NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Important Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point. Why?
Year of Question:(2020)
Answer:
Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points because the forces of attraction between molecules of covalent compounds are very weak. On applying a small amount of heat these molecular forces break.
Question 2.
What are covalent compounds? Why are they different from ionic compounds? List their three characteristic properties.
Year of Question:(Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Covalent compounds are those compounds which are formed by sharing of valence electrons between the atoms e.g., hydrogen molecule is formed by mutual sharing of electrons between two hydrogen atoms.
They are different from ionic compounds as ionic compounds are formed by the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another e.g., NaCl is formed when one valence electron of sodium gets completely transferred to outer shell of chlorine atom. The characteristic properties of covalent compounds are:
(i) They are generally insoluble or less soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
(ii) They have low melting and boiling points.
(iii) They do not conduct electricity as they do not contain ions.
Question 3.
What are covalent bonds? Show their formation with the help of electron dot structure of methane. Why are covalent compounds generally poor conductors of electricity?
Year of Question:(Delhi 2013C)
Answer:
Covalent bonds are those bonds which are formed by sharing of the valence electrons between two atoms. Electron dot structure of methane is shown in the figure.
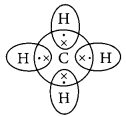
Covalent compounds are generally poor conductors ol electricity because they do not have tree electrons or ions.
Question 4.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Element carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding.
(ii) Diamond has high melting point.
(iii) Graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Year of Question:(3/5, Foreign 2011)
Answer:
(i) As carbon has four valence electrons and it can neither loose nor gain lour electrons thus, it attains noble gas configuration only by sharing of electrons. I bus, it forms covalent compounds.
(ii) In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms forming a rigid three-dimensional structure. This makes diamond the hardest known substance. Thus, it has high melting point.
(iii) In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds in the same plane giving a hexagonal array. Thus, only three valence electrons are used for bond formation and hence, the fourth valence electron is free to move. As a result, graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Question 5.
What is methane? Draw its electron dot structure. Name the type of bonds formed in this compound. Why are such compounds
(i) poor conductors of electricity and
(ii) have low melting and boiling points?
What happens when this compound burns in oxygen?
Year of Question:(Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Methane is the first member of alkane series having formula CH
4.
Refer to answer 3.
(ii) Refer to answer 1.
When methane is burnt in presence of oxygen then carbon dioxide will be produced.
CH
4 + O
2 → CO
2 + H
2O + heat + ligh
Question 6.
Elements forming ionic compounds attain noble gas electronic configuration by either gaining or losing electrons from their valence shells. Explain giving reason why carbon cannot attain such a configuration in this manner to form its compounds. Name the type of bonds formed in ionic compounds and in the compounds formed by carbon. Also explain with reason why carbon compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity.
Year of Question: (Foreign 2015, AI 2014)
Answer:
Ionic compounds are formed either by gaining or losing electrons from the outermost shells, but carbon which has four electrons in its outermost shell cannot form ionic bonds because
1. If carbon forms ionic bonds by gaining four electrons to attain a noble gas configuration then it would be difficult for six protons in the nucleus to hold ten electrons.
2. If carbon forms ionic bonds by loss of four electrons then it would require a lot of energy to remove these electrons from outermost shell.
Due to these reasons carbon forms covalent bonds by sharing the valence electrons.
Type of bonds formed in ionic compounds are called electrovalent bonds and the type of bonds formed in carbon compounds are called covalent bonds.
Refer to answer 3.
Question 7.
State the reason why carbon can neither form C4+ cations nor C4- anions, but forms covalent compounds. Also state reasons to explain why covalent compounds :
(i) are bad conductors of electricity?
(ii) have low melting and boiling points?
Year of Question:(Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 6.
(i) Refer to answer 3.
(ii) Refer to answer 1.
Question 8.
Name a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.
