| Binary fission |
Multiple fission |
| (i) The parent organism, splits to form two new organisms, e.g., Amoeba, Paramecium |
The parent organism splits to form many new organisms at the same time, e.g., Plasmo |
| (ii) The nucleus of the parent body divides only once to produce two nuclei |
The nucleus of the parent body divides repeatedly to produce many nuclei |
Question 28.
List any four reasons for vegetative propagation being practised in the growth of some type of plants?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:
The following are the advantages of vegetative propagation
- The characters of the parent plants are preserved hence a good variety produced can be propagated by vegetative means
- The plants, which do not produce viable seeds or produce very few seeds, can be reproduced by this method. For example, banana, potato, grapes, sugarcane, rose, orange, etc
- It is an easier, quicker and cheaper method of propagation
- It is easier to get rid of pathogen from any part of plant by vegetative propagation
Question 29.
What is vegetative propagation? Write two of its advantages?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:Vegetative propagation is a method of asexual reproduction in plants in which the parts other than seeds are used as propagules
Question 30.
Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival - the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your answer?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction is as follows :
Asexual reproduction:
Gametes are not formed hence fertilisation does not take place.
Sexual reproduction:
Gametes are always formed and fertilisation takes place to form a zygote.
Species reproducing sexually has a better chance of survival as variations occur only during the sexual reproduction. Variations increase the chances of survival of an individual by making them more fit. Selection of variations by environmental factors forms the basis of evolution
Question 31.
What happens when?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (a) accidently, Planaria gets cut into many pieces
- (b) Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil
- (c) on maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts? (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
- (a) When Planaria accidently gets cut into many pieces then its each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration
- (b) When the Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil, the buds present in the notches along the leaf margin develop into new plants. This is known as vegetative propagation
- (c) The sporangia of Rhizopus contain cells or spores that can eventually develop into new Rhizopus individuals when it bursts on maturation
Question 32.
Describe reproduction by spores in Rhizopus?
Year of Question :(2017)
Answer:
Fungus Rhizopus reproduces by spore formation. During the growth of Rhizopus, small rounded, bulb-like structures develop at the top of the erect hyphae. Such structures are called sporangia. Inside each sporangium, nucleus divides several times. Each nucleus gets surrounded by a little amount of cytoplasm to become spore. Large number of spores are formed inside each sporangium. After sometime sporangium bursts and spores are released in the air. When these spores land on food or soil, under favourable conditions, they germinate into new individuals
Question 33.
What is vegetative propagation? State two advantages and two disadvantages of this method?
Year of Question :(2017)
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction in which the plant parts other than seeds are used as a propagule
Advantages of vegetative propagation
- Desirable character of the plant can be preserved through generation
- Seedless plants can be grown through this method
Disadvantages of vegetative propagation :
- Plants produced by this method posses less vigour and are more prone to diseases
- Plants produced by this method show no genetic variation
Question 34.
What is multiple fission? How does it occur in an organism? Explain briefly. Name one organism which exhibits this type of reproduction?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
Multiple fission refers to the process of asexual reproduction in which many individuals are formed from a single parent. This method of reproduction occurs in unfavourable conditions. The unicellular organism develops a protective covering called cyst, over the cell. The nucleus of the cell divides repeatedly producing many nuclei. Later on, each nucleus is surrounded by small amount of cytoplasm and many daughter cells are produced within the cyst.
When conditions are favourable the cyst breaks and small offspring are liberated. This type of reproduction is seen in some protozoans, e.g., malarial parasite (Plasmodium)
Question 35.
Explain the term "regeneration" as used in relation to reproduction of organisms. Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
The process of formation of entire organism from the body parts of a fully differentiated organism is called regeneration. It occurs by process of growth and development.
Simple animal like Hydra shows regeneration. When a small piece of Hydra breaks off it grows into complete new Hydra.
During regeneration, the cells of cut body part of the organism divide rapidly to make a mass of cells. The cells here move to their proper places within the mass where they have to form different types of tissues. In this way complete organism is regenerated
Question 36.
In the context of reproduction of species state the main difference between fission and fragmentation. Also give one example of each?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
The main differences between fission and fragmentation are as follows
| Fission |
Fragmentation |
| (i) Occurs in unicellular organisms |
Occurs in multicellular organisms |
| (ii) Body of organism divides by mitotic divisions into two or more daughter cells. E.g., Leishmania |
Body of the organism splits into one or more fragments and each fragment forms a complete organism. E.g., Spirogyra |
Question 37.
What happens when?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (a) Planaria gets cut into two pieces
- (b) a mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length
- (c) on maturation sporangia burst? (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
- (a) When Planaria is cut into two pieces then each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration
- (b) When a mature Spirogyra filament attains a considerable length it breaks into small pieces called fragments. These fragments grow into new individuals and this mode of reproduction is called fragmentation
- (c) When a sporangium burst, large number of spores are released in the air. When these spores land on food or soil, under favourable conditions they germinate into new individuals
Question 38.
What is vegetative propagation? List with brief explanation three advantages of practising this process for growing some types of plants. Select two plants from the following which are grown by this process : Banana, Wheat, Mustard, Jasmine, Gram?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is an asexual method of reproduction in plants. In this method, new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants (like stems, roots and leaves), without the help of any reproductive organs
Advantages of vegetative propagation are as follows:
- Vegetative propagation is usually used for the propagation of those plants which produce either very few seeds or do not produce viable seeds
- Seedless plants can be obtained by artificial vegetative propagation
- Grafting is a propagation method which is very useful for fruit trees and flowering bushes. It enables to combine the most desirable characteristics of two plants
- Plants like rose, sugarcane, cactus, etc., can be rapidly propagated through stem cuttings as this method produces new plants from just one plant quickly without waiting for flowers and seeds. Banana and jasmine are generally grown through vegetative propagation method
Question 39.
Explain budding in Hydra with the help of labelled diagrams only?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
The given diagram illustrates budding in Hydra
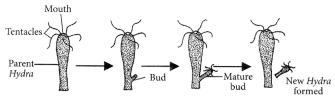
Question 40.
- (a) Name the following
- (i) Thread like non-reproductive structures present in Rhizopus
- (ii) Blobs that develop at the tips of the non- reproductive threads in Rhizopus
- (b) Explain how these structures protect themselves and what is the function of the structures released from the blobs in Rhizopus. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
- (a) (i)Threadlike non-reproductivestructures present in Rhizopus are called hyphae
- (ii) Blobs developing at the tip of hyphae are called sporangia which contain spores
- (b) Ihe structures called spores (released from blobs) are present in sporangia which can develop into new Rhizopus individuals. These spores are covered with thick walls that protect them until they come in contact with another moist surface and can begin to grow
How Do Organisms Reproduce Short Question & Answer:
Question 1.
What is reproduction? Why is it essential for organisms?
Answer:
Reproduction is the biological process by which organisms produce new individuals of their own kind. It ensures the continuity of species generation after generation and plays an important role in the survival and evolution of species.
Question 2.
What is asexual reproduction? Name the methods of asexual reproduction.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction where a single organism can produce offspring without the involvement of gametes or sexual organs.
Methods of asexual reproduction:
Binary fission (e.g., in amoeba)
Fragmentation (e.g., in spirogyra)
Budding (e.g., in yeast and hydra)
Regeneration (e.g., in planaria)
Spore formation (e.g., in fungi)
Question 3.
Explain the process of binary fission with an example.
Answer:
Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction where a single organism divides into two equal halves, each becoming a new individual. This method is common in unicellular organisms like amoeba.
Example:
In amoeba, the nucleus first divides into two (mitosis), followed by the division of the cytoplasm, resulting in two daughter cells. Each daughter cell grows into a full-sized amoeba.
