Contents
- 1 TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Solutions Chapter 4 Addition of Vectors Ex 4(a)
- 2 TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Addition of Vectors Solutions Exercise 4(a)
- 2.1 I. Question 1. ABCD is a parallelogram. If L and M are the middle points of BC CD respectively then find i) AL and AM in terms of AB and AD ii) λ, if AM = λ AC−AL(V.S.A)
- 2.2 Question 2. In AABC, P, Q and R are the mid points of the sides AB, BC and CA respectively. If D is any point i) Then express DA+DB+DC in terms of DP,DQ and DR. ii) If PA+QB+RC=α, then find a.(V.S.A)
- 2.3 Question 3. Let a̅ = i̅ + 2 j̅ + 3k̅ and b̅ = 3 i̅ + j̅. Find the unit vector in the direction of a+b. (V.S.A)
- 2.4 Question 4. If the vectors -3i̅ + 4j̅ + λk̅ and μi̅ + 8j̅ + 6k̅ are collinear vectors then find λ and μ. (May 2014, ’12, Mar. ’14)
- 2.5 Question 5. ABCDE is a pentagon. If the sum of the vectors AB,AE,BC,DC,ED and AC is λ AC , then find the value of λ. (S.A)
- 2.6 Question 6. If the position vectors of the points A, B and C are -2i̅ + j̅ – k̅, -4i̅ + 2j̅ + 2k̅ and 6i̅ – 3j̅ – 13k̅ respectively and AB = λAC then find the value of λ. (March 2011) (S.A)
- 2.7 Question 7. If OA¯=i¯+j¯+k; AB=3i¯−2j¯+k, BC=i¯+2j¯−2k and CD=2i¯+j¯+3k then find the vector OD¯. (March 2013) (V.S.A)
- 2.8 Question 8. If a̅ = 2i̅ + 5j̅ + k̅ and b̅ = 4i̅ + mj̅ + nk̅ are collinear vectors then find m and n. (May 2011) (V.S.A)
- 2.9 Question 9. Let a̅ = 2i̅ + 4j̅ – 5k̅, b̅ = i̅ + j̅ + k̅ and c̅ = i̅ + 2k̅. Find the unit vector in the opposite direction of a̅ + b̅ + c̅. (March 2015-A.P)(May 2012; Mar. ’04, ’12; Board Model Paper) (V.S.A)
- 2.10 Question 10. Is the triangle formed by the vectors 3i̅ + 5j̅ + 2k̅, 2i̅ – 3j̅ – 5k̅ and -5i̅ – 2 j̅ + 3k̅ equilateral ? (V.S.A)
- 2.11 Question 11. If α, β and γ are the angles made by the vector 3i̅ – 6j̅ + 2k̅ with the positive directions of the coordinate axes then find cos α, cos β, cos γ. (S.A)
- 2.12 Question 12. Find the angles made by the straight line passing through the points (1, -3, 2) and (3, -5, 1) with the coordinate axes. (S.A)
- 2.13 II. Question 1. If a̅ + b̅ + c̅ = αd̅, b̅ + c̅ + d̅ = βa̅ and a̅, b̅, c̅ are non-coplanar vectors, then show that a̅ + b̅ + c̅ + d̅ = 0̅. (S.A)
- 2.14 Question 2. a̅, b̅, c̅ are non coplanar vectors. Prove that the following four points are coplanar. i) -a̅ + 4b̅ – 3c̅, 3a̅ + 2b̅ – 5c̅ (May,’14,’12) -3a̅ + 8b̅ – 5c̅, – 3a̅ + 2b̅ + c̅
- 2.15 Question 3. If i̅, j̅, k̅ are unit vectors along the positive directions of the co-ordinate axes, then show that the four points 4i̅ + 5j̅ + k̅, – j̅ – k̅ , 3i̅ + 9j̅ + 4k̅ and -4i̅ +4j̅ +4k̅ are coplanar. (Mar. ’14)
- 2.16 Question 4. If a̅, b̅, c̅ are non coplanar vectors, then test for the collinearity of the following points whose position vectors are given by (i) a̅ – 2b̅ + 3c̅, 2a̅ + 3b̅ – 4c̅, – 7b̅ + 10c̅ (S.A)
