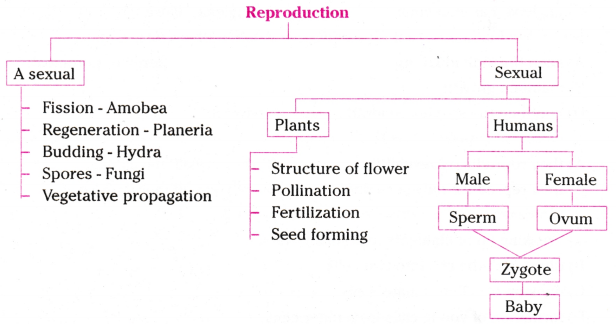
AP 10th Class Biology 7th Lesson How do Organisms Reproduce? Important Questions
Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 Important Questions - 1 Mark
Question 1.
What is reproduction ?
Answer:
Reproduction is the process of producing new individuals of the same kind.
Question 2.
What are the types of reproduction ?
Answer:
Organisms reproduce in two ways- asexually and sexually
Question 3.
What is asexual reproduction ?
Answer:
Asexual reproduction does not involve the fusion of male and female gametes. This takes place in bacteria, amoeba, hydra.
Question 4.
What are the life processes essential for life ?
Answer:
The essential life processes such as nutrition, respiration or excretion.
Question 5.
How do we know that two different individual organisms belong to the same species?
Answer:
Species are organisms that can reproduce within them. Reproducing organisms create new individuals that look very much like themselves.
Question 6.
What is the role of DNA in reproduction ?
Answer:
A basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy. After DNA Copied help to create new cell.
Question 7.
What is variations ?
Answer:
Variation can be defined as any difference between the individuals in a species or groups of organisms of any species.
Question 8.
What is niche ?
Answer:
In ecology, the term "niche" describes the role of an organism plays in a community. A species’ niche encompasses both the physical and environmental conditions it requires.
Question 9.
What is regeneration ?
Answer:
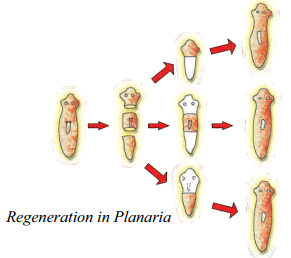
Simple animals like Hydra and Planaria can be cut into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration.
Question 10.
What is vegetative propagation ?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is an asexual method of plant reproduction that occurs in its leaves, roots and stem.
Question 11.
What are the types in vegetative propagation?
Answer:
Layering and grafting are common vegetative propagation process that we follow.
Question 12.
What is the role of vegetative propagation in agriculture?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is used in methods such as layering or grafting to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, or grapes for agricultural purposes.
Question 13.
What is the vegetative process in bryophyllum?
Answer:
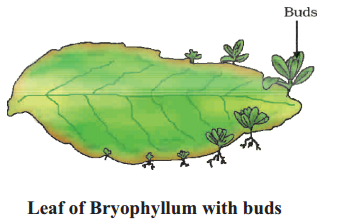
Buds produced in the notches along the leaf margin of Bryophyllum fall on the soil and develop into new plants.
Question 14.
What is germination ?
Answer:
The seed contains the future plant or embryo which develops into a seedling under appropriate conditions. This process is known as germination.
Question 15.
What are the examples for sexually transmitted diseases ?
Answer:
Many diseases can be sexually transmitted. These include bacterial infections such as gonorrhea and syphilis.
Question 16.
How can we prevent STD ?
Answer:
Using a covering, called a condom, for the penis during sex helps to prevent transmission of many of these infections to some extent.
Question 17.
What is HIV-AIDS ?
Answer:
HIV (Human Immuno deficiency Virus ) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. AIDS is Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. AIDS is a disease caused by HIV.
Question 18.
What is radical ?
Answer:
Radicle is defined as the embryonic root of the plant, which develops into the future root of the plant.
Question 19.
What is plumule ?
Answer:
Plumule is the embryonic shoot that gives rise to the shoot system.
Question 20.
What is the cotyledon of a plant ?
Answer:
A cotyledon is part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Often when the seed germinates, or begins to grow, the cotyledon may become the first leaves of the seedling.
Question 21.
What is the significance of this sexual mode of reproduction ?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction is a biological process that involves the fusion of specialized reproductive cells, known as gametes.
Question 22.
Choose the correct order of the stages of binary fission in Leishmania.
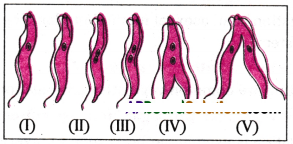
A) I, II, III, IV, V
B) I,III, II, V, IV
C) I, III, V, II, IV
D) I,II, III V, IV
Answer:
A) I, II, III, IV, V
Question 23.
Consider the following three flowers namely X, Y and Z. Which flowers would develop into a fruit ?
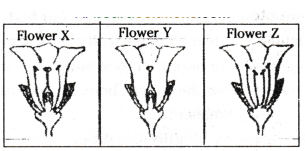
A) ‘X’ only
B) ‘Z’ only
C) ‘X’ and ‘Y’ only
D) ‘Y’ and ‘Z’
Answer:
C) ‘X’ and ‘Y’ only
Question 24.
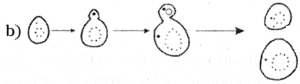
Identify the figures showing the process of budding in yeast.
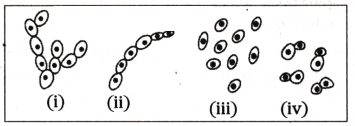
A) i, ii and iii
B) ii, iii and iv
C) i, ii and iv
D) iii, iv and i
Answer:
D) iii, iv, and i
Question 25.
You are asked by your teacher to study the different parts of an embryo of a gram seed. Given below are the steps to be followed for the experiment :
I) Soak the gram seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
II) Cut open the soaked seed and observe its different parts.
III) Take some dry gram seeds in a petri dish.
IV) Drain the excess water.
V) Cover the soaked seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them for a day.
What is correct sequence of these steps ?
Answer:
III, I, IV, V, II
Question 26.
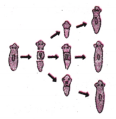
A student after observing a slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba. draws the following diagrams. However these diagrams are not in proper sequence:
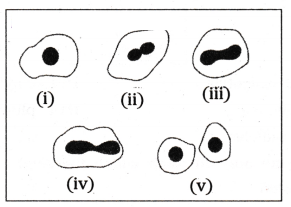
What is the correct sequence ?
Answer:
i, iii, ii, iv, v
Question 27.
Write the correct statements for the process of budding in yeast:
I) A bud arises from a particular region on a parent body.
II) A parent cell divides into two daughter cells, here the parental identity is lost.
III) Before detaching from the parent body a bud may form another bud.
IV) A bud when detaches from the parent body grows into a new individual
Answer:
I, III and IV are the correct statements.
Question 28.
To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of ail require a dicot seed. Write dicot seeds from following groups : Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
Answer:
Dicot seeds are Gram, Pea and Ground-nut.
Question 29.
A student has to perform the experiment "To identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed." Select from the following an appropriate group of seeds :
A) pea, gram, wheat
B) red kidney bean, maize, gram
C) maize, wheat, red kidney bean
D) red kidneybean, pea, gram
Answer:
D) red kidneybeap, pea, gram
Question 30.
The diagram shown below depicts pollination. Choose the options that will show a maximum variation in the offspring.

A) a, b and c
B) b and d
C) b, c and d
D) a and c
Answer:
B) b and d
Question 31.
Identify the parts labelled 1 and 2 in the adjoining figure.
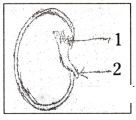
A) 1 - micropyle, 2 - epicotyls
B) 1 - cotyledon, 2 - embryo
C) 1 - radicle, 2 - plumule
D) 1 - plumule, 2 - radicles
Answer:
D) 1 - plumule, 2 - radicles
Question 32.
In a dicot seed, the pore through which the seed absorbs water during seed germination is called
A) Micropyle
B) Hilum
C) Funicle
D) Radical
Answer:
A) Micropyle
Question 33.
For the experiment - To prepare temporary mount of yeast to study budding process; Yeast granules are made to first grow by adding them to
A) Hydrochloric acid
B) Distilled water
C) 10% sugar solution
D) Alcohol
Answer:
C) 10% sugar solution
Question 34.
A farmer wants to grow banana plants genetically similar enough to the plants already available in his field. Which one of the following methods would you suggest for this purpose?
A) Regeneration
B) Budding
C) Vegetative propagation
D) Sexual reproduction
Answer:
C) Vegetative propagation
Question 35.
Assertion : Probability of survival of an organism produced through sexual reproduction is more than that of organism produced through asexual mode.
Reason : Variations provide advantages to individuals for survival.
A) Both A and’R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C) A is true but R is false.
D) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 36.
Identify the device.

