TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Functions Solutions Exercise 1(a)
I.
Question 1.
If the function f is defined by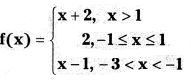
then find the values of
(i) f(3)
(ii) f(0)
(iii) f(-1.5)
(iv) f(2) + f(- 2)
(v) f(- 5)
Answer:
(i) f(3), For x > 1; f(x) = x + 2
f(3) = 3 + 2 = 5
(ii) f(0), For – 1 ≤ x ≤ 1; f(0) = 2
(iii) f(-1.5), For – 3 < x < – 1; f(x) = x – 1
∴ f(-1.5) = -1.5- 1 = – 2.5
(iv) f(2) + f(-2); For x > 1, f(x) = x + 2
∴ f(2) = 2 + 2 = 4
For – 3 < x < – 1;
f(x) = x – 1
f(-2) = -2 – 1 = -3
f(2) + f (-2) = 4 – 3 = 1
(v) f(-5); is not defined such domain of ‘f’ is {x / x > – 3].
Question 2.
If f : R {0} → R defined by f(x) = x3 – 1/x3, then show that f(x) + f(1/x) = 0.
Answer:
Given f(x) = x3 – 1/x3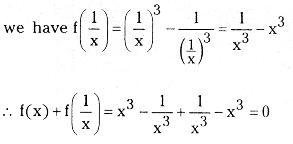
Question 3.
If f: R → R defined by f(x) = 1−x2/1+x2, then show that f(tan θ) = cos 2θ
Answer:
Given f(x) = 1−x2/1+x2 ∀ x ∈ R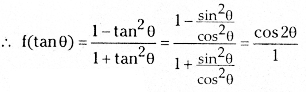
= cos 2θ
Question 4.
If f: R – (±1) → R is defined by f(x) = log∣1+x/1−x∣, then show that f(2x/1+x2) = 2f(x).
Answer:
Given f: R – (±1) → R defined by f(x) = log∣1+x/1−x∣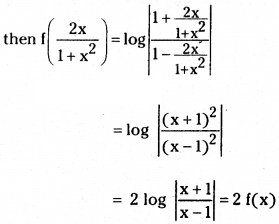
Question 5.
If A = (-2, -1, 0, 1, 2) and f : A → B is a surjection defined by f(x) = x2 + x + 1, then find B. (May 2014)
Answer:
A = {-2,-1,0,1,2} and f: A → B is a surjection and f(x) = x2 + x + 1;
∴ f(-2) = (-2)2 + (-2) + 1=3,
f(-1) = (-1)2 + (-1) + 1 = 1
f(0) = 02 + 0 + 1 = 1
f(1) =12 + 1 + 1 = 3
f(2) = 22 + 2 + 1 = 7
∴ B = f(A) = (1, 3, 7)
Question 6.
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and f: A → R is a function defined by f(x) = x2−x+1/x+1, then find the range of f.
Answer:
Given A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and f(x) = x2−x+1/x+1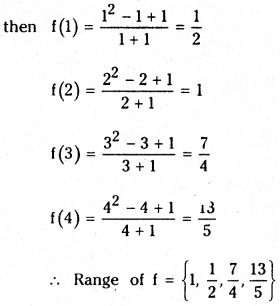
Question 7.
If f (x + y) = f (xy) ∀ x, y ∈ R, then prove that f is a constant function.
Answer:
Given f (x + y) = f(x y) ∀ x, y ∈ R Suppose x = y = 0 then
f(0 + 0) = f(0 x 0)
⇒ f(0) = f(0) ………………..(1)
Suppose x = 1, y = 0 then then f (1 + 0) = f(1 x 0)
⇒ f(D = f (0) ……………(2)
Suppose x = 1, y = 1 then f (1 + 1) = f(1 x 1)
⇒ f(2) = f(1) …………….. (3)
f(0) = f(1) = f(2)
= f(0) = f(2)
Similarly f(3) = f(0), f(4) = f(0) …………. f(n) = f(0)
∴ f is a constant function.
