AP 10th Class Physical Science 4th Lesson Carbon and Its Compounds Important Questions
Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 4 Important Questions - 1 Mark
Question 1.
How much carbon is present on earth and CO2 in atmosphere ?
Answer:
Carbon - 0.02%, CO2 - 0.03%.
Question 2.
What will be the product formed where carbon is burnt in presence of air ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide.
Question 3.
Name three allotropes of carbon.
Answer:
Diamond, graphite and buckminster fullerenes.
Question 4.
Which is purest allotrope of carbon ?
Answer:
Buckminster fullerenes.
Question 5.
What is graphite soft and slippery ?
Answer:
Due to weak vander waal’s forces of attraction between hexagonal layers.
Question 6.
Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell. How d oes carbon attain stable electric configuration?
Answer:
By sharing four electrons with other atoms.
Question 7.
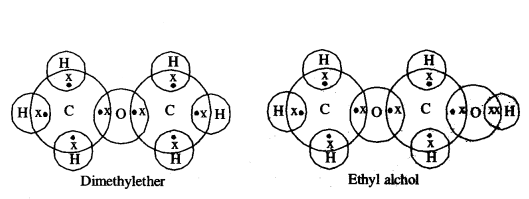
Draw electron dot structure of water molecule.
Answer:
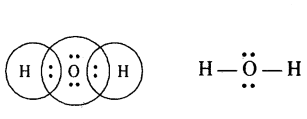
Question 8.
Why is carbon tetravalent ?
Answer:
It is because carbon can share four electrons to complete its octect.
Question 9.
Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why ?
Answer:
Carbon shows catenation to maximum extent because it forms strong covalent bonds.
Question 10.
Which gas is present in biogas and CNG ?
Answer:
Methane.
Question 11.
Write general formula of hydrocarbon alkene. Write the name of simplest alkene.
Answer:
CnH2n Ethene, CH2 - CH2
Question 12.
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Answer:
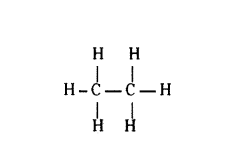
Question 13.
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of propane C3H8.
Answer:
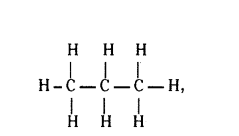 10 covalent bonds.
10 covalent bonds.
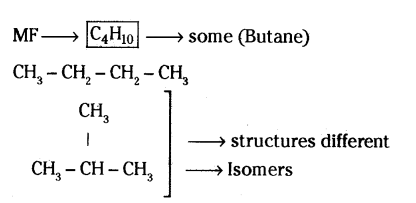
Question 14.
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane, C4H10.
Answer:
13, 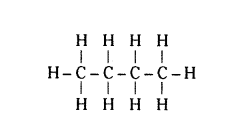
Question 15.
Write the formula and name of first member of ketone.
Answer:
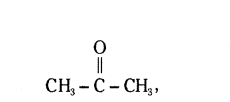 Propane
Propane
Question 16.
Write the molecular formula of benzene and state the number of doubie bonds in its structure.
Answer:
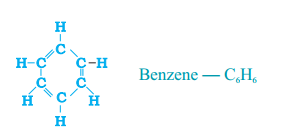
C6H6, 3 double bonds
Question 17.
Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and the 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is methane.
Answer:
C2H6 and C2H6 are molecular formula of 2nd and 3rd member of alkanes.
Question 18.
Write the general formula of hydrocarbon alkene. Write the name of simplest alkene.
Answer:
CnH2n, Ethene
It has one double bond.
Question 19.
Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series with functioned group - OH.
Answer:
Methanol (CH3OH) and Ethanol (CH3CH2OH).
Question 20.
Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group - Cl.
Answer:
CH3Cl and C2H5Cl.
Question 21.
Write the molecular formula of the first two members of the homologous series having functional group - COOH.
Answer:
HCOOH - Methanoic acid
CH3COOH - Ethanoic acid
Question 22.
Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of the series of carbon compounds whose general formula is CnH2n.
Answer:
C3H6, H2C = CH - CH3
Propane is second member of series whose general formula is CnH2n.
Question 23.
Select saturated hydrocarbon from the following
C3H6, C5H10 C4H10, C6H14, C2H4
Answer:
C6H14 and C4H10 are saturated hydrocarbons.
Question 24.
Write the name and molecular formula of the fourth member of alkane series.
Answer:
Butane, C4H10.
Question 25.
Write the name and formula of 2nd member of homologous series having general formula Cn H2n - 2.
Answer:
Propyne, C3H4.
Question 26.
Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general
formula C
n H
2n - 2.
Answer:
Ethane, C2H6.
Question 27.
Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds,
i) C2H5Cl
ii) C2H5OH
Answer:
i) (- Cl) Hologen (chloro)
ii) (- OH) Alcohol
Question 28.
Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds,
a) CH3COCH2
b) C2H5COOH
Answer:
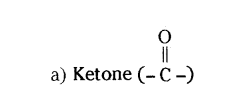
b) Carboxylic acid (- COOH)
Question 29.
Name the functional group present in each of the following compounds.
a) HCOOH
b) C
2H
5CHO
Answer:
a) - COOH (Carboxylic acid)
b) - CHO (Aldehyde)
Question 30.
Draw the structure of butanone molecule, CH3COC2H5.
Answer:
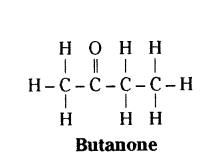
Question 31.
Name the following compound
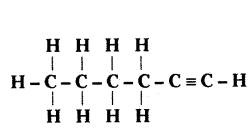
Answer:
1 - Hexyne is IUPAC name of the compound.
Question 32.
Write the name and structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms units molecule.
Answer:

Question 33.
Write molecular formulae of alcohol which can be derived from butane.
Answer:
C4H9OH or CH3CH2CH2CH2OH.
Question 34.
What is glacial acetic acid ?
Answer:
Pure acetic acid (100%) is called glacial acetic acid.
Question 35.
How many covalent bonds are present in ‘pentane’ C5H12 ?
Answer:
There are 16 covalent bonds present in C5H12.
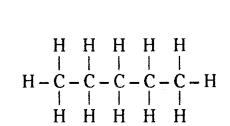
Question 36.
Write molecular formula of an alkyne containing 10 atoms of hydrogen.
Answer:
C6H10, HC ? C - CH2- CH2 - CH2 - CH3
Question 37.
Write the name of each of the following functional group.
a) - OH
b) 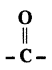
Answer:
a) Alcohol
b) Ketone
Question 38.
Write the name and structure of an aldehyde with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
Answer:
Butanal. 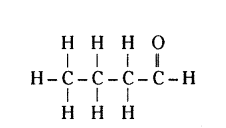
Question 39.
Write the name and molecular formula of the first member of the homologous series of alkynes.
Answer:
C2H2, Ethyne.
Question 40.
Write the next homologue of each of the following.
i) C2H4
ii) C4H8
Answer:
i) C3H6
ii) C5H8
Question 41.
Write the molecular formula of 2nd and 3rd member of homologous series whose first member is ethyne.
Answer:
C3H4 and C4H6
Question 42.
Write the formula of the members of homologous series with functional group 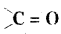
Answer:
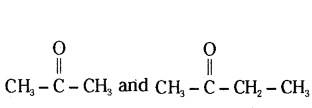

Question 43.
Which hetero atoms sire present in halo alkanes ?
Answer:
-Cl, -Br, -F, -I
Question 44.
When is flame produced ?
Answer:
Volatile substances change into vapours which produce flame.
Question 45.
An organic compound burns with blue flame. It is saturated or unsaturated compound.
Answer:
The compound is saturated. It has higher percentage of hydrogen.
Question 46.
Which type of hydrocarbons burn with yellow smoky flame ? Why?
Answer:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Due to presence of higher percentage of carbon.
Question 47.
Why does combustion of fossil fuels from oxides of sulphur and nitrogen ?
Answer:
Because fossil fuels contain sulphur and. nitrogen along with carbon.
Question 48.
Name one hydrocarbon which undergoes substitution reaction.
Answer:
Methane (CH4).
Question 49.
Which compound is formed when ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol is presence of cone. H2SO4 ?
Answer:
Ethyl ethanoate.
Question 50.
Hard water required for an experiment is not available in a school laboratory. However, following salts are available in the laboratory, Write the name of the salts which may be dissolved in water to make it hard for the experiment
1) Calcium Sulphate
2) Sodium Sulphate
3) Calcium Chloride
4) Potassium Sulphate
5) Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
6) Magnesium Chloride
Answer:
1) Calcium Sulphate,
3) Calcium Chloride
6) Magnesium Chloride
Question 51.
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Select the
most appropriate answer from the options given below :
Assertion (A) : Melting point and boiling point of ethanol are lower than that of sodium chloride.
Reason (R): The forces of attraction between the molecules of ionic compounds are very strong.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation .of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 52.
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
Assertion (A) : Following are the members of a homologous series :
CH3OH, CH3CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2OH
Reason (R) : A series of compounds with same functional group but differing by- CH2-unit is called a homologous series.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 53.
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
Assertion (A) : Vegetable oils are healthier than animal fats.
Reason (R) : Vegetable oils generally have long unsaturated carbon chains while animal fats have saturated carbon chains.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 54.
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
Assertion (A) : Esterification is a process in which a sweet smelling substance is produced.
Reason (R) : When esters react with sodium hydroxide an alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid are obtained.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 55.
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Answer:
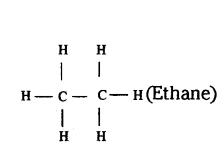
Ethane molecule has seven covalent bonds
Question 56.
Draw the electron dot structure for ethyne
Answer:
Ethyne HC = CH
Electron dot structure : 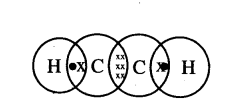
Question 57.
Heating an alcohol with concentrated sulphuric acid results in the dehydration of the alcohol to give the alkene as shown by the reaction of ethanol to given ethene.

Pramila heated 2-butanol (shown below) with concentrated sulphuric acid.