Answer:
Its intra uterus device known as copper T.
Question 37.
Identify the cell.

Answer:
Human Sperm cell
Question 38.
What is the process shown in the figure?
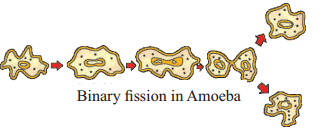
Answer:
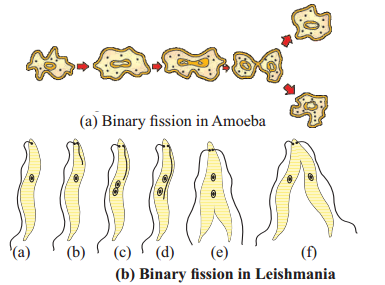
Binary fission in Amoeba.
Question 39.
Name the organism that is shown in the figure.
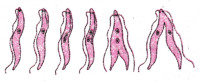
Answer:
Binaray fission in Leishmania.
Question 40.
What is the name of a sexual process that is shown in Planaria?
Answer:
Regeneration.
Question 41.
Name the organism that shows the Budding.

Answer:
Hydra and Yeasts.
Question 42.
Identify the leaf that has buds on its margins.

Answer:
Leaf of Bryophyllum with Buds.
Question 43.
What is the other name for Rhizopus that produces the spores?
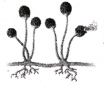
Answer:
Bread mould.
Question 44.
What are names for primary roots and shoots?
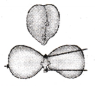
Answer:
Primary root is radicle, primary shoot is plumule.
Question 45.
Expand STD
Answer:
Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
Question 46.
What are the permanent contraception methods.
Answer:
Vasectomy and Tubectomy.
Question 47.
What are the vegetative propagation methods used by humans.
Answer:
Cuttings, grafting and budding and tissue culture.
How do Organisms Reproduce? Class 10 Important Questions - 2 Marks
Question 1.
How the information pass one generation to next generation?
Answer:
- Chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell contain information for inheritance of features from parents to next generation in the form of DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) molecules.
- The DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source for making proteins.
Question 2.
Is the DNA copy always same ?
Answer:
- It will depend on how accurately the copying reactions involved occur. No bio-chemical reaction is absolutely reliable.
- Therefore, it is only to be expected that the process of copying the DNA will have some variations each time.
Question 3.
What are the modes in asexual reproduction ?
Answer:
Primitive organisms shows different types os asexual modes. They are
- fission
- multiple fission
- budding
- regeneration
- fragmentation
Question 4.
How plasmodium reproduce asexually ?
Answer:
The malarial parasite, Plasmodium, divide into many daughter cells simultaneously by multiple fission.
Question 5.
How the yeast reproduce ?
Answer:
Yeast, on the other hand, can put out small buds that separate and grow further,this process called budding.
Question 6.
What is fragmentation ?
Answer:
An organism simply breaks up into smaller pieces upon maturation. These pieces or fragments grow into new, for example, spirogyra
Question 7.
Write about fission.
Answer:
Fission:
- For unicellular organisms, cell division, or fission, leads to the creation of new individuals.
- Many bacteria and protozoa simply split into two equal halves during cell division.
- In organisms such as Amoeba, the splitting of the two cells during division can take place in any place.
Question 8.
Write about regeneration.
Answer:
- Simple animals like Hydra and Planaria can be cut into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration.
- Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells. These cells proliferate and make large numbers of cells. From this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues.
Question 9.
Write about budding.
Answer:
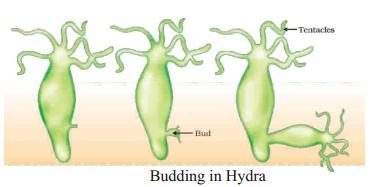
- Organisms such as Hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction in the process of budding
- In Hydra, a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site
- These buds develop into tiny individuals and when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals.
Question 10.
Why organisms prefer sexual mode of reproduction ?
Answer:
The DNA copying mechanism, cannot be absolutely accurate, and the resultant errors are a source of variations in populations of organisms. Every individual organism cannot be protected by variations, but in a population, variations are useful for ensuring the survival of the species. It would therefore make sense if organisms came up with sexual reproductive modes that allowed more and more variation to be generated.
Question 11.
What is the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction ?
Answer:
- Meiosis is a special cell division that decrease the chromosome number into two half and formed haploid cells called gametes.
- By the combination of these gametes zygote is formed to gives rise to new individual.
Question 12.
What are the whorls in flower ?
Answer:
- The reproductive parts of angiosperms are located in the flower.
- The different parts of a flower - sepals, petals, stamens and pistil.
- Stamens and pistil are the reproductive parts of a flower which contain the germ-cell.
Question 13.
What is unisexual and bisexual flowers ?
Answer:
- The flower that has only male or female reproductive parts ie, either stamens or carpels are present are unisexual flowers. Examples of unisexual flowers are bitter- gourd, papaya, pumpkin, and cucumber.
- The flower possessing both male and female reproductive parts are a bisexual flower that is both stamens and carpels are present in the same flower. Examples of bisexual flowers are rose, sunflower, hibiscus, lily, and mustard.
Question 14.
What is the role of stamens in flower ?
Answer:
Stamen is the male reproductive part and it produces pollen grains that are yellowish in colour. We must have seen this yellowish powder that often sticks to our hands if we touch the stamen of a flower.
Question 15.
What is pistil ?
Answer:
- Pistil is present in the center of a flower and is the female reproductive part. It is made of three parts.
- The swollen bottom part is the ovary, middle elongated part is the style and the terminal part which may be sticky is the stigma. The ovary contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell.
Question 16.
How the zygote is formed ?
Answer:
The male germ-cell produced by pollen grain fuses with the female gamete present in the ovule. This fusion of the germ-cells or fertilization gives us the zygote which is capable of growing into a new plant.
Question 17.
How the sperms are delivered ?
Answer:
- The sperms formed are delivered through the vas deferens which unites with a tube coming from the urinary bladder.
- The urethra thus forms a common passage for both the sperms and urine.
Question 18.
What is role of glands in male reproductive system ?
Answer:
- Along the path of the vas deferens, glands like the prostate and the seminal vesicles add their secretions.
- So that the sperms are now in a fluid which makes their transport easier and this fluid also provides nutrition.
Question 19.
What are the sperms ?
Answer:
The sperms are tiny bodies that consist of mainly genetic material and a long tail that helps them to move towards the female germ-cell.
Question 20.
What is child birth ?
Answer:
The development of the child inside the mother’s body takes approximately nine months. The child is born as a result of rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus its called child birth.
Question 21.
Why should we know about reproductive health ?
Answer:
Reproductive health is important because it affects the individual, their family, and their community. Sexual and reproductive health is an essential part of overall health and well-being. It is a person’s right to control their body and the education to make informed decisions about sex.
Question 22.
Why should we follow certain age for marriage ?
Answer:
The sexual act always has the potential to lead to pregnancy. Pregnancy will make major demands on the body and the mind of the woman, and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected.
Question 23.
Prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law ?
Answer:
- For a healthy society, the female-male sex ratio must be maintained.
- Because of reckless female foeticides, child sex ratio is declining at an alarming rate in some sections of our society
- Although prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law.
Question 24.
Why do organisms reproduce ?
Answer:
- Organisms reproduce for several essential reasons that are central to their survival and the continuation of their species.
- Reproduction is a fundamental biological process that ensures genetic diversity, adaptability, and the persistence of life on Earth.
Question 25.
Write slogans against female foeticide.
Answer:
Promoting slogans against female foeticide is "Save the girl child, save the future."
Question 26.
Try and work out the advantages of seed-formation for the plant ?
Answer:
- The seeds protect the embryo from harsh environmental conditions
- They provide nourishment and parental care to the developing embryo.
- The dispersal of the seeds to far-off places prevents competition among the members of the same species, thus preventing their extinction.
Question 27.
Why does the body show sexual maturation at puberty age ?
Answer:
- Sex is a complex biological process, it need maturity of body and energy.
- So in the age of puberty body ready to maintain this process.
- Sexual maturity and another physical maturity that occurs during the time of puberty are the results of various hormonal changes which occur in their body.
- For example hormones, estrogen in combination with FSH and LH prepares a girl’s body to mature and prepare her for pregnancy.
Question 28.
How do we decide if the body or the mind is ready for this major responsibility?
Answer:
- Reproduction is the major responsibility for every organism.
- It needs maturity of body and mind.
- Well developed body and secondary sexual characters indicate the state.
- Thats why our elders suggest age for marriage.
Question 29.
Is it possible to prevent the transmission of such diseases during the sexual act ?
Answer:
- It is possible to prevent the sexual transmitted diseases by using physical barriers like condoms and loops.
- Avoid sex with unknown partners.
- Reduce Number of Sex Partners.
- And maintain Mutual Monogamy (having sex with only life partner).
Question 30.
Distinguish between pollination and fertilization. Mention the site and the product of fertilization in a flower.
Answer:
- Pollination : Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called pollination.
