered as an endothermic reaction ?
Answer:
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction because energy, in the form of sunlight is absorbed during the process of photosynthesis by green plants.
Question 12.
What type of reaction is represented by the digestion of food in our body ?
Answer:
Decomposition reaction.
Question 13.
Can a double displacement reaction take place when the products are highly soluble or highly ionised ?
Answer:
No, double displacement reaction takes place when there is a formation of a slightly soluble salt.
Question 14.
Name the oxidising and reducing agent in the following reaction
2 H2S + SO2 → 2H2O + 3S↓
Answer:
H2S is the reducing agent while SO2 is the oxidising agent.
Question 15.
A dilute ferrous sulphate solution was gradually added to the beaker containing acidified potassium permanganate solution. The light purple colour of the solution fades and finally disappears. Write the correct explanation for this observation.
Answer:
Potassium permanganate solution (KMnO4) is an oxidising agent. It oxidises ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) to ferric sulphate [Fe2(SO4)3].
Question 16.
Define rancidity.
Answer:
The oxidation of oils or fats in food resulting in a bad taste and smell is called rancidity.
Question 17.
Identify the oxidising agent in the following
MnO2(s) + 4 HCl → MnCl2(aq) + Cl2(g) + 2H2O
Answer:
MnO2 is the oxidising agent in the given reaction.
Question 18.
Complete the missing component / variable given as X and Y in the following reaction.
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(X) + H2(Y)
Answer:
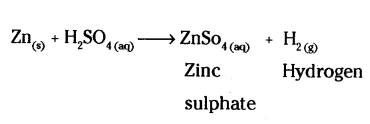
Question 19.
Identify the reducing agent in the following reaction.
Fe2O3 + 3 CO → 2 Fe + 3 CO2
Answer:
CO is the reducing agent in the given reaction.
Question 20.
What can be seen when a strip of copper metal is placed in a solution of silver nitrate ?
Answer:
Metallic silver is precipitated and a blue solution containing copper nitrate is obtained
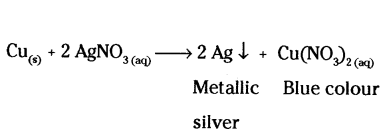
Question 21.
State one industrial application of reduction process.
Answer:
It is used in the metallurgical processes for the refining of metals.
Question 22.
Which one of the following is a chemical change ? Give reason also,
a) Burning of wax
B) Melting of wax
Answer:
Burning of wax. Because candle wax is a hydrocarbon which burns to produce CO2 and H2O and it is an irreversible change.
Question 23.
Which one is a chemical change ? Rusting of iron or melting of iron ?
Answer:
Rusting of iron.
Question 24.
State one basic difference between a physical change and a chemical change.
Answer:
In a physical change, no new substance is formed while in a chemical change, a new substance is formed.
Question 25.
What type of coating is formed on silver articles when they get corroded ?
Answer:
The silver articles from black coating of silver sulphide (Ag2S).
Question 26.
What type of coating is formed on copper articles when they get corroded ?
Answer:
The copper articles form green coating of basic copper carbonate (CuCO3 . Cu(OH)2)
Question 27.
Which one is a chemical change ? Electrolysis of water or sodium chloride exposed to sunlight ?
Answer:
Electrolysis of water.
Question 28.
If copper metal is heated over a flame, it develops a coating. What is the colour and composition of this coating ?
Black, CuO or Copper oxide.
Question 29.
What is balanced chemical equation ?
Answer:
The equation in which the number of atoms of all the molecules is equal on both sides of the equation is called balanced chemical equation.
Question 30.
Name the type of chemical reaction which takes place when quick lime is added to water.
Answer:
When quick lime is added to water, rise in temperature observed. Hence, it is an example of exothermic reaction.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
Question 31.
W hat is meant by a chemical reaction ?
Answer:
The reaction representing a chemical change is called chemical reaction.
Question 32.
On what basis is a chemical equation balanced ?
Answer:
It is based on law of conservation of mass.
Question 33.
Hydrogen being a highly inflammable gas and oxygen being a supporter of combustion, yet water which is a compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen is used to extinguish fire. Why ?
Answer:
It is because properties of compound (H2O) are different from properties of its constituting elements, i.e., H2 and O2.
Question 34.
What change in colour is observed when white silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight ? State the type of chemical reaction in this change.
Answer:
Silver chloride becomes grey. It is a photochemical decomposition reaction.
Question 35.
Potato chips manufacturers fill the packet of chips with nitrogen gas. Why ?
Answer:
To provide an inert atmosphere to prevent chips from getting oxidised. N2 does not allow chips to get spoiled by oxidation.
Question 36.
Why do gold and platinum not corrode in moist air ?
Answer:
They are least reactive and do not react with substances present in moist air.
Question 37.
Write two characteristics associated with rancid food.
Answer:
Unpleasant smell and unpleasant taste.
Question 38.
Give reason for the following :
The burning of natural gas is an exothermic reaction.
Answer:
Burning of natural gas is an exothermic reaction because heat is produced in this reaction.
Question 39.
Give one example of a redox reaction which is also a combination reaction.
Answer:
2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO.
Question 40.
How will you define a reducing agent ?
Answer:
Reducing agent is a substance which can add hydrogen or remove oxygen.
Question 41.
Write the name of the product which represents the solid state in the below reaction.
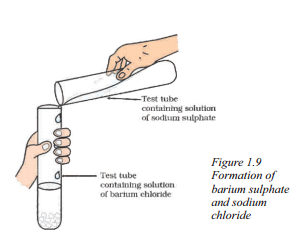
Answer:
The product that represents the solid state in the above reaction is Barium sulphate.
Question 42.
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + xHyO + zCl2
In order to balance the above chemical equation, what are the values of x, y and z respectively ?
Answer:
In order to balance the chemical equation MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2, + yHyO + zCl2, the values of x, y, and z respectively are 2, 2, 1.