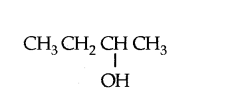
Write the structural formulae of all the possible product of the reaction.
Answer:
CH3 CH = CHCH8 and CH3 CH2 CH = CH2
Question 58.
Name the following compound.

Answer:
The compound is ethanal.
Question 59.
Write an equation showing saponification v
Answer:
Saponification: 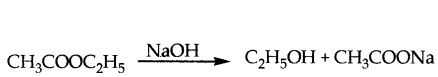
Question 60.
Draw electron dot structure of Ethanol.
Answer:
Ethanol (CH3 CH2 OH) 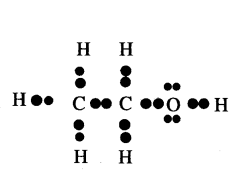
Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Important Questions - 2 Marks
Question 1.
What is Allotropy ?
Answer:
It is a property due to which an element can exist in more than one form which differ in physical properties but have similar chemical properties. E.g. Carbon’ Sulphur, Phosphorus, Oxygen show allotropy.
Question 2.
Why carbon considered to be the most important element ?
Answer:
Carbon is considered to be most important element because it forms largest number of compounds which are useful in our daily life.
Question 3.
Name the following compounds :
a) CH3 - CH2 - OH
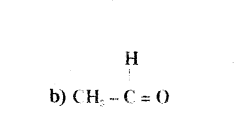
Answer:
a) Ethanol
b) Ethanal
Question 4.
Write the name and formula of the 3rd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n.
Answer:
Butene, C4H8
CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3 (Or) 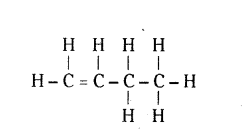
Question 5.
What are fossil fuels ?
Answer:
The fuels which were formed by the decomposition of the remains of plant and animals buried under the earth millions of years ago are called fossil fuels.
Ex : coal, petroleum, natural gas.
Question 6.
Why coal and petroleum and considered as fossil fuels ?
Answer:
Coal and petroleum are considered to be the fossil fuels as they are the remains of plants and animals that lived million years ago.
Question 7.
The table shows the electronic structures of four elements.
| Element |
Electronic Structure |
| P |
2, 6 |
| Q |
2, 8, 1 |
| R |
2, 8, 7 |
| S |
2, 8, 8 |
a) Identify which element(s) will form covalent bonds with carbon.
b) "Carbon reacts with an element in the above table to form several compounds." Give suitable reason.
Answer:
a) P and R
b) Carbon has a valency four or Tetravalency & Catenation.
Question 8.
"Carbon forms strong bonds with most other element making the compounds exceptionally stable". Give reason to justify this statement.
Answer:
Carbon has small atomic size and four valance electrons. It shares 4 electrons with other elements to form covalent bonds which are very strong and stable because octect of carbon become complete.
Question 9.
Write the electron dot structure of methane (CH4) and ethene (C2H4).
Answer:
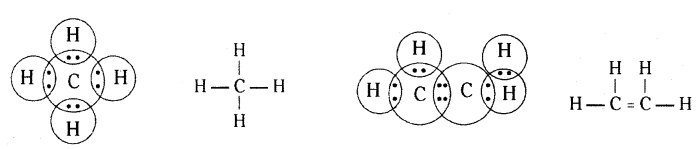
Question 10.
Explain why carbon generally forms compounds by covalent bonds.
Answer:
Carbon cannot lose four electrons easily because very high energy is required. It cannot gain four electrons easily because six protons cannot hold 10 electrons. It can easily share four electrons forming covalent bonds.
Question 11.
Select alkene and alkyne from the following
C6H12, C3H4, C2H4, CH4, C4H8, C5H8.
Answer:
Alkenes : C6H12, C2H4, C4H8
Alkynes: C3H4, C5H8
Question 12.
Write the name and molecular formula of an organic compound having its name suffixed with -ol and having two carbon atoms in the molecule with the help of a balanced chemical equation indicate. What happens when it is heated with excess of cone. H2SO4.
Answer:
It is ethanol, its molecular formula is C2H6O and structural formula is CH3CH2OH Ethanol forms ethene, when heated with cone. H2SO4.
Question 13.
What is the IUPAC name of
i) CH3 - CH2 - CH = CH2
ii) CH3CHO
Answer:
i) But-1-ene
ii) Ethanol
Question 14.
An aldehyde as well as ketone can be represented by the same molecular formula, say C3H6O. Write their structures and name them. State the relation between the two in the language of science.
Answer:
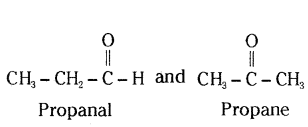
They are functional isomers.
Question 15.
C3H6, C4H8 and C5H10 belong to the same homologous series.
a) Why the melting and boiling points of C5H10 is higher than C4H8 ?
b) Arrange these hydrocarbons in order of increasing boiling points.
Answer:
a) It is because C5H10 has higher molecular weight, more vander wall’s force erf attraction and higher boiling points and melting points.
b) C3H6 < C4H8 < C5H10 is increasing order of boiling point.
Question 16.
Atom of an element contains five electrons in its valence shell. This element is major component of air. It exists as a diatomic molecule.
a) Identify the element.
b) Show bond formed between two atoms of this element.
Answer:
a) Nitrogen
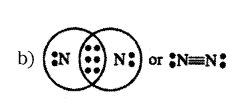
Question 17.
Why are most carbon compounds poor conductors of electricity ?
Answer:
Carbon compounds are covalent in nature and do not dissociate and form ions because of which they are poor conductor of electricity.
Question 18.
Write the name and structure of saturated compound in which the carbon atoms are arranged in a ring. Give the number of single bonds present in this compound.
Answer:
Cyclohexane is the saturated compound in which the carbon atoms are arranged in a ring. It has 18 single bonds
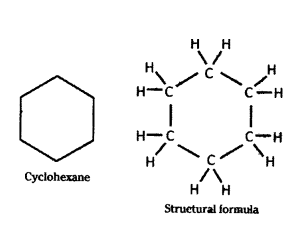
Question 19.
An organic acid ‘X’ is a liquid often freezes during winter time in cold countries, has the molecular formula C2H4O2. On warming it with ethanol in the presence of a few drops of cone. H2SO4, a compound ‘Y’ with a sweet smell is formed.
i) Identify X’ and Y’.
ii) Write chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
i) X = Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)
Y = Ethyl ethanoate (CH3COOC2H5)
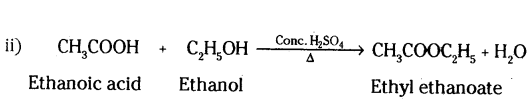
Question 20.
In an organic compound, which parts, largely determine its physical and chemical properties?
Answer:
The alkyl (carbon chain) of an organic compound determines its physical properties whereas the functional group determines its chemical properties.
Question 21.
An organic compound ‘X’ of molecular formula C2H4O2 gives brisk effervescence with sodium bicarbonate. Give the name and formula of X.
Answer:
‘X’ is ethanoic acid (an organic acid)
‘X’ → CH3COOH
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + CO2↑ + H2O
Organic acid decomposes sodium bicarbonate and gives brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide gas.
Question 22.
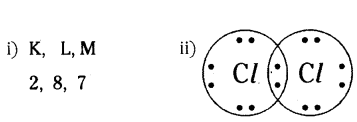
In electron dot structure, the valance shell electrons are represented by crosses or dots.
i) The atomic number of chlorine is 17. Write its electronic configuration.
ii) Draw the electron dot structure of chlorine molecule.
Answer:
Question 23.
Name the gas evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate. How would you identify this gas ?
Answer:
The gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO2). The reaction is as follows :
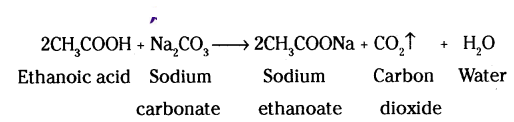
When this gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky. The milky colour of lime water confirms that the gas is carbon dioxide (CO2).
Question 24.
A gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium. Name the gas evolved and also write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Answer:
Gas evolved is hydrogen
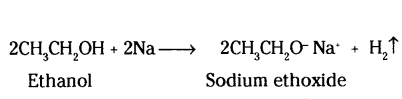
Question 25.
Why are detergents better cleansing agents than soaps ?
Answer:
Detergents work as cleansing agent in hard and soft water both because the charged ends of detergents do not form insoluble precipitates with calcium and magnesium ions in hard water.
Question 26.
What is hydrocarbon ? Give its one example.
Answer:
Compounds of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. For example, Methane, Ethane, etc.
Question 27.
Give the structural difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
Answer:
i) Saturated hydrocarbons contain carbon - carbon single bonds.
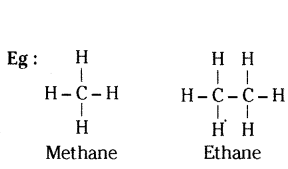
ii) Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain atleast one carbon - carbon double or triple bond.
Question 28.
W hat is vinegar ? State its one use.
Answer:
A 5 - 8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar. It is used as preservative in pickles.
Question 29.
What is soap ? Give examples.
Answer:
Soap is the sodium (or potassium) salt of a higher fatty acid like Palmitic, Oleic or Stearic acid.
Ex :
i) Sodium Palmitate (C15H3 COONa)
ii) Sodium Oleate (C10H33COONa)
Question 30.
What are esters ? Define esterification.
Answer:
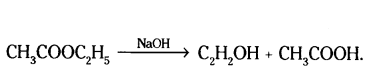
Esters are sweet smelling substances. These are used in making perfumes and flavouring agents. Esters are obtained when an alcohol is warned with a carboxylic acid in the presence of cone. Sulphuric acid. This is called esterification.
Question 31.
Name the following compounds :

Answer:
a) Propene
b) Propyne
Question 32.
Select saturated hydrocarbons from the following :
C3H6; C5H10; C4H10; C6H14; C2H4
Answer:
- Saturated hydrocarbons have general formula, CnH2n + 2.
- Among the given compounds only C4H10 and C6H14 satisfy the above formula. Thus, these are saturated hydrocarbons.
