Stars and the solar system
Choose the correct answer in Questions 1-3:
Question 1.
Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
- (a) An asteroid
- (b) A satellite
- (c) A constellation
- (d) A comet
Answer.
(c) A constellation.
Question 2.
Which of the following is NOT a planet of the Sun?
- (a) Sirius
- (b) Mercury
- (c) Saturn
- (d) Earth
Answer.
(a) Sirius.
Question 3.
Phases of the moon occur because:
- (a ) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
- (b) our distance from the moon keeps changing.
- (c) the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the moon"s surface.
- (d) the thickness of the moon"s atmosphere is not constant.
Answer.
(a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks:
- 1.The planet which is farthest from the Sun is………….
- 2.The planet which appears reddish in colour is…………
- 3.A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a……………
- 4.A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as…………
- 5.Shooting stars are actually not…………..
- 6.Asteroids are found between the orbits of and.…………
Answer.
- 1.Neptune
- 2.Mars
- 3.constellation
- 4.satellite
- 5.meteors
- 6.Mars, Jupiter.
Question 5.
Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F):
- 1.Pole star is a member of the solar system. ( )
- 2.Mercury is the smallest planet in the solar system. ( )
- 3.Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system. ( )
- 4.INSAT is an artificial satellite. ( )
- 5.There are nine planets in the solar system. ( )
- 6.Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ( )
Answer.
- 1.False
- 2.True
- 3.False
- 4.True
- 5.False
- 6.False
Question 6.
Match items in column A with one or more items in column B.

Answer.
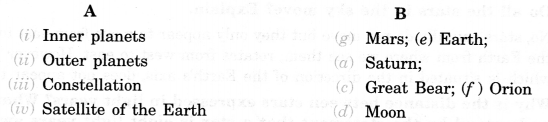
Question 7.
In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answer.
Venus appears in the western sky just after sunset.
Question 8.
Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Answer.
Jupiter (Brihaspati).
Question 9.
What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answer.
A group of stars that has a recognizable shape is called a constellation. Ursa Major and Orion are two examples of constellations.
Question 10.
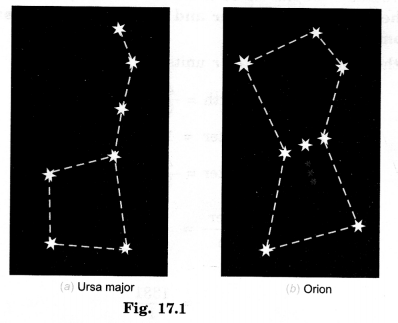
Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in:
(a) Ursa Major and (b) Orion.
Answer.
Question 11.
Name two objects other than planets which are members of the solar system.
Answer.
Satellites and asteroids are the objects that too, are members of the Solar system.
Question 12.
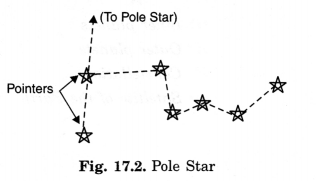
Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer.
Pole stars can be located with the help of the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. Imagine a straight line passing through these stars as shown in Fig. 17.2. Extend this imaginary line towards the north direction. (About five times the distance between the two stars). This line will lead to a star which is not too bright. This is the Pole Star.
Question 13.
Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Answer.
No, no star moves in the sky. They appear to move from east to west because the Earth rotates from west to east about its axis.
Question 14.
Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light-years away from the Earth?
Answer.
The distance between stars is so large that it cannot be expressed in terms of a kilometer. That is why very large distances, are expressed in another unit known as light year. One light-year is the distance traveled by light in one year. If the distance of a star is eight light-years, it means that this distance is the distance traveled by light in eight years.
Question 15.
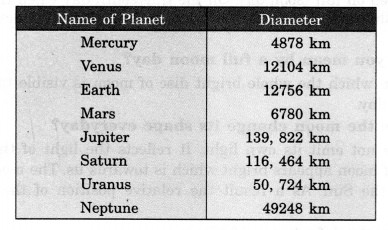
The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Answer.

Question 16.
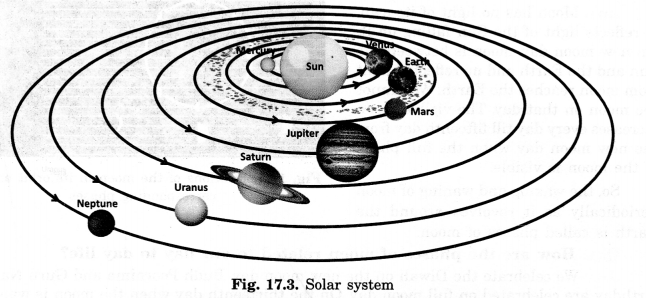
Boojho made the following sketch (See Fig. 17.29 of NCERT) of the solar system.
Is the sketch correct? If not, correct it.
Answer.
It is not correct. Figure 17.3 is a correct sketch of the solar system.