Year of Question:(2020)
Answer:
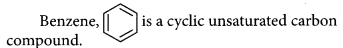
Question 9.
Assertion (A) : Following are the members of a homologous series :
CH3OH, CH3CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2OH
Reason (R) : A series of compounds with same functional group but differing by -CH2 unit is called homologous series.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Year of Question: (2020)
Answer:
(a): The given compounds are members of homologous series of alcohol.
Question 10.
Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group -Cl.
Year of Question:(Delhi 2017)
Answer:
The molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having -Cl functional group are CH3Cl and CH3CH2Cl.
Question 11.
Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group -OH.
Year of Question: (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
The molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having -OH functional group are CH3OH and CH3CH2OH.
Question 12.
Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is ethene.
Year of Question:(AI 2017)
Answer:
Homologous series of alkenes have general formula, CnH
2n whose first member is ethene.
2nd member of homologous series of alkenes is C
3H
6 i.e., propene.
3rd member of homologous series of alkenes is C
4H
8 i.e., butene.
Question 13.
Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is methane.
Year of Question:(AI 2017)
Answer:
Methane, CH
4 is an alkane. Alkanes have general formula, CnH
2n+2.
2nd member of homologous series of alkanes is C
2H
6 i.e., ethane.
3rd member of homologous series of alkanes is C
3H
8 i.e., propane.
Question 14.
Write the next homologue of each of the following:
(i) C2H4
(ii) C4H6
Year of Question:(Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(i) C
2H
4 belongs to alkene series having general formula, CnH
2n.
Thus, next homologue will be C
3H
2×
3 = C
3H
6
(ii) C4H6 belongs to alkyne series having general formula, CnH
2n-2.
Thus, next homologue will be C
5H
2×
5-
2 = C5H8
Question 15.
Name the following compounds :
(a) CH3 - CH2 - OH
Year of Question:(Delhi 2016)
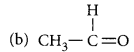
Answer:
(a) CH3 - CH2 - OH : Ethanol
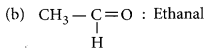
Question 16.
Select saturated hydrocarbons from the following : C3H6; C5H10; C4H10; C6H14; C2H4
Year of Question:(AI 2016)
Answer:
Saturated hydrocarbons have general formula, CnH2n+2.
Among the given compounds only C4H10 and C6H14 satisfy the above formula. Thus, these are saturated hydrocarbons.
Question 17.
Write the name and structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule.
Year of Question:(AI 2016)
Answer:
An alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule is propanol. The structure of propanol is
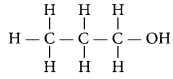
Question 18.
Write the name and structure of an alcohol with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
Year of Question:(AI 2016)
Answer:
An alcohol with four carbon atoms is butanol and its structure is :
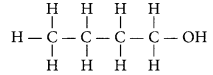
Question 19.
Write the name and structure of an aldehyde with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
Year of Question:(AI 2016)
Answer:
An aldehyde with four carbon atoms is butanal and its structure is.
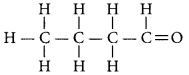
Question 20.
Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why?
Year of Question:(Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation. Carbon shows catenation due to its small size and Stronger carbon-carbon bond strength.
Question 21.
Write the name and molecular formula of the fourth member of alkane series.
Year of Question:(Foreign 2016)
Answer:
The general formula of the alkane series is CnH2n+2. For fourth member of alkane series, n = 4
∴C4H2×4+2 = C4H10 i.e., butane.
Question 22.
What is homologous series of carbon compounds?
Year of Question:(Foreign 2016)
Answer:
A homologous series is the family of organic compounds having the same functional group, similar chemical properties but the successive (adjacent) members of the series differ by a -CH2 unit or 14 mass units.
Question 23.
Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n.
Year of Question:(Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 12.
Question 24.
Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n+2.
Year of Question:(Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 13.
Question 25.
Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n-2.
