Contents
- 1 Question 1. Solve the following systems of equations. (i) By using Cramer’s rule and Matrix inversion method, when the coefficient matrix is non-singular. (ii) By using Gauss Jordan Method. Also deter-mine whether the system has a unique solution or infinite number of solutions or no solution and find the solutions if exist. I) 5x – 6y + 4z = 15 7x + 4y-3z = 17 2x + y + 6z = 46
- 2 Question 2. x + y + z = 1 2x + 2y + 3z = 6 x + 4y + 9z = 3
- 3 Question 4. 2x + 6y + 11 = 0 6x + 20y – 6z + 3 = 0 6y – 18z + 1 = 0
- 4 Question 5. 2x – y + 3z = 9 x + y + z = 6 x – y + z = 2 (May 2014, Mar. ’14, ’05, ’02) Answer: i) Cramer’s rule : ii) Martix Inversion Method: det A = 2(2) + 1(0) + 3(- 2) = 4 -6 = -2 ≠ 0 ∴ A-1 exists and A-1 = AdjAdetA ∴ x = 1, y = 2, z = 3 is the solution. iii) Gauss Jordan Method: Augmented matrix of the system Since ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3; the system is consistent and has a unique solution given by x = 1, y = 2, z = 3. Question 6. 2x- y + 8z = 13 3x + 4y + 5z = 18 5x – 2y + 7z = 20 (March 2004, 03, ’01) (Board New Model Paper)
- 5 Question 7. 2x – y + 3z = 8 -x + 2y + z = 4 3x + y – 4z = 0
- 6 Question 8. x + y + z = 9 2x + 5y + 7z = 52 2x + y-z = 0 (May 2011)
Question 1.
Solve the following systems of equations.
(i) By using Cramer’s rule and Matrix inversion method, when the coefficient matrix is non-singular.
(ii) By using Gauss Jordan Method. Also deter-mine whether the system has a unique solution or infinite number of solutions or no solution and find the solutions if exist.
I) 5x – 6y + 4z = 15
7x + 4y-3z = 17
2x + y + 6z = 46
Answer:i) Cramer’s rule
Δ =
= 5(24 + 3) + 6(42 + 6) + 4(7 – 8)
= 135 + 288-4 = 419 ≠ 0
Hence Cramer’s rule is applicable.
Δ1 =
= 15(24 + 3) + 6(114 + 138) + 4(19 -184)
= 405 + 1512 – 660
= 1917 – 660
= 1257
Δ2 =
= = 5(114 + 138) -15(42 + 6) + 4(322 – 38)
= 1260 – 720 + 1136
= 1676
Δ3 =
= 5(184 – 19) + 6 (322 – 38) + 15 (7 – 8)
= 825 + 1704 – 15
= 2529 – 15
= 2514
∴ x =
y =
z =
∴ Solution is x = 3, y = 4, and z = 6
ii) Matrix Inversion method:
Use the formula A-1 =