Question 33.
The molecular formulae of two alkynes, A and B are CxH2 and C3Hyv respectively.
a) Find the values of x and y.
b) Write the names of A and B.
Answer:
a) General formula of alkyne CnH2n - 2
For CxH2, 2n - 2 = 2 ? n = 2 ? x = 2.
For C3Hyy, n = 3, y = 2n - 2 = 2 × 3 - 2 = 4
Hence, x = 2, y = 4
b) A is ethyne (C2H2 and B is propyne (C3H4.
Question 34.
Write the name and structure of a saturated compound in which the carbon atoms are arranged in a ring. Give the number of single bonds present in this compound. (OR) Draw the structure of Cyclohexane.
Answer:
Cyclohexane - C6H12
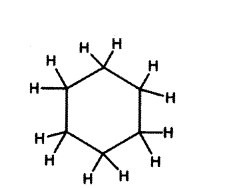
Number of single bonds are 18
Question 35.
Draw the structure of the following compounds :
Answer:
a) Butanoic acid
b) Chloropentane
Answer:
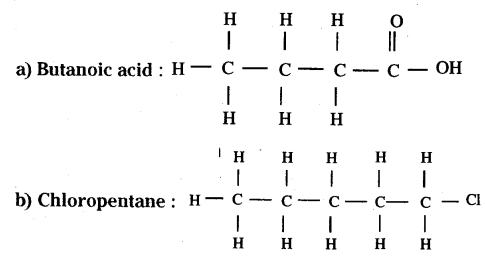
Question 36.
How are structure (i) and structure (ii) given below related to one another? Given reason to justify your answer.
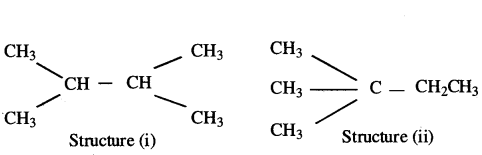
Draw one more possible structure for above case.
Answer:
- Structure (i) and (ii) have the same molecular formula but different structures. Therefore they are structural isomers.
- Another structure for the compound

Question 37.
Alkanes are saturated compounds of carbon any hydrogen that can be represented by the general formula CnH2n, where ‘n’ is the number of carbon atoms: An example such a compound is ethane C2H6
Maya has a compound of carbon and hydrogen who formula is C3H4
i) What is true about the type of flame this compound will be give on combustion?
ii) Draw all the possible straight chain structure of this compound.
Answer:
i) The compound being unsaturated will burn with smoky flame.
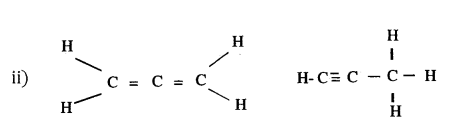
Question 38.
An open-chain hydrocarbon X having the gene formula of Cn H2n - 2 is hydrogenated
in the presence of catalyst.
a) State the number of moles of hydrogen required completely saturate 1 mole of compound X.
b) The hydrocarbon X contains carbon-carbon single bonds. Apart from the single bonds, state the numerical and the type of other carbon-carbon bonds that conduct possibly be present in the compound X.
Answer:
a) 2 moles
b) two C - C double bonds, one C - C triple bond
Question 39.
Write the molecular formula of ethene and draw its electron dot structure.
Answer:
Molecular formula of ethene is C2H4
Electron dot structure: 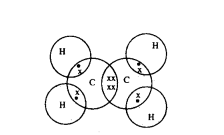
Question 40.
The table given below shows the hints given by the quiz master in a quiz.
| S.No |
HINT |
| i) |
Substance ‘C’ is used as a preservative. |
| ii) |
‘C’ has two carbon atoms; ‘C’ is obtained by the reaction of ‘A’ in presence of alkaline Potassium permanganate followed by acidification. |
| ii) |
Misuse of ‘A’ in industries is prevented by adding Methanol, Benzene, and pyridine to ‘A’ |
| iv |
F is formed on heating ‘A’ in presence of conc.Sulphuric acid. |
| v) |
‘F reacts with Hydrogen gas in presence of Nickel and Palladium catalyst. |
Based on the above hints answer the following questions.
a) Give the IUPAC names of A and F
b) Illustrate with the help of chemical equations the changes taking place. (A → C and A → F)
Answer:
a) A-Ethanol and F- Ethene
Answer:
a) A-Ethanol and F- Ethene
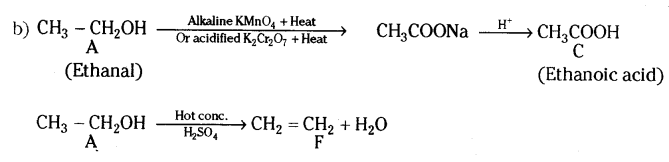
Question 41.
Ethyl propanoate is a colourless compound with a pineapple-like smell. It is present naturally in some fruits such as kiwis and strawberries.
The structural formula of ethyl propanoate is given below.
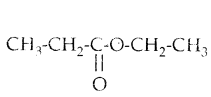
a) Write the names of the carboxylic acid and the alcohol from which this compound is formed.
b) Apart from mixing the carboxylic acid and the alcohol, what should be done to form this compound ?
Answer:
a) acid - propanoic acid/propionic acid ; alcohol - ethanol /ethy alcohol
b) add an acid catalyst ; heat the reaction mixture
Question 42.
3 mL of ethanol is taken in a test tube and warmed gently in a water bath. A 5% solution of alkaline potassium permanganate is added first drop by drop to this solution, then in excess.
i) How is 5% solution of KMnO prepared?
ii) State the role of alkaline potassium permanganate in this reaction. What hap¬pens on adding it in excess?
iii) Write chemical equation of this reaction.
Answer:
a) 5% solution of KMnO4 is prepared by dissolving 5g of KMnO4 in 100 mL of water.
b) alkaline potassium permagnate act as oxidising agent in the reaction.
c) CH3CH2OH + alk. KMnO4 → CH3COOH

Question 43.
A compound ‘X’ on heating with excess cone, sulphuric acid at 443 K gives an unsaturated compound "Y ‘. ‘X ‘also reacts with sodium metal to evolve a colourless gas ‘Z’. Identify ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’. Write the equation of the chemical reaction of formation of ‘Y’ and also write the role of sulphuric acid in the reaction.
Answer:
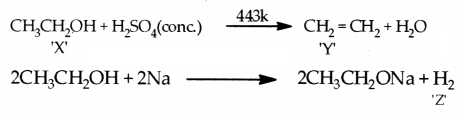
Role of sulphuric acid (H2SO4 : Acts as a dehydrating agent.
Question 44.
When ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in the presence of cone. H2SO4 a substance with fruity smell is produced.
Answer the following:
i) State the class of compounds to which the fruity smelling compounds belong. Write the chemical equation for the reaction and write the chemical name of the product formed.
State the role of cone. H
2SO
4 in this reaction.
Answer:
i) Esters the compounds which have fruity small.
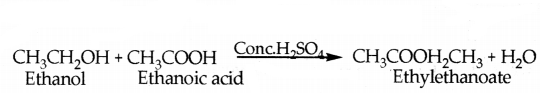
ii) Cone. H2SO4 acts as catalytic agent in the reaction.
Question 45.
Write the number of single and double covalent bonds present in a molecule of benzene.
Answer:
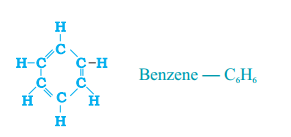
- Six single bonds between Carbons and Hydrogens, three single bonds between six Carbons and Hydrogens (alternatively).
- Three double bonds present between carbons (alternatively in hexagonal ring).
- So a total of nine single bonds, three double bonds are present in benzene ring.
Question 46.
A carbon compound A’ having melting point 156 K and boiling point 351 K, with molecular formula C2H6O is soluble in water in all proportions.
a) Identify ‘A’ and draw its electron dot structure.
b) Give the molecular formula of any two homologues of A’.
Answer:
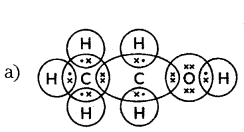
b) CH3OH and C3H7OH are homologues of ethanol (OR) CH4O and C3H8O
Question 47.
What happens when a small piece of sodium is dropped in ethanol? Write the equation for this reaction.
Answer:
1) When a small piece of sodium metal is dropped in ethanol, Hydrogen gas is evolved that gives a pop sound when a burning candle is brought near.
2) 2CH3CH2-OH + 2Na → 2CH3CH2-O Na+ + H2.
Question 48.
Carbon can neither form C4+ cation nor C4- anion. Why ?
Answer:
- Carbon cannot form C4+ cation because the removal of four electrons requires a large amount of energy leaving behind a carbon cation with six protons in its nucleus holding on to just two electrons.
- Carbon cannot form C4- anion because it would be difficult for the nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons.
- Thus, carbon atom share electrons and form Covalent compounds.
Question 49.
Identify hetero atom(s) in the following compounds :
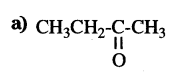
b) CH
3CH
2Cl
Answer:
a) In  hetero atom is Oxygen(O).
hetero atom is Oxygen(O).
b) In CH3CH2Cl, hetero atom is chlorine (Cl)
Question 50.
Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent ? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer:
- No, we are not able to check if water is hard by using a detergent as detergent works well in hard water as well.
- This is because calcium and magnesium salts of detergents are soluble in Water and hence, detergents can be used for washing even in hard water.
Important Questions on Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 - 4 Marks
Question 1.
Name the elements which has
a) the electronic configuration (2, 8, 1).
b) a total of two shells with 4 electrons in the valence shell.
c) a total of three shells with 3 electrons in the valence shell.
d) one shell which is completely filled with electrons.
Answer:
a) Sodium (2, 8, 1)
b) Carbon (2, 4)
c) Aluminium (2, 8, 3)
d) Helium (2)
Question 2.
