NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Question1.
Give an example of a metal which?
- is a liquid at room temperature
- can be easily cut with a knife
- is the best conductor or heat
- is the poorest conductor of heat
Answer:
- Mercury
- Sodium
- Silver/copper
- Lead/mercury
Question2.
Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile?
Answer:
Malleable The property due to which a substance can be beaten into thin sheet is known as malleability. For example, gold and silver
Ductile The property due to which a substance can be drawn into thin wires is known as ductility. Many metals are ductile in nature. For example, gold and silver
Question3.
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Answer:It is a highly reactive metal. Sodium reacts both with air and water. When kept in open, it readily combines with the oxygen present in air to form its oxide. Similarly, it reacts with water or moisture to form sodium hydroxide.
4Na(s) + O
2(g) → 2Na
2O(s)
2Na(s) + 2H
2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H
2(g)
In order to preserve sodium metal, we generally keep it under kerosene so that neither air nor moisture comes in contact with it
Question4.
Write the equations for the reactions of?
- iron with steam
- calcium until water
Answer:
- 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
- Ca(s) + 2H2O(7) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Question5.
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and were added to the following solutions one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated and answer the questions that follows?
| Metal |
Solution in which metal is added |
|
Iron(II)
sulphate |
Copper(II)
sulphate |
Zinc
Sulphate |
Silver
nitrate |
|
No reaction |
Displacement |
|
|
|
|
No reaction |
|
|
|
No reaction |
No reaction |
No reaction |
Displacement |
|
No reaction |
No reaction |
No reaction |
No reaction |
Answer:Based on the activity series, the relative position of the metals involved in solutions is: Zn > Fe > Cu > Ag. On the basis of the results given in the table.
- Metal A is more reactive than copper and less reactive than iron
- Metal B is more reactive than iron and less reactive than zinc
- Metal C is more reactive than silver and less reactive than copper
- Metal D is equally or less reactive than silver. In the light of above the information, we can conclude that
- Metal B is the most reactive
- Since B is more reactive than iron, it is also more reactive than copper. This means that it would displace copper from copper(II) sulphate solution. The blue colour of solution will slowly fade
- The decreasing order of reactivity of metals is: B > A > C > D
Question6.
Which gas is produced when dil. hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal? Write the chemical reaction when Iron reacts with dil. H2SO4?
Answer:Hydrogen gas (H2) is produced when a reactive metal reacts with dil. hydrochloric acid. Iron and dil. H2SO4 react as follow:
Fe(s) + H2SO4(dil.) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Question7.
What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron(II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place, [2010] Ans. The green colour of the solution would slowly disappear. Zinc would gradually dissolve and iron would get precipitated at the bottom of the beaker. The reaction that takes place is?
AnswerZn(s) + FeSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
Question8.
- Give electron dot structures for sodium, magnesium and oxygen
- Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by the transfer of electrons
- What are the ions present in these compounds
Answer:
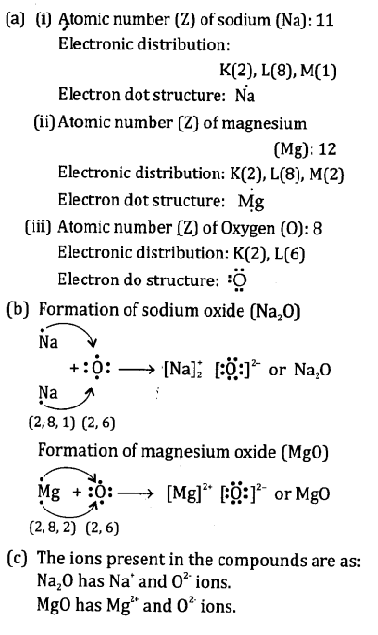
Question9.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting - points?
Answer:In the formation of ionic compounds, positive ions (cat ions) and negative ions (anions) participate. These are closely packed and the ionic compounds exist as crystalline solids.
They have strong inter ionic forces of attraction and have high melting and boiling points
Question10.
Define the following terms?
Answer:
- Minerals The naturally occurring com-pounds of metals along with some impurities are called minerals
- Ores The minerals from which metals can be conveniently and profitably extracted are called ores
- Gangue The associated impurities of minerals and ores are called gangue
Question11.
Name two metals which are formed in nature in free state?
Answer:The metals are gold (Au) and platinum (Pt)
Question12.
Which chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Answer:The chemical process is known as reduction
Question13.
Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals?
| Metal |
Zinc |
Magnesium |
Copper |
Zinc oxide
|
|
|
| Magnesium oxide |
|
|
|
| Copper oxide |
|
|
|
Question13.
In which cases, will you find displacement reactions taking place?
Answer:Magnesium (Mg) will displace both zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) from their oxides
Mg + ZnO → MgO + Zn
Mg + CuO → MgO + Cu
Zinc will displace copper from copper oxide.
Zn + CuO → ZnO + Cu
Copper is the least reactive metal and will not participate in the displacement reaction
Question14.
Which metals do not corrode easily?
Answer:Metals such as gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) present at the bottom of the reactivity series do not corrode easily
Question15.
What are alloys?
Answer:Alloys are the homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or even metals and non-metals
Chapter End Questions
Question1.
Which of the following will give displacement reactions?
- NaCl solution and copper metal
- MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal
- FeSO4 solution and silver metal
- AgNO3 solution and copper metal
Answer:
- AgNO3 solution and copper metal
Question2.
Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting?
