NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Question1.
What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer:A reflex is an involuntary, rapid response to a stimulus. It does not involve any thinking. For example, we pull back our hand on touching any hot surface. It is an instant reaction. We do not have any control over the movement. On the other hand, walking is a voluntary action. It is a part of our routine and we have a full control over walking
Question2.
What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer:The gap between the two neurons is called synapse. At the synapse, the nerve impulse from one neuron gets transmitted to the other neuron. This takes place by the virtue of special neurotransmitters released by the axon terminal of a neuron. These neurotransmitters travel through the synapse to reach the dendrites of the adjacent neuron. The nerve impulses travel along with these neurotransmitters
Question3.
Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer:Cerebellum
Question4.
How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
ans:We have some olfactory receptors in our nose. These receptors are specialised to pick up the smell. Once they detect any smell, they send the message to the brain. The brain interprets and analyses those signals and tells the body that it is the smell of an incense stick
Question5.
What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer:Brain does not play any direct role in reflex action. Reflex action is mainly controlled by the spinal cord. The brain function as a relay centre for transferring impulses from sensory to motor neurons in the form of cerebral reflexes Control and Coordination such as closure of eyes on exposure to flash of light and salivation in the mouth at the good smell of food. In spinal reflexes, it acts as a collection centre of information without any direct involvement in reflex action
Question6.
What are plant hormones?
Answer:Plant hormones are the special chemicals which help in the growth of various parts of the plant
Question7.
How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer:The movement of leaves of the sensitive plant exhibits nastic movement. This means that the movement does not depend on the direction of the stimulus. Whereas, the movement of a shoot towards light is an example of tropic movement. This movement is dependent on the direction of the light
Question8.
Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth?
Answer:Auxin
Question9.
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer:The concentration of, auxin hormone varies in different parts of the plant. It is more in the part of the tendril which is away from the support. Auxin hormone promotes the cell division. Hence, there is increased cell division in that part compared to the part which is nearer to the support. So, the external part of the tendril grows more than the internal part making the tendril coil around the support
Question10.
Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer:Iodine is an important constituent required by the body to synthesise thyroxin hormone. The deficiency of iodine leads to a disease called goitre. In this disease, the neck region swells up. Hence, it is advisable to consume iodised salt to prevent chances of goiter
Question11.
Design an experiment to show hydrotropism?
Answer:
Procedure
- Take a big tray which should be able to accommodate a porous pot
- Fill the tray with sand. Put some seeds in it
- Make a pit in the sand to insert the pot in it
- Fill the porous pot with water.
- Do not disturb the set up for about a week
- After a week, locate the seeds and observe
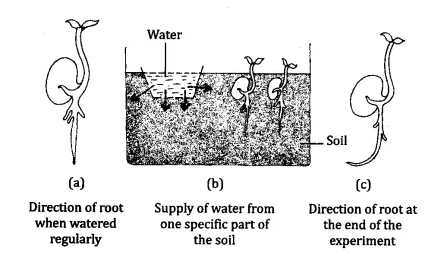 Observation
Observation When seeds are taken out, you will see that the roots show bending towards the direction from which water is diffusing. This shows the hydrotropic movement in roots.
Question12.
How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer:Chemical coordination in animals involves hormones which are secreted by endocrine glands. These hormones help in regulating different metabolic functions in the body. For example, growth hormone is a hormone which regulates the growth of the body. If this hormone is secreted in excess, it leads to gigantism. If this hormone is secreted in less quantity, it leads to dwarfism
Question13.
How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer:Adrenaline is commonly known as fight or flight hormone. This is because, the hormone prepares the body for any emergency situation. If there is an increased secretion of this hormone in the blood, it causes increased blood supply to limbs and face. It also increases the heart rate and breathing rate. All of these responses enable the body to deal with any situation-be it a fight or; if need be; a flight from the scene
Question14.
Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer:Insulin controls the sugar levels of the body. In some diabetic patients, insulin hormone level is not normal. Hence, insulin injection is given to such patients to compensate for the reduced insulin hormone secretion. Such cases of diabetes are called Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM). such as closure of eyes on exposure to flash of light and salivation in the mouth at the good smell of food. In spinal reflexes, it acts as a collection centre of information without any direct involvement in reflex action
Chapter End Questions
Question1.
Which of the following is a plant hormone?
- Insulin
- Thyroxin
- Oestrogen
- Cytokinin
Answer:
Question2.
The gap between two neurons is called a?
- dendrite
- synapse
- axon
- impulse
Answer:
Question3.
The brain is responsible for?
- thinking
- regulating the heartbeat
- balancing the body
- all of the above
Answer:
Question4.
What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer:Receptors are the sensory structures which provide information about the external environment to the body. This helps the brain to instruct a related organ to take the required action. Receptors are very important for our survival. For example, if a person is blind, performing certain ordinary task may be very difficult for him. Since, one of the receptors (eyes) are not functional in his body, he may not be able to see the obstruction in his path or may even fall in a pit
Question5.
Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function?
Answer:
Structure of neuron
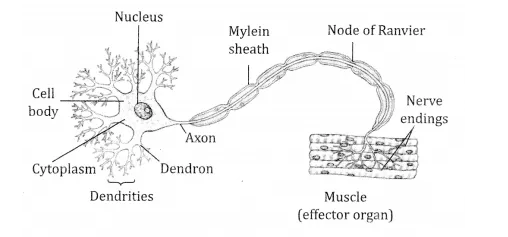 Function Neuron helps in transmitting the nerve impulses.
Function Neuron helps in transmitting the nerve impulses.
Question6.
Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer:The spinal cord is a junction where various nerves meet. In case of spinal cord injury, the communication between the spinal nerves and the brain would get disturbed
Question7.
How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer:The concentration of auxin differs in different parts of the plant in response to the direction of light. For example, in a stem the concentration of auxin is more in the parts which are away from the light. Presence of auxin hormone increases the cell division in that part. This causes the stem to bend towards the light. That is how phototropism occurs in plants
Question8.
How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer:Plant hormones play a very important role in chemical coordination. Most of the plant hormones stimulate growth in certain parts of the plant. For example, hormones auxin and gibberellins stimulate growth. However, hormone abscisic acid inhibits the growth of the plant
Question9.
What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Answer:A living organism constantly interacts with its external environment. For example, a deer has to move in search of its food. It also needs to quickly run in case there is some danger. Hence, there is a need for control and coordination in not just deer but any organism
Question10.
How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Answer:Involuntary actions are those reactions which take place during our daily routine activities, e.g. beating of heart, peristaltic movement of intestines, etc. Reflex actions are the reactions which are involuntary in actions that evoked in response to a sudden danger
Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
ans:
| Nervous control
mechanism |
Hormonal control
mechanism |
| It is a fast mechanism |
It is a slow mechanism |
| The information is conveyed in form of nerve impulses |
The information is conveyed in form of chemical messengers |
| It is facilitated by neurotransmitters |
It is facilitated by hormones
|
Question.11
Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and
coordination in animals?
Answer:
Nervous system:
A nervous system is described as " a system in an organism that receives the stimulus, transfers it to other parts of body and results corresponding effects.
The activity of various parts of the body is organized and co-ordinated by the nervous system to control all internal activities.
With the help of sense organs attached to them, they make sensations; vision, hearing, taste, smell and pain are so.
The nervous system functions in the response to changes in the external environment
Hormonal system:
And so hormones will cross the plasma membrane of the target cell and bind to a receptor protein located in there cytoplasm.
This binding leads to a series of events which trigger the formation of secondary messengers.
Secondary messengers trigger a sequence of molecular interactions that alters the physiological state of a cell.
This process is also known as signal transduction
Question12.
What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Answer:The movement in a sensitive plant is controlled by hormones which are a part of hormonal mechanism. The movement in our legs is controlled by nervous control mechanism