Explain the formation of covalent bonds in
a) Chlorine molecule
b) ammonia
Answer:
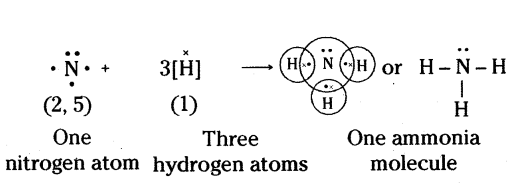
a) Formation of Chlorine Molecule (Cl2) : Two chlorine atoms share one electron of each and acquire stable electronic configuration as shown.

b) Formation of Ammonia Molecule (NH3) : Nitrogen (N) atom has 5 electrons (2,5) in the outer most shell. It shares one electron each of three hydrogen atoms to form ammonia molecule as shown.
Question 3.
What is meant by double bond ? Give some examples.
Answer:
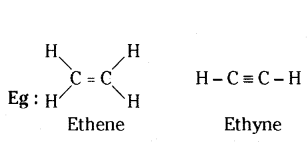
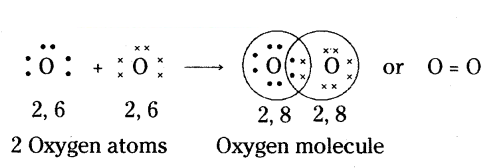
The bond between two atoms formed by sharing of two pairs of electrons is called a double bond. Two horizontal lines between two atoms denote a double bond.
Eg : O = O(O2)
Example:
Formation of Oxygen Molecule (O2 : Oxygen atom has six electrons in its outermost shell, two short of forming a complete octect. Thus each oxygen atom in O2 shares
2 electrons with the other oxygen atom and attains stable configuration as shown.
Question 4.
What is triple bond or triple covalent bond ? Explain the formation of triple bond giving two examples.
Answer:
The bond formed between two atoms through the sharing of three electron pairs is called a triple bond. Three horizontal lines between two atoms denote a triple bond. Eg. nitrogen molecule is given as N ? N
Example :
Formation of N2 Molecule : Nitrogen atoms have five electrons in their outermost shells. Therefore, in N2 molecules, two nitrogen atoms share 3 electrons with each other. Thus, acquiring the stable structure and forming a N2 molecule with triple bonds.
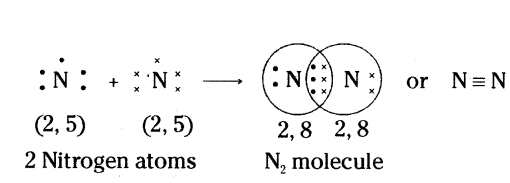
Question 5.
State any four physical properties of carbon compounds.
Answer:
Carbon forms covalent compounds which exhibit the following properties.
a) These have low melting points and boiling points.
b) They do not conduct electricity either in the solid state or in molten state or in solution form. They are non-electrolytes.
c) These are readily soluble in non-polar solvents like benzene, carbon tetrachloride etc., but do not dissolve in polar solvents like water.
d) The covalent bond is directional in nature.
Question 6.
How are hydrocarbons classified ?
Answer:
Hydrocarbons can be classified either on the basis of nature of bonds or nature of chains between carbon atoms.
a) On the basis of bonds, hydrocarbons are calssified as
i) Saturated hydrocarbons, E.g. CH4 (methane)
ii) Unsaturated hydrocarbons, E.g. C2H4 (ethane)
b) On the basis of chains, hydrocarbons are classified as
i) Aliphatic hydrocarbons : They have straight or branched chains of carbon atoms, e.g. butane, isobutane.
ii) Cyclic hydrocarbons : These contain rings of carbon atoms, e.g. cyclohexane, benzene.
Question 7.
Give the name and formula of some common functional groups.
Answer:
Some functional groups In carborn compounds
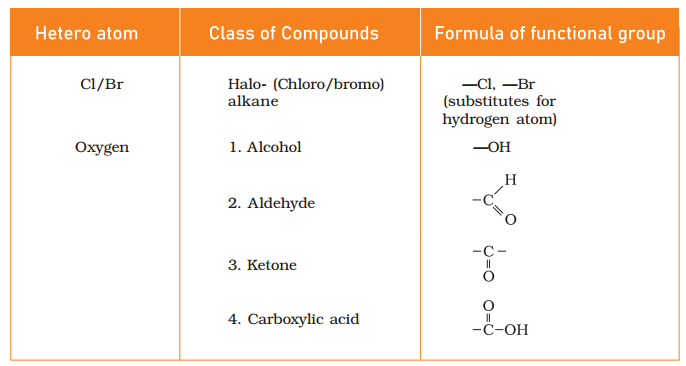
Question 8.
State the characteristics of isomers.
Answer:
Characteristics of isomers :
a) They have the same molecular formula.
b) They have different structural formulae.
c) They have different melting and boiling points.
d) They have different chemical properties.
Question 9.
How would you name the following compounds ?
i) CH3 - CH2 - CH = CH2
ii) CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - C(CH3)2 - CH3
iii) CH3 - CH2 - CHO
iv) CH3 - CH(OH) - CH3
Answer:
i) 1 - Butene
ii) 2, 2 - Dimethyl pentane
iii) Propanal
iv) 2 - propanol
Question 10.
How are carboxylic acids named ?
Answer:
General formula of carboxylic acid is R - COOH.
They are named by replacing suffix ‘e’ of corresponding alkane as given from the total number of carbon atoms by ‘oic’ and then adding at the end.
Examples:
| Formula |
Common name |
Name (IUPAC) |
| HCOOH |
Formic acid |
Methanoic acid |
| CH3COOH |
Acetic acid |
Ethanoic acid |
| C2H5COOH |
Propionic acid |
Propanoic acid |
Question 11.
Identify the functional group present in the following compounds and give their name CH3COCH3, CH3CH2CH2COOH, CH3COCH2CH2CH3, CH3CH2CHO.
Answer:
| Compound |
Functional group |
Name |
| CH3COCH3 |
Ketonic |
Acetone |
| CH3CH2CH2COOH |
Carboxylic acid |
Butanoic acid |
| CH3COCH2CH2CH3 |
Ketonic |
Methyl propyl ketone (Proponone) |
| CH3CH2CHO. |
Aldehyde |
Propanal |
Question 12.
An organic compound A of molecular formula C2H4 on reduction gives another compound B of molecular formula C2H6. B on chlorination in the presence of sunlight gives C of molecular formula C2H5Cl.
a) Name the compound A, B and C.
b) Write the equation for the conversion of A to B and name the type of reaction.
Answer:
a) A is ethene
B is ethane
C is ethyl chloride or Chloroethane
b) C2H4 + H2 → C2H6
It is called addition reaction.
Question 13.
State physical properties of alcohols.
Answer:
a) Most common alcohols are liquids.
b)They do not conduct electricity.
c) They are quite soluble in water.
d) They react with sodium to produce hydrogen.
e) They readily burn like hydrocarbons.
Question 14.
State the uses of ethanoic acid.
Answer:
Uses of acetic acid or ethanoic acid :
a) It is used as vinegar for preparing pickles.
b) It is used for the preparation of aspirin used for relieving headache.
c) It is used for preparing cellulose acetate which is an important artificial fibre.
d) It is used to coagulate rubber from latex.
Question 15.
Write four uses of ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
a) It is used in the manufacture of paints, medicines, dyes, soaps, etc.
b) It is used in the preparation of organic compounds like ether and chloroform.
c) It is used as a fuel in internal combustion engines.
d) It is used in low temperature thermometers.
Question 16.
With the help of a diagram, explain cleansing action of soap.
Answer:
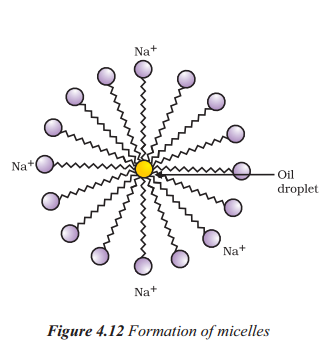 I
I
- Soap molecule form structures called micelles.
- Where one end is towards the oil droplet while the ionic end faces outside.
- The micelle stay in solution as an emulsion.
- The soap solution thus helps in dissolving the dirt in water and we can wash the clothes clean.
Question 17.
Explain the reactions of ethanol, including its reaction with sodium and its dehydration.
Answer:
Reaction with sodium :
- Sodium reacts with ethanol to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas.
- Equation : 2Na + 2CH3CH2OH → 2CH3CH2O - 2Na+ + H2
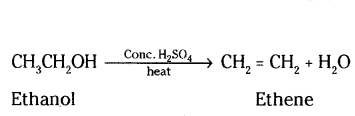
Dehydration of ethanol :
- Heating ethanol with concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K results in the formation of ethene (an unsaturated hydrocarbon).
- Equation : CH3CH2OH → CH2 = CH2 + H2O
Question 18.
Explain the difference between soaps and detergents.
Answer:
- Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids.
- Detergents are sodium salts of sulphonic acids or ammonium salts with various ions.
- Soaps form scum in hard water due to calcium and magnesium ions, while detergents do not.
- Detergents are commonly used in shampoos and cleaning products.
Question 19.
Observe the structure answer the questions.
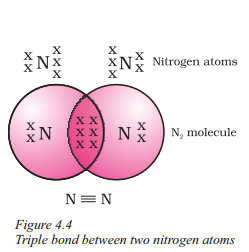
a) What is the electronic configuration and valency of nitrogen ?
Answer:
Nitrogen has the atomic number 7, and its electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p3. It has a valency of 3 as it forms three shared pairs of electrons to attain an octet in a molecule of nitrogen.
b) What is the nature of bonding between the two nitrogen atoms in a molecule of nitrogen ?
Answer:
The two nitrogen atoms in a molecule of nitrogen are bonded by a triple bond, which consists of three shared pairs of electrons.
Question 20.
a) What is the structure of ethene ?
Answer:
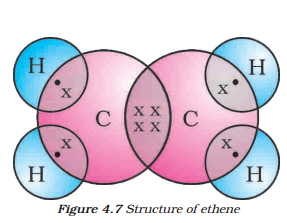
The structure of ethene can be represented as two carbon atoms linked together with a double bond.
b) What is the formula of ethene ?
Answer:
The formula of ethene is C2H4.
c) Is ethene a saturated or unsaturated carbon compound ?
