NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
Question1.
How do Mendel experiments show that the traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer:
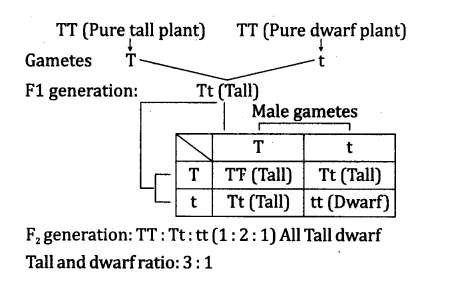
Mendel Experiments: Monohybrid Inheritance (One Visible Con¬trasting Character): Mendel first took pea plants with different characteristics such as a pure bred tall plant and a dwarf plant and crossed them. He found that only tall pea plants were produced in the F1 progeny. Then he allowed the F1, tall plants to reproduce by self-pollination, and found that the F2 progeny of the F1 tall plants were not all tall. Both tall and dwarf plants were obtained in the ratio of 3 :1. This ratio is known as the monohybrid ratio.
This indicated that both tallness and shortness traits were inherited in F1 generation but only tallness trait was expressed which was dominant over the unexpressed trait, i.e. shortness.
Question2.
If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an a sexually reproducing species and a trait B exisis in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Answer:Trait B is likely to have arisen earlier than trait A. The new traits in a population occurs due to inaccuracies while DNA copying mechanism. Hence, the new traits would be present in a veiy small proportion compared to the old one which is already exists
Question3.
How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer:Variations enable a species to adapt according to the changes and new needs and thus provide survival of species
Question4.
How do Mendel experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer:
Dihybrid Inheritance (Two Visible Contrasting Characters): Mendel took pea plants having two different characteristics: of seeds such as round shape with yellow colour and wrinkled shape with green colour, and crossed them. He found that only round-yellow seeds were produced in the F1 progeny. Then he used F1 progeny to generate F2 progeny by self-pollination. He got four different combinations of seeds: round - yellow, round - green, wrinkled - yellow and wrinkled-green in the ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. This ratio is known as dihybrid ratio.

Question5.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group 0 and their daughter has blood group 0. Is this information enough to tell you which of the trait - blood group A or 0 - is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer:No, this information is not enough to tell us which of the traits - blood group A or 0, is dominant. Because a pair of genes determines the blood group. In this case child has inherited 1° from mother as well as father. (Father having I°I° and mother having I°I°.)
Question6.
How is the sex of a child determined in human beings?
Answer:
Sex Chromosomes A male has XY sex chromosome and produces two types of sperms; 50% of them carrying X chromosomes and another 50% carrying the Y chromosomes. A female carries XX sex chromosomes and hence produces only X - carrying eggs. If X-carrying egg fuses with the X -carrying sperm, the child born will be a girl. If X - carrying egg fuses with the Y carrying sperm, the child born will be a boy.
Question7.
What are the different ways in which individuals with a particular trait may increase in a population?
Answer:
- Natural selection
- Genetic drift
- Geographical isolation
Question8.
Why are traits acquired during the lifetime of an individual not inherited?
Answer:
Inherited Trait The transmission of certain genetically controlled traits from parents to their offspring or from one generation to the next, which bear all the basic features with a great deal of variation are called inherited traits.
Question9.
Why are the small numbers of surviving tigers a cause of worry from the point of view of genetics?
Answer:As the number of surviving tigers is small, the sets of genes will be limited. This results in limited variation in characters during sexual reproduction, thereby causing danger for their survival in changing conditions
Question10.
What factors could lead to the rise of a new species?
Answer:
- Natural selection
- Genetic drift
- Geographical isolation
Question11.
Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of a self-pollinating plant species? Why or why not?
Answer:In a self-pollinating plant species, geographical segregation cannot be a major factor in speciation. This is because in self-pollinating plants, pollination is occurring in the same plant.
So a natural barrier cannot cause hindrance
Question12.
Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of an organism that reproduces asexually? Why or why not?
Answer:In case of an asexually reproducing organism, geographical isolation cannot be a major factor in speciation. This is because in asexual reproduction, only one parent is involved and natural barrier cannot pose a problem
Question13.
Give an example of characteristics being used to determine how close two species are in evolutionary terms?
Answer:Homologous characteristics are being used to determine how close two species are in evolutionary terms. For example, the forelimbs of human and bird have similar basic structure
though they are modified to perform different functions in them. The basic structure or anatomical similarity points to the existence of a common ancestor from these have evolved
Question14.
Can the wing of a butterfly and the wing of a bat be considered homologous organs? Why or why not?
Answer:No, they are not to be considered as homologous organs because they perform the same function but they do not have same structures and origins. In fact, they are the examples of analogous organs
Question15.
What are fossils? What do they tell us about the process of evolution?
Answer:Fossils are the remains or traces of dead plants and animals that lived in the past They provide the proof of changes and the relationship between various groups of organisms. They show how one species gives rise to another species with certain modifications. They allow us to make estimates of how far back evolutionary relationships go
Question16.
Why are human beings who look so different from each other in terms of size, colour and looks said to belong to the same species?
