TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Functions Solutions Exercise 1(c)
I.
Question 1.
Find the domains of the following real valued functions. (May 2014, Mar. 14)
(i) f(x) = 1/(x2−1)(x+3)
Answer:
Domain of f is the value of all real x for which (x2 – 1) (x + 3) ≠ 0
⇔ (x + 1) (x – 1) (x + 3) ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ – 1, 1, -3
∴ Domain of f is, R – {-1, 1, – 3}
(ii) f(x) = 2x2−5x+7/(x−1)(x−2)(x−3)
Answer:
Here (x – 1) (x – 2) (x – 3) + 0
⇔ x ≠ 1, x ≠ 2, x ≠ 3.
Domain of f is, R – {1, 2, 3}
(iii) f(x) = 1/log(2−x)
Answer:
f(x) = 1/log(2−x) ∈ R
⇔ log (2 – x) ≠ 0 and 2 – x > 0
⇔ 2 – x ≠ 1 and 2 > x
⇔ x ≠ 1 and x < 2
⇔ x ∈ (-∞, 1) U (1, 2)
(or) x ∈ (-∞, 2) – {1}
Domain of f = x ∈ {∞, 2} – {1}
(iv) f(x) = |x – 3|
Answer:
f(x) = |x – 3| ∈ R
⇔ x ∈ R
∴ Domain of f = R
(v) f(x) = √4x−x2. (May 2005)
Answer:
f(x) = √4x−x2 ∈ R
⇔ 4x – x2 ≥ 0
⇔ x(4 – x) ≥ 0
⇔ x ∈ [0, 4]
∴ Domain of f = [0, 4]
(vi) f(x) = 1/√1−x2
Answer:
f(x) = 1/√1−x22 0 ⇔ (1 – x)(1 – x) > 0 ⇔ x ∈ (-1, 1) ∴ Domain of f = {x/x ∈ (-1, 1)} (vii) f(x) = 3x/x+1
Answer:
f(x) = 3x/x+1 ∈ R
⇔ 3x ∈ R, ∀ x ∈ R and x + 1 ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ – 1
∴ Domain of f = R – {-1}
(viii) f(x) = √x2−25 (May 2012)
Answer:
f(x) = √x2−25 ∈ R
⇔ x2 – 25 ≥ 0
⇔ (x + 5)(x – 5) ≥ 0
⇔ x ∈ (-∞, -5] ∪ [5, ∞)
⇔ x ∈ R – (-5, 5)
∴ Domain of f is R – (-5, 5)
(ix) f(x) = √x−[x]
Answer:
f(x) = √x−[x] ∈ R
⇔ x – [x] ≥ 0
⇔ x ≥ [x]
⇔ x ∈ R
∴ Domain of f is R
(x) f(x) = √[x]−x
Answer:
f(x) = √[x]−x ∈ R
⇔ [x] – x ≥ 0
⇔ [x] ≥ x
⇔ x ≤ [x]
⇔ x ∈ z
∴ Domain of f is Z (Set of injection)
Contents
- 1 Question 2.Find the ranges of the following real valued functions,(i) log |4 – x2|
- 2 Question 3.If f and g are real valued functions defined by f(x) – 2x – 1 and g(x) = x2, then find(i) (3f – 2g)(x)
- 3 Question 4.If f = {(1, 2), (2, -3), (3, -1)}, then find(i) 2f(ii) 2 + f(iii) f2(iv) √f[May 2012, May 2008]
- 4 Question 1.Find the domains of the following real valued functions(i) f(x)= √x2−3x+2
- 5 Question 2.Prove that the real valued function f(x) = x/ex−1 + x/2 + 1 is an even function on R – {0} –
- 6 Question 3.Find the domain and range of the following functions.(i) f(x) = tanπ[x]/1+sinπ[x]+[x2]
Question 2.
Find the ranges of the following real valued functions,
(i) log |4 – x2|
Answer:
Let y = f(x) = log |4 – x2| ∈ R
⇔ 4 – x2 ≠ 0 ⇒ x ≠ ± 2
y = log|4 – x2|
⇒ |4 – x2| = ey
ey > 0 ∀ y ∈ R
∴ Range of f is R.
