Important Questions of Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Science Chapter 10
Question 1.
The laws of reflection hold true for?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (a) plane mirrors only
- (b) concave mirrors only
- (c) convex mirrors only
- (d) all reflecting surface
Answer:
- (d) The laws of reflection holds true for all reflecting surface
Question 2.
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:
Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror are
- (i) imagedistanceissameasthatofobjectdistance
- (ii) image formed is virtual and erect
- (iii) image formed is of the same size as that of the object
- (iv) image formed is laterally inverted (left appears right and right appears left)
Question 3.
State the two laws of reflection of light?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:
Laws of reflection of light states that
- (i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
- (ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane
Question 4.
When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (a) real
- (b) inverted
- (c) virtual and inverted
- (d) virtual and erect (2020)
Answer:
- (d) When an object is placed between the principal focus and pole of a concave mirror, an enlarged virtual and erect image is formed behind the mirror
Question 5.
What is the magnification of the images formed by plane mirrors and why?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
Magnification of images formed by plane mirrors is unity because for plane mirrors, the size of the image formed is equal to that of the object
Question 6.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it?
Year of Question :(2019)
Answer:
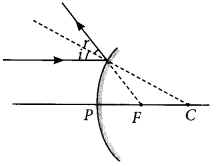
Question 7.
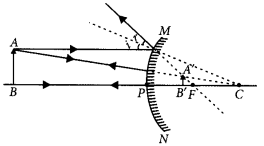
If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished , what type of mirror is it? Draw a labelled ray diagram to support your answer?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
If the image formed by a spherical mirror is always erect and diminished then it is convex mirror.
Question 8.
An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Write four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror?
Year of Question :(2017)
Answer:
Four characteristics of the image formed by the given convex mirror are
- (i) Virtual
- (ii) Erect
- (iii) Diminished
- (iv) Image is always formed behind the mirror between pole and focus
Question 9.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
Radius of curvature (R) = 30 cm, object distance is 12 cm in front of the mirror. Thus we can say that object is placed between focus and pole. Four characteristics of the image formed by die given concave mirror when object is placed between pole and focus are
- (i) Virtual
- (ii) Erect
- (iii) Enlarged
- (iv) Image is formed behind the mirror
Question 10.
A ray of light is incident on a convex mirror as shown. Redraw the diagram and complete the path of this ray after reflection from the mirror. Mark angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it?
Year of Question :(2016)
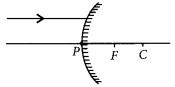
Answer:
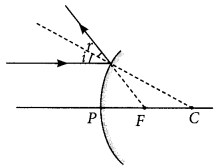
Question 11.
Name the type of mirrors used in the design of solar furnaces. Explain how high temperature is achieved by this device?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
Concave mirrors are used in the designing of solar furnaces.
When a solar furnace is placed at the focus of a large concave mirror, it focuses a parallel beam of light on the furnace. Therefore, a high temperature is attained at the point after some time
Question 12.
"The magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -3". List four informations you obtain from this statement about the mirror/ image?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
Negative sign of magnification indicates that the image is real and inverted. Since the image is real and inverted, the mirror is concave and magnification of -3 indicates that the image is magnified
Question 13.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = frac { 1 }{ 2 } arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why?
Year of Question :(2012)
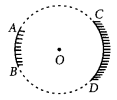
Answer:
Focal length of a mirror is given by
Focal length = frac { Radius of curvature }{ 2 }
Since both the mirrors have same radius of curvature, therefore focal length of the two mirrors will be same, i.e.,
frac { f_1 }{ f_2 } = frac { 1 }{ 1 }
Since virtual image is always formed by convex mirror. The mirror AB will always form virtual image
Question 14.
List two properties of the images formed by convex mirrors. Draw ray diagram in support of your answer?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
Convex mirrors always form diminished, virtual and erect images.