iii) Gauss Jordan Method:
Augmented matrix of the system is
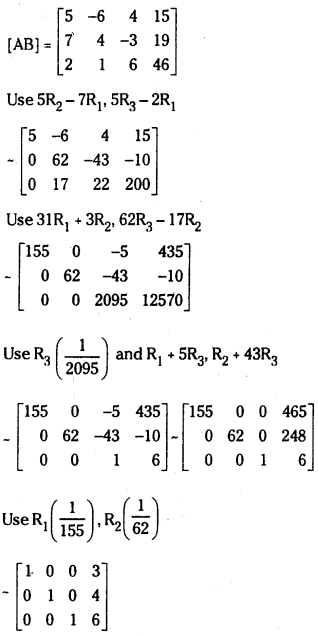
The given system is consistent and has a unique solution given by x = 3, y = 4, z = 6.
Question 2.
x + y + z = 1
2x + 2y + 3z = 6
x + 4y + 9z = 3
Answer:
i) Cramer’s rule :
Δ =
= 1(18 – 12) – 1(18 – 3) + 1(8 – 2)
= 6- 15 + 6
= -3
Δ1 =
= 1(18 – 12) – 1(54 – 9) + 1(24 – 6)
= 6 – 45 + 18
= -21
Δ2 =
= 1(54 – 9) – 1(18 – 3) + 1(6 – 6)
= 45 – 15
= 30
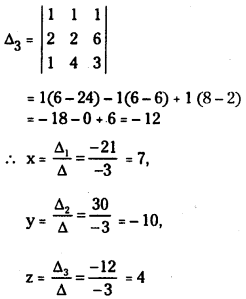
∴ Solution is x = 7, y = -10, and z = 4.
ii) Matrix Inversion Method:
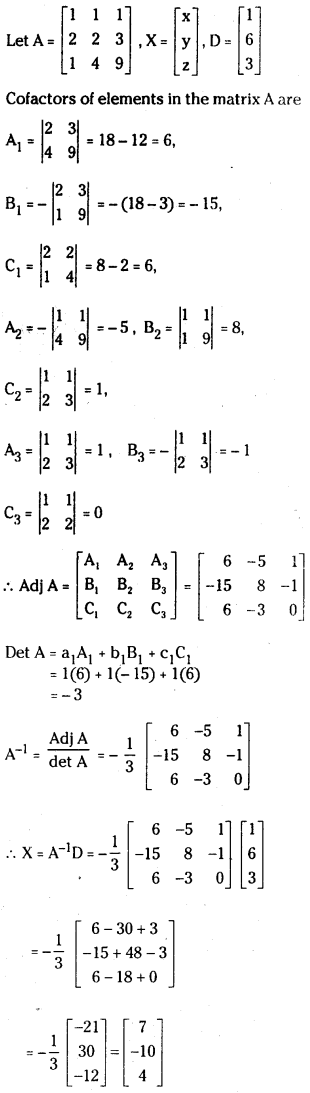
∴ Solution is x = 7, y = -10 and z = 4
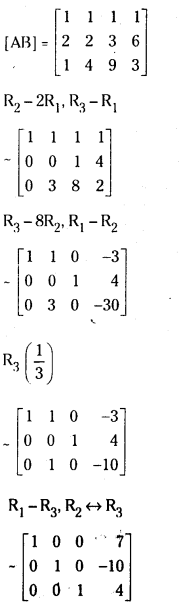
The given system is consistent and has a unique solution given by x = 7,y = -10,z = 4. [∵ ρ(A) = ρ(AB)]
Question 3.
x – y + 3z = 5 (March 2015-T.S)
4x + 2y – z = 0
-x + 3y + z = 5
Answer:
i) Cramer’s rule
Δ =
= 1(2 + 3) + 1(4-1) + 3(12 + 2)
= 5 + 3 + 42
= 50 ≠ 0
Cramer’s rule is applicable.
Δ1 =
= 5(2 + 3) + 1(0+ 5) + 3(0 -10)
= 25 + 5 – 30
= 0
Δ2 =
= 1(0+ 5)-5(4-1)+ 3(20)
= 5 – 15 + 60 = 0
Δ3 =