Answer:
Human beings who look so different from each other in terms of size, colour and looks said to belong to the same species because of the following reasons:
- They have same number of chromosomes
- They have a common ancestor
- They interbreed to produce fertile offsprings
Question17.
In evolutionary terms, can we say which among bacteria, spiders, fish and chimpanzees have a better body design? Why or why not?
Answer:Chimpanzees have more complex body design than fish, followed by spiders and then bacteria. Yet, we cannot say that chimpanzees have a better body design, because evolution does not necessarily mean progress. Evolution simply means the generation of diversity and selection by nature. It is the adaptability of an organism to the environment that supports its survival, not its complexity. Bacteria which are the simplest life forms still survive today. They are found in varied habitats like hot springs, in ice sheets, etc. only because of their adaptability to the changing environment. Thus, in evolutionary terms, we cannot say that a particular organism has a better body design
Chapter End Questions
Question1.
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as?
Answer:
Question2.
An example of homologous organs is?
- our arm and a dog fore leg
- our teeth and an elephant tusks
- potato and runners of grass
- all of the above
Answer:
Question3.
In evolutionary terms, we have more in common with?
- A Chinese school-boy
- A chimpanzee
- A spider
- A bacterium
Answer:
Question4.
A study found that children with light-coloured eyes are likely to have parents with light- coloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
Answer:Yes, we can say that the light eye colour trait is dominant because children born from the parents having light-coloured eyes also had light-coloured eyes
Analogous Organs:
Question5.
Explain the terms analogous and homologous organs with examples?
Answer:
Analogous Organs:
Homologous organs :
Structures which perform similar functions in different organisms and have a common evolutionary origin are called homologous organs. Analogous organs : Organs by different organisms having similar functions but with different anatomy ( structure ) can analogous. Such organs are considered examples of convergence - where species not closely related independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches.
Homologous //structures or organs -are those which have got similar origin in two different species, i,e structures evolved from common ancestors. The may have same function or they may not. Such organs are a product of divergent evolution that makes species evolve in other directions from an ancestral species.
Human and whale forelimb:
Humans have a very similar bone arrangement which consists of the humerus, radius, and ulna in their forlimbs to those found in whales because both inherited it from their common ancestor Though in whales, they have evolved to swim whereas humans require manipulation with these limbs
Question6.
Outline a project which aims to find the dominantcoat colour in dogs?
Answer:Let a dog with black colour homozygous trait (BB) mate with dog with white homozygous trait (bb). If the offspring of Ft generation are black, then the black trait is dominant. If the offspring of F1 generation are all white, then the white trait is dominant

Question7.
How are the areas of study - evolution and classification, interlinked?
Answer:Classification of organisms into groups is based on the similarities and differences between them. The more characteristics two species or organisms will have in common, the more closely they are related and the more recently they will have had a common ancestor. Classification shows that how closely organisms are related with respect to evolution. It is in fact a reflection of their evolutionary relationship
Question8.
Explain the importance of fossils in deciding evolutionary relationships?
Answer:Fossils are the remains or traces of dead plants and animals that lived in the past They provide the proof of changes and the relationship between various groups of organisms. They show how one species gives rise to another species with certain modifications. They allow us to make estimates of how far back evolutionary relationships go
Question9.
What evidence do we have for the origin of life from inanimate matter?
Answer:In 1953, Miller and Urey assembled an early earth atmosphere which consisted gases like NH3, CH4 and H2S, etc. except oxygen, over water. They maintained it at the temperature just below the 100°C and passed electric sparks in the mixture of gases to stimulate lightning. This was continued about one week. After that they found that 15% carbon from CH4 had been converted to simple organic compound like sugar and amino acids which constitute into protein molecules. This experiment gives the evidence for origin of life from inanimate matter
Question10.
Explain how sexual reproduction gives rise to more viable variations than asexual repro-duction. How does this affect the evolution of those organisms-that reproduce sexually?
Answer:In sexual reproduction, the DNA comes from two parents. Therefore, the variations are more obvious. When the next generation reproduces, it passes on the characteristics inherited from the parents as well as its own individual traits. This results in similarities and variations
Question11.
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
Answer:Individually both male and female parents possess 23 pairs of chromosomes, i.e. they have a total of 46 chromosomes. During gametes formation, this diploid chromosome number gets halved. The female gamete has 22 + X chromosomes and the male gamete has 22 + X or 22 + Y chromosomes. When the female and the male gametes fuses, the diploid condition again get restored in the zygote
The zygote has 44 + XX or 44 + XY chromosomes.
In this way, the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents is ensured in the progeny.
Question12.
Only variations that confer an advantage to an individual organism will survive in a population. Do you agree with this statement? Why or why not?
Answer:Yes, we agree with this statement because advantageous variations enable an organism to cope with changes in the environment. For example, there is a sudden drop in environ-mental temperature of an area where bacteria live. Under such condition only those bacteria that can tolerate low temperature will survive in a cold wave, while others do not. These survivors pass on their advantageous characters to their offspring resulting in the formation of new species