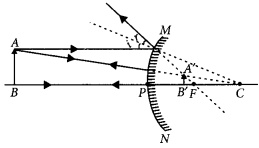
Question 15.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is +3. Analyse this value and state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
Positive value of the magnification indicates that image is virtual and erect
- (i) Since the image is magnified, the mirror is concave
- (ii) The object is between pole and focus of the mirror as shown
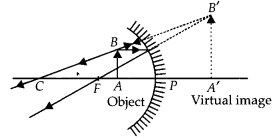 The image produced in second case will be real and inverted
The image produced in second case will be real and inverted
Question 16.
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer::
Four characteristics of the image formed by the given convex mirror are
- (i) Virtual
- (ii) Erect
- (iii) Diminished
- (iv) Image is always formed behind the mirror between pole and focus
Question 17.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray which is directed towards the principal focus of a convex mirror. Mark on it the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
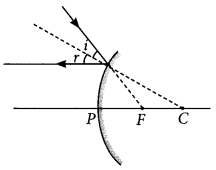
Question 18.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray which is directed parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror, Mark on it the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer::

Question 19.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
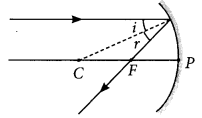
Question 20.
List two possible ways in which a concave mirror can produce a magnified image of an object placed in front of it. State the difference if any between these two images?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
A concave mirror can produce a magnified image of an object when object is placed
- (1) In between its pole and its focus
- (2) In between its focus and its centre of curvature
- Difference,between these two images
- The image produced in first case will be virtual and erect.
The image produced in second case will be real and inverted
Question 21.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be relative to the mirror? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The position of the object should be between P and F
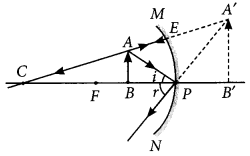
Question 22.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is +1/3. Analysing this value state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw any diagram to justify your answer.?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- (i) Convex mirror
- (ii) Between infinity and the pole of the mirror.
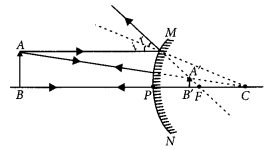
Question 23.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -1. Analysing this value state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw any diagram to justify your answer?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- (i) Concave mirror because the image is real, inverted
- (ii) Object is placed at C.
Question 24.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -1/5. Analysing this value state the (i) type of spherical mirror and (ii) the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw ray diagram to justify your answer?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- (i) Concave mirror
- (ii) Object is placed beyond C
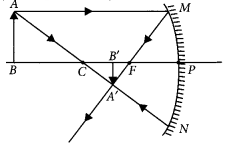
Question 25.
Draw ray diagrams for the following cases when a ray of light?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (i) passing through centre of curvature of a concave mirror is incident on it
- (ii) parallel to principal axis is incident on convex mirror
- (iii) is passing through focus of a concave mirror incident on it. (2020)
Answer:
- i) Ray of light passing through centre of curvature of concave mirror, after reflection
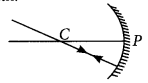
- (ii) Ray of light parallel to the principal axis is incident on a convex mirror after reflection appear to diverge from the principal focus of a convex mirror.
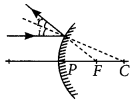
- (iii) Ray of light passing through focus of a concave mirror after reflection will emerge parallel
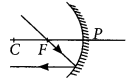
Question 26.
A concave mirror is used for image formation for different positions of an object. What inferences can be drawn about the following when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from the pole of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (a) Position of the image
- (b) Size of the image
- (c) Nature of the image
Draw a labelled ray diagram to justify your inferences. (2020)
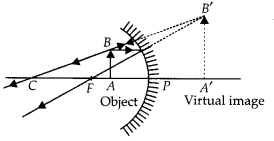
Answer:
Given, f = -15 cm, u = -10 cm.
Thus the object is placed between the principal focus and pole of the mirror
- (a) The position of the image will be behind the mirror
- (b) The size of the image will be highly enlarged
- (c) The nature of the image will be virtual and erect.
Question 27.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a 4 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror? Also calculate the size of the image formed.?
Year of Question :(2019)
Answer:
Given f = -20 cm v = -30 cm u = ?
Using 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
1/u = 1/f -1/v = 1/-20 - 1/-30 = -3+2/60
⇒ u = -60 cm
∴ Object placed at 60 cm from the mirror.