= 1(10 – 0) + 1(20 – 0)+ 5(12 + 2)
= 10 + 20 + 70
= 100
∴ x =
y =
z =
∴ x = 0, y = 1 and z = 2.
ii) Matrix Inversion Method:
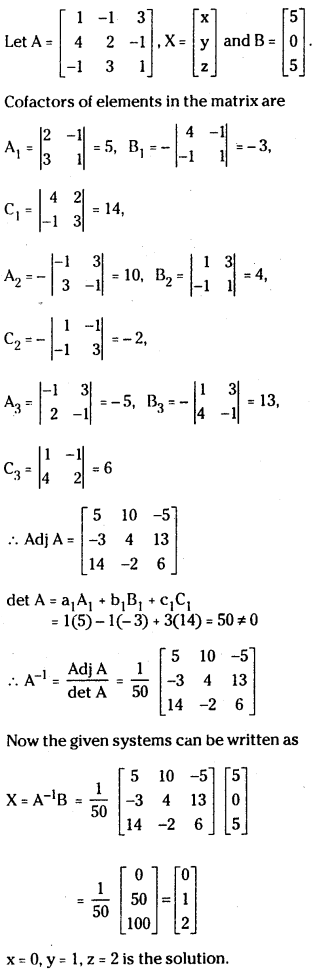
iii) Gauss Jordan Method:
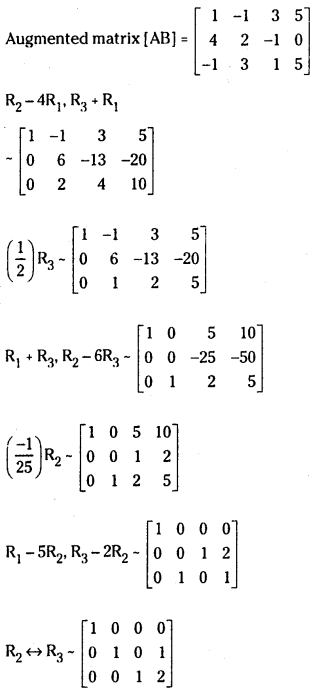
The given system of equations is consistent since ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3 and the system has a unique solution. x = 0, y = 1, z = 2.
Question 4.
2x + 6y + 11 = 0
6x + 20y – 6z + 3 = 0
6y – 18z + 1 = 0
Answer:
Δ =
= 2(- 360 + 36) – 6(-108-0) + 0(36)
= -648 + 648 = 0
Cramer’s and matrix inversion methods are not applicable.
Gauss Jordan Process:
The augmented matrix of the given system is
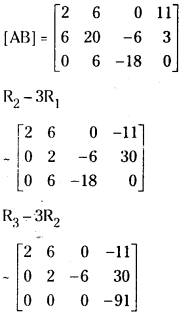
Since ρ(A) = 2 and ρ(AB) = 3, the given system is not consistent and has no solution.
Question 5.
2x – y + 3z = 9
x + y + z = 6
x – y + z = 2 (May 2014, Mar. ’14, ’05, ’02)
Answer:
i) Cramer’s rule :
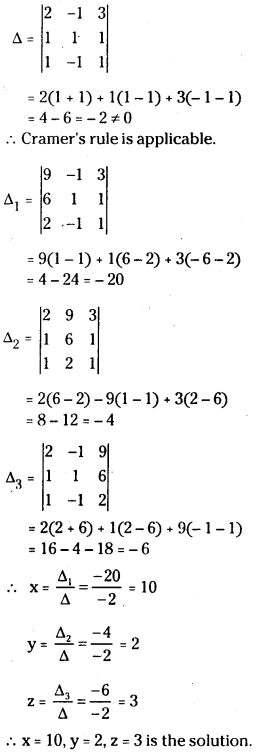
ii) Martix Inversion Method:
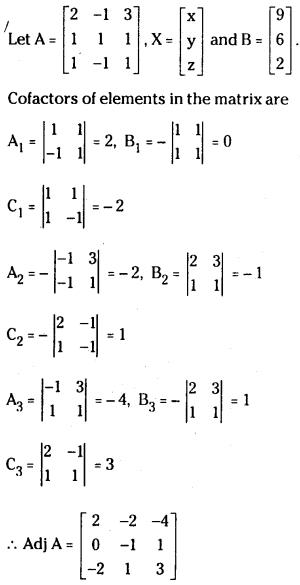
det A = 2(2) + 1(0) + 3(- 2)
= 4 -6 = -2 ≠ 0
∴ A-1 exists and A-1 = AdjAdetA

