Question 1.
For each of the given solid, the two views are given. Match for each solid the corresponding top and front views. The first one is done for you.
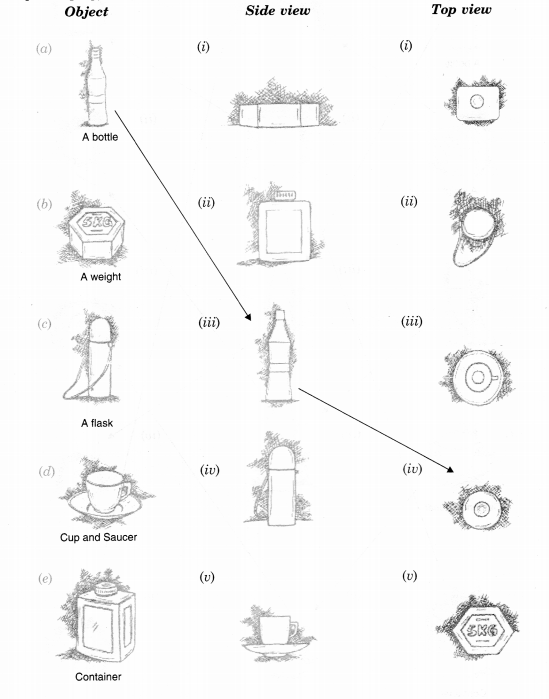
Solution.
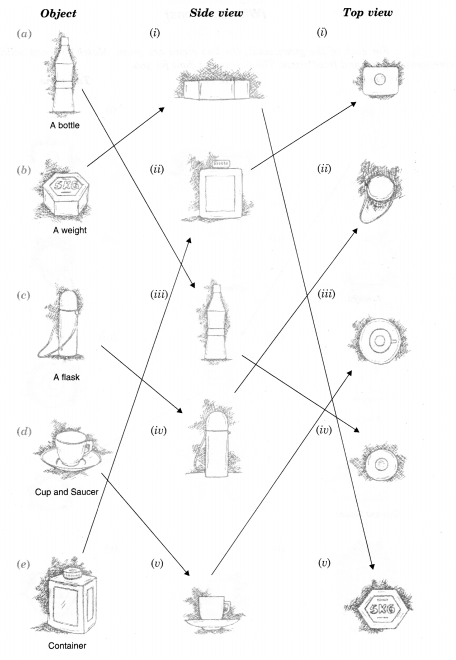
Question 2.
For each of the given solid, the three views are given. Identify for each solid the corresponding top, front and side views.

Solution.
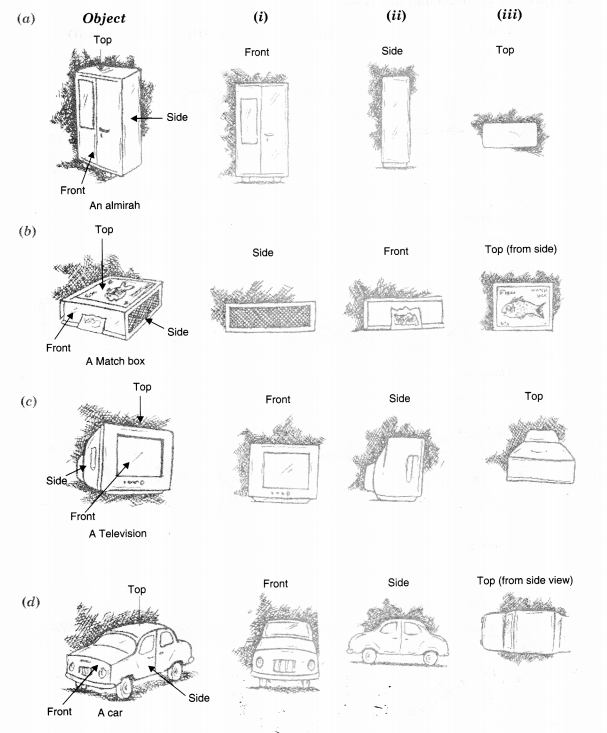
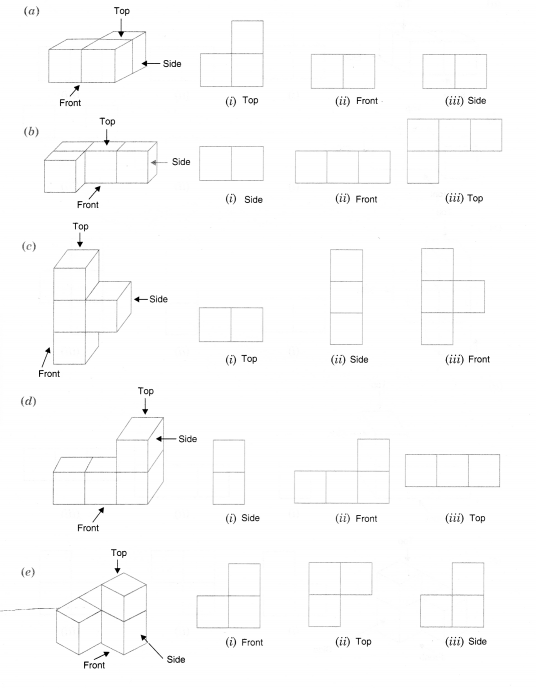
Question 3.