- Fertilization: Pollen of male and female gametes (or germ cells) is called fertilization.
- Site of fertilization : Ovary/ovule product of fertilization is zygote.
Question 31.
Students were asked to observe the permanent slides showing different stages of budding in yeast under high power of a microscope.
a) Which adjustment screw (coarse/fine) were you asked to move to focus the slides?
b) Draw three diagrams in correct sequence showing budding in yeast.
Answer:
a) A fine screw is used to focus the slides of budding in yeast under high power of a microscope.
Question 32.
In the following figure showing a germinating gram seed, name the parts labelled as A, B and C.
Why is part ‘B’ considered to be important during germination ?
Answer:
The parts labelled are A is Plumule, B is Cotyledon and C is Radicle. Part B is the cotyledon which serves as a food store during germination. It also provides required nutrients to the growing embryo during germination.
Question 33.
Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation.
Answer:
Bryophyllum leaves bear buds on their notches along their margins. When such a leaf with buds on margin falls, the buds come in contact of the soil and develop into plant- lets. These plantlets later grow into new plants.
Question 34.
Mention about the four events that occur during binary fission in amoeba.
Answer:
The four events that occur during binary fission in amoeba are :
- The dividing cell elongates.
- The amount of cytoplasm and nucleus gets doubled.
- A furrow forms.
- The cell divides to give rise to two daughter cells.
Question 35.
Rajesh observed a patch of greenish black powdery mass on a stale piece of bread.
a) Name the organism responsible for this and its specific mode of asexual reproduction.
b) Name its vegetative and reproductive parts.
Answer:
a) The greenish black powdery mass on a stale piece of bread is due to bread mould Rhizopus which reproduces by spore formation,
b) Hyphae or thread like structures are the vegetative part and tiny blob like structures or sporangia are the reproductive parts of the bread mould Rhizopus.
Question 36.
After examining a prepared slide under the high power of a compound microscope, a student concludes that the given slide shows the various stages of binary fission in a unicellular organism. Write two observations on the basis of which such a conclusion may be drawn.
Answer:
Stages of binary fission in unicellular organism :
- In the centre of Amoeba dense nucleus is seen.
- In second stage, Amoeba shows the nucleus division, called as karyokinesis.
- In third stage, the division of cell body occurs called as cytokinesis.
- In the fourth stage two daughter cells of amoeba reformed.
Question 37.
Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where
i) fertilisation takes place,
ii) implantation of the fertilised egg occurs.
Answer:
i) In human female reproductive system fertilisation takes place in the Fallopian tube
ii) In human female reproductive system implantation of the fertilised egg occurs in uterus.
Question 38.
Name the types of asexual reproduction in the following organisms.
a) Paramoecium
b) Yeast:
Answer:
a) Paramoecium : It reproduces by splitting into two called Binary fission,
b) Yeast: Yeast reproduces by Budding.
Question 39.
What is regeneration ? Give examples.
Answer:
- If the individual is broken up into many pieces, these pieces grow into separate individuals.
- The ability of an organism give rise to new individual organisms, when it is cut into pieces.
- Ex : Hydra, Planaria.
Question 40.
Pollen leaves of Bryophyllum on the ground produce new plants whereas the leaves of rose do not ? Explain the difference between the two plants.
Answer:
- In Bryophyllum, vegetative propagation occur through leaves, where buds occur on their margins.
- Rose leaves do not form buds.
Question 41.
List any two contraceptive methods practised only by woman. Mention how these methods work.
Answer:
- Oral pills : Change hormonal balance so eggs are not released.
- Loop/copper-T : Place in the uterus. Prevent pregnancy by checking the entry of sperms through the vagina.
Question 42.
i) What is the fate of the ovules and the ovary in a flower after fertilization ?
ii) How is the process of pollination different from fertilization ?
Answer:
i) After fertilization ovules become seeds and ovary forms the fruit.
ii) Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a flower. Fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes.
Question 43.
Read the paragraph and answer the following questions.
In tissue culture, new plants are grown by removing tissue or separating cells from the growing tip of a plant. The cells are then placed in an artificial medium where they divide rapidly to form a small group of cells or callus. The callus is transferred to another medium containing hormones for growth and differentiation.
1. Which type of reproduction is tissue culture ?
Answer: Tissue culture is an asexual reproduction.
2. What is the use of tissue culture ?
Answer: By the tissue culture we gain more desirable plants in less time.
Important Questions on How do Organisms Reproduce? Class 10 - 4 Marks
Question 1.
How the cell gives rise to new cell ?
Answer:
- A basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy.
- Cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell, and they will need to be separated from each other.
- However, keeping one copy of DNA in the original cell and simply pushing the other one out would not work, because the copy pushed out would not have any organized cellular structure for maintaining life processes.
- Therefore, DNA copying is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, and then the DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus. Effectively, a cell divides to give rise to two cells.
Question 2.
Are new cell likely to be absolutely identical ?
Answer:
- The answer to this question will depend on how accurately the copying reactions involved occur.
- No bio-chemical reaction is absolutely reliable. Therefore, it is only to be expected that the process of copying the DNA will have some variations each time.
- As a result, the DNA copies generated will be similar, but may not be identical to the original.
Question 3.
How variations help to service an organism ? Give example.
Answer:
- A population of reproducing organisms were suited to a particular niche and if the niche were drastically altered, the population could be wiped out.
- However, if some variations were to be present in a few individuals in these populations, there would be some chance for them to survive.
- If there were a population of bacteria living in temperate waters, and if the water temperature were to be increased by global warming, most of these bacteria would die, but the few variants resistant to heat would survive and grow further. Variation is thus useful for the survival of species over time.
Question 4.
Why multicellular organisms have complex in their reproduction?
(OR)
Why multicellular organisms does not follow simple divisions?
Answer:
- The reason is that many multicellular organisms, as we have seen, are not simply a random collection of cells.
- Specialised cells are organized as tissues, and tissues are organized into organs, which then have to be placed at definite positions in the body.
- In such a carefully organized situation, cell-by-cell division would be impractical.
- Multi-cellular organisms, therefore, need to use more complex ways of reproduction.
Question 5.
Does the plants shows sexual reproduction which propagate through vegetative process ?
Answer:
- Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- Such methods also make possible the propagation of plants.
- Such as banana, orange, rose and jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
- Another advantage of vegetative propagation is that all plants produced are genetically similar enough to the parent plant to have all its characteristics.
Question 6.
Write about tissue culture.
Answer:
- In tissue culture, new plants are grown by removing tissue or separating cells from the growing tip of a plant.
- The cells are then placed in an artificial medium where they divide rapidly to form a small group of cells or callus.
- The callus is transferred to another medium containing hormones for growth and differentiation. The plantlets are then placed in the soil so that they can grow into mature plants.
- Using tissue culture, many plants can be grown from one parent in disease-free conditions. This technique is commonly used for ornamental plants.
Question 7.
Write about asexual modes with examples.
Answer:
| S.No. |
Mode of asexual |
Example |
| 1. |
Fission |
Amoeba, leishmania |
| 2. |
Multiple fission |
Plasmodium |
| 3. |
Budding |
Hydra, yeast |
| 4. |
Fragmentation |
Spirogyra |
| 5. |
Regeneration |
Planaria, |
| 6. |
Spores |
Rhizopus |
Question 8.
Write about spore formation.
Answer:
- Spores are a sexual mode of reproduction mostly seen in fungi.
- The thread-like structures that developed on the bread above are the hyphae of the bread mould (Rhizopus). They are not reproductive parts.
- On the other hand, the tiny bulb-on-a-stick structures are involved in reproduction.
- The bulbs are sporangia, which contain cells, or spores, that can eventually develop into new Rhizopus individuals.
- The spores are covered by thick walls that protect them until they come into contact with another, moist surface and can begin to grow.
Question 9.
What are the variations ? How they formed ?
Answer:
- The DNA copying mechanism, cannot be absolutely accurate, and the resultant errors are a source of variations in populations of organisms.
- Every individual organism cannot be protected by variations, but in a population, variations are useful for ensuring the survival of the species.
- It would therefore make sense if organisms came up with reproductive modes that allowed more and more variation to be generated.
Question 10.
How sexual reproduction help for new variations ?
Answer:
- Each new variation is made in a DNA copy that already has variations accumulated from previous generations.
- Thus, two different individuals in a population would have quite different patterns of accumulated variations.
- Since all of these variations are in living individuals, it is assured that they do not have any really bad effects.