Also magnification, m = h’/h = -v/u
⇒ h’ = -(-30)/-60 × 4 = -2 cm
∴ The size of the image is 2 cm.
Question 28.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted. (Delhi 2017)
Given:
Object distance, u = - 30 cm, image size, h =
Year of Question :(2017)
Answer:Image distance, v = - 60 cm,
Object size ,h = 2.4 cm,
Focal length, f = ?
Using mirror formula,
1/f=1/v+1/u or 1/f=-1-2/60= -3/60= - 1/20
or f = - 20 cm
Hence, focal length is 20 cm
Also, magnification, m = h’/h = -v/u
or, m = (-60)/(-30) = -2 or h’/h = -2
h = -2 × 2.4 = -4.8 cm
As the image formed is real, therefore the mirror is concave.
The height of the image is 4.8 cm.
The image formed is enlarged and inverted
Question 29.
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image?
Year of Question :(2017)
Answer:
Given : object distance, u = -15 cm,
object height, h = 4 cm, focal length f = -10 cm;
Image distance, v = ?
Using mirror formula,
1/v+1/u=1/f⇒1/v+1/(-15)=1-10⇒1/v=1/15-1/10
or 1/v=10-15/150=-5/150=-1/30 or v = -30
In order to obtain a sharp image of the object on the screen, screen should be placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of the mirror.
Also, magnification, m = h/h=-v/u
or h/4=-(-30)/(-15) or h = -(30)×4/(15) = -2 × 4
or h = -8 cm
Thus, the height of the image is 8 cm
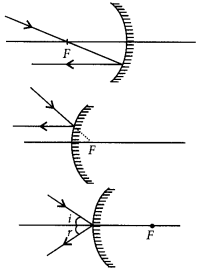
Question 30.
Draw the following diagram in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror, on your answer sheet. Show the path of this ray, after reflection, in each case?
Year of Question :(2012)

Answer:
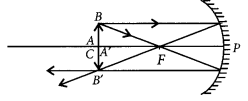
The path of the rays are shown in figure.
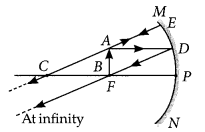
Question 31.
The image of an object formed by a mirror is real, inverted and is of magnification -1. If the image is at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Where would the image be if the object is moved 20 cm towards the mirror? State reason and also draw ray diagram for the new position of the object to justify your answer?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
Since the image formed by the mirror is real and inverted, therefore the mirror is concave and magnification of the mirror will be
m = -v/u ⇒ -1 = -v/u ⇒ v = u
i.e., object and image both are formed at the centre of curvature, i.e., 40 cm from the mirror.
Now, if the object is moved 20 cm towards the mirror, the object will be at the focus of the mirror and therefore the image will be formed at infinity.
Question 32.
The image formed by a spherical mirror is real, inverted and its magnification is -2. If the image is at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Find the focal length of the mirror. List two characteristics of the image formed if the object is moved 10 cm towards the mirror?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
Since the image formed is real and inverted, the mirror is concave.
Magnification, m = -v/u ⇒ -2 = -v/u ⇒ v = 2u
Now, if v = - 30 cm then u = - 15 cm
As focal length of the mirror is
f = uv/u+v=-15×-30/-15-30 =f = 450/-45 = -10 cm
If the object is shifted 10 cm towards the mirror, then the object is between principal focus and the optical centre and the image formed will be virtual and erect
Question 33.
If the image formed by mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always virtual and diminished, state the type of the mirror. Draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. Where are such mirrors commonly used and why?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
Convex mirrors are widely used as rear view mirrors in cars, motorcycles etc. It produces an erect image that is smaller in size than the object hence giving a wide view
Question 34.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
We use two rays of light, one passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, and another is parallel to the principal axis. After reflection, the ray passing through the centre of a concave mirror is reflected back along the same path and the ray parallel to the principal axis will pass through the principal focus.