- 2.17 III. Question 1. In the cartesian plane, O is the origin of the coordinate axes. A person starts at O and walks a distance of 3 units in the North-East direction and reaches the point P. From P he walks 4 units of distance parallel to North-West direction and reaches the point Q. Express the vector OQ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ in terms of i̅ and j̅ (observe that (∠XOP=45°) (S.A)
- 2.18 Question 2. The points O, A, B, X and Y are such that OA¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ = a̅, OB¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ = b̅, OX¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ = 3a̅ and OY¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ = 3b̅. Find BX¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ and AY¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ interms of a and 5. Further, if the point P divides AY in the ratio 1 : 3, then express BP¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ in terms of a and b. (S.A)
- 2.19 Question 3. In ΔOAB, E is the midpoint of AB and F Is a point on OA such that OF = 2 FA. If C Is the point of intersection of OE¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ and BF¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ then find the ratios OC : CE and BC : CF. (S.A)
- 2.20 Question 4. The point E divides the segment PQ internally in the ratio 1 : 2 and R is any point not on the line PQ. If F is a point on QR such that QF: FR = 2 : 1, then show that EF is parallel to PR. (S.A)
TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Solutions Chapter 4 Addition of Vectors Ex 4(a)
TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Addition of Vectors Solutions Exercise 4(a)
I.
Question 1.
ABCD is a parallelogram. If L and M are the middle points of BC CD respectively then find
i) AL and AM in terms of AB and AD
ii) λ, if AM = λ AC−AL(V.S.A)
Answer:
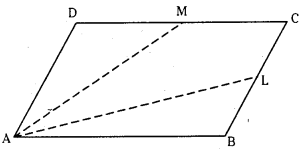 ABCD is a parallelogram and hence AB=DC and BC=AD
We have BC = 12BC
(∵ L is the mid point of BC)
= 1/2 AD (∵ BC = AD)
ABCD is a parallelogram and hence AB=DC and BC=AD
We have BC = 12BC
(∵ L is the mid point of BC)
= 1/2 AD (∵ BC = AD)
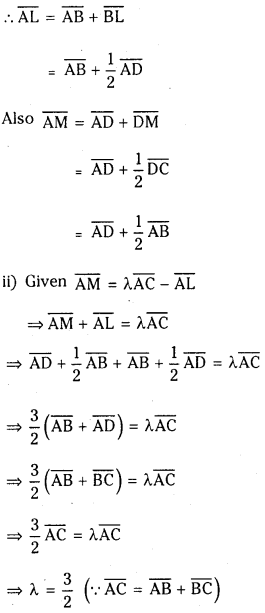
Question 2.
In AABC, P, Q and R are the mid points of the sides AB, BC and CA respectively. If D is any point
i) Then express DA+DB+DC in terms of DP,DQ and DR.
ii) If PA+QB+RC=α, then find a.(V.S.A)
Answer:
Let D be the origin.
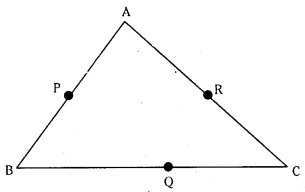 and DA¯=a , DB=b and DC=c
P.V. of P is mid point of AB=DP=a+b/2
P.V. of Q is mid point of BC=DQ¯=b+c/2
P.V. of R is mid point of AC=DR¯=c+a/2
and DA¯=a , DB=b and DC=c
P.V. of P is mid point of AB=DP=a+b/2
P.V. of Q is mid point of BC=DQ¯=b+c/2
P.V. of R is mid point of AC=DR¯=c+a/2
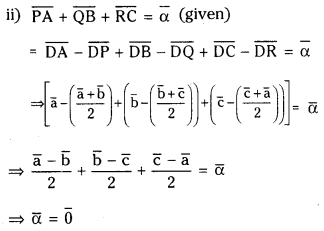
Question 3.