- Variations from two or more individuals would thus create new combinations of variants.
- Each combination would be novel, since it would involve two different individuals.
- The sexual mode of reproduction incorporates such a process of combining DNA from two different individuals during reproduction.
Question 11.
Why the gametes or germ cells are different in higher organisms ?
Answer:
- In very simple organisms, it is seen that the two germ-cells are not very different from one another, or may even be similar.
- But as the body designs become more complex, the germ-cells also specialise.
- One germ-cell is large and contains the food-stores while the other is smaller and likely to be motile. Conventionally, the motile germ cell is called the male gamete.
- And the germ-cell containing the stored food is called the female gamete. Which is round and comparatively large in size.
- These two gametes combine and formed a new organism.
Question 12.
What is pollination ? What are the types in it?
Answer:
1. Transfer of pollen from the stamen to the stigma is called pollination. It is two types
- self pollination
- cross pollination
2. If this transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower, it is referred to as self-pollination.
3. On the other hand, if the pollen is transferred from one flower to another, it is known as cross pollination.
4. This transfer of pollen from one flower to another is achieved by agents like wind, water or animals.
Question 13.
What is fertilization?
Answer:
- Fertilization is the process in which a new cell is formed when two gametes (sex cells) - pollen and ovary fuse together.
- After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, it has to reach the female germ-cells which are in the ovary.
- For this, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary.
- Mostly double fertilization takes place in developed plants.
Question 14.
What are the changes in flower after fertilization ?
Answer:
- After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule.
- The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into a seed.
- The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit.
- Meanwhile, the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off.
Question 15.
How the sperms are produced ?
Answer:
- The formation of germ-cells or sperms takes place in the testes.
- These are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum.
- Because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature.
- We have discussed the role of the testes in the secretion of the hormone, testosterone, in the previous chapter.
- In addition to regulating the formation of sperms, testosterone brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty.
Question 16.
How the ovum is formed in females ?
Answer:
- When a girl is born, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs.
- On reaching puberty, some of these start maturing.
- One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
- The egg is carried from the ovary to the womb through a thin oviduct or fallopian tube.
- The two oviducts unite into an elastic bag-like structure known as the uterus. The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
Question 17.
How the embryo is formed female reproductive system ?
Answer:
- The sperms enter through the vaginal passage during sexual intercourse.
- They travel upwards and reach the oviduct where they may encounter the egg.
- The fertilized egg (zygote) starts dividing and form a ball of cells or embryo.
- The embryo is implanted in the lining of the uterus where they continue to grow and develop organs to become foetus.
- The mother’s body is designed to undertake the development of the child. Hence the uterus prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the growing embryo.
- The lining thickens and is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
Question 18.
What is the role of placenta in development of embryo ?
Answer:
- The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta.
- This is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi.
- This provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo.
- The developing embryo will also generate waste substances which can be removed by transferring them into the mother’s blood through the placenta.
Question 19.
What happens when the Egg is not Fertilized ?
Answer:
- The ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilized egg.
- Thus its lining becomes thick and spongy. This would be required for nourishing the embryo.
- If fertilization had taken place, it lives for about one day.
- Now, however, this lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous.
- This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstruation. It usually lasts for about two to eight days.
Question 20.
Draw the neat labeled diagram LS of flower.
Answer:
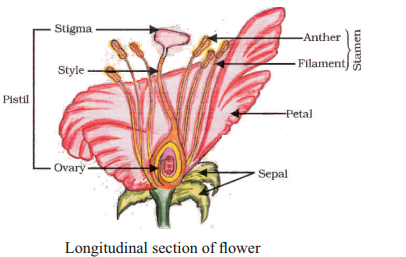
Question 21.
Draw the neat labeled diagram of male reproductive system.
Answer:
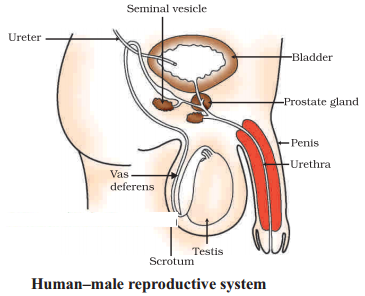
Question 22.
Draw the neat labeled diagram female reproductive system.
Answer:
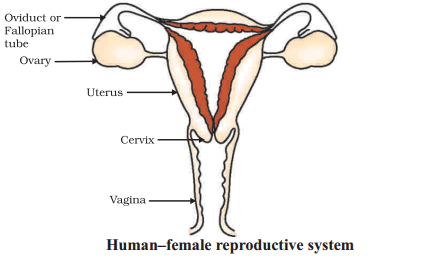
Question 23.
Draw the neat labeled diagram Germination of pollen on stigma.
Answer:
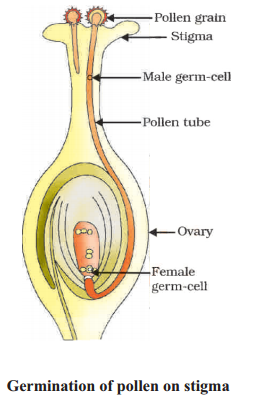
Question 24.
How do we know that two different individual organisms belong to the same species?
Answer:
Species, are related organisms that share common characteristics and are capable of interbreeding. Generally we know that two different individual organisms belong to the same species by
- Morphological Similarity: If two organisms look very similar in terms of size, shape, color, and other external features, they are more likely to belong to the same species.
- Interbreeding : The biological species concept, a species as a group of individuals that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
- Genetic Similarity : Organisms belonging to the same species generally share a high degree of genetic similarity.
- Geographic Distribution : The geographic distribution of organisms can also be a clue to their species identity.
Question 25.
Do organisms create exact copies of themselves ?
Answer:
- No, it is not possible to create exact copies of organisms themselves.
- Because organisms are developed from the zygote which forms from fusion of two gametes.
- Both these gametes have genetic material and take crossing over between them.
- It leeds to variations and formed new characters.
- Even in asexual reproduction DNA does not copied exactly, so its not possible to create exact copies of organisms.
Question 26.
What is the importance of variations ?
Answer:
- Variations can be defined as differences among the organisms.
- The variations formed due to variations in DNA sequences.
- It makes one organism different from the other organism.
- Variations are essential for natural selection.
- Variations in a species of an organism helps to adapt in the environment.
- It also prevents the extinction of a species.
Question 27.
How do all the changes that we have talked about link to the reproductive process?
Answer:
- All changes in the puberty are linked to reproductive process.
- Main changes in the puberty is body development to produce gametes and bear the pregnancy.
- Hormones have key role in this puberty
- In males testosterone is released to develops sperm production, and muscles for energy.
- In female estrogen controls menstrual cycle and progesterone supports the pregnancy.
Question 28.
What happens when the Egg is not Fertilized ?
Answer:
- Since the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilized egg.
- Thus its lining becomes thick and spongy. This would be required for nourishing the embryo if fertilization had taken place.
- Now, however, this lining is not needed any longer.
- If the egg is not fertilized, it lives for about one day.
- So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous.
- This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstruation. It usually lasts for about two to eight days.
Question 29.
What can we identify as the most important reason(s) for poor living standards ?
Answer:
India, like many other countries, faces a variety of challenges that contribute to poor living standards for a significant portion of its population.
Some of the key reasons for poor living standards in India include :
1. Income Inequality: India has a high degree of income inequality, with a small portion of the population enjoying significant wealth while the majority struggles to make ends meet. This inequality can result in poor living standards for a large segment of the population.
2. Poverty : A substantial portion of India’s population lives below the poverty line. This means that they lack access to basic necessities such as food, clean water, housing, and health care.
3. Lack of Access to Education : Many individuals in India do not have access to quality education. This limits their ability to secure well-paying jobs and improve their living standards.
Question 30.
Different organisms reproduced by different methods suitable to their body designs.
Justify the above statement using examples of three different organisms which reproduce by different methods of asexual reproduction.
Answer:
Amoeba : Binary fission.
Plasmodium: Multiple fission Hydra: Budding
Planaria : Regeneration
- Binary fission in Amoeba : In this method the nucleus first divides mitotically into two followed by the division of cytoplasm. The cell finally splits into two daughter cells.
- Budding in Hydra : In budding, a small part of the body of the parent grows out as a bud. It develops as an outgrowth in Hydra due to repeated cell division at the specific site.
When fully mature, the bud detaches itself from the parent body and develops into a new independent individual.
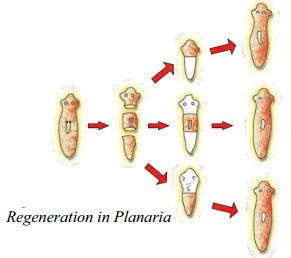
- Regeneration in Planaria : In this method, small cut or broken parts of the organisms body grow or regenerate into separate individuals. Planaria can be cut into any number of pieces and each piece grow into a complete organism.
Question 31.
Name the process by which an Amoeba reproduces. Draw the various stages of its reproduction in a proper sequence.
Answer:
Amoeba reproduces by binary fission, in which organism simply split into two equal halves during cell division.