II.
Question 1.
If A = {x / – 1 ≤ x ≤ 11, f(x) = x2, g(x) = x3 Which of the following are surjections
(i) f : A → A
(ii) g : A → A.
Answer:
i) Given A {x / – 1 ≤ x ≤ 1}, f(x) = x2
and f : A → A
Suppose y ∈ A
then x2 = y ⇒ x = ± √y
If x = √y and if y = – 1 then x = √-1 ∈ A
f : A → A is not a surjection.
ii) Given A = {x/-1 ≤ x ≤ 1), g(x) = x3
and g : A → A
Suppose ye A then x2 = y ⇒ x = y√3 ∈ A
If y = -1 then x = -1 ∈ A
y = 0 then x = 0 ∈ A
y = 1 then x = 1 ∈ A
g : A → A is a surjection.
Question 2.
Which of the following are injections or surjections or Bisections ? Justify your answers.
i) f : R → R defined by f(x) = 2x+1/3
Answer:
Given f(x) = 2x+1/3
Let a1, a2 ∈ R
∴ f(a1) = f(a2)
⇒ 2a1+1/3=2a2+1/3
⇒ 2a1 + 1 = 2a2 + 1
⇒ a1 = a2
f(a1) = f(a2) ⇒ a1 = a2 ∀ a1, a2 ∈ R
f(x) = 2x+1/3 is an injection.
Suppose y ∈ R (codomain of f) then
y = 2x+1/3 ⇒ x = 3y−1/2
Then f(x) = f(3y−1/2)=2(3y−1)/2+1/3 = y
f is a surjection f: R → R defined by f(x) = 2x+1/3 is a bijection.
ii) f : R → (0, ∞) defined by f(x) = 2x
Answer:
Let a1, a2 ∈ R then f(a1) = f(a2)
⇒ 2a1 = 2a2
⇒ a1 = a2 ∀ a1, a2 ∈ R
f(x) = 2x, f: R → (0, ∞) is injection.
Let y ∈ (0, ∞) and y = 2x ⇒ x = log2 y
then f(x) = 2x = 2 log2y = y
∴ f is a surjection.
Since f is injection and surjection, f is a bijection.
iii) f : (0, ∞) → R defined by f(x) = logex.
Answer:
Let x1, x2 ∈ (0, ∞)and = logex. then f(x1) = f(x2)
⇒ logex1 = logex2 ⇒ x1 = x2
∴ f(x1) = f(x2)
x1 = x2 and f is injection.
Let y ∈ R then y = logex ⇒ x = ey
f(x) = logex = logeey = y and f is a surjection.
Since f is both injective and surjective, f is a bijection.
iv) f : [0, ∞) → [0, ∞) defined by f(x) = x2
Answer:
Let x1, x1 ∈ [0, ∞) given f(x) = x2
f(x1) = f(x2)
⇒ x1 = x2
x1 = x2 (∵ x1, x2 > 0)
f(x) = x2,
∴ f: [0, ∞) → [0, ∞) is an injection.
Let y ∈ [0, ∞)then y = x2 ⇒ x = √y (∵ y > 0)
f(x) = x2 = (√y)2 = y
and f is a surjection
∴ f is a bijection.
v) f : R → [0, ∞) defined by f(x) = x2
Answer:
Let x1 x2 ∈ R and f(x) = x2
∴ f(x1) = f(x2)
⇒ x12 = x22
⇒ x1 = ±x2 (∵ x1, x2 ∈ R)
f is not an injection
Let y ∈ [0, ∞] then y = x2 ⇒ x = ±√y
where y ∈ [0, ∞] then f(x) = x2 = (√y )2 = y.
∴ f is a surjection.
Since f is not injective and only surjective, we say that f is not a bijection.
vi) f : R → R defined by f(x) = x2
Answer:
Let x1 x2 ∈ R then f(x1) = f(x2)
⇒ x12 = x22
⇒ x1 = ± x2 (∵ x1, x2 ∈ R)
f(x) is not an injection.