Let a̅ = i̅ + 2 j̅ + 3k̅ and b̅ = 3 i̅ + j̅. Find the unit vector in the direction of a+b. (V.S.A)
Answer:
Unit vector in the direction of a+b is
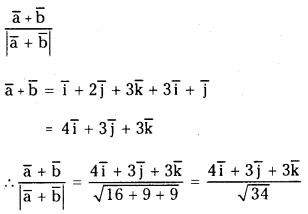
Question 4.
If the vectors -3i̅ + 4j̅ + λk̅ and μi̅ + 8j̅ + 6k̅ are collinear vectors then find λ and μ. (May 2014, ’12, Mar. ’14)
Answer:
If the vectors a1 i̅ + b1 j̅ + c1k̅ and a2 i̅ + b2 j̅ + c2k̅ are collinear then
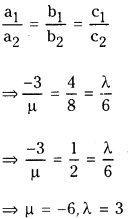
Question 5.
ABCDE is a pentagon. If the sum of the vectors AB,AE,BC,DC,ED and AC is λ AC , then find the value of λ. (S.A)
Answer:
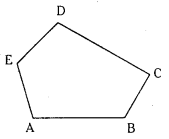 Given ABCDE is a pentagon and
Given ABCDE is a pentagon and
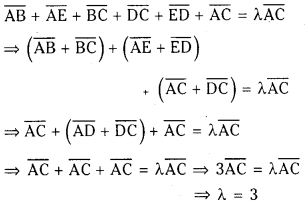
Question 6.
If the position vectors of the points A, B and C are -2i̅ + j̅ – k̅, -4i̅ + 2j̅ + 2k̅ and 6i̅ – 3j̅ – 13k̅ respectively and AB = λAC then find the value of λ. (March 2011) (S.A)
Answer:
Let O be the origin and given
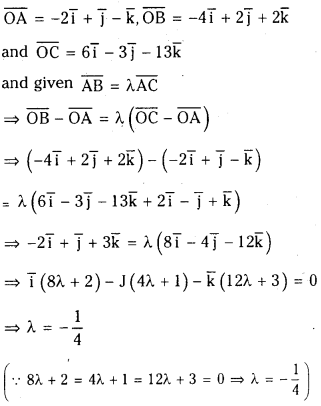
Question 7.
If OA¯=i¯+j¯+k; AB=3i¯−2j¯+k, BC=i¯+2j¯−2k and CD=2i¯+j¯+3k then find the vector OD¯. (March 2013) (V.S.A)
Answer:
Since OA¯+AB+BC+CD=OD¯
⇒ OD¯ = (i̅ + j̅ + k̅) + (3i̅ – 2j̅ + k̅) + (i̅ + 2 j̅ – 2k̅) + (2 i̅ + j̅ + 3k̅)
= 7i̅ + 2j̅ + 3k̅
Question 8.
If a̅ = 2i̅ + 5j̅ + k̅ and b̅ = 4i̅ + mj̅ + nk̅ are collinear vectors then find m and n. (May 2011) (V.S.A)
Answer:
Since a̅ = 2i̅ + 5j̅ + k̅ and
b̅ = 4i̅ + mj̅ + nk̅ are collinear
⇒ 2/4=5/m=1/n
⇒ 1/2=5/m and 1/2=1/n ⇒ m = 10 and n = 2
Question 9.
Let a̅ = 2i̅ + 4j̅ – 5k̅, b̅ = i̅ + j̅ + k̅ and c̅ = i̅ + 2k̅. Find the unit vector in the opposite direction of a̅ + b̅ + c̅. (March 2015-A.P)(May 2012; Mar. ’04, ’12; Board Model Paper) (V.S.A)
Answer:

Question 10.
Is the triangle formed by the vectors 3i̅ + 5j̅ + 2k̅, 2i̅ – 3j̅ – 5k̅ and -5i̅ – 2 j̅ + 3k̅ equilateral ? (V.S.A)
Answer:
Let ABC be the triangle with AB = 3i̅ + 5 j̅ + 2k̅
BC = 2i̅ – 3 j̅ – 5k̅
CA = -5i̅ – 2j̅ + 3k̅
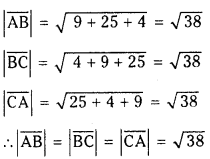 ∴ The given vectors formed on equilateral triangle.