∴ x = 1, y = 2, z = 3 is the solution.
iii) Gauss Jordan Method:
Augmented matrix of the system

Since ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3; the system is consistent and has a unique solution given by x = 1, y = 2, z = 3.
Question 6.
2x- y + 8z = 13
3x + 4y + 5z = 18
5x – 2y + 7z = 20 (March 2004, 03, ’01) (Board New Model Paper)
Answer:
i) Cramer’s rule :

ii) Matrix Inversion Method:

∴ Solution is x = 3, y = 1 and z = 1
iii) Gauss Jordan Method:
Augmented matrix of the system

Since ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3, the system is consistent and has a unique solution given by x = 3, y = 1 and z = 1.
Then the cofactors of elements in the matrix A are
Question 7.
2x – y + 3z = 8
-x + 2y + z = 4
3x + y – 4z = 0
Answer:
i) Cramer’s rule :
Δ = ∣∣∣∣2−13−12131−4∣∣∣∣
= 2(- 8 – 1) + 1(4 – 3) + 3(- 1-6)
= -18 + 1 – 21 = -38 ≠ 0
Cramer’s rule is applicable.
Δ1 = ∣∣∣∣840−12131−4∣∣∣∣
= 8(- 8 – 1) + 1(- 16 – 0) + 3(4 – 0)
= -72 – 16 + 12
= -76
Δ2 = ∣∣∣∣2−1384031−4∣∣∣∣
= 2(- 16 – 0) – 8(4 – 3) + 3(0 – 12)
= – 32 – 8 – 36 = – 76
Δ3 = ∣∣∣∣2−13−121840∣∣∣∣
= 2(0 – 4) + 1(0 – 12) + 8(-1 – 6)
= -8 – 12 – 56
= -76
∴ x = Δ1Δ=−76−38 = 2
y = Δ2Δ=−76−38 = 2
z = Δ3Δ=−76−38 = 2
∴ Solution is x = 2, y =2, z = 2.
Matrix Inversion Method:
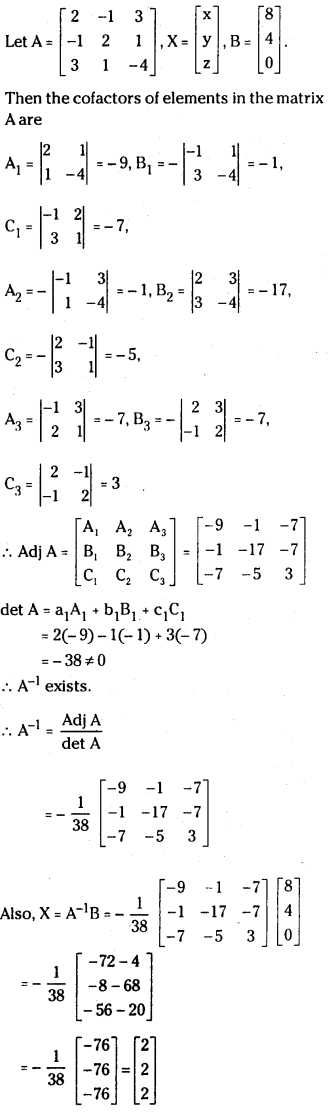
∴ Solution is x = 2, y = 2 and z = 2
iii) Gauss Jordan Method:
The augmented matrix of the system is