Balanced Equation : MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Question 43.
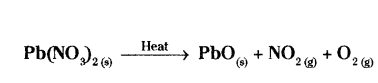
Why is the emission of brown fumes in the given experimental set-up ?
Answer:
The emission of brown fumes in the given experimental set-up is due to the thermal decomposition of lead nitrate which produces brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide.
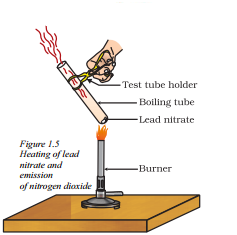
Question 44.
Observe the experimental set-up carefully.
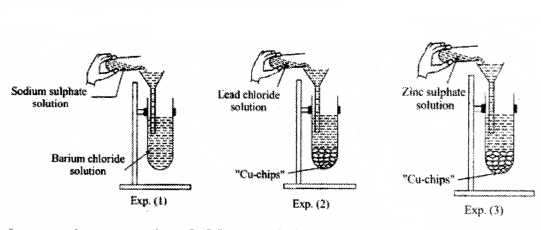
In which experiment an Insoluble precipitate is formed and of which substance?
Answer:
Exp1,BaSO4
Question 45.
Observe this experiment carefully.
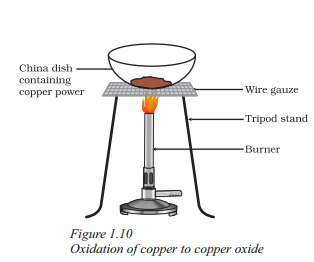
In above experiment copper powder turned to black coloured product on heating. What is the reason for this ?
Answer:
Copper (II) oxide is formed.
Question 46.
Identify ‘x, ‘y’ and ‘z’ in the following reaction
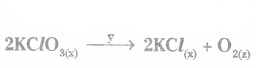
Answer:
x - physical state of KClO3 and KCl
y = reaction condition
z = physical state of Oz.
Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Important Questions - 2 Marks
Question 1.
Give the chemical name of the reactants as well as the products of the following chemical equation
HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
Answer:
Chemical name of reactants
HNO3 - Nitric acid
Ca(OH)2 - Calcium hydroxide
Chemical name of products
Ca(NO3)2 - Calcium Nitrate
H2O - Water
Question 2.
Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
i) Silver bromide on exposure to sunlight decomposes into silver and bromine.
ii) Sodium metal reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer:
i) 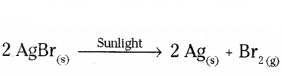
ii) 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Question 3.
Define combination reaction. Give one example of a combination reaction which is also exothermic.
Answer:
A reaction in which two elements or compounds combine to form a single compound is called combination reaction.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
It is also an exothermic reaction because heat is evolved.
Question 4.
When magnesium ribbon burns in air or oxygen, a product is formed. State the type of chemical reaction and name the product formed in the reaction. Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
Answer:
The type of reaction is combination reaction and the product formed is magnesium oxide.

Question 5.
A zinc plate was put into a solution of copper sulphate kept in a glass container. It was found that hflue colour of the solution gets fader and fader with the passage of time. After a few days when zinc plate was taken out of the solution, a number of holes were observed on it.
i) State the reason for changes observed on the zinc plate,
ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
i) A number of holes were observed because zinc has displaced copper from CuSo4. Zinc metal has been used to form zinc sulphate, therefore, number of holes were observed.
ii) 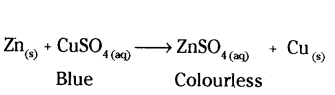
Question 6.
Identify the following changes as chemical or physical,
a) Crumpling a sheet of aluminium foil
b) Baking a cake
c) Sublimation of dry ice
d) Burning paper
Answer:
a) Physical change
b) Chemical change
c) Physical change
d) Chemical change
Question 7.
Write the chemical equation of the reaction in which the following changes have taken place with an example of each.
a) Change in temperature
b) Formation of precipitate
Answer:
a) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O + Heat
b) 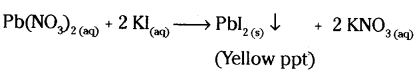
Question 8.
Write chemical equation for the reactions taking place when
a) Magnesium reacts with dil, HCl
b) Copper is heated in air
Answer:
a) Mg + 2 HCl → MgCl2 + H2
b) 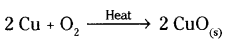
Question 9.
Define the term decomposition reaction. Give an example, each of thermal decomposition and electrolytic decomposition reactions.
Answer:
Decomposition reactions: Those reactions in which a compound splits up into two or more simpler substance are called decomposition reactions.
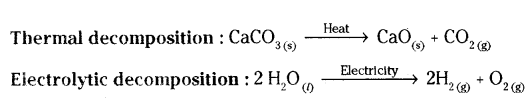
Question 10.
2g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a dry boiling tube.
a) List any two observations
b) Name the type of chemical reactions taking place
c) Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer:
a) Green colour of FeSO4 disappears and reddish brown Fe2O3 is formed smell of burning sulphur.
b) Decomposition reaction.
c) 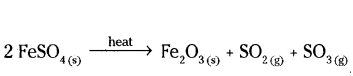
Question 11.
Decomposition reactions require energy either in the form of heat or light or electricity for breaking down the reactants. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity.
Answer:

Question 12.
In the reaction
MnO2 + 4 HCl → MnCl2 + 2 H2O + Cl2
a) Name the compound i) oxidised ii) reduced
b) Define oxidation and reduction on its basis.
Answer:
a) i) HCl is getting oxidised
ii) MnO2 is getting reduced
b) The removal of hydrogen from a substance is called oxidation. The removal of oxygen from a . substance is called reduction.