∴ The given vectors formed on equilateral triangle.
Question 11.
If α, β and γ are the angles made by the vector 3i̅ – 6j̅ + 2k̅ with the positive directions of the coordinate axes then find cos α, cos β, cos γ. (S.A)
Answer:
Unit vectors along the coordinate axes are respectively i̅, j̅, k̅
Let p̅ = 3i̅ – 6j̅ + 2k̅
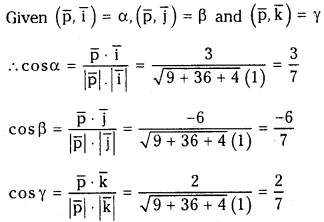
Question 12.
Find the angles made by the straight line passing through the points (1, -3, 2) and (3, -5, 1) with the coordinate axes. (S.A)
Answer:
Let the vectors along the coordinate axes be i̅, j̅, k̅ respectively. Let O be the origin and the points A(1, -3, 2) and B(3, -5, 1).
i. e. OA = i̅ – 3 j̅ + 2k̅, OB¯ = 3 i̅ – 5 j̅ + k̅
AB¯=OB¯−OA = (3i̅ – 5j̅ + k̅) – (i̅ – 3j̅ + 2k̅) = 2i̅ – 2j̅ – k̅
Let α be the angle between AB¯ and i̅ then

II.
Question 1.
If a̅ + b̅ + c̅ = αd̅, b̅ + c̅ + d̅ = βa̅ and a̅, b̅, c̅ are non-coplanar vectors, then show that a̅ + b̅ + c̅ + d̅ = 0̅. (S.A)
Answer:
Given a̅ + b̅ + c̅ = αd̅ ……………. (1)
b̅ + c̅ + d̅ = βa̅ …………….. (2)
From (2), d̅ = pa̅ – b̅ – c̅
From (1), a̅ + b̅ + c̅ = a, (pa̅ – b̅ – c̅)
⇒ (1 – αβ)a̅ + (1 + a)b̅ + (1 + a)c̅ = 0
∴ a̅, b̅, c̅ are non coplanar vectors
1 – αβ = 0 ⇒ αβ = 1 and
1 + α = 0 ⇒ α = -l β = -1
Hence from (1); a̅ + b̅ + c̅ = -d̅
⇒ a̅ + b̅ + c̅ + d̅ = 0
Question 2.
a̅, b̅, c̅ are non coplanar vectors. Prove that the following four points are coplanar.
i) -a̅ + 4b̅ – 3c̅, 3a̅ + 2b̅ – 5c̅ (May,’14,’12)
-3a̅ + 8b̅ – 5c̅, – 3a̅ + 2b̅ + c̅
Answer:
Let 0 be the origin and A, B, C, D are the four points given by
OA = -a̅ + 4b̅ – 3c̅, OB = 3a̅ + 2b̅ – 5c̅
OC = -3a̅ + 8b̅ – 5c̅, OD = -3a̅ + 2b̅ + c̅
AB¯=OB¯−OA = (3a̅ + 2b̅ – 5c̅) – (-a̅ + 4b̅ – 3c̅)
= 4a̅ – 2b̅ – 2c̅
AB¯=OB¯−OA = (-3a̅ + 2b̅ – 5c̅) – (3a̅ + 2b̅ – 5c̅)
= -6a̅ – 4b̅ + 3c̅
AC¯=OC−OA = (-3a̅ + 8b̅ – 5c̅) – (-a̅ + 4b̅ – 3c̅) = -2a̅ + 4b̅ – 2c̅
AD=OD−OA = (3a̅ + 2b̅ + c̅) – (-a̅ + 4b̅ – 3c̅) = -2a̅ – 2b̅ + 4c̅
Let a vector be expressed as a linear combination of other two.
Suppose AB¯ = x(AC¯) + y (AD) where x, y are scalars.