∴ ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3 ; the system is consistent and has a unique solution, x = 2, y = 2 and z = 2.
Question 8.
x + y + z = 9
2x + 5y + 7z = 52
2x + y-z = 0 (May 2011)
Answer:
i) Cramer’s rule :
Δ = ∣∣∣∣12215117−1∣∣∣∣
= 1(-5 – 7) – 1(-2 – 14) + 1(2 – 10)
= – 12 + 16-8 = -4 ≠ 0
∴ The Cramer’s method is applicable.
Δ1 = ∣∣∣∣952015117−1∣∣∣∣
= 9(-5 – 7) -1(-52) + 1(52)
= -108 + 52 + 52 =-4
Δ2 = ∣∣∣∣122952017−1∣∣∣∣
= 1(- 52 – 0) – 9(- 2 – 14) + 1(0 – 104)
= -52 + 144 – 104
= -12
Δ3 = ∣∣∣∣1221519520∣∣∣∣
= 1(0 – 52) -1(0 – 104) + 9(2 – 10)
= -52 + 104 – 72
= -20
∴ x = Δ1Δ=−4−4 = 1
y = Δ2Δ=−12−4 = 3
z = Δ3Δ=−20−4 = 5
x = 1, y = 3, z = 5 is a solution.
ii) Matrix Inversion Method:
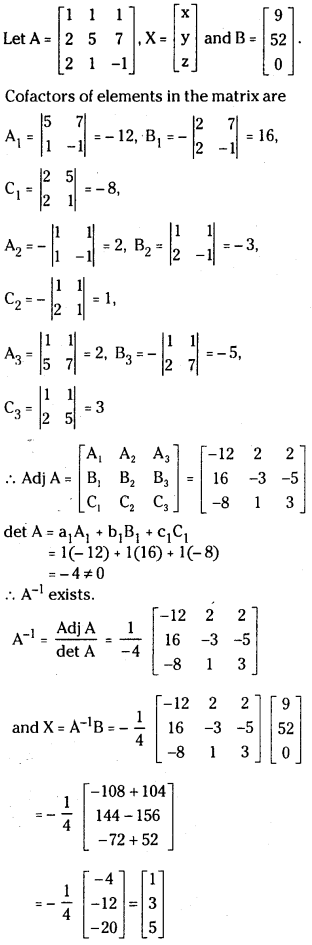
∴ x = 1, y = 3, z = 5 is the solution.
iii) Gauss Jordan Method:
Augmented matrix
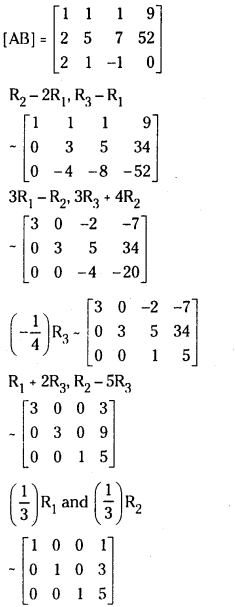
ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3 and the system is consistent.
The system has a unique solution given by
x = 1, y = 3 and z = 5.
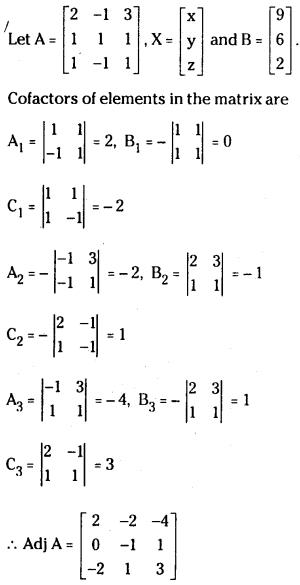
det A = 2(2) + 1(0) + 3(- 2)
= 4 -6 = -2 ≠ 0
∴ A-1 exists and A-1 =

∴ x = 1, y = 2, z = 3 is the solution.
Augmented matrix of the system

Since ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3; the system is consistent and has a unique solution given by x = 1, y = 2, z = 3.
2x- y + 8z = 13
3x + 4y + 5z = 18
5x – 2y + 7z = 20 (March 2004, 03, ’01) (Board New Model Paper)
i) Cramer’s rule :