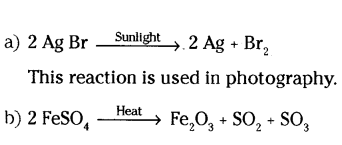
Question 13.
a) Write the essential condition for the following reaction to take place
2 Ag + Br → 2 Ag + Br
2
Write one application of this reaction,
b) Complete the following chemical equation of a chemical reaction
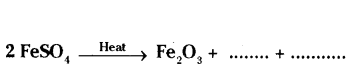
Answer:
Question 14.
State the type of chemical reaction with chemical equation that take place in the following
a) Magnesium ribbon is burnt in air.
b) Electric current is passed through water.
Answer:
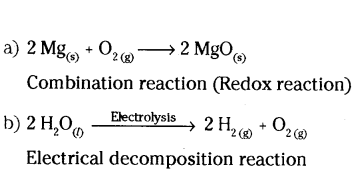
Question 15.
a) What happens when water is added to quick lime ? Write chemical equation.
b) What happens Ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases are mixed ? Write chemical
equation.
Answer:
a) Slaked lime is formed with hissing sound and lot of heat is evolved
CaO + H2 → Ca(OH)2 + Heat
b) NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s)
Combination reaction.
Question 16.
The carbonate of metal X is a white solid. It decomposes when heated to form carbon dioxide and a yellow solid oxide. What is metal X ?
Answer:
Metal X is lead (pb). The name of metal carbonate is lead carbonate (PbCO3).
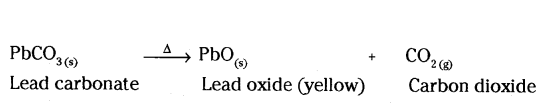
Question 17.
What is the difference between the following two reactions ?
a) Mg + 2 HCl → MgCl2 + H2
b) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O.
Answer:
a) Here, Mg is more reactive than H. Hence, displaces hydrogen. Therefore, it is a displacement reaction.
b) In this reaction, exchange of ions between the reactants occur. Hence, it is a double displacement reaction.
Question 18.
Why do not a wall immediately acquire a white colour when a coating of slaked lime applied on it ?
Answer:
When a solution of slanked lime is applied on the wall, CO2 gas present in air slowly reacts with thin layer of calcium hydroxide to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate, that is quite white.
Therefore, the newly formed calcium carbonate impart white look to the walls.
Question 19.
State one example each characterised by the following along with the chemical equation.
a) Change id state
b) Evolution of gas
Answer:
a) Burning of coal C(s) + O2(g) → C02(g)
b) Evolution of gas Zn(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(s) + H2(g)↑
Question 20.
Write chemical equations for the reaction taking place when
a) Magnesium reacts with dilute UNO
b) Sodium reacts with water
Answer:
a) Mg(s) + 2 HNO3(aq) → Mg(NO)32(aq) + H2(g)
b) 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) → H2(g) + 2 NaOH(aq)
Question 21.
A metal salt MX when exposed to light, split up to form metal M and a gas X2. Metal M is used in making ornaments. Whereas gas X2 is used in making bleaching powder. The salt MX is itself used in black and white photography.
a) Identify metal M and gas X2.
b) Mention the type of chemical reaction involved when salt MX is exposed to light.
Answer:
a) The metal (M) is silver (Ag) and gas (X2) is chlorine (Cl2)
b) The chemical reaction involved is decomposition
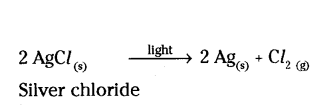
Question 22.
Mention with reason the colour changes observed when
a) Silver chloride is exposed to sunlight.
b) Copper powder is strongly heated in the presence of oxygen.
Answer:
a) White to grey
Reason : Silver chloride decomposes to produce silver and chloride.
b) Brown to black
Reason : Copper oxide is produced on heating.
Question 23.
2g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish and the china dish is placed in sunlight for some time. What will be your observation in this case ? Write the chemical reaction involved in the form of a balanced chemical equation. Identify the type of chemical reaction.
Answer:
White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight
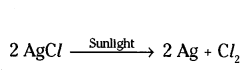
Decomposition reaction / Photolytic decomposition.
Question 24.
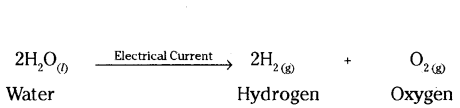
In electrolysis of water, why is the volume of gas collected over one electrode double that of gas collected over the other electrode ?
Answer:
Because during electrolysis, water splits into two molecules of hydrogen and one molecule of oxygen
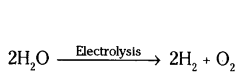
Here, the gases hydrogen and oxygen present on both electrodes are in the ratio 2 : 1.
Question 25.
On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to copper oxide powder, the solution formed is blue green. Predict the new compound formed which imparts a blue green colour to the solution.
Answer:
The new compound formed is copper chloride (CuCl2) which imparts a blue green colour to the solution.
Question 26.
Complete and balance the following chemical equations
a) CaCO3 + HCl →
b) Al + HCl →
Answer:
a) CaCO3 + 2 HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
b) 2 Al + 6 HCl → 2 AlCl3 + 3H2
Question 27.
Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions.
a) 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
b) 2H2 + O → 2H2O
Answer:
a) Ammonia (NH3)
b) Hydrogen (H2)
Question 28.
A substance ‘X’ is used as a building material and is insoluble in water. When it reacts with dil. HCl, it produces a gas which turns lime water milky.
i) Write the chemical name and formula of ’X’.
ii) Write chemical equations for the chemical reactions involved in the above statements.
Answer:
Substance ‘X’ is used as a building material and is insoluble in water. When it reacts with dil. HCl, it produces a gas that turns lime water milky.
i) The chemical name and formula of ‘X’ is calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
ii) The chemical equations for the reactions involved are :
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
CO2(g) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Question 29.