Answer:
Ethene is an unsaturated carbon compound, as it contains a double bond between the two carbon atoms.
Question 21.
Describe the process of combustion in carbon and its compounds, and why is it important ?
Answer:
- Combustion involves the burning of carbon and its compounds in oxygen.
- Carbon in all its forms, including compounds, burns to produce carbon dioxide, heat, and light.
- Balanced equations for combustion reactions :
i) C + O2 → CO2 + heat and light
ii) CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat and light
iii) CH3CH2OH + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat and light
- Combustion is essential for energy production and is a primary source of heat and light.
Question 22.
How do unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions, and why is hydrogenation important in the food industry ?
Answer:
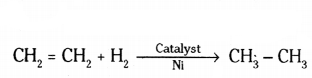
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions where hydrogen is added in the presence of catalysts like palladium or nickel.
- Catalysts speed up reactions without being consumed in the process.
- Example : Hydrogenation of unsaturated vegetable oils to saturated fats using a nickel catalyst.
- Importance in food industry : Produces solid fats from oils, affecting texture and shelf life of food products.
Question 23.
Read the paragraph and answer the questions.
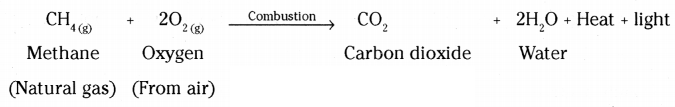
Carbon, in all its allotropic forms, burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light. Most carbon compounds also release a large amount of heat and light on burning. These are the oxidation reactions that you learnt about in the first Chapter - (i) C + O2 → CO2 + heat and light (ii) CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat and light (iii) CH3CH2OH + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat and light.
i) What does carbon burn in to produce carbon dioxide ?
Answer:
Carbon burns in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide.
ii) What is released along with heat when carbon compounds burn ?
Answer:
Light is released along with heat when carbon compounds burn.
iii) Can you write the balanced equation for the reaction of methane burning in oxygen?
Answer:
The balanced equation for the reaction of methane burning in oxygen is CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + heat and light.
Question 24.
Read the paragraph and answer the questions.
Carbon, an element of immense significance, is explored in both its elemental form and as a compound. This chapter starts by introducing various carbon based compounds including food, clothes, and medicines. It also highlights that all living structures are carbon-based. The bonding in carbon compounds is explained, focusing on the difference between covalent bonds and ionic bonds. The chapter further explores the versatile nature of carbon, its ability to form bonds with other atoms, and the formation of large and complex molecules. The valency of carbon, being four, enables it to bond with four other atoms. This chapter also introduces saturated and unsaturated carbon compounds. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of carbon in our daily lives and its unique and versatile properties.
i) Which element is explored in Chapter 4 ?
a) Hydrogen
b) Carbon
c) Oxygen
d) Nitrogen
Answer:
b) Carbon
ii) What is the valency of carbon ?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
Answer:
d) Four
iii) Which type of bond does carbon form with other atoms ?
a) Covalent bonds
b) Ionic bonds
c) Metallic bonds
d) Hydrogen bonds
Answer:
a) Covalent bonds
iv) Which compound is widely used as a fuel and is a major component of bio-gas and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) ?
a) Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
b) Chloroform (CHCl3)
c) Ethanol (CH3CH2OH)
d) Methane (CH4)
Answer:
b) Chloroform (CHCl3)
Question 25.
Consider the carbon compounds having following molecular formula:
i) C3H6
ii) C3H8
iii) C4H6
iv) C6H6
v) C6H12
a) State the number of double covalent bonds present in C3H6.
b) Write the formula of first member of the homologous series to which the carbon
compound C4H6belongs.
c) Which one of the above compounds forms ring structure of carbon atoms?
d) Identify, which of the above compounds, is a member of alkane series.
Answer:
a) C3H6 (or CnH2n, n = 3) i.e, alkene series thus, has one double covalent bond.
b) C4H6 (or CnH2n - 2, n = 4) i.e., alkyne series.
The first member of alkyne series is ethyne (C2H2) HC = CH.
c) C6H12 can form ring structure of C-atoms.
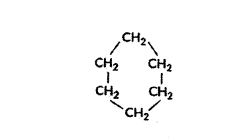
d) Alkane series: CnH2n + 2
Only C3H8 is a member of alkane series CH3 - CH2 - CH3
Question 26.
Draw the electron-dot structure for ethyne. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is burnt for welding. In your opinion, why cannot we use a mixture of ethyne and air for this purpose ?
Answer:
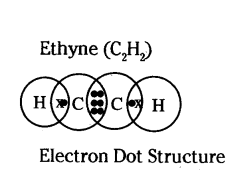
When a mixture of ethyne and oxygen is burnt, it gives clean flame with very high temperature (in 3000°C). Hence, this mixture is used for welding purpose.
2C2H2 + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2H2O + Heat
When a mixture of ethyne and air is burnt, it gives sooty flame due to incomplete combustion and it also does not give very high temperature. Thus, it is not used for welding.
Question 27.
Write the chemical formula of two consecutive homologous of organic compounds having functional groupOH. What happens to the (i) boiling point and (ii) solubility of organic compounds of a homologous series at the molecular mass increases.
Answer:
In a homologous series the consecutive member differ by -CH2 unit, For alcohol functional group the consecutive homologous are
a) CH3OH
b) CH3CH2OH
i) Boiling point increases with increase in the molecular mass in the homologous series.
ii) Solubility in water decreases with increase in the molecular mass in the homolo-gous series.
Question 28.
Consider the following organic compounds:
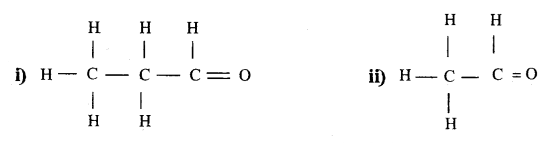
a) Name the functional group present in their compounds.
b) Write the general formula for the compounds of this functional group.
c) State the relationship between these compounds and draw the structure of any other compound having similar functional group.
Answer:
a) Aldehyde functional group (-CH0) is present in both the compounds (i) and (ii).
b) General Formula : CnH2n + 1 CHO
c) These two compounds are homologous compound of (-CHO) functional group series. They differ by -CH2 unit from each other. Another compound of the same functional group can be written as follows.
CH3 CH2 CH2 CHO
Structural formula: 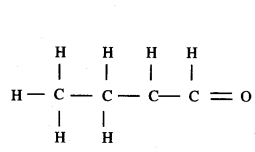
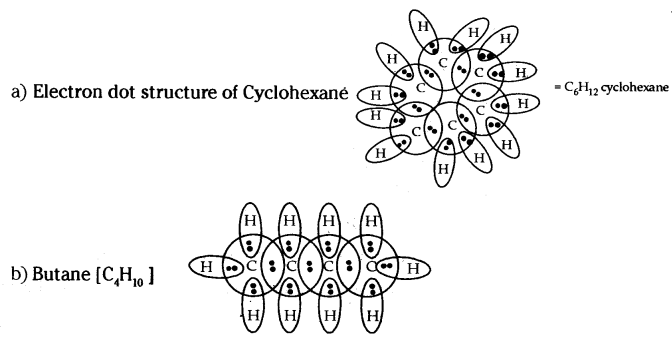
Question 29.
Draw the electron dot structure of the following,
a) Cyclohexane
b) Butane
Answer:
Question 30.
What happens when ethanol is treated with sodium metal ? State about the behaviour of ethanol in this reaction.
Answer:
- Ethanol reacts with sodium metal to form sodium ethoxide and hyderogen.
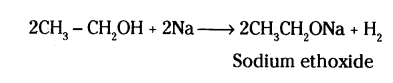
- Ethanol behave like an acide as it reacts with a metal to given a salt and hydrogen.
- Ethanol loses an atom of hydrogen an replaces it with Na even some bases show this behaviour.
Question 31.
Home-made vinegar is produced from wine. The wine is taken in a clean glass jar and shaken well to aerate it. Some water is added to the jar and then it is kept undisturbed in a dark place at room temperature to undergo fermentation. After 3 - 4 weeks, the vinegar would be ready to use.
a) Name the functional groups of the MAIN organic compounds present in wine and vinegar.
b) Based on the atoms getting added/removed when wine is converted to vinegar, name the type of reaction that happens;
c) Name any themical reagent that would be used for the same reaction if it is carried out in the laboratory.
Answer:
Question 32.
Distinguish between esterification and saponification reactions with the help of the chemical equations for each. State one use of each (i) esters, and (ii) saponi-fication process.
Answer:
- Esterification is a process in which a carboxylic acid react with an alcohol to form ester in presence of an acid.
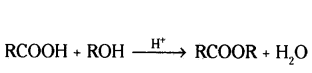
- In saponification, as ester reacts with a strong base or an acid to give alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid or carboxylic acid.
- RCOOR + NaOH → RCOONa + ROH
- Esters are used as a constituent of perfumes, essential oils, food flavourings etc.
- Saponification process is used in the manufacturing of soap used as cleansing agent.
Question 33.
List two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid and describe how these tests are performed.
Answer:
Alcohols and carboxylic acids can be experimentally distinguished by the following tests:
i) Carboxylic acids on reaction with NaHCO3 gives brisk effervescence of CO2 and water, whereas alcohol does not gives this reaction.
R-COOH + NaHCO3 → RCOONa + CO2↑ + H2O
ii) Alcohol on reaction with sodium metal gives hydrogen gas, whereas carboxylic acid does not gives this reaction.
2R-OH + 2Na → 2R-ONa + H2↑
Question 34.
Draw two different possible structures of a saturated hydrocarbon having four carbon atoms in its molecule. What are these two structures of the hydrocarbon having same molecular formula called ? Write the molecular formula and the common name of this compound. Also write the molecular formula of its alkyne.
Answer:
Saturated hydrocarbon : no double / triple bond
Only single bonds
MF of its alkyne = HC ? C - CH2 - CH3 / H3C - C ? C - CH3
Molecular formula of alkyne C4H6.
Question 35.