Question 32.
Name the reproductive parts of an angiosperm. Where are these parts located ? Explain the structure of its male reproductive part.
Answer:
1. The reproductive parts of an angiosperm are :
- Stamen the male part.
- Carpel the female part.
2. The reproductive parts are present in the flower.
3. Stamen is the male reproductive part and it produces pollen grains that are yellowish in colour.
Question 33.
Name the reproductive and non-reproductive parts of bread mould (Rhizopus).
Answer:
List any two advantages of vegetative propagation :
Rhizopus has tiny blob-on-a-stick structures called sporangia, which contain spores and are involved in reproduction. Hyphae are thread-like structures that are developed on the bread and these are non-reproductive parts.
Advantages of vegetative propagation :
- This process makes the propagation of plants such as banana, orange etc., that do not produce seeds.
- Plants produced are genetically similar enough to the parent plant to have all its characteristics.
Question 34.
Draw a labelled diagram in proper sequence to show budding in hydra.
Answer:

Question 35.
Draw a labelled diagram to show that particular stage of binary fission in Amoeba in which its nucleus elongates and divide into two and a constriction appears in its cell membrane.
Answer:
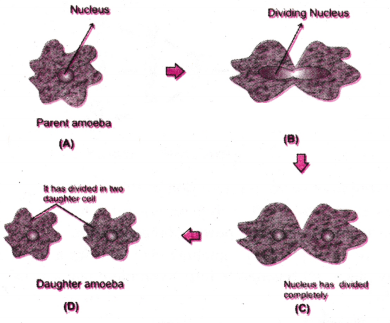
Question 36.
A student observed a permanent slide showing asexual reproduction in yeast. Draw diagrams of the observations he must have made from the slide. Name the process also.
Answer:
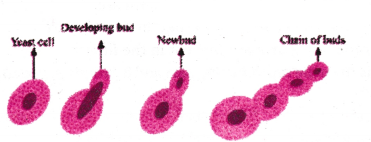
The process of asexual reproduction in yeast is called budding.
Question 37.
a) Trace the path a male gamete takes to fertilise a female gamete after being released from the penis.
b) State the number of sets of chromosomes present in a zygote.
Answer:
a)
- The sperm enters the female body through the vagina.
- From the vagina, it enters the uterus through the cervix.
- From the uterus, the sperm enter the fallopian tube where the ovum released by the ovary will fuse with one of the sperm resulting in fertilizations.
b)
- Male and female gametes combine to form a zygote.
- The zygote in humans is diploid, with 23 pairs of chromosomes totaling 46.
- One pair of chromosomes is passed down from the mother, while the other is passed down from the father.
Question 38.
Draw diagrams to explain the regeneration that takes place in each of the body parts of planaria when its body is cut into three pieces. Name any other organism in which a similar process can be observed. (OR)
With the help of a neat diagram explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
Answer:
Planaria has the amazing capacity to regenerate its lost body part. When the flatworm is cut horizontally, separating the head from the tail, the tail will regenerate the lost head and the head will regenerate the lost tail. This process is known as regeneration. Regeneration is observed in Hydra also.
Question 39.
a) Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
b) How is regeneration different from reproduction ?
Answer:
a.
- Planaria possesses great power of regeneration.
- If the body of planaria somehow gets cut into a number of pieces, then each body piece can regenerate into a complete planaria by growing all the missing parts.
b. During the process of reproduction, new organism is formed from the complete parent organism. However, during fragmentation, a fragment of original parent body grows into new individual.
Question 40.
"Use of a condom is beneficial for both the sexes involved in a sexual act." Justify this statement giving two reasons.
Answer:
a)
- Use of condom prevents meeting of sperm and ova.
- Use of condom protects against sexually transmitted diseases.
b) Oral pills contain hormones which prevent the ovaries from releasing ovum into the oviduct. This helps avoiding pregnancies.
c) Selective abortion means, (termination) of abortion of pregnancy, especially female foeticide.
Effect: Society will have imbalance in the male female ratio.
Question 41.
Identify A,B and C in the given diagram and write their functions.
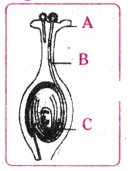
Answer:
A. A - Stigma. It is a sticky surface where the pollen lands and later germinates.
B - Pollen tube. It carries the pollen to the egg cell for fertilization.
C - Egg cell. It fuses with the male gamete and leads to the formation of zygote.