For each given solid, identify the top view, front view, and side view.
Solution.
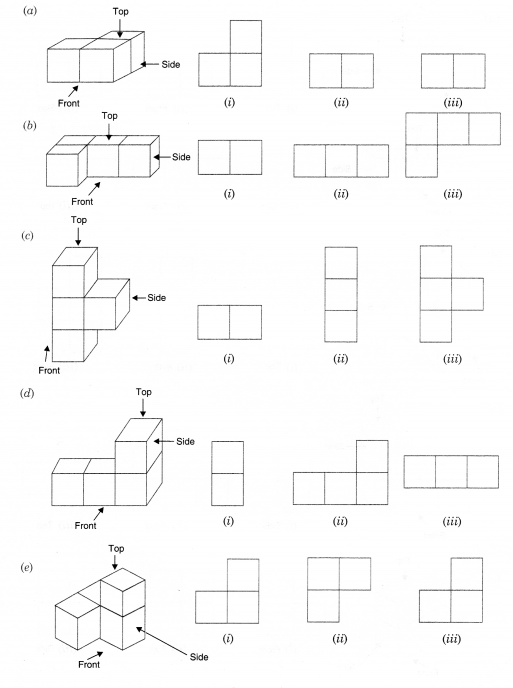
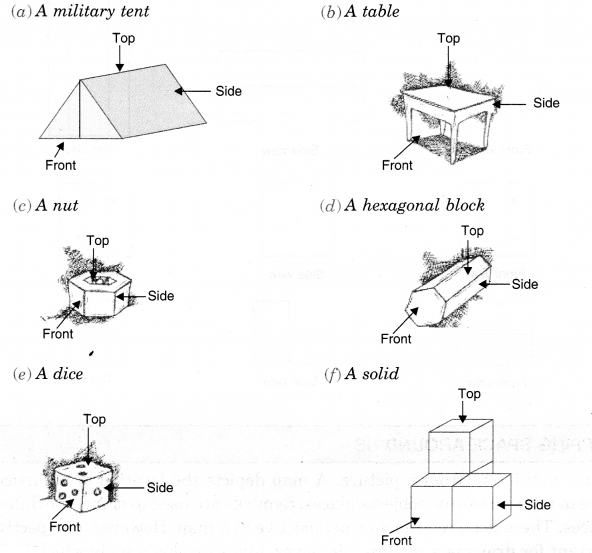
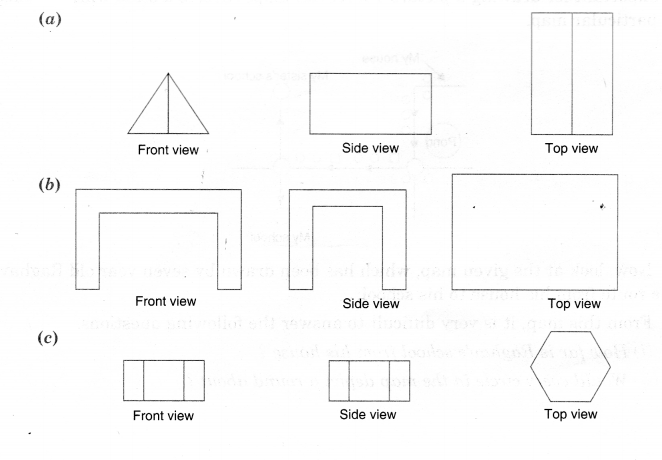
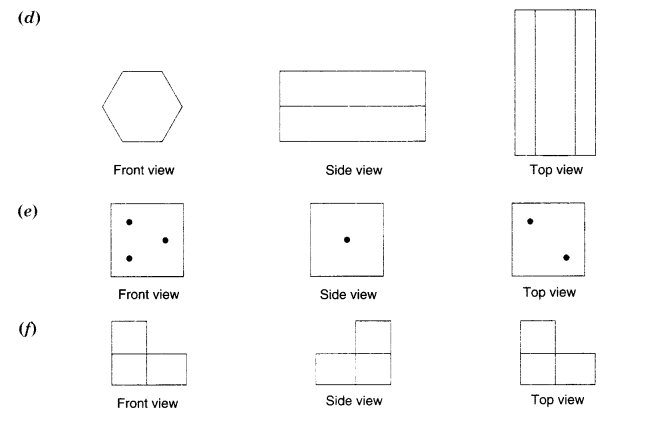
Question 4.
Draw the front view, side view and top view of the given objects,
Solution.
Question 1.
Look at the given map of a city.
Answer the following.
- (a) Colour the map as follows: Bluewater, Red-fire station, Orange-Library, Yellow-schools, Green-Parks, Pink-Community Centre, Purple-Hospital, Brown-Cemetery.