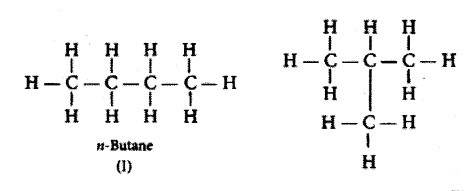
What is meant by isomers? Draw the structures of two isomers of butane, C4H10. Explain why we cannot have isomers of first three members alkane series.
(OR)
Define the term ‘structural isomerism’. Explain why propane cannot exhibit this property. Draw the structures of possible isomers of butane, C4H10.
Answer:
Isomers are those molecules which have the same molecular formula but different structural formula i.e., show different properties.
The structures of possible isomers of butane (C4H10) are:
The first three, members of alkane series are:
i) CH4 (methane)
ii) C2H6 (ethane)
iii) C3H8 (propane)
In the above members of alkane series, it is not possible to have different arrangements of carbon atoms. Thus, we cannot have isomers of first three members of alkane series.
Question 36.
An acid X and an alcohol Y react with each other in the presence of an acid catalyst to form a sweet smelling substance ’Z’. Identify X, Y and Z. Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved and name it. The substance ’Z’ on treatment with sodium hydroxide produces back the alcohol Y and sodium ethanoate. Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved and name it, giving justification for the name.
Answer:
1) When an ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in presence of an acid catalyst, it gives an ester (ethyl acetate) which is a sweet smelling substance. This reaction is known as esterification reaction.
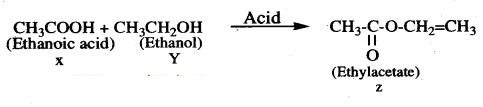
2) When ester is treated with sodium hydroxide, the ester is converted into ’ethanol’ and sodium ethanoate. This reaction is known as saponification because it is used in the preparation of soap.
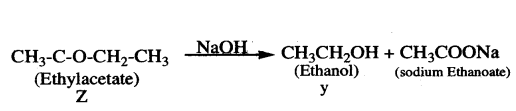
Question 37.
Detergents are better than soaps. Justify.
Answer:
- Detergents works as cleansing agent both in hard and soft water.
- The charged ends of detergents do not form insoluble precipitates with calcium’ and magnesium ions in water.
- Thus, they remain effective in hard water.
- Soaps cannot be used with hard water.
- The cleansing action of detergents is stronger than soaps.
Question 38.
Shristi heated ethanol with a compound A in presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid and observed a sweet smelling compound B is formed. When B is treated with sodium hydroxide it gives back ethanol and a compound C.
a) Identify A and C.
b) Give one use each of compounds A and B.
c) Write the chemical reactions involved a name the reactions.
Answer:
a) A - Ethanoic acid/ Or any other carboxylic acid , C- Sodium salt of ethanoic acid/any other carboxylic acid/sodium ethanoate
b) Use of A- dil solution, used as vinegar in cooking/preservative in pickles Use of B - making perfumes, flavouring agent.
c) CH3COOH + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3COONa + C2H5OH
Extra Questions on Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 - 8 Marks
Question 1.
Carbon is a versatile element. Justify with reason.
Answer:
- Carbon has two unique features :
i) It has the property of catenation (Bonding of same element)
ii) It is tetravalent.
- The above two features enable carbon to form a large number of compounds with varying size, shape.
- Carbon has the unique property to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, i.e. carbon have long chains or even are arranged in branches or rings,
- Carbon atoms in its compounds are linked by single, double or triple bonds.
- Since carbon has a valency of four, it is capable of bonding with four atoms of carbon or four other monovalent elements. .
- Carbon atoms are also bonded with oxygen, hydrogen, chlorine, nitrogen and sulphur.
- They giving rise to compounds with specific properties typical of the elements other than carbon present in the molecule.
Question 2.
What are the chemical properties of hydrocarbons ? Discuss in brief.
Answer:
Chemical properties of hydrocarbons:
1) Combustion in air : Hydrocarbons burn in air and react with oxygen gas to give carbon dioxide, water and heat.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + Heat
2) Reaction with halogens:
a) Saturated hydrocarbons are inert, they do not react with bromine. However, they do react with chlorine in the presence of light or at high temperature. These are called substitution reactions because the hydrogen atoms are substituted by chlorine atoms.
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
b) The unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo additional reactions. They are more reactive because of the tendency of the doubly bonded carbon atoms to become saturated.
CH2 = CH2 + Br2 → CH2Br - CH2Br
3) Reaction with hydrogens :
a) Saturated hydrocarbons do not react at all with hydrogen.
b) Unsaturated hydrocarbons react with hydrogen by adding in the presence of metal catalyst like nickel. The reaction is called catalytic hydrogenation or addition reaction.
Question 3.
Give reasons for the following :
a) Element carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding.
b) Diamond has a high melting point.
c) Graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
d) Acetylene burns with a sooty flame.
Answer:
a) It is because carbon has four valance electrons, it cannot gain or lose four electrons because high energy is needed. It can only share four electrons.
b) It is due to strong covalent bonds and compact structure of diamond.
c) It is due to presence of free electrons in graphite because each carbon is linked to three more carbon atoms.
d) R is due to high percentage of carbon, it burns with sooty or smoky flame.
Question 4.
Observe the table of boiling points of alcohols and carboxylic acids, study this table and answer the questions related to studied concepts.
| Compound |
Boiling Point |
| 1. Methanol |
64° C |
| 2. Ethanol |
78° C |
| 3. Propanol |
97° C |
| 4. Butanol |
117° C |
| 5. Methanoic acid |
101° C |
| 6. Ethanoic acid |
118° C |
| 7. Propanoic acid |
141° C |
| 8. Butanoic acid |
164° C |
a) Why do acids have higher boiling points than alcohol ?
b) Why does ethanol have higher boiling point than CH3OH ?
c) What is vinegar ?
d) What is glacial acetic acid ?
e) Which acid is present in red ants sting ?
f) Which acid is present in rancid butter ?
g) What happens when 5% alkaline solution of KMnO4 is added to ethanol ?
h) How are ester formed ? Give one of their use.
Answer:
a) It is because acids have stronger forces of attraction than alcohols.
b) C2H5OH has higher molar mass, more vander waals forces of attraction than CH3OH.
c) 5 to 8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar.
d) Pure acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid.
e) Methanoic acid.
f) Butanoic acid.
g) Acetic acid formed.
h) They are formed by reaction of carboxylic acid with ethanol in presence of cone. H2SO4. Esters are used in food flavouring and used in making perfumes.
Question 5.
Which type of bond does carbon form ? Support your answer by giving two justified reasons.
Answer:
- The electronic configuration of carbon is K(2), L(4). Thus it has 4 electrons in the outermost shell.
- In order to react or to achieve noble gas configuration, it should either gain or lose 4 electrons.
- It cannot gain 4 electrons and become C4+ because a very large amount of energy would be required to remove four electrons from a small atom like carbon having a very close nucleus with 6 protons.
- Carbon overcomes above problem and forms a large number of compounds by sharing its valance electrons with other atoms of carbon or with atoms of other elements.
- These by satisfying requirement to attain noble configuration of its own and of all the combining atoms.
- For example, carbon forms methane as shown below.
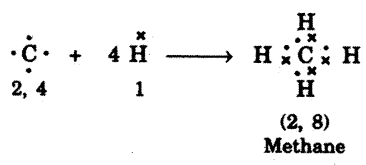
- In methane, carbon shares its four valance electrons with four valence, electrons, one each from four hydrogen atoms.
- Thus carbon attains the configuration (2, 8) as that of nearest noble gas, neon.
- And all four hydrogen atoms individually attain the configuration of helium gas (K = 2).
- Bond so formed due to sharing of electrons is called covalent bond.
Question 6.
Differentiate between soaps and detergents.
Answer:
| Soaps |
Detergent |
| a) There are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids. |
a) There are sodium or potassium salts of long chain sulphuric acids. |
| b) They have - COONa group |
b) They have - SO3Na or SO4 Na group |
| c) They do not work well with hard water. |
c) They work well with hard water. |
| d) It is obtained easily from edible oil. |
d) It is obtained from costly petroleum products. |
Question 7.
What are the properties and uses of ethanol ?
Answer:
Properties of ethanol :
1) Liquid at room temperature.
2) Commonly known as alcohol and a key ingredient in alcoholic drinks.
3) Soluble in water in all proportions.
4) Small quantities cause drunkenness, while pure ethanol is lethal.
5) Prolonged consumption leads to health problems.
Uses of ethanol :
1) Used in alcoholic beverages.
2) Serves as a solvent in medicines and tonics.
3) Found in products like tincture iodine and cough syrups.
Question 8.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent compounds, and how do their properties relate to their bonding ?
Answer:
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points, while covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity in solution or when molten, whereas covalent compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity.
- The strong forces of attraction between ions in ionic compounds explain their high melting and boiling points.
- Covalent compounds do not form ions; instead, they share electrons to achieve stability.
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
- The shared electrons belong to the outermost shells of both atoms.
- Covalently bonded molecules have strong intramolecular bonds but weak intermo- lecular forces.
- Weak intermolecular forces contribute to the low melting and boiling points of co-valent compounds.
- Covalent compounds’ inability to conduct electricity is due to the absence of charged particles.
Question 9.
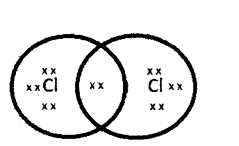
Describe the electron dot structure of chlorine (Cl2 and oxygen (O2) molecules.
Answer:
- Chlorine (Cl2) consists of two chlorine atoms.
- Each chlorine atom has seven valence electrons.
- The electron dot structure of Cl2 shows a single covalent bond with a shared pair of electrons.
- Oxygen (O2) has an atomic number of 8, needing two more electrons for an octet.
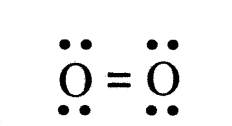
- Each oxygen atom shares two electrons with another oxygen atom.
- The electron dot structure of O2 depicts a double bond with two shared pairs of electrons.
Question 10.