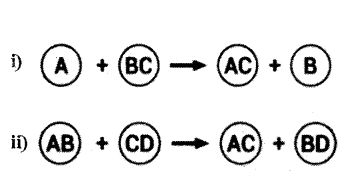
Identify the types of reaction mentioned above in (i) and (ii). Give one example for each type in the form of a balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
i) Displacement reaction :
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s).
(or)
Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s).
(or)
Pb(s) + CuCl2 (s) → PbCl2 (aq) + Cu (s).
ii) Double displacement reaction :
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq).
Question 30.
Represent each of the following word equations with a balanced chemical equation.
a) Disilane gas (Si2H6) undergoes combustion to form solid silicon dioxide and water.
b) Solid aluminium hydride is formed by a combination reaction of its two elements.
c) When solid calcium bisulfite is heated, it decomposes to solid calcium oxide, sulfur dioxide gas, and water.
Answer:
a) 2Si2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4SiO2 + 6H2O(l)
b) 2Al(s) + 3H2 (g) → 2AlH3(S)
c) Ca(HSO3)2(s) → CaO(s) + 2SO2(s) + H2O(l)
Question 31.
i) Write two observations when lead nitrate is heated in a test tube.
ii) Name the type of reaction.
iii) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the reaction.
Answer:
i) When lead nitrate is heated in a test tube, two observations can be made: the white crystals of lead nitrate turn yellow and then red, and a brown gas with a pungent smell evolves.
ii) The type of reaction is thermal decomposition.
iii) The balanced chemical equation to represent the reaction is :
2Pb(NO3)2(s) → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g).
Question 32.
A compound ‘X’ of sodium is used as an antacid and it decomposes on strong heating.
i) Name the compound ‘X’ and give its chemical formula.
ii) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the decomposition ‘X’.
iii) Give one use of compound ‘X’ besides an antacid;
Answer:
i) The compound ‘X’ of sodium used as an antacid is sodium hydrogen carbonate with the chemical formula NaHCO3.
ii) The balanced chemical equation to represent the decomposition of compound ‘X’ is :
2NaHCO3(s) → Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(g).
iii) Besides being an antacid, compound ‘X’ is also used in baking as a leavening agent.
Question 33.
A student took a small amount of copper oxide in a conical flask and added dilute hydrochlorie acid to it with constant stirring. He observed a change in colour of the solution.
i) Write the name of the compound formed and its colour.
ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
i) The compound formed is copper chloride (CuCl2) and its colour is blue-green,
ii) The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: copper oxide + hydrochloric acid → copper chloride + water, i.e., CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
Question 34.
You are provided with 90 mL of distilled water and 10 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid to prepare dilute sulphuric acid.
i) What is the correct way of preparing dilute sulphuric acid ? Give reason,
ii) How will the concentration of H
3O
+ ions change on dilution ?
Answer:
i) The correct way of preparing dilute sulphuric acid is to add the 10 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid slowly to 90 mL of distilled water while stirring continuously. This is because adding water to acid can cause a violent reaction.
ii) The concentration of H3O+ ions decreases on dilution.
Question 35.
Complete and balance the following chemical equations :
i) NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) →
ii) CaCO3(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) →
iii) HCl(aq) + H3O(l) →
Answer:
The balanced chemical equations for the given reactions are:
i) 2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
ii) CaCO3(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) → Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
iii) HCl(aq) + H2O(aq) → H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Important Questions on Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 - 4 Marks
Question 1.
Classify the following chemical reactions as exothermic or endothermic
a) Electrolysis of water
b) Burning of natural gas
c) Decomposition of calcium carbonate
d) Burning of magnesium ribbon in air
Answer:
a) Endothermic reaction
b) Exothermic reaction
c) Endothermic reaction
d) Exothermic reaction
Question 2.
Identify the type of reaction in each of the following reactions :
a) Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
b) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
c)
d) AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s)↓ + MaNO3(aq)
Answer:
a) Displacement reaction
b) Combination reaction
c) Decomposition reaction
d) Double displacement reaction
Question 3.
Define a chemical equation. What is an unbalanced chemical equation called ?
Answer:
A chemical equation is a short hand representation of a chemical reaction using the symbols and formulae of substance involved in the chemical reaction.
Unbalanced chemical equation is only a skeletal chemical equation which gives the information about reactants and produces and not about their actual number involved.’
Question 4.
State applications of a decomposition reaction.
Answer:
Applications of a decomposition reaction :
a) White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight due to the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine.
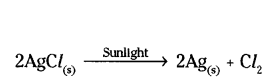
It is used in black and white photography.
b) Quick lime can be prepared by thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate (lime stone)
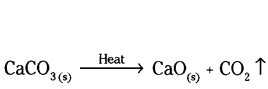
CaO is used to prepare slaked time which is used in white washing.
Question 5.
Which two observations will be made when quick lime is added to water ? Mention two uses of the product.
Answer:
Observations:
a) Reaction takes place vigorously.
b) A large amount of heat is produced.
Uses of the product Ca(OH)2 :
a) It is used for white washing walls. It slowly reacts with the CO2 in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate on the walls.
b) It is used as a laboratory reagent for testing the presence of CO2 gas.
Question 6.
A metal ‘P’ when exposed to the moist air for longer period of times, losses its shiny brown surface and gains green coat. Why has its happened ? Identify the metal, write the name and chemical formula of this green coloured compound. List two ways to prevent this process.
Answer:
a) The metal has been corroded.
b) Metal is copper.
c) Green coating is basic copper carbonate CuCO3 . Cu(OH)2.
d) Protect from moisted CO2 air.
e) Making alloys of copper.
Question 7.
What happens when a piece of
a) Zinc metal is added to copper sulphate solution.
b) Silver metal is added to copper sulphate solution.
Also write balanced chemical equation, if the reaction occurs.
Answer:
a) Zinc displaces Cu from its solution.
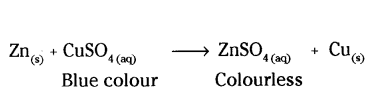
b) Silver metal being less reactive than copper cannot displace copper from the salt solution, therefore, no reaction occurs.
Ag(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → No reaction.
Question 8.
A magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen to give a white compound ‘X’ accompanied by the emission of light. If the burning ribbon is now placed in an atmosphere of nitrogen, it continues to burn and forms a compound Y.
a) Write the chemical formulae of X and Y.
b) Write a balanced chemical equation, when X is dissolved in water ?
Answer:
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
a) X is MgO, Y is Mg3N2
b) MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
Question 9.
Which among the following are physical or chemical changes ?
a) Evaporation of petrol
b) Burning of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
c) Heating of an iron rod to red hot
d) Curdling of milk
Answer:
a) Physical change
b) Chemical change
c) Physical change
d) Chemical change
Question 10.
How do we come to know that a chemical reaction has taken place ?
Answer:
The presence of any of the following changes helps us to determine that a chemical reaction has taken place.
a) Formation of new substance(s)
b) Change in state
c) Change in dolour
d) Change in temperature
e) Formation of a precipitate
f) Evolution of a gas
For example, if on mixing two substances a gas is evolved, then we can say that a chemical reaction has taken place.
Question 11.
Which among the following changes are exothermic or endothermic in nature ?
a) Decomposition of ferrous sulphate
b) Dilution of sulphuric acid
c) Dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water
d) Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water
Answer:
a) Is endothermic as heat is abosrbed in these changes.
b) Is exothermic as heat is released in these changes.
c) Is exothermic as heat is released in these changes.
d) Is endothermic as heat is absorbed in these changes.
Question 12.
What is an oxidation reaction ? Give an example of oxidation reaction. Is oxidation an exothermic or an endothermic reaction ?
Answer:
The reaction in which oxygen combines with other elements or compounds is known as an oxidation reaction. For example, burning of hydrogen is an oxidation process in which hydrogen combines with oxygen to form water.
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O(l)
Oxidation reactions are exothermic
Question 13.
Complete the missing components/variables given as x and y in the following reactions.
a) Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) → PbI2(x) + 2KNO3(y)
b) Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(x) + 2Ag(s)
c) Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnS4(x) + H2(y)
d)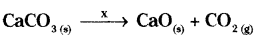
Answer:
a) x - (s) ; y - (aq)
b) x - (aq)
c) x - (aq) ; y - (g)
d) x - Heat
Question 14.
Identify the substance oxidised, substance reduced, oxidising agent and reducing agent.
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Answer:
Substance oxidised : HCl
Substance reduced : MnO2
Oxidising agent: MnO2
Reducing agent: HCl
Question 15.
Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions.
a) 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
b) H2O + F2 → HF + HOF
c) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
d) 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Answer:
a) Ammonia (NH3)
b) Water (H2O) as F2 is getting reduced to HF
c) Carbon monoxide (CO)
d) Hydrogen (H2)
Question 16.
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and balance them
a) Lead nitrate reacts with sulphuric acid to form a precipitate of lead sulphate and nitric acid.
b) Calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride, water and carbon dioxide.
c) Aluminium metal strip is added in hydrochloric acid to produce aluminium chloride and hydrogen gas.
d) Sodium carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid gives sodium chloride and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Answer:
a) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) → PbSO4 (s) + 2HNO3 (aq)
b) CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + H2O(l) + CO2 (g)
c) 2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2 (g)
d) Na2CO3 (s) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + NaHCO3 (s)
Question 17.
Classify the following reactions into different types :
a) AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3 (aq)
b) CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
c) 2KClO3 (s) 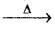 2KCl(aq) + 3O2 (g)
2KCl(aq) + 3O2 (g)
d) Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Answer:
a) Double displacement reaction, precipitation reaction.
b) Combination reaction.
c) Thermal decomposition reaction.
d) Displacement reaction.
Question 18.
A silver article generally turns black when kept in the open for a few days. The article when rubbed with toothpaste again starts shining.
a) Why do silver articles turn black when kept in the open for a few days ? Name the phenomenon involved.
b) Name the black substance formed and give its chemical formula.
Answer:
a) Metals such as silver when attacked by substances around it such as moisture, acids, gases etc., are said to corrode and this phenomenon is called corrosion.
b) The black substance is formed because silver (Ag) reacts with H2S present in air. It forms thin black coating of silver sulphide (Ag2S)
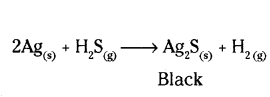
Question 19.
Decomposition reactions require energy either in the form of heat or light or ele- ctncity for breaking down the reactants. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity.
Answer:
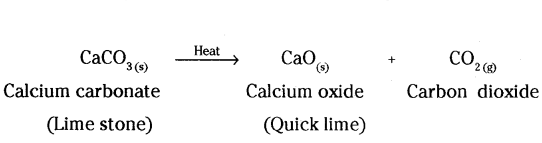
Decomposition reaction : A reaction in which a single reactant breaks down to form two or more products is known as decomposition reaction.
a) When a decomposition reaction is carried out by heating, then it is known as thermal decomposition reaction.
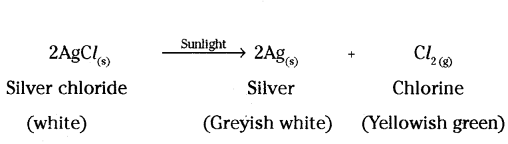
b) A decomposition reaction in which energy is supplied in the form of light, is known as photochemical decomposition reaction.
c) A decomposition reaction in which energy is supplied in the form of electricity is known as electrolytic decomposition reaction.
Question 20.
a) Define corrosion.
b) What is corrosion of iron called ?
c) How will you recognise the corrosion of silver ?
d) Why corrosion of iron is a serious problem ?
e) How can we present corrosion of iron ?