Question 42.
Identify the given diagram. Name the parts 1 to 5.
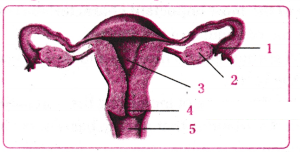
Answer:
The given diagram is the sectional view of human female reproductive system
The labelled parts are:
- Funnel of fallopian tube or oviduct
- Ovary
- Uterus or Womb
- Cervix
- Vagina.
Question 43.
Read the paragraph and answer the following questions.
The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of population.
a) List two common signs of sexual maturation in boys and girls.
b) What is the result of reckless female foeticide ?
c) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body ?
d) Write two factors that determine the size of a population.
Answer:
a) Two common signs of sexual maturation in boys and girls are :
- Broadening of shoulder and chest in boys and development of mammary gland or breast in girls.
- The appearance of hairs on various body parts like the pubic area, armpits and face.
b) The number of females will become very low in comparison to the males. Hence, there will be a huge imbalance between the male-female ratio in the population.
c) Chemical method of contraception like Oral pills interfere with the hormonal balance of the body.
d) Birth rate and death rate are factors that determine the size of the population.
Question 44.
i) What is meant by vegetative propagation ?
ii) How will a plant be benefited if it reproduces by vegetative propagation ?
Answer:
i) Propagation by vegetative parts such as the roots, stems and leaves is called vegetative propagation.
ii) Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
Such methods also make possible the propagation of plants that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
Question 45.
Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of living beings. Give some reasons in support of the statement.
Answer:
Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of living beings because:
- It is necessary for the continuity of the species.
- Parents produce off springs like themselves and thus, preserve a species and maintain continuity of the race.
- Reproduction is also the means of increasing the population of a species.
- It includes creation of variations that are the basis of evolution.
- It regulates population.
Question 46.
What happens when :
a) Accidently planaria gets cut into many pieces ?
b) Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil ?
c) On maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts ?
Answer:
a) Accidently, planaria gets cut into many pieces, each piece regeneration into new planaria.
b) If the Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil, leaf buds on the leaf notches develop into new Bryophyllum plants.
c) On maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts, it releases spores which germinate into new Rhizopus in moist conditions.
Question 47.
What is multiple fission ? How does it occurs in an organism ? Explain briefly. Name one organism which exhibits this type of reproduction.
Answer:
Multiple fission : The process of reproduction in which many individuals are formed or produced from the parent cell. In this process the nucleus divides repeatedly to produce large number of nuclei. Each nucleus gathers a bit of cytoplasm around itself, develops a member around each structure.
Many daughter cells develop into adult organism.
Plasmodium exhibits this type of fission.
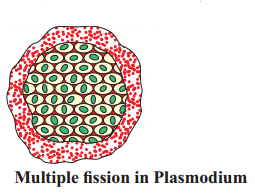
Question 48.
How are variations important ?
Answer:
- The consistency of DNA replication during reproduction is important for the maintenance of body design features that allow an organism to use a particular ecological niche.
- However DNA replication is not fool-proof phenomenon as it may result in subtle variations which may be harmful or beneficial to the individual according to the ecological niche it copies.
- The niches may also change and any variation in an individual which makes it suitable for that niche, would be beneficial for the survival.
- Variations are the raw material of evolution.
Question 49.
How does the process of budding differ from the process of spore formation ?
Answer:
Differences between Budding and Spore formation :
| Budding |
Spore formation |
| 1) A bud as in Hydra, develops as an out-growth due to repeated cell divisions at a specific site. |
1) In spore formation as in Rhizopus, a specific part called sporangia produces spores. The spores are covered by thick walls that protect from unfavourable conditions. |
| 2) The bud when matures detaches from the parent body and becomes new individuals. |
2) Spores on getting favourable conditions germinate to give rise to new individuals. |
Question 50.
Distinguish between the functions of ovary and testes
Answer:
| Ovary |
Testes |
| 1) Ovary produces female germ cells or eggs. |
1) Testes produces male germ cells or sperms. |
| 2) Ovary secretes female hormone, estrogen which brings about changes in girls at puberty and also regulates egg formation. |
2) Testes produce male hormone, testosterone which brings about changes in boys at puberty and also regulates sperm formation. |
Question 51.
Leaves of Bryophylium fallen on the ground produce new plants. Why ?
Answer:
Bryophylium leaves bear buds on their notches along their margins. When such a leaf with buds on margin falls, the buds come in contact of the soil and develop into plant- lets. These plantlets later grow into new plants.

Question 52.
Why is vegetative propagation is practised for growing some types of plants ?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is practiced in some plants because :
- It is the only method of reproduction in seedless plants.
- We get fully mature plants in a very short time.
- It is a short cut method for rapid multiplication.
- It helps to preserve the type of character that a plant breeder desires.
- It is very easy and economical method for the multiplication of ornamental plants.
Question 53.
Observe the flow chart and answer the following questions.
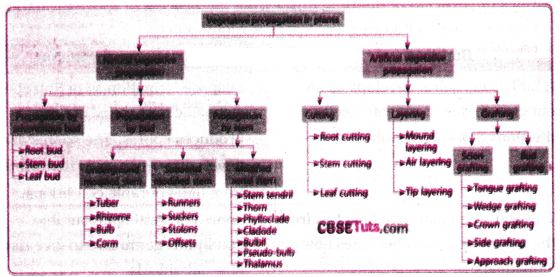
Answer:
1. What are the two types in vegetative propagation ?
Answer: Natural propagation, artificial propagation.
2. What are the underground stem modifications ?
Answer: Tuber, Bulb, Rhizomes.
3. What are the types of artificial propagation?
Answer: Cutting, layering, grafting.
4. Which type of stems are the runners?
Answer: Subaerial stems.
Question 54.
look at the table and answer the following questions.
1. What are the types of reproduction?
Answer: Asexual and sexual
2. What are the types in asexual reproduction?
Answer: Fission, fragmentation and so on
3. What are the examples for spore formation?
Answer: Rhizopus
4. Which organism shows budding?
Answer: Planaria.
Question 55.
Observe the diagram and answer the following

1. What is the outer whorl of a flower?
Answer: Sepals
2. What is the attractive part of a flower?
Answer: Petals
3. What are the male reproductive organs in flowers?
Answer: Anther
4. What are the three major parts in pistil?
Answer: Stigma, style, ovary
Question 56.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

1. What is the female part of a flower?
Answer: Pistil
2. Where the pollen grains reach to pistil?
Answer: Stigma
3. What is the tube that travels through the style?
Answer: Pollen tube
4. Where are the female germ cells found in pistil?
Answer: Ovary
Question 57.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

1. What are the male gametes ?
Answer: Sperm
2. Where the male gametes are produced ?
Answer: Testis
3 Name the glands that are related to male reproductive system.
Answer: Prostate and Cowper’s glands
4. What is the common passage for urine and sperms ?
Answer: Urethra.
Question 58.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

1. What is the female gamete?
Answer: Ovum.
2. Where the female gametes are produced?
Answer: Ovary.
3. Where the fertilization takes place in the female reproductive system?
Answer: Fallopian tube.
4. Where the embryo develops in the female reproductive system?
Answer: Uterus.
Question 59.
How do you maintain genital hygiene?
Answer:
Genital hygiene is as important as our health, for this health we must follow some tips :
- Don’t use soaps or shower gel, including feminine hygiene products to cleanse your genitals. These products are often the leading cause of genital dryness, itching and irritation.
- Don’t over wash
- Don’t douche
- Don’t use sanitary wear unnecessarily.
Question 60.
What are the contraceptive methods?
Answer:
Methods of contraception that are available include :
Implants, intrauterine devices (IUDs), injections, pills, vaginal rings, barrier methods, sterilization, emergency contraception and natural methods. Condoms are the best available protection against sexually transmissible infections.
Question 61.
What is the difference between Vasectomy and Tubectomy ?
Answer:
| Vasectomy |
Tubectomy |
| 1. It is a sterilisation method of contraception in males. |
It is a sterilisation method of contraception in females. |
| 2. In this method, a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up through a small incision on the scrotum. |
In this method, a small part of Fallopian tube is removed or tied up through a small incision in the abdomen/vagina. |
| 3. Man’s body continues to produce sperms, they are simply reabsorbed back into body and not ejaculated. |
This keeps egg away from the uterus, site of its fertilisation. |
Extra Questions on How do Organisms Reproduce? Class 10 - 8 Marks
Question 1.
Write about fertilization process in plants.
Answer:
Fertilization Process in plants contain following steps
a) Pollen Germination : When pollen lands on the stigma, it may germinate. A pollen tube grows down through the style toward the ovary. The tube contains two sperm cells.
b) Double Fertilization : When the pollen tube reaches the ovary, it enters the ovule through a small pore called the micropyle. Inside the ovule, there are two female gametes, one in the egg cell and another in the central cell. When the pollen tube reaches the ovule, it releases the two sperm cells. One sperm cell fuses with the egg cell, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote. The other sperm cell fuses with the two nuclei in the central cell, giving rise to a triploid endosperm nucleus.
c) Zygote Development: The zygote undergoes mitosis and develops into an embryo, which will become the new plant. The endosperm nucleus, which is triploid, develops into a nutrient-rich tissue that will nourish the developing embryo.