Year of Question:(Delhi 2015)
Answer:
General formula, CnH2n-2 belongs to alkyne series. The second member of this series is propyne i.e., (C3H4) or CH3 - C ? CH.
Question 26.
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Year of Question:(AI2015, Delhi 2014)
Answer:
The structural formula of ethane (C2H6) is
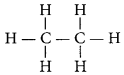
There are total 7 covalent bonds. Six C - H covalent bonds and one C - C covalent bond.
Question 27.
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane, C4H10.
Year of Question:(AI 2015)
Answer:
Butane (C
4H
10) has the following structural formula as:
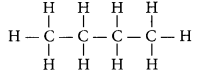
Total number of covalent bonds is 13 in which there are 10 C - H and 3 C - C covalent bonds.
Question 28.
Write the name of each of the following functional groups:
Year of Question:(Foreign 2015, Delhi 2013)
(a) -OH
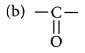
Answer:
(a) -OH : Alcohol
Question 29.
Write the name and molecular formula of the first member of the homologous series of alkynes.
Year of Question:(Foreign 2015)
Answer:
General formula for alkyne is CnH
2n-2
First member of homologous series of alkyne has the formula, C
2H
2×
2-
2 = C
2H
2 i.e., ethyne.
Question 30.
Define the term functional group. Identify the functional group present in
Year of Question:(Delhi 2012)
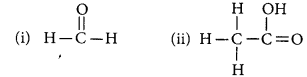
Answer:
An atom or a group of atoms present in a molecule which largely determines its chemical properties, is called functional group.
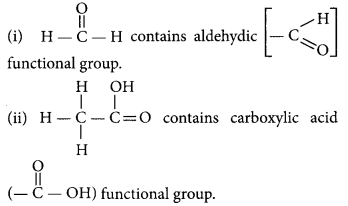
Question 31.
Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds:
(i) C2H5Cl
(ii) C2H5OH
Year of Question:(Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) C
2H
5Cl contains -Cl (chloro) group which belongs to halo functional group.
(ii) C
5H
5OH contains -OH group which belongs to alcoholic functional group.
Question 32.
Write the name and formula of the second member of the carbon compounds having functional group -OH.
Year of Question:(AI 2012)
Answer:
Those having -OH as functional group belong to alcohol family. Second member of this family is ethanol, C
2H
5OH.
Question 33.
Write the name and formula of the first member of the series of carbon compounds having functional group
Year of Question:(Foreign 2012)
Answer:
Carbon compound containing
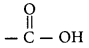
group is called carboxylic acid. The first member of this family is methanoic acid (HCOOH).
Question 34.
Butanone is a four-carbon per molecule compound. Name the functional group present in it.
Year of Question:(Foreign 2011)
Answer:
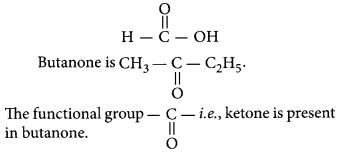
Question 35.
State two properties of carbon which lead to a very large number of carbon compounds.
Year of Question:(2/5, AI 2011)
Answer:
Carbon forms a large number of carbon compounds like long chains which may be straight or branched chains or ring of different sizes due to its tetravalency ahd unique property of catenation. Carbon due to its small size forms exceptionally stable compounds by forming strong bonds.
Important Questions and Answers: "Carbon and its Compounds"
Question 1.
What are the properties of covalent bonds in carbon compounds?
Answer
Covalent bonds are formed by the "sharing" of electrons between atoms.
These bonds do not create ions.
Carbon compounds have:
Low melting and boiling points because the forces between the molecules are weak.
Poor conductivity of electricity because no ions are formed.
Question 2.
What is the unique nature of carbon that allows it to form a large number of compounds?
Answer
Tetravalency: Carbon has four valence electrons, allowing it to bond with four other atoms.
Catenation: Carbon can form long chains or rings by bonding with other carbon atoms.