Illustrate the bonding in a molecule of water (H2O) and a diatomic molecule of nitrogen (N2).
Answer:
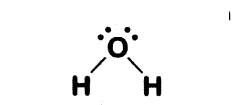
- In a molecule of water (H2O), each hydrogen atom shares one electron with an oxygen atom.
- Oxygen contributes two electrons, forming two single covalent bonds.
- Water has single bonds.
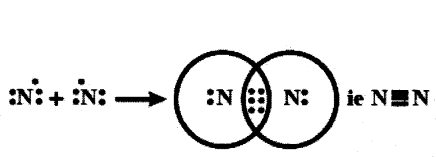
- In a diatomic molecule of nitrogen (N2) each nitrogen atom shares three electrons.
- This sharing results in three shared pairs of electrons, forming a triple bond.
- Nitrogen (N2) has triple bonds between its atoms.
Question 11.
Explain the covalent bonding in methane (CH4).
Answer:
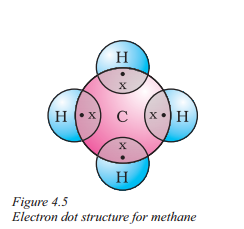
- Methane (CH4) consists of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
- Carbon has four valence electrons and shares them with four hydrogen atoms.
- Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron.
- This sharing forms four single covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen.
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
- Methane molecules have strong intramolecular bonds and weak intermolecular forces.
- Methane is tetravalent due to carbon’s four valence electrons, and it achieves stability through covalent bonding.
Question 12.
What is a homologous series in organic chemistry, and how does it relate to carbon compounds?
Answer:
- A homologous series consists of compounds with the same functional group, which replace hydrogen atoms in a carbon chain.
- These compounds have similar chemical properties but different physical properties due to varying molecular masses.
- In alkanes, the general formula is CnH2n, while in alkenes, it’s CnH2n - 2.
- Chemical properties are determined by the functional group, ensuring similarity within the series.
- Carbon’s unique ability is due to catenation, forming long chains, branches, or rings.
- Carbon can form single, double, or triple bonds with other carbon atoms.
- Carbon’s valency of four enables bonding with multiple other elements.
- Strong carbon-carbon bonds contribute to compound stability.
- Larger atoms in other elements result in weaker bonds.
- Saturated compounds have single bonds and low reactivity.
- Unsaturated compounds have double or triple bonds and higher reactivity.
- Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different structures.
- A homologous series consists of compounds with the same functional group.
- Similar chemical properties within a homologous series due to the functional group.
Question 13.
Explain the reactions of ethanoic acid, including esterification and its reactions with bases, carbonates, and hydrogencarbonates.
Answer:
Esterification :
- Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form an ester and water.
- Ester is often sweet-smelling and used in perfumes and flavours.
Reaction with bases :
- Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium ethanoate (salt) and water.
- Equation : NaOH + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O
Reaction with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates :
- Ethanoic acid reacts with these compounds to produce salt, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Example : CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
- This reaction is also observed with sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Question 14.
State the reason why
a) carbon compounds have low melting and boiling points
b) carbon compounds do not conduct electricity.
c) carbon can form only covalent compounds.
Answer:
a) 1) Carbon compounds have low melting and boiling points.
2) They have strong bond within molecules but the intermolecular forces are weak.
3) So carbon compounds have low melting and boiling points.
b) 1) Carbon compounds are formdd by sharing of electrons.
2) They have )no charged particle or free valence electron.
3) Hence they do not conduct electricity in any state.
c) 1) Carbon can form only covalent compounds because they cannot lose their 4 valence electron to form C4+ action as they have large atomic size and weak force of attraction and a large energy is required to remove valence electron.
2. Carbon cannot gain electrons to from C4+ anion as it is 1m possible for protons
hold 10 electrons in its valence shell.
3) So carbon share 4 valance electrons with other atoms to from covalent compound.
Question 15.
What is a homologous series of carbon compounds? Give an example and list its three characteristics.
Answer:
1) Homologous series of carbon compounds is the series of compounds having same general formula and having same functional group but the successive compounds in the homologous series differ by -CH2-unit,
2) For example homologous series for alkene
3) General formula : CnH2n
n = 2, C2H4 Ethene
n = 3, C3H6 Propene
n = 4, C4H8 Butene
n = 5, C5H10 Pentene
4) Characteristics :
i) Melting and boiling point increases with increasing molecular mass.
ii) All the members are differ by -CH2-unit.
iii) All the members show nearly same chemical properties that are exhibit by double bond in alkenes.
Question 16.
Write the name and the structural formula of the compound formed when ethanol is heated at 443 K with excess of cone. H2SO4. State the role of cone. H2SO4, in this reaction. Write chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer:
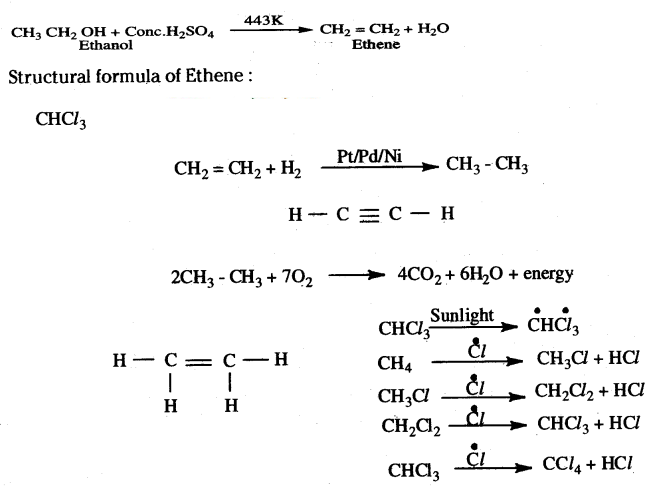
Concentrated H2SO4 acts as a dehydrating agent in the reaction.
Question 17.
What is meant by functional group in carbon compounds? Write in tabular form the structural formula and the functional group present in the following compounds:
i) Ethanol
ii) Ethanoic acid
(OR)
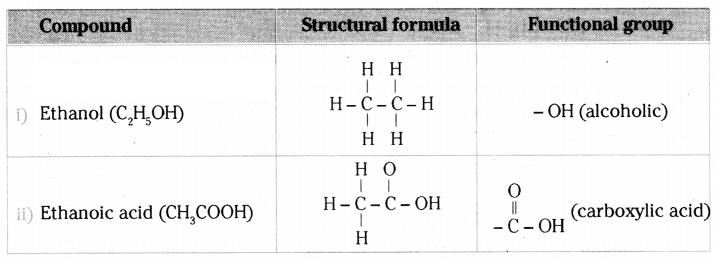
State the meaning of functional group in a carbon compound. Write the functional group present in (i) ethanol and (ii) ethanoic acid and also draw the structures.
Answer:
An atom or a group of atoms present in a molecule which largely determines its chemi¬cal properties, is called functional group.
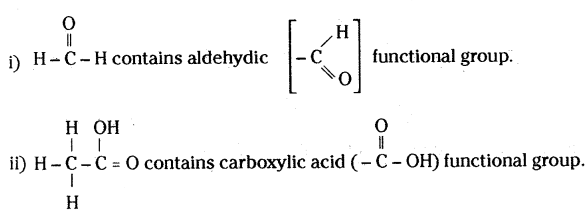
(OR)
Question 18.
Complete the following chemical equations :
i) CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH →
ii) CH3COOH + NaOH →
iii) C2H5O + CH3COOH 
iv) C2H5OH + O2 →
v) C2H5OH 
vi) CH3COOH + NaHCO3 →
Answer:
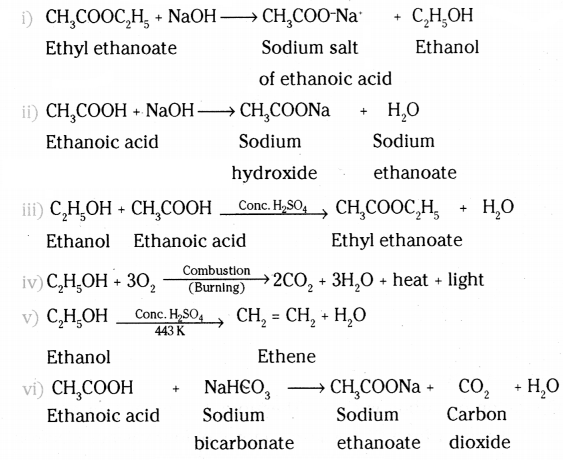
Question 19.
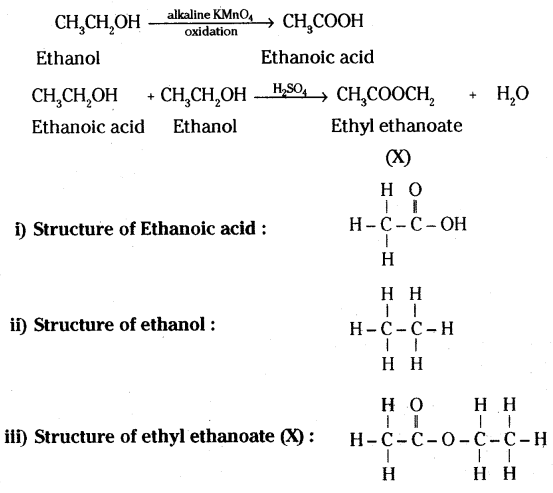
A carboxylic acid (molecular formula C2H4O2) reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form a compound X. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid C2H4O2. Write the name and structure of (i) carboxylic acid, (ii) alcohol and (iii) the compound ‘X’.
Answer:
The molecular formula of carboxylic acid is C2H4O2. Thus, it should be acetic acid (Ethanoic acid).
Ethanoic acid : 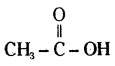
It reacts with alcohol in presence of acid catalyst to give compound ‘X’.
As alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 gives the same acid i.e. Ethanoic acid, hence alcohol must contain two carbon atoms. Thus, formula for alcohol is CH3CH2OH i.e. ethanol.
Reactions involved are :
Question 20.
State the reason why carbon can neither form C4+ Creations nor C- anions, but forms covalent compounds. Also state reasons to explain why covalent compounds:
i) are bad conductors of electricity?
ii) have low melting and boiling points?