Answer:
a) Corrosion is a process in which metals are deteriorated by action of air, moisture, chemicals etc.
b) Rusting
c) Silver - black copper green
d) It causes destruction of car bodies, bridges, railing, etc.
e) By painting, alloying, greasing, etc.
Question 21.
a) Write one example for each of decomposition reaction carried out with help of
i) Electricity
ii) Heat
iii) Light
b) Which of the following statements is correct and why ?
i) Copper can displace silver from silver nitrate.
ii) Silver can displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
Answer:
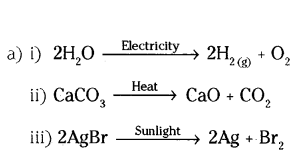
b) Statement (i) is correct.
Copper can displace silver from AgNO3 as copper is more reactive than Ag.
Question 22.
What observations can be made when comparing the iron nails and copper sulphate solutions before ami after the s dment depicted in Figure?
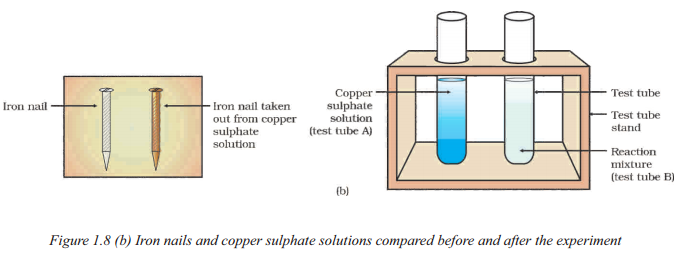
Answer:
When comparing the iron nails and copper sulphate solutions before and after the
experiment depicted in Figure, the following observations can be made :
- The intensity of the blue colour of the copper sulphate solution in test tubes (A) and (B) can be compared.
- The colour of the iron nails dipped in the copper sulphate solution can be compared with the one kept aside.
- These observations will help determine the changes that occur in the copper sulphate solution and the iron nails during the experiment.
Question 23.
Write balanced chemical equations to explain what happens, when
i) Mercuric oxide is heated.
ii) Mixture of cuprous oxide and cuprous hide is heated.
iii) Aluminium is reacted with manganese dioxide,
iv) Ferric oxide is reduced with aluminium.
v) Zinc carbonate undergoes calcination
Answer:
i) Mercuric oxide is heated.
2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
ii) Mixture of cuprous oxide and cuprous sulphide is heated.
2Cu2O(s) + Cu2S(s) → 6Cu(s) + SO2(g)
iii) Aluminium is reacted with manganese dioxide.
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s) → 3Mn(s) + 2Al2O3(s)
iv) Ferric oxide is reduced with aluminium.
Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(s) + Al2O3(s)
v) Zinc carbonate undergoes calcination.
ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g).
Question 24.
i) While electrolysing water before passing the current some drops of an acid are added. Why ? Name the liberated at cathode and anode. Write the relationship between the volume of gas collected at anode and the volume of gas collected at cathode.
ii) What is observed when silver chloride is exposed to sunlight ? Give the type of reaction involved.
Answer:
i) Adding drops of an acid during electrolysis of water helps to increase its conductivity.
The gases liberated at the cathode and anode are hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) respectively.
The relationship between the volumes of gas collected at the anode-and cathode is 1 : 2, as the molar ratio of the gases produced during electrolysis of water is 2 : 1.
ii) When silver chloride is exposed to sunlight, it undergoes a photochemical reaction.
The silver chloride decomposes and forms silver metal and chlorine gas.
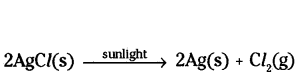
Question 25.
You might have noted that when copper powder is heated in a China dish, the reddish brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance.
a) Why has this black substance formed ?
b) What is the black substance ?
c) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place.
d) How can the black coating on the surface be turned reddish brown ?
Answer:
a) Black coloured substance is formed by the oxidation of copper.
b) Black substance is copper (II) oxide.
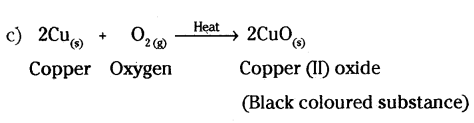
d) On passing hydrogen gas (H2) over the heated material.
Question 26.
What happens when food materials containing fats and oils are left for a long time? List two observable changes and suggest three ways by which this phenomenon can be prevented.
Answer:
- Food becomes rancid due to oxidation of oils and fats.
- There is a changed in smell.
- There is a change in taste.
- Antioxidants are added to the food.
- Food should be kept in air-tight containers.
- Flush the bags of chips with nitrogens.
Question 27.
When a magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen, it gets converted to magnesium oxide. This description of a chemical reaction in a sentence form is quite long. It can be written in a shorter form. The simplest way to do this is to write it in the form of a word-equation.
The word-equation for the above reaction would be -
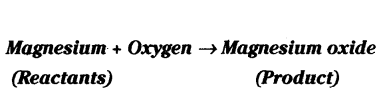
1. What is the purpose of writing a chemical reaction in the form of a word-equation?
Answer:
a) The purpose of a word-equation is to represent a chemical reaction in a simplified and concise form using words.
b) It helps convey the essential information about the reactants and products involved in the reaction.
2. How does the word-equation format differ from a full sentence description of a chemical reaction?
Answer:
a) A word-equcftion is a shorter and more compact representation of a chemical reaction compared to a full sentence description.
b) It uses words to indicate the reactants on the left-hand side (LHS) and the produces) on the right-hand side (RHS) with arrows in between, making it easier to understand quickly. ,
3. Can you.provide an example of another chemical reaction described using a word- equation?
Answer:
Sure! Here’s an example: "Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water" (Reactants) → (Product). This word-equation represents the formation of water when hydrogen and oxygen react.
4. Why is it important to use word-equations in chemistry?
Answer:
a) Word-equations are important in chemistry because they offer a concise way to communicate chemical reactions.
b) They simplify complex reactions, making it easier for students and scientists to understand and remember the essential components of a reaction.