∴ 4a̅ – 2b̅ – 2c̅ = x (-2a̅ + 4b̅ – 2c̅) + y(-2a̅ – 2b̅ + 4c̅)
Comparing coefficients of a̅, b̅, c̅ we get
(∵ a̅, b̅, c̅ are non coplanar vectors)
-2x – 2y = 4 ……………(1)
4x – 2y = -2 ……………(2)
-2x + 4y = -2 ………….(3)
Solving (1) and (2) we get 2x + 2y = – 4 and 4x – 2y = – 2
6x = – 6 ⇒ x = -1
x + y = -2 ⇒ y = -1
x = – 1 and y = -1 satisfy equation (3).
⇒ A, B, C, D are coplanar and
AB¯,AC¯,AD are coplanar.
and AB¯,AC¯,AD are coplanar.
∴ The given points A, B, C, D are coplanar.
ii) 6a̅ + 2b̅ – c̅, 2a̅ – b̅ + 3c̅, -a̅ + 2b̅ – 4c̅, -12a̅ – b̅ – 3c̅
Answer:
Let O be the origin and A, B, C, D be the given points.
OA = 6a̅ + 2b̅ – c̅, OB¯ = 2a̅ – b̅ + 3c̅
OC = -a̅ + 2b̅ – 4c̅, OD = -12a̅ – b̅ – 3c̅
∴ AB¯=OB¯−OA
= (2a̅ – b̅ + 3c̅) – (6a̅ + 2b̅ – c̅)
= – 4a̅ – 3b̅ + 4c̅
AC¯=OC−OA = (-a̅ + 2b̅ – 4c̅) – (6a̅ + 2b̅ – c̅) = -7a̅ – 3c̅
AD=OD−OA = (-12a̅ – b̅ – 3c̅) – (6a̅ + 2b̅ – c̅)= -18a̅ – 3b̅ – 2c̅
∴ Let a vector be expressed as a linear combination of other two.
Suppose AB¯ = xAC¯ + yAD
⇒ -4a̅ – 3b̅ + 4c̅ = x(-7a̅ – 3c̅) + y(-18a̅ – 3b̅ – 2c̅)
Comparing coefficients of a̅, b̅, c̅ since a̅, b̅, c̅ are non coplanar,
-7x – 18y = – 4 …………(1)
-3y = -3 ⇒ y = 1 ……….(2)
∴ -7x – 18 = – 4 ⇒ – 7x = 14 ⇒ x = -2
Comparing coefficient of c,
-3x – 2y = 4 ………..(3)
x = – 2 and y = 1 satisfy equation (3)
and hence A, B, C, D are coplanar.
Alternate Method For Above Problem :
Use scalar triple product of vectors
= -4 (-9) + 3 (14 – 54) + 4 (21)
= 36- 120 + 84 = 0
∴ Vectors AB, AC, AD are coplanar
⇒ The given points A, B, C, D are coplanar.
Question 3.
If i̅, j̅, k̅ are unit vectors along the positive directions of the co-ordinate axes, then show that the four points 4i̅ + 5j̅ + k̅, – j̅ – k̅ , 3i̅ + 9j̅ + 4k̅ and -4i̅ +4j̅ +4k̅ are coplanar. (Mar. ’14)
Answer:
Let O be the origin and let A, B, C, D be the given points. Then
Now AB = OB — OA = (-j̅ – k̅) – (4i̅ + 5j̅ + k̅) – 4i̅ – 6j̅ – 2k̅
AC = OC – OD = -i̅ + 4j̅ + 3k̅,
AD = OD – OA = -8i̅ – j̅ + 3k̅
Let
⇒ – 4i̅ – 6j̅ – 2k̅ = x(- i̅ + 4j̅ + 3k̅) + y(-8i̅ – j̅ + 3k̅)
⇒ (x + 8y – 4) i̅ + (-4x + y – 6)j̅ + (-3x – 3y – 2)k̅ = 0
∴ i̅, j̅, k̅ are non coplanar
x + 8y – 4 = 0 …………..(1)
4x – y + 6 = 0 …………..(2)
3x + 3y + 2 = 0 ………….(3)
Solving (1) and (2) we get
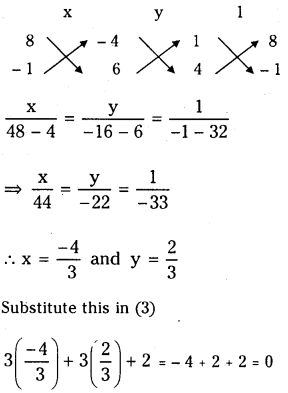
Hence the vectors AB, AC and AD are coplanar
⇒ The given points A, B, C, D are coplanar.