u = -15 cm, f= -10 cm
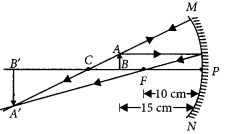 From ray diagram, v = -30 cm, i.e., beyond C Nature of image is real, inverted and magnified
From ray diagram, v = -30 cm, i.e., beyond C Nature of image is real, inverted and magnified
Question 35.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray in each of the following cases. A ray of light incident on a convex mirror?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (a) strikes at its pole making an angle 0 from the principal axis
- (b) is directed towards its principle focus
- (c) is pardllel to its principal axis. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:

- (b)

Question 36.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 50 cm from the mirror?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (a) Write the type of mirror
- (b) Find the distance of the image from the object
- (c) What is the focal length of the mirror
- (d) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014, AI 2014)
Answer:
(a) Concave mirror
(b) Magnification, m = - v/u or v = u
∴ Distance of the image from the object is, v - u = 0
(c) As the image is formed at centre of curvature i.e., v = R.
∴ focal length of the mirror, f = -50/2 = -25 cm
Question 37.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror?
Year of Question :(2013)
- (i) Write type of mirror
- (ii) What is the nature of the image formed
- (iii) How far is the object located from the mirror
- (iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
- (i) This is a concave mirror
- (ii) The image is real and inverted and of same size
- (iii) As m = - 1
∴ m = - v/u ⇒ -1 = -v/u ⇒ u = v
Hence, object is located at centre of curvature i.e., at distance of 40 cm from the pole of the mirror
Question 38.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (i) Write the type of mirror in this case
- (ii) What is the focal length of the mirror
- (iii) What is the nature of the images formed
- (iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
- (i) The mirror is concave mirror
- (ii) Distance the image from the mirror = - 30 cm
Magnification, m = -v/u
Here m = - 1 and v = - 30 cm
-1 = --30/u
∴ u = - 30 cm
As v = u, object is placed at centre of curvature. Therefore, focal length of the mirror,
f = -30/2 = - 15 cm
- (iii) Image formed is real and inverted and of the same size of the object
Question 39.
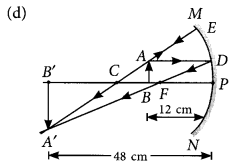
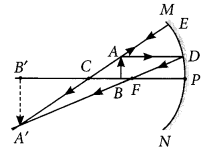
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 48 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 12 cm from its pole?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (a) Suggest the type of mirror he should use
- (b) Find the linear magnification of the image produced
- (c) How far is the image from its object
- (d) Draw ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (AI 2014)
Answer:
- (a) Concave mirror
- (b) Linear magnification,
m = -/u = -(-48)/-12 = -4
- (c) The distance between the image and the object
= 48 - 12 = 36 cm
Question 40.
A student wants to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of 12 cm focal length. What should be the range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror? State the nature and size of the image he is likely to observe. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
To obtain an erect image, the object is placed in between pole and the focus of the concave mirror. So range of distance of the candle llame from the mirror is in between 12 cm.
Nature of the image = Virtual and erect.
Size of the image = Enlarged
Question 41.
A student wants to obtain an erect image of a candle flame using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror?
State the nature and size of the image he is likely to observe. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
To obtain an erect image of an object, the object should be placed in between pole and focus. Range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror is in between 15 cm.
Nature of the image = Virtual and erect
Size of the image = Enlarged
For ray diagram
Question 42.
A student has a concave mirror of 20 cm focal length and he wants to see an erect image of his face in the mirror. What should be the range of distance of the mirror from his face? State the nature and size of the image he is likely to observe. Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
Focal length of a concave mirror = 20 cm Range will be in between 20 cm.
Nature of the image = Virtual and erect
Size of the image = Enlarged
For ray diagram
Question 43.
Mention the types of mirrors used as (i) rear view mirrors, (ii) shaving mirrors. List two reasons to justify your answer in each case?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
- (i) Convex mirror is used as rear view mirror because
- (a) it gives erect image
- (b) it gives diminished image thus provides wider view of traffic behind the vehicle
- (ii) Concave mirror is used as shaving mirror becaus
- (a) it gives erect image when mirror is close to the face
- (b) it gives enlarged image of the face so that a person can shave safely
Question 44.
Calculate the magnification of the image of an object placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. The object is at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror?