Let y ∈ R then y = x2
⇒ x = ±√y
For elements that belong to (-∞, 0).
codomain R of f has no pre-image in f.
∴ f is not a surjection.
Hence f is not a bijection.
Question 3.
If g = 1(1,1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)) is a function from A = {1, 2, 3, 4} to B = {1, 3, 5, 7}. If this is given by the formula g(x) = ax + b then find a and b.
Answer:
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}, B = {1, 3, 5, 7}
g = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)}
∵ g(1) = 1, g(2) = 3, g(3) = 5, g(4) = 7
Hence for an element a ∈ A f ∃ b ∈ B such that g : A → B is a function.
Given g(x) = ax + b ∀ x ∈ A
g(1) = a + b = 1
g(2) = 2a + b = 3
solving a = 2, b = -1
Question 4.
If the function f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3x+3−x/2, then show that f (x+y) + f (x-y) = 2 f(x) f(y).
Answer: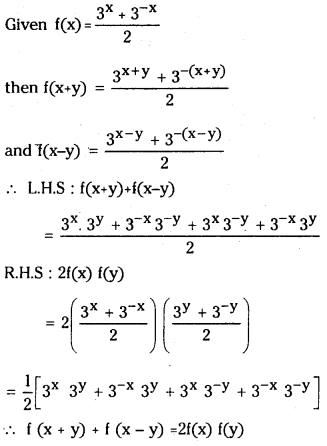
Question 5.
If the function f : R → R defined by f(x) = 4x/4x+2, then show that f (1 – x) = 1 – f(x) and hence reduce the value of f(14) + 2f(12) + f(34).
Answer: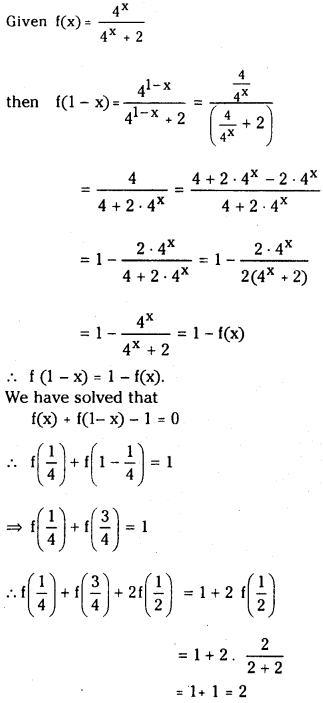
Question 6.
If the function f : {-1, 1} → {0, 2} defined by f(x) = ax + b is a subjection, then find a and b.
Answer:
Since f: {-1, 1} → {0, 2} and f(x) = ax + b is a surjection.
Given f (-1) = 0, f (1) = 2 (or) f (-1) = 2, f (1)=0
Case I : f (-1) = 0, f (1) = 2
∴ – a + b = 0, a + b = 2
Solving b =1 , a = 1
Case II : f (-1) = 2, and f (1) = 0
then – a + b = 2 and a + b = 0
Solving b = 1, a = -1
Hence a = + 1 and b = 1
Question 7.
If f(x) = cos (log x), then show that f(1/x) f(1/y) – (1/2)[f(x/y) + f(x/y)] = 0
Answer:
Given f(x) = cos(log x)
then f(1/x) = cos(log(1/x))
= cos(-log x) = cos(log x) (∵ log 1 = 0)
Similarly f(1/x) = cos(log y)
f(x/y) = cos(log(xy)) = cos(log x – log y)
f(x/y) = cos (log xy) = cos [log x + log y]
f(x/y) + f(x y) = cos(log x – log y) + cos (log x + log y)
= 2 cos (log x) cos (log y) (∵ cos (A – B) + cos (A + B))
= 2 cos A cos B
f(1/x) f(1/y) – (1/2)[f(x/y) + f(x/y)] = cos (log x) cos (log y) – 1/2 [2cos (log x) cos (logy)]
= 0