Question 2.
What are the changes seen in adolescence?
Answer:
- Some of these changes are common to both boys and girls in the age of teenage.
- Begin thick hair growing in new parts of the body such as armpits and the genital area between the thighs, which can also become darker in colour.
- Thinner hair can also appear on legs and arms, as well as on the face.
- The skin frequently becomes oily and we might begin to develop pimples.
- Boys begin to have new thick hair growth on the face and their voices begin to crack.
- Further, the penis occasionally begins to become enlarged and erect, either in day dreams or at night.
- On the other hand, there are also changes taking place that are different between boys and girls.
- In girls, breast size begins to increase, with darkening of the skin of the nipples at the tips of the breasts.
- Also, girls begin to menstruate at around this time.
Question 3.
Describe the structure of flower.
Answer:
The structure of a typical flower can be divided into several parts.
Sepals : The outermost whorl of floral parts, the sepals are usually green and enclose and protect the inner parts of the flower in the bud stage. Collectively, the sepals are called the calyx.
Petals : The petals are often the most colorful part of the flower and are responsible for attracting pollinators with their shape, color, and fragrance. Collectively, the petals are called the corolla.
Stamens: The stamens are the male reproductive organs of the flower and are composed of two main parts:
- Anther: The anther is the top part of the stamen and produces pollen, which contains the male gametes (sperm).
- Filament: The filament is the slender stalk that supports the anther.
Carpels (Pistils): The carpels are the female reproductive organs of the flower and are composed of several parts :
- Stigma: The stigma is the sticky, often lobed, tip of the carpel that receives pollen during pollination.
- Style: The style is a slender tube-like structure that connects the stigma to the ovary.
- Ovary: The ovary is the swollen base of the carpel that contains one or more ovules. It is here that fertilization occurs, resulting in the development of seeds.
- Ovules: Ovules are the female reproductive structures within the ovary. Each ovule has the potential to develop into a seed when fertilized.
Testes : The testes (singular: testis) are two small, egg-shaped organs located in the scrotum, a pouch of skin that hangs below the penis. The testes produce sperm and the hormone testosterone, which plays a key role in the development of male sexual characteristics.
Epididymis : The epididymis is a tightly coiled tube that sits on the back of each testis. It serves as a storage and maturation site for sperm, allowing them to develop the ability to move and fertilize an egg.
Vas Deferens : The vas deferens is a long, muscular tube that carries mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. During ejaculation, sperm are propelled through the vas deferens to be mixed with seminal fluids.

Seminal Vesicles : These are two glands located near the base of the bladder. They produce a significant portion of the seminal fluid that combines with sperm to form semen. Seminal fluid contains various substances, including fructose to nourish sperm and prostaglandins, which are involved in the fertilization process.
Prostate Gland : The prostate is a gland situated just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, which carries both urine and semen. It produces a milky fluid that contributes to the semen’s volume and helps protect the sperm.
Cowper’s (Bulbourethral) Glands: These small glands are located beneath the prostate gland. They produce a clear, lubricating fluid that is released just before ejaculation. This fluid helps neutralize any remaining acidity in the urethra and provides lubrication for the sperm to pass through.
Urethra : The urethra is a tube that runs through the penis and serves as a passagewayfor both urine and semen. It allows for the controlled release of semen during ejaculation.
Penis: The penis is the external male reproductive organ. It contains three columns of erectile tissue, which can become engorged with blood during sexual arousal, leading to an erection. The penis also houses the urethra for the release of semen.
The male reproductive system’s primary function is to produce and deliver sperm to fertilize a female’s egg, thereby enabling reproduction. Sexual arousal and the release of semen occur during sexual intercourse, allowing for the transfer of sperm into the female’s reproductive tract.

Question 4.
Describe the female reproductive system of humans.
Answer:
The female reproductive system is a complex and vital system responsible for the production of female gametes (ova or eggs), the development of the embryo and foetus during pregnancy, and the nourishment and protection of the growing foetus. It consists of several organs, including:
Ovaries : These are a pair of small, almond-shaped organs located on each side of the lower abdomen. Ovaries produce and release eggs during the menstrual cycle and also produce hormones like estrogen and progesterone.

Fallopian Tubes There are two fallopian tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. These tubes transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Fertilization typically occurs in the fallopian tubes when sperm meets an egg.
Uterus Also known as the womb, the uterus is a muscular organ where a fertilized egg implants and grows into a foetus during pregnancy. If no pregnancy occurs, the uterine lining is shed during menstruation.
Cervix : The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It serves as a passage for menstrual blood to exit the body and also plays a role in protecting the uterus from infections.
Vagina : The vagina is a muscular tube that connects the cervix to the external genitalia. It serves as the birth canal during childbirth and also allows for sexual intercourse. External Genithlia The external genitalia, also known as the vulva, include the labia (outer and inner lips), clitoris, and vaginal opening. These structures are involved in sexual arousal and play a role in reproductive and urinary functions.
The female reproductive system is regulated by hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone, which control the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and various other processes related to fertility and pregnancy. It is a highly intricate and interconnected system that plays a crucial role in human reproduction and the continuation of the species.