Year of Question :(2013)
Answer:
Given, focal length of concave mirror,
f = -15 cm
Object distance, u = -20 cm
Image distance, v = ?
Using mirror formula,
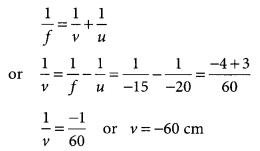 Using magnification formula,
Using magnification formula,
m = -v/u = -(-60)/-20 or m = -3
So, the magnification, m = -3
Question 45.
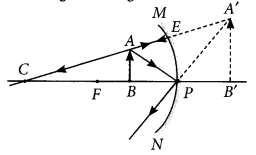
To construct ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection. Use these rays to locate the image of an object placed between centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
A ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus in case of a concave mirror or appear to diverge from the principal focus in case of a convex mirror.
A ray passing through the centre of a curvature of a concave mirror or directed in the direction of the centre of curvature of a convex mirror, after reflection, is reflected back along the same path. The light rays come back along the same path because the incident rays fall on the mirror along the normal to the reflecting surface.
Question 46.
State the types of mirrors used for (i) headlights and (ii) rear view mirrors, in motorcycles. Give reason to justify your answer in each case?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
- (i) Concave mirrors are used in headlights of cars to get powerful beams of light
- (ii) Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors of vehicle to get a wider field of view and and erect image of traffic behind
Question 47.
An object is placed between infinity and the pole of a convex mirror. Draw a ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of the image formed?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:
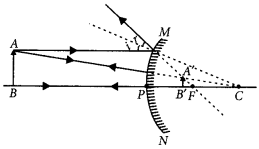 Position: Image is formed between pole and principal focus of the mirror.
Position: Image is formed between pole and principal focus of the mirror.
Relative size : Image formed is diminished.
Nature : Image formed is virtual and erect
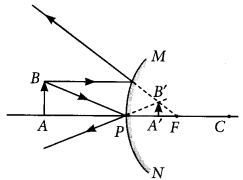
Question 48.
With the help of a ray diagram explain why a convex mirror is preferred for rear view mirrors in the motor cars?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:
Convex mirror is preferred for rear view mirrors in motor cars because no matter where the object is located in front of convex mirror, it always gives erect and diminished image of the object, so that driver is able to see the large traffic view in small area and the image is erect. This can be interpreted from the following diagram.
Question 49.
An object 4.0 cm in size, is placed 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15.0 cm?
Year of Question :(2012)
- (i) At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image
- (ii) Find the size of the image
- (iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (2020)
Answer:
(i) Given, h = 4 cm,
u = -25 cm (concave mirror), f = -15 cm
Using mirror formula,
 Thus, the image is real and inverted.
Thus, the image is real and inverted.
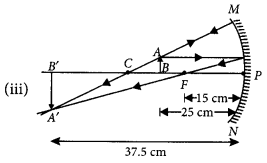
Question 50.
- (a) A concave mirror of focal length 10 cm can produce a magnified real as well as virtual image of an object placed in front of it. Draw ray diagrams to justify this statement
- (b) An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 10 cm. The distance of the object from the pole of the mirror is 10 cm. Find the position of the image formed. (2020)
Answer:
- (a) A magnified real image is produced in a concave mirror when the object is placed between principal focus and centre of curvature.
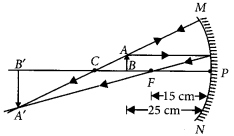 A magnified virtual image is produced in a concave mirror when the object is placed between the pole and the principle focus of the mirror.
A magnified virtual image is produced in a concave mirror when the object is placed between the pole and the principle focus of the mirror.
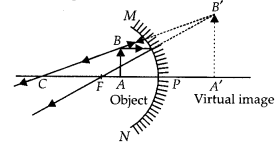
- (b) Given, f = +10 cm (convex mirror) and u = -10 cm
From mirror formula,
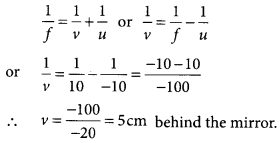
Important Questions and Answers for Chapter 10: Light - Reflection and Refraction
Question 1.
What are the "Laws of Reflection"?