Quetion 28.
Writing Symbols of Physical States Carefully examine the balanced Eq : 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O + 4H2. No information has been given in this equation about their physical states.
To make a chemical equation more informative, the physical states Of the reactants and products are mentioned along with their chemical formulae. The gaseous, liquid, aqueous and solid states of reactants and products are represented by the notations (g), (0, (aq) and (s), respectively. The word aqueous (aq) is written if the reactant or productis present as a solution in water.
The balanced Eq. 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
becomes: 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
1. Why is it important to include physical state symbols in a chemical equation ?
Answer:
a) Including physical state symbols provides valuable information about whether the reactants and products are in gaseous (g), liquid (l), aqueous (aq), or solid (s) form.
b) This helps in understanding the conditions and phases of substances involved in the reaction.
2. How is the gaseous state represented in a chemical equation?
Answer:
The gaseous state is represented by the notation "(g)" placed after the chemical formula of a substance, such as "H2O(g)" for water vapour.
3. When is the notation "(aq)" used in a chemical equation?
Answer:
The notation "(aq)" is used when a reactant or product is present as a solution in water, indicating an aqueous state. For example, "NaCl(aq)" represents sodium chloride dissolved in water.
Question 29.
During d chemical reaction atoms of one element do not change into those of another element. Nor do atoms disappear from the mixture or appear from elsewhere. Actually, chemical reactions involve the breaking and making of bonds between atoms to produce new substances.
1. What does Eq. 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2 become when physical state symbols are included ?
Answer:
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g), indicating that iron and water are in solid and gaseous states, respectively, in this reaction.
2. Do atoms of one element change into atoms of another element during a chemical reaction ?
Answer:
No, during a chemical reaction, atoms of one element do not change into atoms of another element.
3. What happens to atoms during a chemical reaction?
Answer:
a) Atoms in a chemical reaction do not disappear or appear from elsewhere.
b) Chemical reactions involve the breaking and making of bonds between atoms to produce new substances.
4. How can we describe the fundamental process in a chemical reaction?
Answer:
The fundamental process in a chemical reaction is the breaking and making of chemical bonds between atoms.
Question 30.
When fats and oils are oxidised, they become rancid and their smell and taste change. Usually substances which prevent oxidation(antioxidants) are added to foods containing fats and oil. Keeping food in air tight containers helps to slow down oxidation. Do you know that chips manufacturers usually flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen to prevent the chips from getting oxdised.
1. What happens to fats and oils when they undergo oxidation?
Answer:
When fats and oils undergo oxidation, their smell and taste change, and they become rancid.
2. How is oxidation in fats and oils prevented in food products?
Answer:
Oxidation in fats and oils is prevented by adding substances known as "antioxidants" to foods that contain fats and oils.
3. What is one effective method for slowing down the oxidation of food containing fats and oils?
Answer:
Storing food in airtight containers is an effective method to slow down the oxidation of fats and oils.
4. How do chips manufacturers prevent chips from getting oxidized?
Answer:
Chips manufacturers often flush bags, of chips with gases like nitrogen to displace oxygen inside the bags, preventing the chips from undergoing oxidation and maintaining their freshness.
Extra Questions on Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 - 8 Marks
Question 1.
Explain the balancing a chemical equation with an example.
Answer:
Step 1 : Write the chemical equation Fe + 4 H2O → Fe2O3 + H2
Step 2 : Count the number of atoms of each element on both the sides of the chemical equation.
| Element |
Number of atoms at reactants side |
Number of atoms at products side |
| 1) |
1 |
3 |
| 2) |
2 |
2 |
| 3) |
1 |
4 |
Step 3 : Equalize the number of the atoms of element which has the maximum number by putting infront of it
Fe + 4H2O → Fe2O3 + H2
Step 4 : Try to equalize all the atoms of elements on reactant and product side by adding co-efficient infront of it
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
Now, all the atoms of elements are equal on both sides.
Step 5 : Write the physical states of reactants and products.
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(l) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Solid state = (s), Liquid state = (l), Gasesous state = (g), Aqueous state = (aq)
Step 6 : Write necessary conditions of temperature, pressure or catalyst at above or below the arrow.
Question 2.
Identify the type of chemical reaction in the following statements and define each of them.
a) Digestion of food in our body
b) Rusting of iron
c) Heating of manganese dioxide with aluminium powder.
d) Dilute hydro chloric acid is added to sodium hydroxide solution to form sodium chloride and water.
Answer:
a) Decomposition Reaction : Carbohydrates are broken down to form glucose.
b) Oxidakion Reaction : When an iron objects is left in moist air for a considerable time, it gets covered with a red brown flaky substance called rust.
c) Displacement Reaction : More reactive metal displaces less reactive metal form its salt solution.
d) Neutralisation Reaction : When acids react with base they give salt and water.
Question 3.
There are different types of chemical reactions occuring around us or being carried out for the benefit of mankind, e.g. combination reactions, decomposition reactions, displacement reactions, precipitation reactions, reduction - oxidation (redox) reactions, photochemical reactions etc.
Now, answer the following questions.
a) Combustion of coke is a combination reaction CO2 formed during reaction is not a pollutant. Then why is combustion of coke harmful?
b) Which reaction followed by two combination reactions are involved in white wash of walls ?
c) Give one use of tin plating in daily life.
d) How photochemical reactions have played an important role in photography.
Answer:
a) CO2 is not a pollutant when present in the atmosphere upto a certain percent. Rather is helps to maintain the temperature of the earth. Combustion of coke is harmful as it increases the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere.
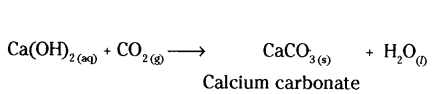
b) Reaction of calcium with oxygen gives quick lime (CaO) which combines with water to form slaked lime, Ca(OH)2 which after putting on the walls, combines with CO2 of the air to form CaCO3
c) Tiffin boxes made up of steel are either tin plated or nickel plated to protect them from rusting. How ever, tin plating is preferred because tin is non-poisonous and hence, does not contaminate the food kept in them.