(ii) √[x]−x
Answer:
Let y = f(x) = √[x]−x ∈ R
⇔ [x] – x > 0
⇔ [x] ≥ x ⇔ x ≤ [x]
∴ Domain of f is z
Then Range of f is {0}
∴ The Range of f = [1, ∞]
(iii) sinπ[x]/1+[x]2
Answer:
Let y = f(x) = sinπ[x]/1+[x]2 ∈ R
⇔ x ∈ R
∴ Domain of f is R
For x ∈ R, [x] is an integer and sin n [x]= 0 ∀ n ∈ R Range of f is {0}
(iv) x2−4/x−2
Answer:
Let y = f(x) = x2−4/x−2 = (x + 2) ⇔ x – 2 ≠ 0
∴ Domain of f is R – {2}
Then y = x + 2 ∴ x ≠ 2, we have y ≠ 4
∴ Range of f is R – {4}.
(v) √9+x2
Answer:
Let y = √9+x2 f(x) ∈ R
Domain of f is R.
When x = 0, f (0) = √9 = ± 3, But when f(0) = 3,
For all values of x e R – {0}, f (x) > 3
Range of f = {3, ∞).
Question 3.
If f and g are real valued functions defined by f(x) – 2x – 1 and g(x) = x2, then find
(i) (3f – 2g)(x)
Answer:
(3f – 2g) (x) = 3 f(x) – 2 g(x)= 3 (2x – 1) – 2(x2)
= -2x2 + 6x – 3
(ii) (fg) (x)
Answer:
(fg)(x) = f(x) g(x) = (2x – 1)(x2) = 2x3 – x2
(iii) (√f/g)(x)
Answer:
√f(x)/g(x)=√2x−1/x2
(iv) (f + g + 2)(x)
Answer:
(f + g + 2) (x) = f(x) + g(x) + 2
= 2x – 1 + x2 + 2
= x2 + 2x + 1 = (x + 1)2
Question 4.
If f = {(1, 2), (2, -3), (3, -1)}, then find
(i) 2f
(ii) 2 + f
(iii) f2
(iv) √f
[May 2012, May 2008]
Answer:
Given f = {(1, 2), (2, -3), (3, -1)} we have f(1) = 2, f(2) = -3 and f(3) = -1
(i) 2f = {(1, 2 x 2), (2, 2 (-3), (3, 2(-1))}
= {(1. 4). (2, – 6). (3, -2)}
(ii) 2 + f = {(1, 2+2), (2, 2+(-3), (3, 2+(-1))}
= {(1, 4), (2, -1), (3. 1)}
(iii) f2 = {(1, 22), (2, (-3)2), (3, (-1)2)]
= {(1, 4), (2, 9), (3, 1)}
(iv) √f = {(1, √2)| (∵ √-3 and √-1 are not real)
II.
Question 1.
Find the domains of the following real valued functions
(i) f(x)= √x2−3x+2
Answer:
f(x) = √x2−3x+2 ∈ R
Domain of f is x2 -3x + 2 > 0
⇒ (x – 2) (x – 1) > 0
⇒ x ∈ [-∞, 1] u [2, ∞]
∴ Domain of f = R – [1, 2]
(ii) f (x) = log (x2 – 4x + 3)
Answer:
f(x) = log (x2 – 4x + 3) ∈ R
⇔ x2 – 4x + 3 > 0
⇔ (x – 3) (x – 1) > 0
x ∈ (-∞, 1) ∪ (3, ∞)
Domain f = R – (1, 3)
(iii) f(x) = √2+x+√2−x/x
Answer:
f(x) = √2+x+√2−x/x ∈ R
⇔ 2 + x > 0 2 – x > 0, x ≠ 0
⇔ x > -2, x < 2 x ≠ 0 ⇔ -2 < x < 2, x ≠ 0 Domain of f is [-2, 2] – {0} (iv) f(x) = 1/3√x−2 log (4−x)10 Answer: f(x) = 1/3√x−2log(4−x)10 ∈ R ⇔ 4 – x > 0, 4 – x ≠ 1 and x – 2 ≠ 0
⇔ x < 4, x ≠ 3, x ≠ 2 Domain of f is [-∞, 4] – {2, 3} (v) f(x) = √4−x2/[x]+2 Answer: f(x) = √4−x2/[x]+2 ∈ R ⇔ 4 – x > 0, [x] + 2 > 0 or
4 – x2 < 0 and [x] > + 2 < 0 When 4 – x2 > 0, and [x] + 2 > 0
we have (2 – x) (2 + x) > 0 and [x] > – 2
⇔ x ∈ [-2, 2] and x ∈ [-1, ∞)
⇔ x ∈ [-1, 2] …………….(1)
When 4 – x2 < 0, and [x] + 2 < 0 ⇔ (2 + x) (2 – x) < 0 and [x] + 2 < 0 ⇔ x ∈ [-∞, -2] ∪ [2, ∞] and [x] < – 2 ⇔ x ∈ [- ∞, -2] ∪ [2, ∞] and x ∈ (- ∞,-2) ⇔ x ∈ [-∞, -2] ………………(2) ∴ from (1) and (2) ∴ Domain of f is [-∞, -2] ∪ {-1, 2} (vi) f(x) = √log0.3(x−x2) Answer: f(x) = √log0.3(x−x2) ∈ R ⇔ log0.3 (x – x2) > 0 .