Answer:
Law 1: The angle of "incidence" is equal to the angle of "reflection".
Law 2: The incident ray, the normal to the surface, and the reflected ray lie in the same "plane".
Question 2.
What is a "Concave Mirror"? Explain its uses.
Answer:
Concave Mirror: A mirror that is "curved inward", like the inside of a spoon.
Uses:
Used in "torches" and "car headlights" to produce a parallel beam of light.
Used by "dentists" to see enlarged images of teeth.
In "solar furnaces", concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight and produce heat.
Question 3.
What is the "Principal Focus" of a "Convex Mirror" and a "Concave Mirror"?
Answer:
Concave Mirror: The "Principal Focus" is the point where rays "converge" or meet after reflection.
Convex Mirror: The "Principal Focus" is the point from which rays appear to "diverge" or spread out.
Question 4.
State the "Mirror Formula" and explain its components.
Answer:
Formula: 1/v + 1/u - 1/f
Components:
v: "Image distance" (distance between mirror and image).
u: "Object distance" (distance between mirror and object).
f: "Focal length" (distance between mirror and principal focus).
Question 5.
What is "Refraction of Light"? Give an example from daily life.
Answer:
Refraction: The bending of light when it passes from one "medium" to another.
Example:
When a "pencil" is partly immersed in water, it appears bent or broken at the "water surface" due to refraction.
Question 6.
Explain the "Laws of Refraction" of light.
Answer:
Law 1: The incident ray, the "refracted ray", and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane.
Law 2 (Snell’s Law): The ratio of the "sine of the angle of incidence" to the "sine of the angle of refraction" is constant for a given pair of media.
Question 7.
What is "Refractive Index" and how is it calculated?
Answer:
Refractive Index (n): A measure of how much light slows down in a "medium".
Formula:
n - Speed of light in air (c)/Speed of light in the medium (v)
Question 8.
What are the uses of "Convex Mirrors"?
Answer:
Convex Mirrors are used in:
"Vehicles" as rear-view mirrors because they give a wide field of view.
"Shops" and "parking lots" to provide a broad view of surroundings.
Question 9.
Define "Power of a Lens". What is the unit of power?
Answer:
Definition: The power of a lens is the ability of the lens to "converge" or "diverge" light.
Formula:
P - 1/f
The unit of power is "dioptre" (D).
Question 10.
Differentiate between "Concave" and "Convex" Lenses.
Answer:
Concave Lens:
Shape: Thicker at the edges, thinner at the center.
Effect: Diverges light, forms a "virtual", "erect", and "diminished" image.
Convex Lens:
Shape: Thicker at the center, thinner at the edges.
Effect: Converges light, can form "real" and "virtual" images depending on object position.
Question 11.
What is the "Lens Formula" and how is it related to the object and image distance?
Answer:
Formula:
1/v - 1/u - 1/f
Explanation:
v: Image distance from the lens.
u: Object distance from the lens.
f: Focal length of the lens.
Question 12.
Why do we prefer using "Convex Mirrors" for rear-view mirrors in vehicles?
Answer:
They give an "erect" image.
They provide a "wider field of view", allowing the driver to see more of the road behind.
The image is "diminished" but shows a large area, making it suitable for traffic observation.
Question 13.
How does a "Convex Lens" form an image?
Answer:
When light rays pass through a "convex lens":
Parallel rays converge at a point called the "principal focus".
The image can be "real", "inverted", and "magnified" if the object is placed beyond the focal point.
The image is "virtual" and "erect" if the object is placed between the lens and focal point.
Question 14.
What is "Magnification" and how is it calculated for mirrors and lenses?
Answer:
Definition: Magnification tells how much larger or smaller the image is compared to the object.
Formula:
m - Height of the image (h)/Height of the object (h)
For mirrors: m - -v/u
For lenses: m - v/u
Question 15.
What is the difference between "Real" and "Virtual" images?
Answer:
Real Image:
Formed by "actual convergence" of light rays.
Can be projected on a screen.
Inverted.
Virtual Image:
Formed by "apparent divergence" of rays.
Cannot be projected on a screen.
Erect.