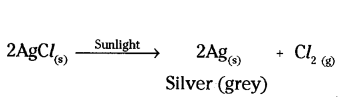
d) A photographic film used in black and white photography is a celluloid film coated with silver chloride.
Its working is based on the decomposition of silver chloride in the presence of sunlight.
Question 4.
Explain the process of balancing a chemical equation using the given steps.
Use Mg + O2 → MgO as an example.
Answer:
- Identify Elements : Begin by identifying all the elements present in the chemical equation and count how many of each element appear on both sides.
- Start with Single-Compound Elements : Begin balancing the equation by adjusting the coefficients of compounds containing elements that appear only once on each side of the equation. In Eq. Mg + O2 → MgO, we started by addressing the oxygen atoms in O2.
- Adjusting Coefficients : To balance the oxygen atoms, we added a coefficient of 2 in front of MgO to ensure there were equal numbers of oxygen atoms on both sides.
- Recheck Element Counts : After adjusting coefficients, re-evaluate the counts of each element on both sides of the equation to ensure that they are balanced.
- Further Simplification: If possible, simplify the equation by dividing all coefficients by their greatest common factor. In this case, we divided all coefficients by 2 to simplify the equation further.
- Final Balanced Equation: The final balanced equation should have equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides, and it should represent the law of conservation of mass.
This process ensures that the equation accurately reflects the chemical reaction and obeys the principle of mass conservation. In Eq. Mg + O2 → MgO, we successfully balanced it to 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO, where the number of magnesium and oxygen atoms is the same on both sides of the arrow.
Question 5.
What is a combination reaction, and can you provide examples?
Answer:
1) A combination reaction is a type of chemical reaction where two or more substances (elements or compounds) combine to form a single product.
2) It involves the synthesis of a new substance from reactants.
3) Examples of combination reactions include:
a) The reaction of calcium oxide (CaO) with water (H2O) to form slaked lime (Ca(OH)2).
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
b) The burning of coal (C) in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2).
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
c) The formation of water (H2O) from hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2).
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)
Question 6.
What are exothermic reactions, and can you provide examples?
Answer:
1) Exothermic reactions are chemical reactions that release heat energy to the surroundings.
2) In these reactions, the products have lower energy than the reactants.
3) Examples of exothermic reactions include :
a) The burning of natural gas (CH4 in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H20).
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
b) Respiration, where glucose (C6H12O6) combines with oxygen (O2) in cells to release energy, producing carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
c) The decomposition of vegetable matter into compost, which generates heat.
Question 7.
Explain what is a decomposition reaction and provide examples.
Answer:
1) A decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction where a single reactant breaks down into simpler products.
2) It involves the breakdown of compounds into their constituent elements or simpler compounds.
3) Examples of decomposition reactions include:
a) The thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) upon heating.
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
b) The decomposition of ferrous sulfate crystals (FeSO4) upon heating to produce ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and sulfur trioxide (SO3).
2FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3(s) + SO2(g) + SO3(g)
c) The decomposition of silver chloride (AgCl) into silver (Ag) and chlorine (Cl2)
when exposed to sunlight.
2AgCl(s) → 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g)
Question 8.
What are displacement reactions, and can you provide examples?
Answer:
1) Displacement reactions are chemical reactions in which one element displaces or replaces another element in a compound.
2) These reactions typically involve more reactive elements displacing less reactive ones.
3) Examples of displacement reactions include :
a) Iron (Fe) displacing copper (Cu) from copper sulfate (CuSO4 solution to form iron sulfate (FeSO4) and copper metal (Cu).
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
b) Zinc (Zn) displacing copper (Cu) from copper sulfate (CuSO4) solution to form zinc sulfate (ZnSO4),) and copper metal (Cu).
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
c) Lead (Pb) displacing chlorine (Cl) from copper chloride (CuCl2) solution to produce lead chloride (PbCl2) and copper metal (Cu).
Pb(s) + CuCl2(aq) → PbCl2(aq) + Cu(s)
Question 9.
How can you make a chemical equation more informative ?
Answer:
Include the state of each substance. This can be done by using the following symbols:
- (s) for solid
- (l) for liquid
- (g) for gas
- (aq) for aqueous (dissolved in water)
- Include the energy change of the reaction. This can be done by using the following symbols :
- ∆H° for the enthalpy change of the reaction at standard conditions
- ∆H for the enthalpy change of the reaction at any temperature
- Include the yield of the reaction. This can be done by placing a number in front of the product(s). For example, 2H2O(l) means that two moles of water are produced.
- Include the catalyst, if any. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Catalysts are usually placed above the arrow in a chemical equation.
Question 10.
a) Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions:
i) 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
ii) H2O + F2 → HF + HOF
iii) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
iv) 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
b) Define a redox reaction in terms of gain or loss of oxygen.
Answer:
a) The reducing agent can be identified in the following reactions:
i) 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O : In this reaction, NH3 acts as the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation, losing hydrogen.
ii) H2O + F2 → HF + HOF : In this reaction, H2O acts as the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation, losing hydrogen.
iii) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2 : In this reaction, CO acts as the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation, losing oxygen.
iv) 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O : In this reaction, H2 acts as the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation, losing hydrogen.
b) Redox reaction in terms of gain or loss of oxygen :
- A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one substance to another.
- In terms of gain or loss of oxygen, oxidation is the gain of oxygen by a substance, while reduction is the loss of oxygen by a substance.
- The substance that gains oxygen is considered to be reduced, while the substance that loses oxygen is considered to be oxidized.
- The overall reaction involves both oxidation and reduction, hence the term redox reaction.