Second method :
= – 4 (12 + 3) + 6 (- 3 + 24) – 2 (1 + 32)
= – 60 + 126 – 66 = 0
The vectors
⇒ The given points A, B, C, D are coplanar.
Question 4.
If a̅, b̅, c̅ are non coplanar vectors, then test for the collinearity of the following points whose position vectors are given by
(i) a̅ – 2b̅ + 3c̅, 2a̅ + 3b̅ – 4c̅, – 7b̅ + 10c̅ (S.A)
Answer:
Given a, b, c are the non coplanar vectors
Let
and
Then
and
∴
∴ The points A, B, C are collinear.
(∵
III.
Question 1.
In the cartesian plane, O is the origin of the coordinate axes. A person starts at O and walks a distance of 3 units in the North-East direction and reaches the point P. From P he walks 4 units of distance parallel to North-West direction and reaches the point
Q. Express the vector OQ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ in terms of i̅ and j̅ (observe that (∠XOP=45°) (S.A)
Answer:
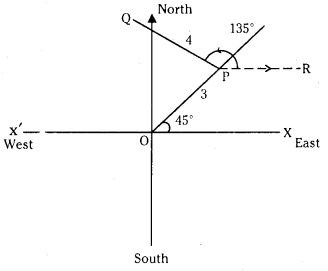
O is the origin and ∠XOP = 45°
The person starts at 0 and walks a distance of 3 units in North-East direction.
∴
=
PQ = 4 units
and pp is parallel to X axis
∴ ∠RPQ = 135°
PQ is parallel to North-West direction
Question 2.
The points O, A, B, X and Y are such that OA¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ = a̅, OB¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ = b̅, OX¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ = 3a̅ and OY¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ = 3b̅. Find BX¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ and AY¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ interms of a and 5. Further, if the point P divides AY in the ratio 1 : 3, then express BP¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ in terms of a and b. (S.A)
Answer:
Given
If P divides
Question 3.
In ΔOAB, E is the midpoint of AB and F Is a point on OA such that OF = 2 FA. If C Is the point of intersection of OE¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ and BF¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ then find the ratios OC : CE and BC : CF. (S.A)
Answer:
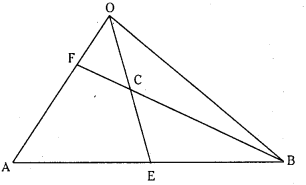
Let O be the origin and
Since E is the midpoint of AB,
and OF = 2 FA ⇒ F divides OA in the ratio 2 : 1
Let C divides
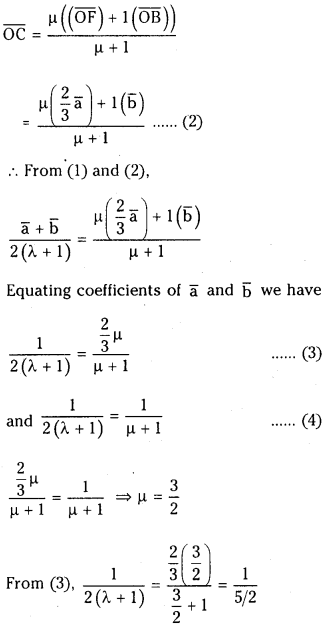
⇒ 4(λ + 1) = 5
⇒ 4λ = 1 ⇒ λ =
Let C divides
Question 4.
The point E divides the segment PQ internally in the ratio 1 : 2 and R is any point not on the line PQ. If F is a point on QR such that QF: FR = 2 : 1, then show that EF is parallel to PR. (S.A)
Answer:
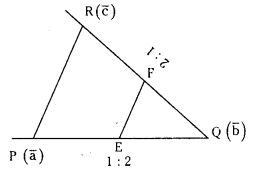
Let O be the origin and
E divides PQ in the ratio 1: 2