∴ Solution is x = 3, y = 1 and z = 1
Augmented matrix of the system

Since ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3, the system is consistent and has a unique solution given by x = 3, y = 1 and z = 1.
Then the cofactors of elements in the matrix A are
2x – y + 3z = 8
-x + 2y + z = 4
3x + y – 4z = 0
i) Cramer’s rule :
Δ =
= 2(- 8 – 1) + 1(4 – 3) + 3(- 1-6)
= -18 + 1 – 21 = -38 ≠ 0
Cramer’s rule is applicable.
= 8(- 8 – 1) + 1(- 16 – 0) + 3(4 – 0)
= -72 – 16 + 12
= -76
= 2(- 16 – 0) – 8(4 – 3) + 3(0 – 12)
= – 32 – 8 – 36 = – 76
= 2(0 – 4) + 1(0 – 12) + 8(-1 – 6)
= -8 – 12 – 56
= -76
∴ x =
y =
z =
∴ Solution is x = 2, y =2, z = 2.
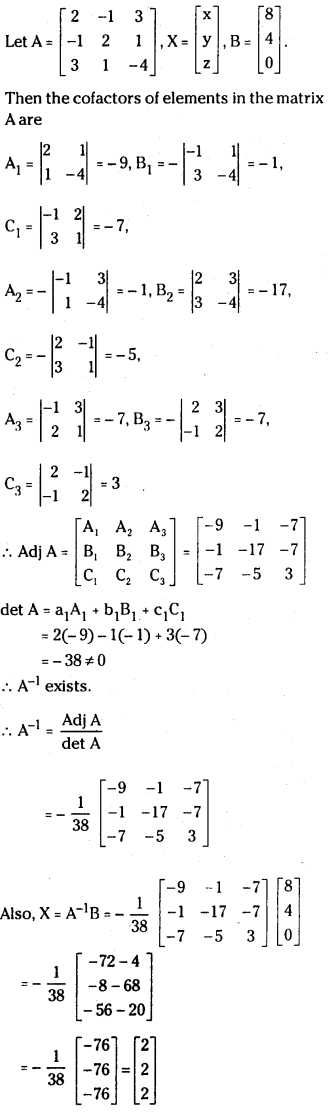
∴ Solution is x = 2, y = 2 and z = 2
The augmented matrix of the system is

∴ ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3 ; the system is consistent and has a unique solution, x = 2, y = 2 and z = 2.
x + y + z = 9
2x + 5y + 7z = 52
2x + y-z = 0 (May 2011)
i) Cramer’s rule :
Δ =
= 1(-5 – 7) – 1(-2 – 14) + 1(2 – 10)
= – 12 + 16-8 = -4 ≠ 0
∴ The Cramer’s method is applicable.
= 9(-5 – 7) -1(-52) + 1(52)
= -108 + 52 + 52 =-4
= 1(- 52 – 0) – 9(- 2 – 14) + 1(0 – 104)
= -52 + 144 – 104
= -12
= 1(0 – 52) -1(0 – 104) + 9(2 – 10)
= -52 + 104 – 72
= -20
∴ x =
y =
z =
x = 1, y = 3, z = 5 is a solution.
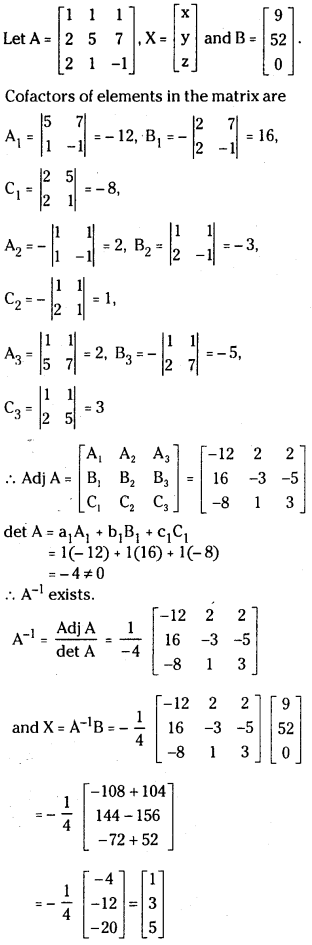
∴ x = 1, y = 3, z = 5 is the solution.
Augmented matrix
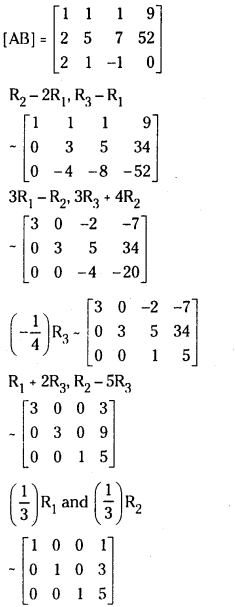
ρ(A) = ρ(AB) = 3 and the system is consistent.
The system has a unique solution given by
x = 1, y = 3 and z = 5.