- (b) Mark a green X’ at the intersection of Road ‘C’ and Nehru Road, Green Y’ at the intersection of Gandhi Road and Road A.
- (c) In red, draw a short street route from Library to the bus depot.
- (d) Which is further east, the city park or the market?
- (e) Which is further south, the primary school or the Sr. Secondary School?
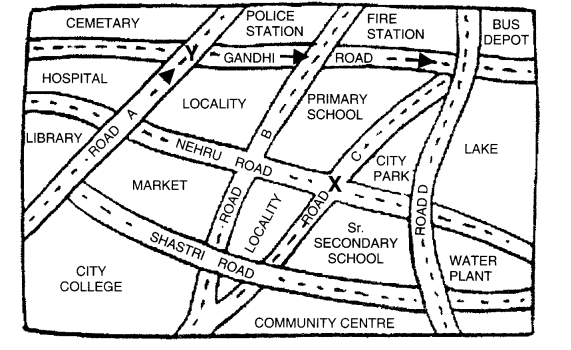
Solution.
- (a) Please color yourself.
- (b) See the above figure.
- (c) See the above figure.
- (d) City Park.
- (e) Senior Secondary school.
Question 2.
Draw a map of your classroom using a proper scale and symbols for different objects.
Solution.
Please draw yourself.
Question 3.
Draw a map of your school compound using a proper scale and symbols for various features like playground main building, garden etc.
Solution.
Please draw yourself.
Question 4.
Draw a map giving instructions to your friend so that she reaches your house without any difficulty.
Solution.
Please draw yourself.
Question 1.
Can a polyhedron have for its faces
- (i) 3 triangles?
- (ii) 4 triangles?
- (iii) a square and four triangles?
Solution.
- (i) No
- (ii) Yes
- (iii) Yes
Question 2.
Is it possible to have a polyhedron with any given number of faces? (Hint: Think of a pyramid).
Solution.
Possible, only if the number of faces is greater than or equal to 4.
Question 3.
Which are prisms among the following?
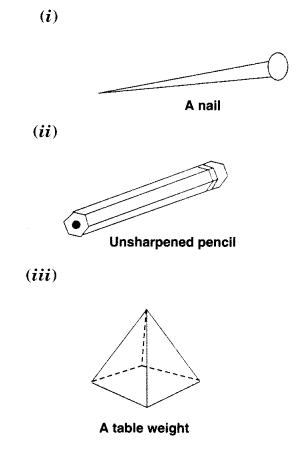
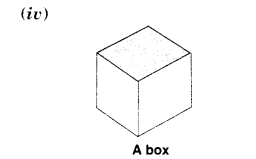
Solution.
We know that a prism is a polyhedron whose base and top faces are congruent and parallel and other (lateral) faces are parallelograms in shape. So, only (ii) and (iv) are prisms.
Question 4.
- (i) How are prisms and cylinders alike?
- (ii) How are pyramids and cones alike?
Solution.
- (i) The prisms and cylinder, both, have their base and top faces as congruent and parallel to each other. Also, a prism becomes a cylinder as the number of sides of its base becomes larger and larger.
- (ii) The pyramids and cones are alike in the sense that their lateral faces meet at a point (called vertex). Also, a pyramid becomes a cone as the number of sides of its base becomes larger and larger.
Question 5.
Is a square prism same as a cube ? Explain.
Solution.
No; not always as it can be a cuboid also.
Question 6.
Verify Euler’s formula for these solids
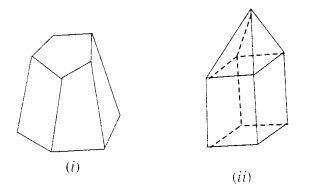
Solution.
(i)
F = 7
V= 10
E = 15
F + V = 7 + 10 = 17
E + 2 = 15 + 2 = 17
So, F + V = E + 2
Hence, Euler’s Formula is verified,
(ii)
F = 9
V = 9
E = 16
F + V = 9 + 9 = 18
E + 2 = 16 + 2 = 18
So, F + V = E + 2
Hence, Euler’s Formula is verified
Question 7.
Using Euler’s formula find the unknown.
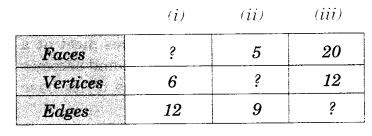
Solution.
(i)
F + V = E + 2
⇒ F + 6 = 12 + 2
⇒ F + 6 = 14
⇒ F = 14 – 6 = 8
(ii)
F + V = E + 2
⇒ 5 + V = 9 + 2
⇒ 5 + V = 11
⇒ V= 11-5 = 6
(iii)
F + V = E + 2
⇒ 20 + 12 = E + 2
⇒ 32 = E + 2
⇒ E = 32 – 2
⇒ E = 30
Question 8.
Can a polyhedron have 10 faces, 20 edges, and 15 vertices?
Solution.
Here F = 10
E = 20
V= 15
So, F + V = 10 + 15 = 25
E + 2 = 20 + 2 = 22
∵ F + V ≠ E + 2
∴ Such a polyhedron is not possible.