Question 5.
What are the contraceptive methods ?
Answer:
To avoid unnecessary we follow contraceptive methods. These contraceptive methods fall in a number of categories.
1. One category is the creation of a mechanical barrier, so that sperm does not reach the egg. Condoms on the penis or similar coverings worn in the vagina can serve this purpose.
2. Another category of contraceptives acts by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilization cannot occur. These drugs commonly need to be taken orally as pills. However, since they change hormonal balances, they can cause side-effects too.
3. Other contraceptive devices such as the loop or the copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. Again, they can cause side effects due to irritation of the uterus.
4. Surgical methods If the vas deferens in the male is blocked, sperm transfer will be prevented. If the fallopian tube in the female is blocked, the egg will not be able to reach the uterus. In both cases fertilization will not take place. Surgical methods can be used to create such blocks. While surgical methods are safe in the long run, surgery itself can cause infections and other problems if not performed properly.
Question 6.
Are there any limitations of the asexual mode of reproduction ?
Answer:
The disadvantages of asexual reproduction include :
- It does not lead to genetic variation in a population.
- The species may only be suited to one habitat.
- Disease may affect all the individuals in a population.
- The offspring produced in asexual reproduction is a clone, and any harmful mutation will also pass on to the offspring.
- The organisms produced have shorter lifespans.
- It is hard to control the increasing population.
- There is only limited diversity within the life forms.
Question 7.
What possible functions could the petals and sepals serve ?
Answer:
Sepals: The sepals are the lower, or outermost, part of the flower. These functions are
- Provide support to the flowers.
- Prevents the flower from drying out.
- Protects the reproductive organs within the flower.
- In some plants with no petals, sepals function as petals.
- Safeguard the bud and flowers from harsh environmental conditions.
Petals : Petals are the second whorl of the flower.
They are sterile floral parts.
The major function of petals is to attract insects for pollination and to protect the reproductive organs, which are at the center of the flower.
Question 8.
List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country.
Answer:
The general awareness regarding reproductive health in a society is significant as :
- Maintenance of personal hygiene among youngsters and proper knowledge of their reproductive parts helps them adjust with the physical changes and cope with emotional disturbances.
- Reproductively healthy society must be free from the curse of child marriage which begets. Many complications at the level of individual and society both.
- Proper case of expecting another, monitoring their health after child birth and care of new born help in building a healthy society.
- Married couples aware of contraceptive methods lead a better married life as they are capable of avoiding unwanted pregnancies and have negligible chances of contracting sexually transmitted diseases.
Reproductive health has improved in the following areas :
- Awareness regarding various reproduction related aspects majorly amongst the youth helps in controlling unwanted pregnancies in the youth.
- Knowledge about various sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) helps in controlling spread of various STDs like HIV, syphilis, gonorrhoea, etc.
Question 9.
Define pollination. Explain the different types of pollination. List two agents of pollination. How does suitable pollination lead to fertilization ? What is the significance of pollination ?
Answer:
1. Pollination : Transfer of pollen grain from anther or stamen to stigma of a flower.
2. Types of pollination :
- Self pollination : Transfer of pollen from anther/stamen to stigma occurs in the same flower.
- Cross pollination : Pollen is transferred from anther/stamen of one flower to stigma of another flower.
3. Agents of pollination : Wind, water, insects and animals.
4- A tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style, to reach the female germ cell in the ovary to cause fertilization.
5. Significance of pollination :
- It is a significant event because it precedes fertilization.
- It brings the male and female gametes closer for the process of fertilization.
- Cross pollination, introduces variations in plants because of the mixing of different genes. These variations further increase the adaptability of plants towards the environment or surroundings.
Question 10.
How do organisms, whether reproduced asexually or sexually maintain a constant chromosome number through several generations ? Explain with the help of suitable example.
Answer:
1. When organisms reproduce asexually, only mitotic divisions are involved and the chromosome number remains the same.
2. During asexual reproduction, the DNA (in the chromosome) or the cells involved are copied and then equally divided among the two daughter cells. Thus, chromosome number remains unchanged.
3. In sexual reproduction, organisms produced gametes through a special type of division called meiosis reductional division, in which the original number of chromosomes is reduced to half. These two male and female gametes fuse to form the zygote and the original number of chromosomes is reduced.
4. In sexual reproduction, specialized cells or germ cells with only half the number of chromosomes are formed.When these germ cells from two individuals combine to form a new individual, the original chromosome number is restored.
Example : In humans the parents (father and mother) each have 46 or 23 pairs of chromosomes in the gametes. The sperm has half the number of chromosomes 23 and the egg also has 23 chromosomes.When the sperm and the egg fuse, the zygote has 46 or 23 pairs of chromosomes. Thus, the chromosome number remains constant.
Question 11.
Give reason for the following :
a) During reproduction inheritance of different proteins will lead to altered body designs.
b) Fertilization cannot take place in flowers if pollination does not occur.
c) All multicellular organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through fragmentation or regeneration.
d) Vegetative propagation is practised for growing only some type of plants.
e) The parents and off-springs of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes.
Answer:
a) DNA in the nucleus of the cell is the information source for making proteins. If the information is changed, different proteins will be made. Different proteins will eventually lead to altered body designs. Therefore, a basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy.
b) Flower fertilization requires both male and female gametes. If pollination does not occur it means that the male gamete is not available, hence fertilization cannot take place.
c) All multicellular organism cannot reproduce by fragmentation or regeneration process because:
- Their body is highly complicated.
- There are specific organs to do specific functions. There is division of labour in the body of complex organisms.
- Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells, which are not present in complex organisms.
d) Vegetative propagation is practised for growing such plants which usually do not produce seeds or produce non - viable seeds.
e) Gametes of sexually-reproducing animals have half the number of chromosomes as that of the parents. Thus, during fertilisation, when two gametes i.e. male and female gametes, fuse, the offspring produced will have the same amount of DNA or the same number of chromosomes as that of the parent.
Question 12.
How does the amount of DNA remain constant though each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals ?
Answer:
- In sexual reproduction, two gametes, male and female, combines together to form a new cell "zygote".
- The reproductive cells or gametes contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the non - reproductive cells of an organism.
- So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell, "zygote" will have the normal amount of DNA.
- For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg has also 23 chromosomes.
- So when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed
will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes in humans.
Question 13.
List three distinguishing features between sexual and asexual types of reproduction.
Answer:
| Sexual Reproduction |
Asexual Reproduction |
| 1) Two parents are required. |
1) Only one parent is required. |
| 2) Off springs are genetically dissimilar from parents. |
2) Offsprings are identical to parents. |
| 3) Gametes are formed. |
3) Gametes are not formed. |
| 4) Zygote is formed. |
4) Zygote is not formed. |
| 5) New characters are formed. |
5) New characters are formed only through mutations. |
| 6) Takes several months to complete. |
6) Takes very short period to complete. |
Question 14.
Mention the role of gamete ami zygote in sexually reproducing organisms.
Answer:
Role of gametes :
- Gametes play an important role in the sexually reproducing organisms as they carry the entire genetic information of the organism.
- These gametes result in the formation of zygote upon fusion, which develops into a new individual.
- Any deformation in the gametes will lead to the deformity in the newly formed offspring.
Role of zygote :
- It is the diploid cell formed by the fusion of male and female gametes during fertilization in sexual reproduction.
- It is the first stage in the development process of an organism.
- It contains all the genetic information of both the parents, essential for the growth of the new organism.
Question 15.
Describe the various steps involved in the process of binary fission with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
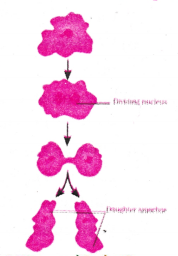
- Amoeba is a single-celled organism.
- It begins the process of reproduction by the division of its nucleus into two nuclei.
- This is followed by division of its body into two, each part receiving a nucleus.
- Finally, two amoebae are produced from one parent amoeba.
- This type of asexual reproduction in which an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals is called binary fission.
Question 16.
Trace the changes that take place in a flower from gamete formation to fruit formation.
Answer:
Changes in flower from gamete formation to fruit formation :
- Stamen is the male reproductive part and it produces pollen grains.
- The ovary contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell.
- The pollen needs to be transferred from the stamen to the stigma.
- If this transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower, it is referred to as self-pollination.
- If the pollen is transferred from one flower to another, it is known as cross-pollination.
- After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, it has to reach the female germ-cells which are in the ovary.
- A tube grows out 6f the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary.
- The male germ-cell produced by pollen grain fuses with the female gamete present in the ovule.
- This fusion of the germ-cells or fertilisation gives the zygote.
- After fertilisation, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule.
- The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into a seed.
- The ovary’grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit.
- Meanwhile, the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may get dried and fall off.
Question 17.
Given below are certain situations. Analyze and describe its possible impact on a person :
a) Testes of a male boy are not able to descend into scrotum during his embryonic development.
b) Vas deferens of a man is plugged.
c) Prostate and seminal vesicles are not functional.
d) Egg is not fertilised in a human female.
e) Placenta does not attach to the uterus optimally.
Answer:
The given situations have the following impact on the person :
a. Sperm formation will be adversely affected because it requires a lower temperature than the body temperature.
b. Vas deferens is a passage for transfer of sperms, so sperms will not be transferred further.
c. When prostate and seminal vesicles are not functional, they will not add secretions for nourishment and medium for the transport of sperms.
d. When an egg is not fertilised in a human female, it lives for about one day. Then, the thickened lining of the uterus breaks leading to discharge of blood and mucus along with the unfertilised egg. This is called menstruation.
e. Nutrition and oxygen will not be provided to the growing embryo affecting growth, which could have serious implications as well.
Question 18.
In the context of reproduction of species state the main difference between fission and fragmentation. Also give one example of each,
Answer:
Fission : It is the method of asexual reproduction in unicellular forms of life.
In this process, the parent organism splits to form two or more daughter cells.
Example : Amoeba, Plasmodium, Paramoecium.

Fission is defined as the splitting of a multicellular organism into two or more than two separate two daughter cells. It is the most common and simplest method of asexual reproduction. It is of two types :
- Binary fission and
- Multiple fission.
In binary fission, parent organism divides into two identical daughter organisms with definite orientation.
Example : Amoeba, Paramoecium.
In multiple fission, parent organism divides into many identical daughter organisms. The nucleus of cell splits repeatedly to form many smaller nuclei called daughter nuclei surrounded by cytoplasm and thin membrane around them.
Fragmentation : It is a form of asexual reproduction in which multicellular organisms like algae, spirogyra breaks up into two or more small fragments or pieces. On maturity, each fragment grows to form a complete new organism.
Conceptual Map