Answer:
Electronic configuration of carbon is (2, 4). Therefore it requires four electrons to complete the octet. It cannot form C4+ because removal of four valence electrons requires a large amount of energy. The cation formed will have six protons and two electrons which make atom highly unstable. It is also unable to form C4- anion as its nucleus has six protons which is unable to hold ten electrons. Therefore carbon will only able to form covalent compounds in which it attain noble gas configuration by sharing of electrons.
i) Covalent compounds are bad conductor of electricity due to the absence of free electrons.
ii) Covalent compounds have covalent bonds which are weak bonds, Therefore lesser energy is required to break the bond. Hence covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Question 21.
a) Define the term isomers.
b) Draw two possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C2H6O and write their names.
c) Give the electron dot structures of the above two compounds.
Answer:
a) Isomers are the compounds that have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
b) Molecular Formula: C2H6O
Isomers : CH2OCH3 and CH3CH2OH
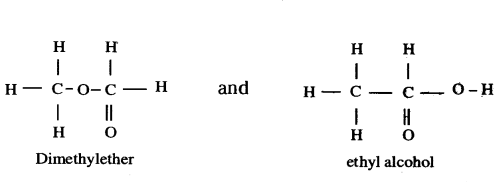
c) Electron dot Structures :
Question 22.
Chlorine gas was prepared using electrolysis of brine solution. Write the chemical equation to represent the change. Identify the other products formed in the process and give one application of each.
Answer:
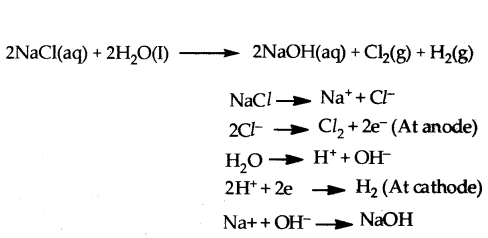
Sodium hydroxide/NaOH/Caustic soda
Hydrogen-
Uses :
1) Sodium hydroxide/NaOH/Caustic soda
. Degreasing of metals
. Preparation of soaps and detergents
. Paper making
. Artificial fibres
2) Hydrogen
. Fuels
. Margarine
. Manufacture of ammonia for fertilizer
Question 23.
i) A compound ‘A’ with a molecular formula of C2H4O2 reacts with a base to give salt and, water. Identify ‘A’, state its nature and the name of the functional group it possesses. Write chemical equation for the reaction involved,
ii) When the above stated compound ‘A’ reacts with another compound ‘B’ having molecular formula C2H6O in the presence of an acid, a sweet smelling compound ‘C’ is forme’d.
1) Identify ‘B’ and ‘C’.
2) State the role of acid in this reaction.
3) Write chemical equation for the reaction involved. ,
Answer:
i) Since the compound gives a salt and water upon reaction with a base, it is an acidic compound. The molecular formula C2H4O2 represents a molecule of ethanolo acid CH3COOH.
‘A’= CH3COOH .
Ethanoic acid is a low-melting and boiling compound with vinegar smell.
Functional Group present = -COOH (Carboxylic group)
Chemical equation for the reation :
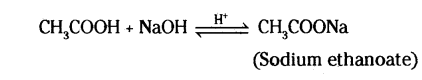
ii) Ethanoic acid (A) reacts with ethanol (CH3CH2OHB) to give a sweet smelling ester (c).
1) ‘B’ = CH3CH2OH (ethanol)
C = CH3COOC2H5 (ester)
2) The presence of an acid (H+) in this reaction catalyses the esterification reaction.
3) 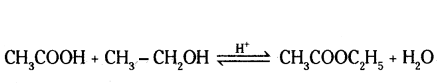
Question 24.
i) Name the simplest saturated hydrocarbon. Draw its electron dot structure. Which type of bonds exist in this compound ?
ii) Name any two mixtures of the carbon compound used as a fuel in daily life, of which the above mentioned compound is an important component
iii) In which homologous series of carbon compounds can this compound be placed? Write the general formula of the series.
iv) Which type of flame is produced on burning it ?
Answer:
i) 1) Simplest saturated hydrocarbon is methane (CH4)
2) Electron dot structure of methane : 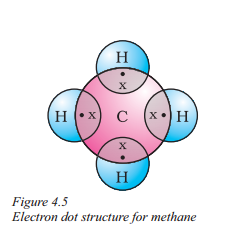
3) Covalent bonds are formed in this molecule. This type of bond is formed by mutual sharing of electrons.
ii) 1) Biogas and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) are used as a fuel in daily life.
2) Methane is a major component of these fuels.
iii) This compound can be placed in alkanes series which have general formula CnH2n - 2.
iv) 1) On burning methane, large amount of heat and light is produced.
2) It produces a clean blue, non-sooty flame on burning in sufficient amounts of oxygen.
Question 25.
Carry out the following conversions, stating the condition (s) for each :
i) Ethanol → Ethene
ii) Ethene → Ethane
iii) Elbane → Chloro ethane
iv) Ethanol → Ethanoic acid
v) Ethanoic acid → Ethyl ethanoate
Answer:
i) Heating ethanol at 443K with excess cone. H2SO4 results in dehydration of ethanol to give ethene.
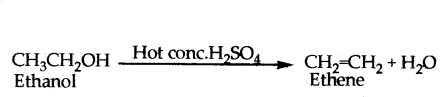
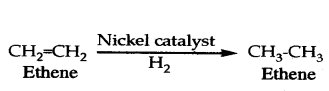
ii) Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts such as pal-ladium or nickel to give saturated hydrocarbons.
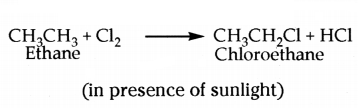
iii) In presence of sunlight, chlorine is added to saturated hydrocarbon in a very fasl reaction. Chlorine can replace the hydrogen atoms one by one.
iv) Ethanol can be oxidised to ethanol acid by heating in presence of oxidising agents such as alkal potassium permanganate or acidified potating dichromate
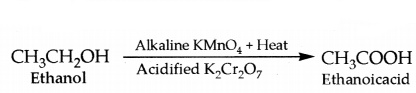
v) Ethanoic acid reacts with absolute alcohol (ethanol) in presence of an acid catalyst to give an ester, ethy, ethanoate.
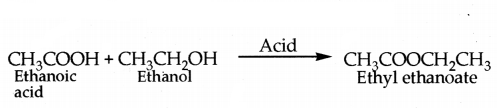
Question 26.
What are straps ? Explain mechanism of cleansing action of soap with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer:
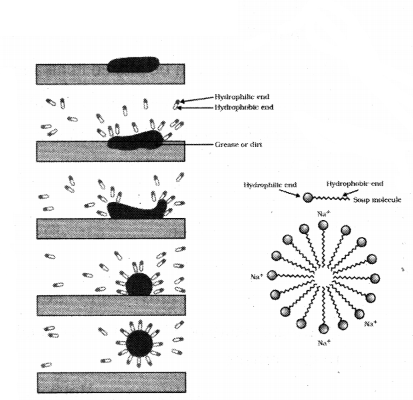
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long- chain carboxylic acids, which have cleansing properties in water.
Cleansing action of soaps :
A soap molecule consists of two parts : a long chain hydrocarbon tail (hydrophobic) and a head (hydrophilic). When soap is added to dirty water then the hydrophobic part gets attached to the dirt while the hydrophilic part remains in contact with the water molecule. Due to this arrangement, the soap molecules form micelles and trap the dirt at the centre. The micelles do not precipitate and maintain their identity due to charge repulsions and remain suspended in the water. This forms a colloidal solution and the trapped dirt can be easily rinsed off.
Question 27.
i) Draw two structural isomers of butane.
ii) Draw the structures of propanol and propanone.
iii) Name the third homologue of :
a) alcohols
b) aldehydes
iv) Name the following :
b) CH3 - CH2 CH = CH2
v) Show the covalent bond formation in nitrogen molecule.
Answer:
i) Structural isomers of butane are the following : 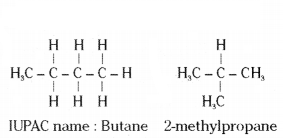
ii) 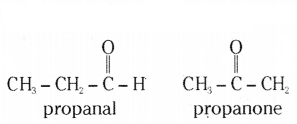
iii) a) Three homologue of alcohol are the following : CH3OH, CH3CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2OH
Third homologue of alcohol is CH3CH2CH2OH
b) Three homologue of aldehyde are the following: HCHO, CH3CHO, CH3CH,CHO
Third homologue of aldehyde is CH3CH2CHO.
iv) a) Benzene
b) But-l-ene
v) Z = 7, 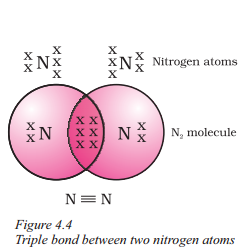
Question 28.
Write the chemical equation for the following :
i) Combustion of methane
ii) Oxidation of ethanol
iii) Hydrogenation of ethene
iv) Esterification reaction
v) Saponification reaction
Answer:
i) The process in which compounds of carbon react with oxygen to give carbon dioxide, water, heat and light, is known as combustion. Alkanes burn in air and release large amount of heat, therefore can be used as excellent fuels.
ii) Oxidation is a process in which oxygen is added to a substance.
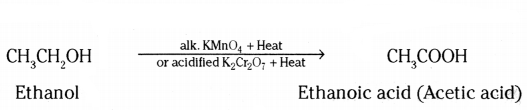
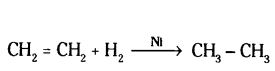
iii) Hydrogenation means addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated compound.
iv) When alcohol is added to carboxylic acid in the presence of acid catalyst then, a fruity smelling ester is formed. This process is called esterification.
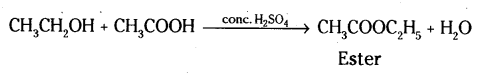
v) Esters react in the presence of an acid or a base to give the alcohol and carboxylic acid. This reaction is known as saponification because it is used in the preparation of soap.