Question 4.
What is budding? Explain with an example.
Answer:
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site.
Example:
In yeast, a small bud forms on the parent cell. The nucleus divides, and one of the nuclei moves into the bud. The bud grows and eventually detaches from the parent, becoming a new individual.
Question 5.
What is vegetative propagation? Give examples of plants that reproduce through this method.
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction in plants where new plants are produced from vegetative parts like roots, stems, or leaves.
Examples:
Potato reproduces through tubers.
Bryophyllum reproduces through leaf buds.
Sugarcane and ginger reproduce through stem cuttings or rhizomes.
Question 6.
What are the advantages of vegetative propagation?
Answer:
The advantages of vegetative propagation include:
It allows plants to reproduce without seeds.
It ensures the rapid spread and multiplication of plants.
The offspring produced are genetically identical to the parent, preserving desirable traits.
It is beneficial for plants that do not produce viable seeds.
Question 7.
Explain the process of fragmentation in organisms.
Answer:
Fragmentation is a type of asexual reproduction where an organism breaks into two or more fragments, and each fragment grows into a complete individual. This method is common in simple multicellular organisms like Spirogyra and seaweeds.
Question 8.
What is sexual reproduction? How is it different from asexual reproduction?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction is the process by which organisms reproduce through the fusion of male and female gametes (sperms and eggs) to form a zygote, which develops into a new organism. It involves two parents and results in offspring with genetic variation.
Differences:
Asexual reproduction involves only one parent and produces genetically identical offspring, while sexual reproduction involves two parents and results in genetic diversity.
Asexual reproduction does not involve gametes, but sexual reproduction requires the formation and fusion of gametes.
Question 9.
Describe the process of fertilization in human beings.
Answer:
Fertilization in humans occurs when the male gamete (sperm) fuses with the female gamete (egg) in the fallopian tube. The fusion of the nuclei of the sperm and egg forms a zygote, which is the first cell of the new individual. The zygote then undergoes multiple divisions and implants into the uterine wall, where it develops into an embryo and eventually a fetus.
Question 10.
What are the functions of the following parts in the human male reproductive system?
Testes
Vas deferens
Urethra
Answer:
Testes: The testes are the primary male reproductive organs that produce sperm and secrete the male hormone testosterone.
Vas deferens: The vas deferens is a tube that transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
Urethra: The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder and semen from the vas deferens to the outside of the body.
Question 11.
What are the functions of the following parts in the human female reproductive system?
Ovaries
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Answer:
Ovaries: The ovaries are the primary female reproductive organs that produce eggs (ova) and secrete the female hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Fallopian tubes: The fallopian tubes are the site of fertilization. They carry the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
Uterus: The uterus is where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus during pregnancy.
Question 12.
What is the role of the placenta in human reproduction?
Answer: The placenta is a temporary organ that forms between the mother and developing fetus. It facilitates the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the mother’s blood and the fetus’s blood without the two mixing directly. It also produces hormones necessary for maintaining pregnancy.
Question 13.
What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? Name two STDs each caused by bacteria and viruses.
Answer:
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are spread through sexual contact.
Bacterial STDs:
Gonorrhea
Syphilis
Viral STDs:
AIDS (caused by HIV)
Genital herpes
Question 14.
What is the significance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer:
DNA copying is essential for the transfer of genetic information from the parent to the offspring. It ensures that the offspring inherit traits from the parent, and variations in DNA can lead to evolution over generations. The accuracy of DNA copying ensures the survival of the species, while minor variations contribute to genetic diversity.
Question 15.
Why is variation important in sexual reproduction?
Answer:
Variation is important in sexual reproduction because it introduces new traits in the population, increasing the genetic diversity. This helps species adapt to changing environments and increases the chances of survival in adverse conditions. Variation is the driving force behind evolution.
Question Papers / Notes Download