⇒ x – x2 < (0.3) 0 ⇒ x – x2 < 1 ⇒ -x2 + x < 1 ⇒ -x2 + x – 1 < 0 ⇒ x2 – x + 1 > 0
This is true for all x ∈ R …..(1)
and x – x2 > 0
⇒ x2 – x < 0
⇒ x (x – 1) < 0
⇒ x ∈ (0, 1) ……….(2)
∴ Domain of f is R n (0, 1) = (0, 1)
∴ Domain of f = (0, 1)
(vii) f(x) = 1/x+|x|
Answer:
f(x) = 1/x+|x| ∈ R
⇔ x + |x| ≠ 0 ⇒ x ∈ (0, ∞)
(∵ |x| = x if x ≥ 0
= -x if x < 0)
∴ Domain of f = (0, ∞)
Question 2.
Prove that the real valued function f(x) = x/ex−1 + x/2 + 1 is an even function on R – {0} –
Answer:
f (x) ∈ R, ex – 1 ≠ 0
⇒ ex ≠ 1 ⇒ x ≠ 0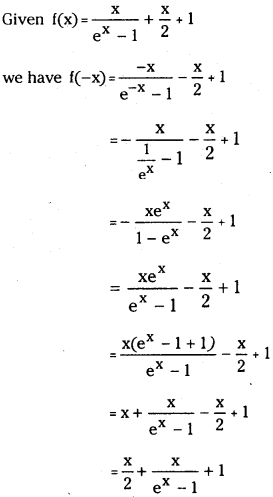
Since f(-x) = f(x), the function f is even function on R – {0}.
Question 3.
Find the domain and range of the following functions.
(i) f(x) = tanπ[x]/1+sinπ[x]+[x2]
Answer:
f(x) = tanπ[x]/1+sinπ[x]+[x2] ∈ R
⇔ x ∈ R; since [x] is an integar so that tan π [x] and sin π [x] are zero. ∀ x ∈ R
Domain of f is R and Range = {0}
(ii) f(x) = x/2−3x
Answer:
f(x) = x/2−3x ∈ R
⇔ 2 – 3x ≠ 0 ⇒ x ≠ 2/3
∴ Domain of f = R – {2/3}
Let y = f(x) = x/2−3x
⇒ 2y – 3xy = x
⇒ 2y = x(1 + 3y)
⇒ x = 2y/1+3y
∴ x ∈ R – {2/3}, 1 + 3y ≠ 0
⇒ y ≠ −1/3
∴ Range of f = R – {−1/3}
(iii) f(x) = |x| + |1 + x|
Answer:
f(x) ∈ R ⇔ x ∈ R
Domain of f = R
∴ |x| = x if x > 0
= – x if x < 0 |1 + x| = 1 + x if 1 + x > 0 ie., x > -1
= – (1 + x) if 1 + x < 0 ie., x < – 1
For x = 0, f(0) = 1,
x= 1, f(1) = |1| + |1 + 1| = 3
x = 2, f(2) = |2| + |1 + 2| = 2 + 3 = 5
x = -2, f(-2) = |-2| + |1 +(-2)| = 2 + 1 = 3
x = -1, f(-1) = |-1| + |1 + (-1)| = 1