Carbon forms single, double, and triple bonds with other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Carbon forms strong and stable bonds because of its small atomic size.
Question 3.
What are saturated and unsaturated carbon compounds?
Answer
Saturated compounds:
Contain only "single" bonds between carbon atoms.
Example: "Methane" (CH
2), "Ethane" (C
2H
6).
Unsaturated compounds:
Contain "double" or "triple" bonds between carbon atoms.
Example: "Ethene" (C
2H
4), "Ethyne" (C
2H
2).
Question 4.
What is a homologous series? Give an example.
Answer
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds that have the same functional group but differ by a -CH
2- unit.
The compounds in this series show a gradual change in physical properties but have similar chemical properties.
Example:
Alkanes: Methane (CH
2), Ethane (C
2H
6), Propane (C
3H
8).
Each member differs by a -CH
2- group.
Question 5.
What are structural isomers? Give an example.
Answer
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms.
Example: Butane (C
2H
5) has two structural isomers:
n-butane (straight-chain structure)
iso-butane (branched-chain structure).
Question 6.
How do soaps and detergents work in cleaning?
Answer
Soaps are made of sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids.
The soap molecule has two ends:
Hydrophilic end: Attracts water.
Hydrophobic end: Attracts oil or dirt.
When soap is added to water, it forms micelles, which trap dirt and oil in the center, allowing them to be washed away.
Question 7.
Explain the process of esterification with an example.
Answer
Esterification is the process of forming an ester by reacting an alcohol with an acid.
Example:
Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid to form ethyl ethanoate (ester) and water.
This reaction is used to make perfumes and flavors.
Question 8.
What is the difference between soaps and detergents?
Answer
Soaps:
Made from natural fats and oils (sodium or potassium salts).
Work well in soft water but form scum in hard water.
Detergents:
Made from petrochemicals.
Work well in both hard and soft water because they do not form scum.
Question 9.
What are the products of combustion of carbon and its compounds?
Answer
Combustion is the burning of carbon or carbon compounds in the presence of oxygen.
It produces:
Carbon dioxide (CO
2)
Water (H
2O)
Heat and light.
Example: Combustion of "Methane" (CH
4) gives CO
2 and H
2O.
Question 10.
Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels?
Answer
Carbon compounds release a large amount of heat and light during combustion.
Examples:
Methane (CH
2) is used in natural gas.
Petrol and diesel are carbon compounds derived from petroleum.
Carbon compounds burn efficiently, making them useful as fuels.
Question 11.
Explain the term ‘functional group’ with examples.
Answer
A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that defines the chemical properties of an organic compound.
Examples:
Alcohol group (-OH): Ethanol (C
2H
5OH)
Aldehyde group (-CHO): Methanal (CH
3O)
Carboxylic acid group (-COOH): Ethanoic acid (CH
3COOH)
Question 12.
What is hydrogenation and where is it used?
Answer
Hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen to unsaturated hydrocarbons in the presence of a catalyst (like nickel).
It is used to convert vegetable oils (which are unsaturated) into solid fats like margarine.
Question 13.
How do you test for unsaturation in hydrocarbons?
Answer
Unsaturated hydrocarbons can be tested using Bromine water.
Procedure:
Add Bromine water to the hydrocarbon.
If the hydrocarbon is unsaturated, the orange color of bromine will disappear.
This indicates the presence of double or triple bonds in the hydrocarbon.
Question 14.
What happens when ethanol reacts with sodium?
When ethanol reacts with sodium, it produces:
Answer
Sodium ethoxide
Hydrogen gas.
Equation: 2C
2H
5OH + 2Na → 2C
3H
5ONa + H
Question 15.
What are oxidizing agents? Provide an example.
Answer
Oxidizing agents are substances that add oxygen to other substances or remove hydrogen from them.
Example:
Potassium permanganate (KMnO2) is an oxidizing agent that converts ethanol to ethanoic acid.