- applying grease
- applying paint
- applying a coating of zinc
- all the above
Answer:
- applying a coating of zinc
Question3.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with high melting point. This compound is also water soluble. The element is likely to be?
- Calcium
- Carbon
- Silicon
- Iron
Answer:
Question4.
Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because?
- Zinc is costlier than tin
- Zinc has higher melting point than tin
- Zinc is more reactive than tin
- Zinc is less reactive than tin
Answer:
- Zinc is more reactive than tin
Question5.
You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch?
- How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals
- Assess the usefulness of these tests to distinguish between ,metals and non-metals
Answer:
- With the help of a hammer, convert both the metal arid non-metal (solid) into plates or rods. Metal will readily form these since they are malleable. Non-metals being brittle will break, when struck with hammer. Now construct a cell in both the cases using these plates as electrodes and switch on the current. If the bulb glows, this means that the electrodes are of metals. In case it does not glow, it means that the electrodes are of non-metals
- From these tests, we conclude that
- Metals are malleable while non-metals are not
Question6.
What are amphoteric oxides? Give examples of two amphoteric oxides?
Answer:These are oxides that can act both as acid and base. For example, aluminium oxide (Al2O3) and zinc oxide (ZnO). The amphoteric character of zinc oxide is shown by the following reactions
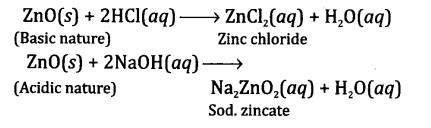
Question7.
Name two metals which can displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals which cannot do so?
Answer:Sodium and calcium can displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Copper and silver cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids
Question8.
In the electrolytic refining of metal M, name anode, cathode and electrolyte?
Answer:
AnodeRod of impure metal
Cathode Rod of pure metal
Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of soluble salt of metal M.
Question9.
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it as shown in the figure?
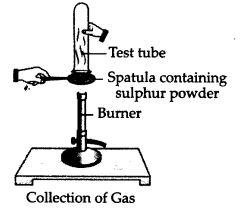
What will be the action of gas on
- dry litmus paper
- moist litmus paper
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Answer:
- The gas is sulphur dioxide (SO2). It will not react with dry litmus paper
- The gas will bleach moist litmus paper. The moist litmus paper changes into red, as the gas is dissolved in moisture to give sulphurous acid.
The balanced chemical equation involving the formation of gas is
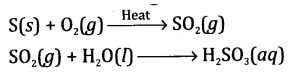
Question10.
State two ways to prevent rusting of iron?
Answer:
Prevention of Rusting: It can be prevented by coating the metal surface with
- red lead
- paints
- enamel
- oil or grease
- plastic coating
- galvanizing
- tinning
- electroplating with nickel or chromium
- converting iron into stainless steel
Question11.
What types of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen?
Answer:The oxides are generally acidic in nature which means that when they are dissolved in water, their solutions change blue litmus into red. For example
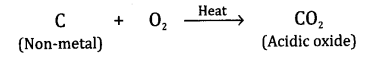
Question12.
Give reasons for the following?
- Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery
- Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil
- Aluminium is a highly reactive metal but still used for making cooking utensils
- Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction
Answer:
- These metals are placed at the bottom of the activity series and are least reactive in nature. Gold and platinum are known as noble metals. They are not affected by air, water or even by chemicals. Since they have lustre, jewellery can be made from them
- All three metals react with water producing lots of heat. As a result, the hydrogen evolved catches fire. They cannot be kept in air because air contains moisture or water vapours. These are kept under kerosene to avoid contact with both air and water
- When exposed to air, the metal changes into its oxide called aluminium oxide (Al2O3). It gets deposited over the surface of the metal and forms a protective coating on the surface. Due to the presence of this layer, aluminium becomes unreactive and can be used for making cooking utensils
- Metal oxides can be easily reduced to metallic form with coke (C) or any other suitable reducing agent. Therefore, carbonates and sulphides are converted to their oxide form by processes of calcination and roasting
Question13.
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels?
Answer:Copper metal slowly reacts with water, carbon dioxide and oxygen present in air to form a layer of basic copper carbonate which is greenish in colour. This layer slowly gets deposited on the surface of the metal.
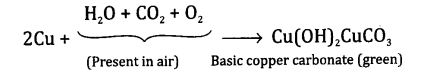 Now lemon juice contains citric acid while tartaric acid is present in tamarind. Both these acids react with basic copper carbonate to form soluble salts such as copper acetate (with citric acid) and copper tartarate (with tartaric acid). The equations for the reactions are complicated and are not given. These salts gets removed from the surface of the copper metal and the surface of the metal shines
Now lemon juice contains citric acid while tartaric acid is present in tamarind. Both these acids react with basic copper carbonate to form soluble salts such as copper acetate (with citric acid) and copper tartarate (with tartaric acid). The equations for the reactions are complicated and are not given. These salts gets removed from the surface of the copper metal and the surface of the metal shines
Question14.
A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter on dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Answer:The man had actually used the solution of aqua regia (mixture of cone. HCl and cone. HNO3 in the ratio of 3 :1 by volume) which has dissolved gold forming soluble auric chloride (AuCl3). Since gold actually reacted, there was a loss in weight of the gold bangles. With the removal of the dull layer of gold from the surface, the original shine on the bangles got restored
Question15.
Give reason why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel?
Answer:Copper is a better conductor of heat than steel which is an alloy of iron. Due to this property, copper is used to make water tanks for storing hot water, even though it is costlier than steel
Question16.
Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of chemical properties?
Answer:
